雄激素受体在乳腺癌中的生物信息学分析
2017-10-09JinhuaWang
李 兵,杜 岗,Jinhua Wang
(1.山西省煤炭工业厅煤矿职业病防治中心,山西 太原 030012; 2.暨南大学附属第一医院,广东广州 510632;3,Center for Health Informatics and Bioinformatics,New York University School of Medicine,New York,NY,USA;4.Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center,New York University School of Medicine,New York,NY,USA)
雄激素受体在乳腺癌中的生物信息学分析
李 兵1,杜 岗2,3,Jinhua Wang3,4
(1.山西省煤炭工业厅煤矿职业病防治中心,山西 太原 030012; 2.暨南大学附属第一医院,广东广州 510632;3,Center for Health Informatics and Bioinformatics,New York University School of Medicine,New York,NY,USA;4.Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center,New York University School of Medicine,New York,NY,USA)
目的:通过数据挖掘探讨雄激素受体(AR)在乳腺癌中发病的机制,探索协同表达基因网络中的潜在干预靶点和信号通路。方法:分别从TCGA数据库和NCBI数据库中下载了两个独立的乳腺癌基因表达谱数据,筛选出AR的关联基因,使用Cytoscape平台中的ClueGo插件对这些基因进行生物信息学分析。结果:以Pearson相关系数>0.40或<-0.40为阈值,共发现21个基因与AR有强的相关性,其中负相关4个,正相关17个;同时发现基因MLPH,SYT17,PIP,ALCAM,TOX3在既往文献报道中较少,可以成为下一步的研究方向。GO功能分析提示AR及其关联基因与上皮细胞分化、细胞形态改变、细胞内的类固醇激素受体信号通路等有关。结论:AR在乳腺癌作用中的信号通路和分子机制复杂,基于乳腺癌的数据挖掘可以为乳腺癌的个体化诊断和治疗提供科学依据。
乳腺癌;雄激素受体;生物信息学
乳腺癌是影响女性健康的主要恶性肿瘤之一,在欧美国家发病率较高,中国的发病率也呈快速增长趋势[1]。乳腺癌呈激素依赖性,雌激素、孕激素及其受体在乳腺癌的发生、发展中起着重要作用;内分泌治疗已经成为雌激素受体(estrogen receptor,ER)、孕激素受体(progesterone receptor,PR)阳性患者的一线治疗方法[2]。然而,绝经后女性体内雌激素的减少并未使乳腺癌的发病率下降,ER、PR阳性患者中也有部分患者内分泌治疗无效,提示除雌激素、孕激素外,雄激素及雄激素受体(androgen receptor,AR)在乳腺癌中亦起着重要作用[3],但相关机制尚不明确。本文对乳腺癌研究的数据进行挖掘,旨在通过分析AR的关联基因,为进一步阐明AR在乳腺癌中发病的机制提供帮助。
1 资料与方法
1.1 资料来源
本文中乳腺癌数据来源于TCGA(the cancer genome atlas project)公共数据库(https://tcga-data.nci.nih.gov/tcga)的 Comprehensive Molecular Portraits of Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer研究[4](该数据简称TCGA-CELL2015)和NCBI(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo)的A Genomic Predictor of Response and Survival Following Taxane-Anthracycline Chemotherapy for Invasive Breast Cancer研究(该数据简称NCBI-JAMA2011)[5]。
1.2 数据处理和分析
采用R语言(版本:3.2.3)对数据进行分析和处理,使用 Cytoscape(版本:3.3)的 ClueGo 插件对筛选出的目标基因进行GO分析和作图[6-7],P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 数据分析结果
通过对NCBI-JAMA2011和TCGA-CELL2015两组数据分析,Pearson值切割点取0.4或-0.40,取两个数据的交集,共发现21个基因与AR相关,其中负相关4个,正相关17个,结果见表1。通过在线软件Pathway Commons[8](http://www.pathwaycommons.org)对目标基因进行相互作用网络分析,发现基因 MLPH,SYT17,PIP,ALCAM,TOX3在相互作用网络图之外,提示该组基因与AR相关研究报道较少,可以作为下一步研究目标。结果见图1。
2.2 GO富集分析结果
将筛选出的21个基因借助Cytoscape软件中的ClueGo插件进行分析并绘制基因富集网络图,共富集到9个生物过程,这些基因与上皮细胞分化、细胞形态改变、细胞内的类固醇激素受体信号通路等有关,结果见图2,表2。
3 讨论
AR属于核受体超家族成员,基因位于X染色体上,基因长度为90 kb,在机体组织中分布广泛,主要存在于靶细胞的核内[9]。试验发现胚胎肾脏中即有AR的表达,其中睾酮可通过AR促进Wolffian 导管的生长和形成[10-12]。Takeda H 等[13]对人体不同组织中AR的表达情况进行了研究,结果显示AR在乳腺组织、生殖系统、前列腺、平滑肌、心脏、肝脏、肾脏及脑组织均有一定的表达。未结合配体的AR位于细胞质中,与蛋白质分子以复合物的形式存在。但AR与雄激素结合后构象发生改变,与结合蛋白分离,转移至细胞核内并形成二聚体后与DNA上的激素反应元件结合,从而激活靶基因的转录。Garreau G等[14]证实ER-/PR-/AR+的乳腺癌细胞对雄激素治疗有效,而ER-/PR-/AR-的细胞对雄激素治疗无反应;当细胞转染AR成为ER-/PR-/AR+的细胞后就会显示出对雄激素治疗的反应,细胞发生凋亡或死亡。提示ER-/PR-且AR+的肿瘤患者以AR为靶向的激素治疗是有效的。
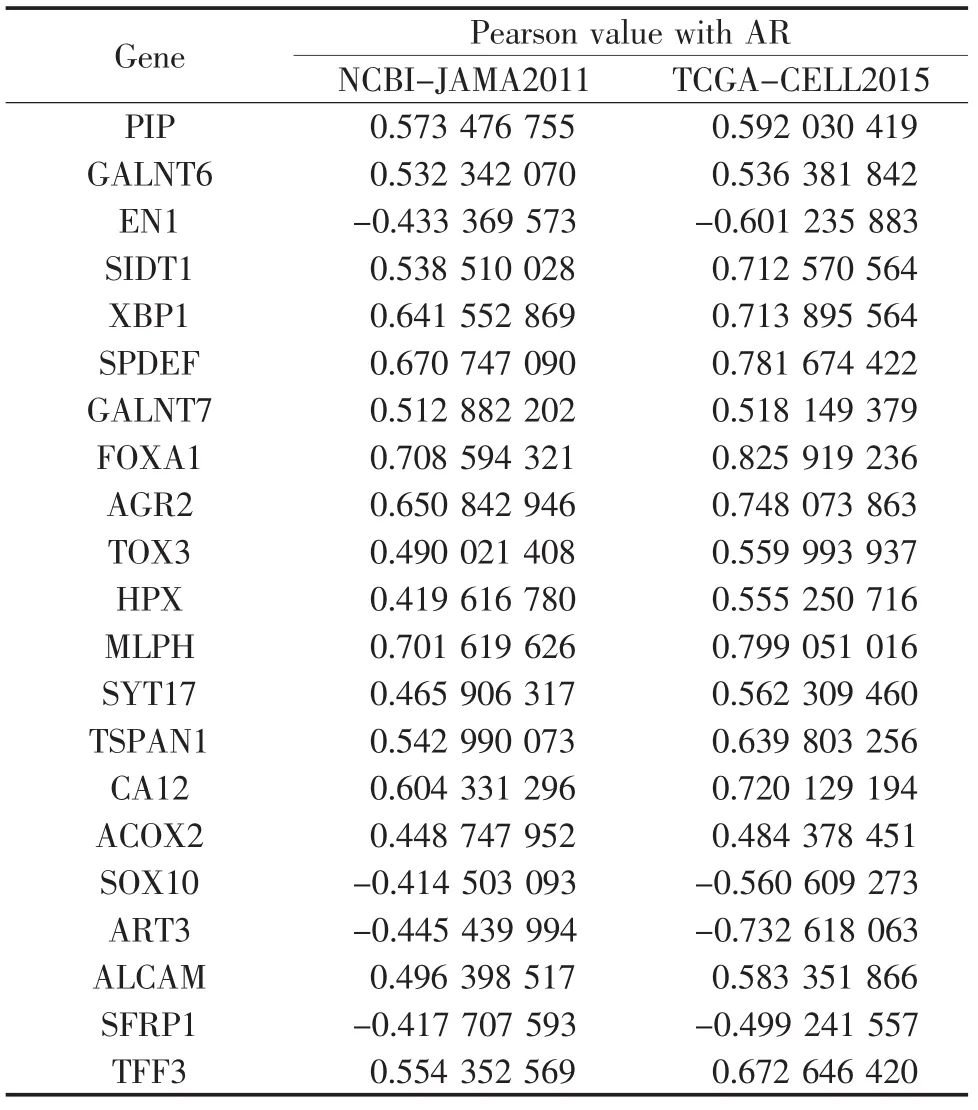
表1 AR关联基因
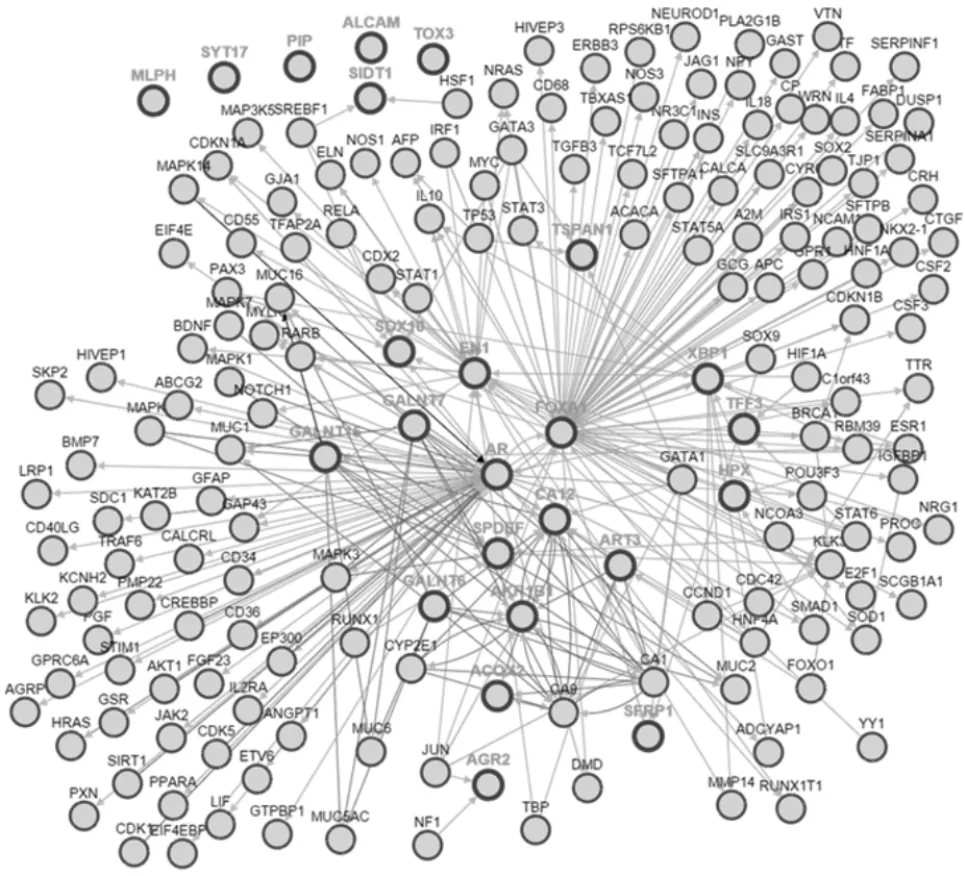

图1 AR关联基因调控网络图
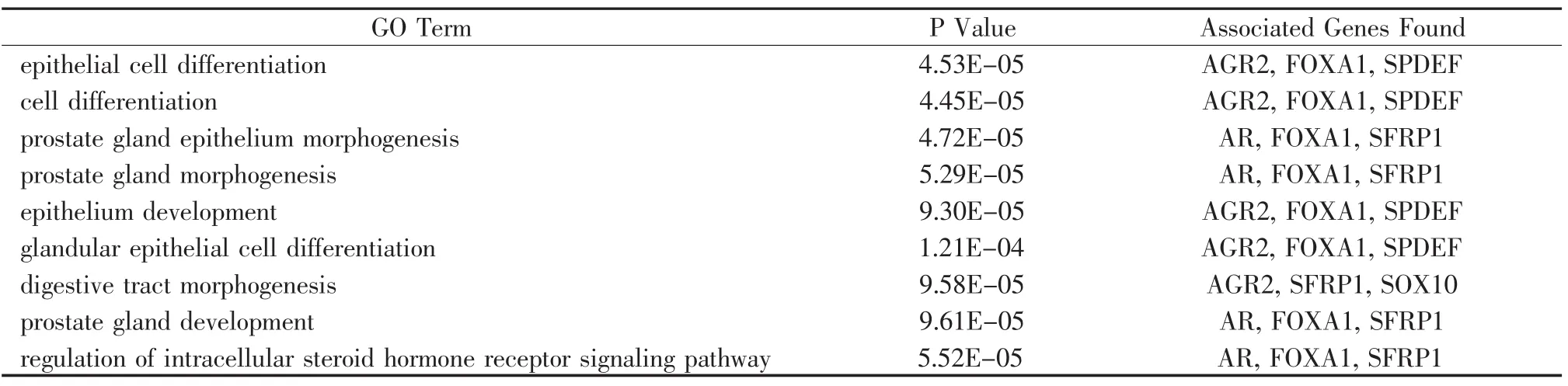

表2 差异表达基因GO生物学过程富集分析结果
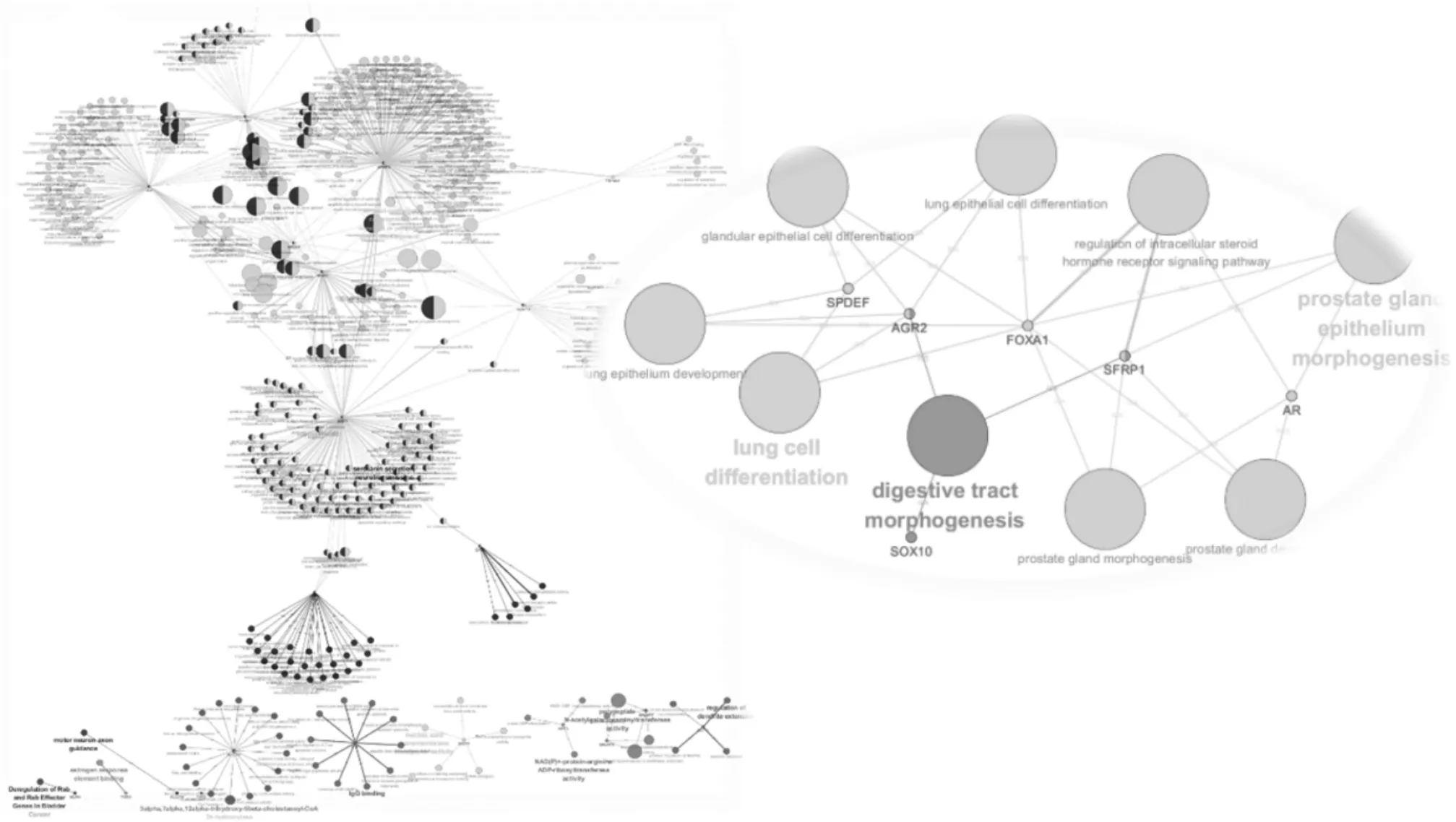
图2 AR及其关联基因的功能富集图
3.1 AR与乳腺癌分型
乳腺癌是一种多因素疾病,其在临床、病理及分子生物学等方面的特征复杂。Perou C M等[15]在2000年最先对乳腺癌分为以下5个亚型:导管A型(LuminalA)、导管B型(Luminal B)、Her-2过表达型、基底细胞样型(basal-like型)和正常乳腺基因表达型(normal-like group)。2006 年 Bryan B B 等[16]首次明确提出三阴乳腺癌(triple negative breastcancer,TNBC),指ER、PR和人表皮生长因子受体2(human epidermal growth factor receptor-2,Her-2) 均表现为阴性的乳腺癌。TNBC相对非三阴乳腺癌有明显不同的临床病理特征,如发病年龄相对较早、组织学分级恶性程度比例高、局部容易出现复发、有着较高远处转移率、预后不良、死亡率高、治疗方案有限,效果欠佳等。AR在乳腺癌组织中有较高的表达率。Qi J P等[17]报道AR的阳性表达率为77%,ER、PR的阳性表达率分别为61%、60%,AR的阳性表达率均高于ER、PR的阳性表达率,并且与ER、PR表达呈正相关(P<0.000 1)。研究还发现肿瘤越小阳性表达率越高,与肿瘤较大者比较差异有统计学意义。Ogawa Y等[18]应用免疫组织化学的方法检测了227例原发性乳腺癌中AR的表达,发现AR阳性率为62.6%,同时检测了ER、PR、Her-2的表达,经分析比较发现,AR与ER和PR均呈正相关,但与Her-2表达无关,在所有病例中18.5%为三阴性乳腺癌,其中有43%表现为AR阳性。目前认为雄激素和雄激素受体在乳腺癌的发生过程中扮演了重要角色,以AR为靶向的治疗方法应该以ER-/PR-/AR+乳腺癌患者为研究对象,并且这种类型肿瘤的其他特征也需要深入探讨。目前有学者将TNBC合并AR阴性的患者定义为TNBC的一个亚型或称为四阴乳腺癌(quadruple-negative breast cancer,QNBC),由于QNBC缺乏有效的治疗靶点,故QNBC将是未来乳腺癌治疗的挑战[19-20]。
3.2 AR及其关联基因在乳腺癌中的信息学分析
本文通过对2个数据库分析筛选出21个与AR 相关的基因,其中 MLPH,SYT17,PIP,ALCAM,TOX3在网络图中缺乏与AR存在强的直接的相互作用证据,提示这些基因可能是尚未明确的与乳腺癌相关的基因。MLPH是色素相关基因,新近研究发现该基因在TNBC中下调,并与ER的表达呈正相关,但该文没有直接分析MLPH与AR的相关性[21]。SYT17为人突触囊泡蛋白ⅩⅦ基因,免疫组化提示SYT17在乳腺组织中有高的表达,但未有SYT17与乳腺癌相关的文献报道。泌乳素诱导蛋白(PIP)是一个敏感度较高的肿瘤标记物,在乳腺癌中过度表达,反映乳腺上皮细胞特异性改变,是临床上乳腺癌微转移标记物之一[22]。活化白细胞黏附分子(ALCAM)在乳腺癌中高表达,可促使细胞黏附能力减弱,肿瘤远处转移[23];基因芯片分析发现ALCAM与AR具有相关性,但未进一步阐明其机制[24]。TOX3基因多态性与乳腺癌相关,但没有发现TOX3与AR相关[25-26]。GO分析是广泛使用的基因注释方法,包括生物过程(biological process)、分子功能(molecular function)和细胞组件(cellular component)。本研究中GO分析发现差异表达基因富集到了9个生物过程,这些基因主要参与调控细胞死亡、凋亡、迁移和免疫效应过程等,提示AR在乳腺癌发病中可能的作用机制。
总之,本文利用生物信息学的方法对乳腺癌数据进行挖掘,探讨了AR在乳腺癌发病中的生物学效应,为进一步阐明其机制及实验研究提供了方向。本文的后续工作为发现和验证更多的AR关联基因,了解AR在乳腺癌作用中的信号通路和分子机制,为乳腺癌的个体化诊断和治疗提供科学依据。
[1]石建伟,唐智柳,蔡美玉,等.2008-2012年我国女性乳腺癌流行状况的系统性综述[J].中国妇幼保健,2014(10):1 622-1 626.
[2]Reiazi R,Norozi A,Etedadialiabadi M.A literature survey on cost-effectiveness of proton beam therapy in the management of breast cancer patients[J].Iran J Cancer Prev,2015,8(6):e4 373.
[3]Grogg A,Trippel M,Pfaltz K,et al.Androgen receptor status is highly conserved during tumor progression of breast cancer[J].BMC Cancer,2015(15):872.
[4]Ciriello G,Gatza M L,Beck A H,et al.Comprehensive molecular portraits of invasive lobular breast cancer[J].Cell,2015,163(2):506-519.
[5]Hatzis C,Pusztai L,Valero V,et al.A genomic predictor of response and survival following taxane-anthracycline chemotherapy for invasive breast cancer[J].Jama,2011,305(18):1 873-1 881.
[6]Shannon P,Markiel A,Ozier O,et al.Cytoscape:a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks[J].Genome Res,2003,13(11):2 498-2 504.
[7]Bindea G,Mlecnik B,Hackl H,et al.ClueGO:a cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks[J].Bioinformatics,2009,25(8):1 091-1 093.
[8]Cerami E G,Gross B E,Demir E,et al.Pathway commons,a web resource for biological pathway data[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2011(39):D685-D690.
[9]Kanda T,Jiang X,Yokosuka O.Androgen receptor signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma and pancreatic cancers[J].World J Gastroenterol,2014,20(28):9 229-9 236.
[10]Jasavala R,Martinez H,Thumar J,et al.Identification of putative androgen receptor interaction protein modules:cytoskeleton and endosomes modulate androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer cells[J].Mol Cell Proteomics,2007,6(2):252-271.
[11]Hu D G,Hickey T E,Irvine C,et al.Identification of androgen receptor splice variant transcripts in breast cancer cell lines and human tissues[J].Horm Cancer,2014,5(2):61-71.
[12]Barbaro M,Oscarson M,Almskog I,et al.Complete androgen insensitivity without Wolffian duct development:the AR-A form of the androgen receptor is not sufficient for male genital development[J].Clin Endocrinol(Oxf),2007,66(6):822-826.
[13]Takeda H,Chodak G,Mutchnik S,et al.Immunohistochemical localization of androgen receptors with mono and polyclonal antibodies to androgen receptor[J].J Endocrinol,1990,126(1):17-25.
[14]Carreau G,Del Casar J M,Corte M D,et al.Local recurrence after mastectomy for breast cancer:analysis of clinicopathological,biological and prognostic characteristics[J].Breast Cancer Res Treat,2007,102(1):61-73.
[15]Perou C M,Sorlie T,Eisen M B,et al.Molecular portraits of human breast tumours[J].Nature,2000,406(6 797):747-752.
[16]Bryan B B,Schnitt S J,Collins L C.Ductal carcinoma in situ with basal-like phenotype:a possible precursor to invasive basal-like breast cancer[J].Mod Pathol,2006,19(5):617-621.
[17]Qi J P,Yang Y L,Zhu H,et al.Expression of the androgen receptor and its correlation with molecular subtypes in 980 chinese breast cancer patients[J].Breast Cancer(Auckl),2012(6):1-8.
[18]Ogawa Y,Hai E,Matsumoto K,et al.Androgen receptor expression in breast cancer:relationship with clinicopathological factors and biomarkers[J].Int J Clin Oncol,2008,13(5):431-435.
[19]Wu X,Li Y,Wang J,et al.Long chain fatty Acyl-CoA synthetase 4 is a biomarker for and mediator of hormone resistance in human breast cancer[J].PLoS One,2013,8(10):e77 060.
[20]Barton V N,D'Amato N C,Gordon M A,et al.Androgen receptor biology in triple negative breast cancer:a case for classification as AR+or quadruple negative disease[J].Horm Cancer,2015,6(5/6):206-213.
[21]He J,Yang J,Chen W,et al.Molecular features of triple negative breast cancer:microarray evidence and further integrated analysis[J].PLoS One,2015,10(6):e0129842.
[22]Vanneste M,Naderi A.Prolactin-induced protein regulates cell adhesion in breast cancer[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2015,468(4):850-856.
[23]Al-Shehri F S,Abd E A E.Activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule(ALCAM)in Saudi breast cancer patients as prognostic and predictive indicator[J].Breast Cancer(Auckl),2015(9):81-86.
[24]Doane A S,Danso M,Lal P,et al.An estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer subset characterized by a hormonally regulated transcriptional program and response to androgen[J].Oncogene,2006,25(28):3 994-4 008.
[25]Chen Q,He Y,Liu C,et al.Associations between TOX3 rs3803662 polymorphisms and immunological markers of breast cancer[J].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi,2015,95(34):2 783-2 786.
[26]He Y,Liu H,Chen Q,et al.Relationship between five GWAS-identified single nucleotide polymorphisms and female breast cancer in the Chinese Han population[J].Tumour Biol,2016,37(7):9 739-9 744.
(编辑:张世霞)
Bioinformatics study of androgen receptor in patients with breast cancer
Li Bing1,Du Gang2,3,Wang Jinhua3,4
(1.Coal Ocupational Disease Prevention and Control Center,Coal Industry Department of Shanxi Province,Taiyuan Shanxi 030012;2.The First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University,Guangzhou Guangdong 510632;3.Center for Health Informatics and Bioinformatics,New York University School of Medicine,New York,NY,USA;4.Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center,New York University School of Medicine,New York,NY,USA)
Objective:To explore the role of Androgen receptor(AR)and its expression-correlated genes in breast cancer.Methods:2 gene expression datas of breast cancer were downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas(TCGA)and NCBI.The AR expression-correlated genes were filtered and analysed by the plug-in of ClueGO in the Cytoscape platform.Results:A total of 21 genes were identified with a high correlation with AR by pearson value >0.40 or <-0.40.Among those genes,4 genes showed a negative correlation with AR,and 17 genes showed a positive correlation with AR.Functional enrichment analysis was performed using ClueGO,and the enrichment biological processes including epithelial cell differentiation,cell differentiation,prostate gland epithelium morphogenesis,prostate gland morphogenesis,epithelium development glandular epithelial cell differentiation,digestive tract morphogenesis.We also found the genes of MLPH,SYT17,PIP,ALCAM,TOX3 were separated from the gene network,and it implied those genes had seldom reported about their correlation with AR and should be considered as objective genes in further study.Conclusion:AR play an important role in breast cancer,deep understanding of AR function could be an enhancement for the precision medicine of breast cancer.
breast cancer;androgen receptor;bioinformatics
R737.9
:A
:1671-0258(2017)03-0060-05
李兵,主治医师,E-mail:20610015@qq.com
