血清IL- 34水平与SLE疾病活动度关系的研究
2017-09-03王红旭赖晓霏
王红旭 赖晓霏
(重庆医科大学附属第一医院检验科,重庆400016)
血清IL- 34水平与SLE疾病活动度关系的研究
王红旭 赖晓霏
(重庆医科大学附属第一医院检验科,重庆400016)
目的:检测系统性红斑狼疮(Systemic lupus erythematosus,SLE)患者血清白细胞介素(Interleukin,IL)- 34水平,并进一步探讨IL- 34与临床和实验室指标及SLE疾病活动度的关系。方法:采用酶联免疫吸附试验(Enzyme- linked immunosorbent assay,ELISA)测定78例SLE组及53名正常对照组血清IL- 34水平,SLE组与正常组血清IL- 34水平分析采用曼- 惠特尼U检验(Mann- WhitneyUtest)。结果:与正常对照相比,SLE组血清IL- 34水平明显高于正常对照组[(Median,128.9 pg/ml) vs (Median,52.4 pg/ml),P<0.001],差异有统计学意义。IL- 34水平与SLE疾病活动度、双链DNA抗体(anti- double stranded DNA antibody,anti- dsDNA)滴度、C反应蛋白(C- reactive protein,CRP)呈正相关,与C3水平呈负相关。结论:血清IL- 34可能成为SLE的一血清标志物,因其在SLE患者中升高,且与疾病活动度相关。
系统性红斑狼疮;白细胞介素34;活动度
系统性红斑狼疮(Systemic lupus erythematosus,SLE)是一种多克隆T、B淋巴细胞激活自身抗体产生及免疫复合物生成而导致组织器官损伤的异质性的系统性自身免疫性疾病。SLE的病理机制复杂,包括遗传、激素、免疫和环境因素[1,2]。然而,SLE的发病机制尚不明确,大量研究显示,细胞因子在其发病过程中发挥重要作用。
白细胞介素(Interleukin,IL)- 34是2008年发现的白介素家族的新成员,它是集落刺激因子受体1(Colony stimulating factor 1receptor,CSF- 1R)的另一个配体[3]。目前,已知IL- 34和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子受体(Macrophage- colony stimulating factor,M- CSF)的功能相似,在各种炎性和自身免疫性疾病中发挥着重要的作用[4,5]。IL- 34可促进单核巨噬细胞、破骨细胞分化。研究显示,IL- 34在类风湿关节炎(Rheumatoid arthritis,RA)中发挥重要作用[6],同时在SLE中升高,但是SLE血清IL- 34水平与临床和实验室指标的关系尚不明确。因此,本研究通过检测SLE患者与正常对照组血清IL- 34水平,分析探讨血清IL- 34水平与SLE临床和实验室指标的关系。
1 资料与方法
1.1 资料 选取2014年1月至2015年12月重庆医科大学附属第一医院收治的SLE门诊及住院患者,诊断均符合1997年美国风湿病协会(American College of Rheumatology)制定的SLE分类标准,均排除感染、肿瘤、糖尿病及其他自身免疫性疾病。正常对照组均来自同期本院体检中心的健康人群,无风湿病史及风湿病家族史。两组一般资料具有可比性。SLE病人疾病活动度依据SLE疾病活动指数(SLEDAI)计算,SLEDAI≥6分定义为活动患者。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 临床指标检测方法 所有SLE患者接受标准的病史采集和体格检查。所有受检者晨起抽取静脉血4 ml,离心取其血清,标本放置于-20℃保存待测。应用双抗体夹心酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)检测血清IL- 34水平(R&D Systems,USA);anti- dsDNA抗体滴度检测采用ELISA(Euroummun,USA);血清补体3(Complement 3,C3)、C4和C反应蛋白(C- reactive protein,CRP)水平检测采用免疫比浊法(Beckman Immage 800);血沉(Erythrocyte sedimentation,ESR)检测采用魏氏法。
1.3 统计学处理 所有统计数据均采用SPSS17.0进行统计学分析,计量资料结果以[中位数(四分位数范围)][Median(interquartile range)],[median(IQR)]表示,两组间比较及IL- 34与其他连续变量间关系分析均采用曼- 惠特尼U检验(Mann- WhitneyUtest)。多组间比较采用Bonferroni法。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 一般资料 共有131个对象被纳入本研究,其中SLE组78例,监控对照组53例。SLE组中有20例SLE疾病活性患者,58例非活动患者,SLE组病程为7(3.6-12.1)年[Median(IQR)]。SLE组和对照组年龄分别为55.2(48.1~66.7)岁,57.6(45.5~66.1)岁[Median(IQR)]。SLE组和对照组性别比例分别为9/69和6/47(男/女)。SLE组与对照组的年龄、性别均无统计学差异。RA疾病组与对照组的指标水平见表1,疾病组的RF、ESR、CRP和CCP水平较对照组均明显增加,并且疾病组稳定期与活动期的CRP和ESR有明显差别。但是SLE组的疾病组和对照组的anti- dsDNA、C3、C4、CRP and ESR水平有显著性差异(P<0.001,表1)。
2.2 SLE患者血清IL- 34水平升高 比较SLE组和健康对照组血清IL- 34水平,结果显示SLE组IL- 34水平(Median,128.9 pg/ml)显著高于健康对照组(Median,52.4 pg/ml;P<0.001,图1),所有健康对照组血清IL- 34水平不高于80 pg/ml。进一步分析SLE活动组和非活动组血清IL- 34水平,统计结果为SLE活动组血清IL- 34水平(Median,312 pg/ml)显著高于非活动组(Median,97 pg/ml;P<0.001,图2)。
2.3 血清IL- 34水平与SLE疾病活动度指标的关系 血清IL- 34水平与SLEDAI呈显著正相关(rs=0.62,P=0.001 1,图3A),同时血清IL- 34还与anti- dsDNA(rs=0.45,P=0.012,图3B)和CRP(rs=0.65,P=0.0013,图3C)呈正相关,但与C3呈负相关(rs=0.54,P=0.002,图3D)。但是,血清IL- 34水平与C4(rs=0.26;P=0.055;图3E),ESR(rs=0.21;P=0.053;图3F)和水平无显著性差异。因此,血清IL- 34水平反应SLE疾病活动度。
表1 SLE患者与健康对照组的临床资料比较
Tab.1 Demographic and clinical characteristics of study subjects
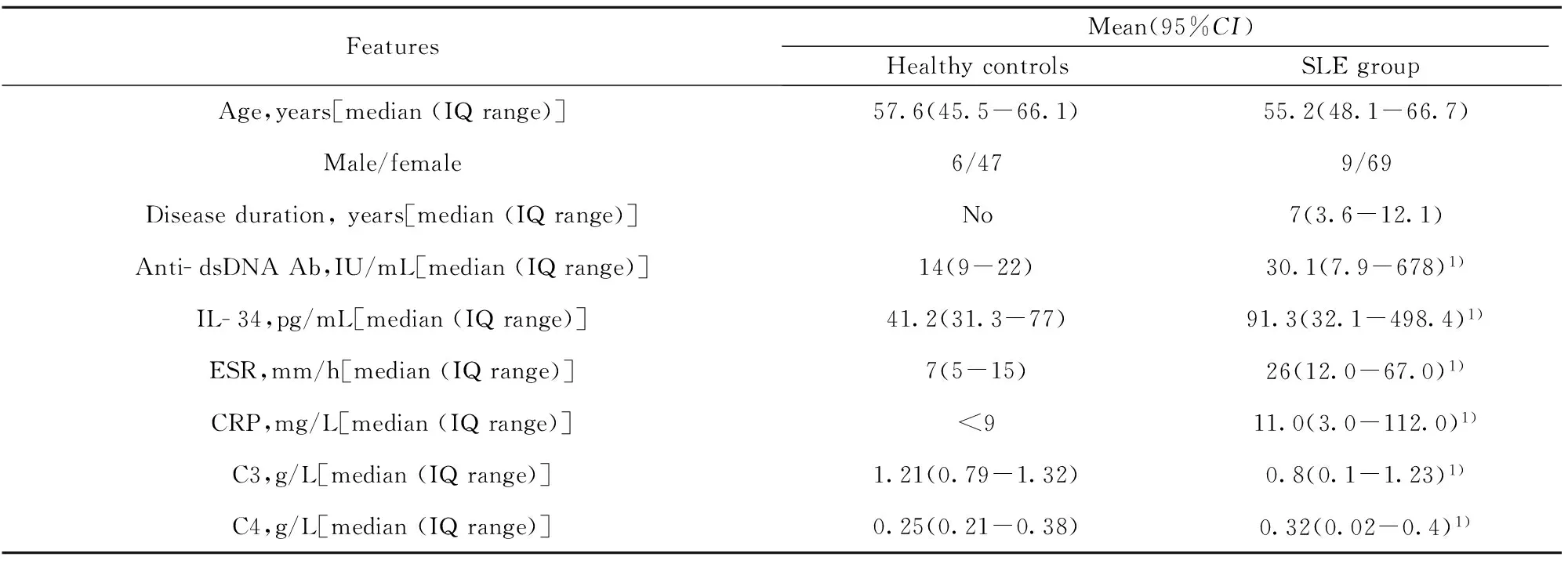
FeaturesMean(95%CI)HealthycontrolsSLEgroupAge,years[median(IQrange)]57.6(45.5-66.1)55.2(48.1-66.7)Male/female6/479/69Diseaseduration,years[median(IQrange)]No7(3.6-12.1)Anti-dsDNAAb,IU/mL[median(IQrange)]14(9-22)30.1(7.9-678)1)IL-34,pg/mL[median(IQrange)]41.2(31.3-77)91.3(32.1-498.4)1)ESR,mm/h[median(IQrange)]7(5-15)26(12.0-67.0)1)CRP,mg/L[median(IQrange)]<911.0(3.0-112.0)1)C3,g/L[median(IQrange)]1.21(0.79-1.32)0.8(0.1-1.23)1)C4,g/L[median(IQrange)]0.25(0.21-0.38)0.32(0.02-0.4)1)
Note:Anti- dsDNA Ab,anti- double-stranded DNA antibody;IL- 34, interleukin- 34;ESR,erythrocyte sedimentation rate;CRP,C- reactive protein;C3,complement 3;C4,complement 4.IQ,interquartile.1)P<0.001 vs control.
2.5 血清IL- 34水平与SLE临床表现的关系 SLE患者依据其临床表现的个数计分,进而SLE患者依据其得分被分为3组,再比较这3组SLE患者的IL- 34水平。阳性临床表现包括:颊部红斑、盘状红斑、脱发、口腔或鼻腔溃疡、浆膜炎、关节炎、活动性肾炎、血管炎、中枢神经系统性红斑狼疮、温度>38℃,血小板减少(<100×109L-1),白细胞减少(<3×109L-1),贫血(<100 g/L)。统计结果显示血清IL- 34水平随着临床表现个数增加而升高(P<0.001;表 2)。因此,高水平的血清IL- 34与SLE临床表现的增多有关系。

图1 IL- 34在健康对照组和SLE组中的血清分布情况Fig.1 Scatter- plots of serum interleukin- 34(IL- 34)levels in healthy control subjects and SLE(systemic lupus erythematosus)patientsNote: The differences between SLE patients and controls were deter mined by non- parametric Mann- Whitney rank sum test.The horizontal lines indicate the median concentration for each group.

图2 IL- 34在SLE活动组和非活动组中的血清分布情况Fig.2 Scatter- plots of serum interleukin- 34(IL- 34)levels in active SLE(systemic lupus erythematosus)patients and inactive SLE patientsNote: The horizontal lines indicate the median concentration for each group.The differences between active SLE patients and inactive SLE patients were deter mined by non- parametric Mann- Whitney rank sum test.
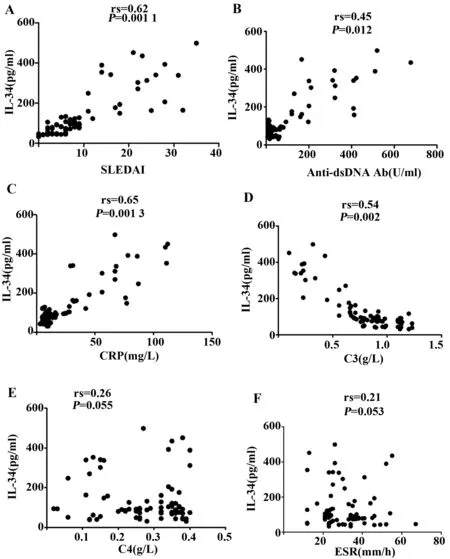
图3 患者血清中IL- 34与SLE疾病活动指数的相关性分析(n=78)Fig.3 Correlation of serum IL- 34 concentrations with systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index(SLEDAI)in all systemic lupus erythemato- sus(SLE)patients(n=78)Note: Spearman′s rank correlation coefficient was employed to assess correlations;P- values are shown.
表2 血清IL- 34水平与SLE临床表现的关系
Tab.2 Associations between SLE clinical features and titer of IL- 34

ClinicalfeaturesNumberMedianIL-34(95%CI)01443(30.1-50.3)1)1-244124.2(50.5-202.4)1)3-820312.0(193.5-498.4)1)
Note:Number of positive clinical features including malar rash/discoid rash,alopecia,oral or nasal ulcers,serositis,arthritis,active nephritis,CNS(central nervous system) lupus,vasculitis,temperature >38℃,thrombocytopenia,leukopenia,anemia.1)P<0.001,Bonferroni test was employed to compared the three clinical feature groups.
3 讨论
细胞因子调节多种免疫功能,当其异常分泌时,可致机体免疫功能失调,甚至诱发自身免疫性疾病。近年来大量研究表明,诸多细胞因子参与SLE发病和疾病进展,许多细胞因子能促进自身反应性T、B 细胞活化,进而破坏免疫稳态,最终导致细胞、组织和脏器损伤。
IL- 34是CSF- 1R的另一个配体,主要表达于单核巨噬细胞、成纤维细胞、小神经胶质细胞[4]。IL- 34有促进炎症的作用。IL- 34能促进单核- 巨噬细胞增殖及分化,后者能产生多种细胞因子,比如TNF和IL- 6[3,7]。另外,IL- 34能诱导炎症因子,比如IL- 6、IL- 8[8]。IL- 34和M- CSF的功能相似,在各种炎性和自身免疫性疾病中发挥着重要的作用[4],比如RA、干燥综合征、狼疮肾炎。IL- 34与RA的发病及炎症反应相关[5],RA患者关节滑膜成纤维细胞表达IL- 34,且与滑膜炎的严重程度相关[6]。同时IL- 34还可促进破骨细胞形成[9]。有研究提示,SLE患者IL- 34水平升高,但是其与SLE临床和实验室指标的关系尚无相关研究。我们研究证实IL- 34水平在SLE患者中升高,特别是在活动性SLE患者中。同时血清IL- 34水平还与SLE活动度呈正相关,且与临床症状累积数量相关,IL- 34水平可在一定程度上提示SLE病情。因此,IL- 34可能在SLE的发病中起重要作用,血清IL- 34可能成为反映SLE疾病活动度的生物学标志物。然而,该研究未覆盖SLE治疗干预前后IL- 34与疾病转归的相关性。在后续研究中,应纳入IL- 34在治疗前后的变化。另外,目前极少有IL- 34与SLE在细胞水平、动物模型中的研究,因此对IL- 34在SLE的发病中的具体机制需要更深入的研究与探索。
[1] Kotzin BL.Systemic lupus erythematosus[J].Cell,1996,85(3):303- 306.
[2] Lisnevskaia L,Murphy G,Isenberg D.Systemic lupus erythematosus[J].Lancet,2014,384(9957):1878- 1888.
[3] Lin H,Lee E,Hestir K.Discovery of a cytokine and its receptor by functional screening of the extracellular proteome.[J]Science,2008,320(5877):807- 811.
[4] Nakamichi Y,Udagawa N,Takahashi N.IL- 34 and CSF- 1:similarities and differences.[J]J Bone Miner Metab,2013,31(5):486- 495.
[5] Masteller EL,Wong BR.Targeting IL- 34 in chronic inflammation.[J]Drug Discov Today,2014,19(8):1212- 1216.
[6] Zhou RP,Wu XS,Xie Y.Functions of interleukin- 34 and its emerging association with rheumatoid arthritis.[J]Immunology,2016,149(4):362- 373.
[7] Hamilton JA,Tak PP.The dynamics of macrophage lineage populations in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.[J] Arthritis Rheum,2009,60(5):1210- 1221.
[8] Eda H,Zhang J,Keith RH.Macrophage- colony stimulating factor and interleukin- 34 induce chemokines in human whole blood.[J] Cytokine,2010,52(3):215- 220.
[9] Chen Z,Buki K,Vaaraniemi J.The critical role of IL- 34 in osteoclastogenesis.[J]PLoS One,2011,12(4):186- 189.
[收稿2017- 02- 16 修回2017- 03- 19]
(编辑 许四平 刘格格)
Relationship between levels of serum IL- 34 and disease activity of systemic lupus erythematosus
WANG Hong- Xu,LAI Xiao- Fei.
Department of Laboratory Medicine,the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University,Chongqing 400016,China
Objective:To investigate levels of serum IL- 34 in SLE patients,and correlation between concentrations of serum IL- 34 and other established serum markers and disease activity indexes.Methods: In all,78 SLE patients and 53 healthy controls were enrolled in the research.Enzyme- linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA) was employed to measuring the concentrations of serological IL- 34.Then,serum IL- 34 levels between SLE group and healthy controls were analyzed by Mann- WhitneyUtest.Meanwhile,the correlation between the serum IL- 34 levels and disease activity indexes and other established serum markers were assessed.Serum IL- 34 levels were significantly higher in SLE patients compared to healthy controls[(Median,128.9 pg/ml) vs (Median,52.4 pg/ml),P<0.001].Results: Their levels were remarkably associated with accumulation of the clinical features of SLE.Additionally,IL- 34 titers were positively correlated with the SLE disease activity indexes,anti- double stranded DNA antibody(anti- dsDNA)titers and C- reactive protein(CRP)levels,but inversely with C3 levels.Conclusion: Serum IL- 34 could be a candidate biomarker for SLE as the elevated serum levels in treatment- naive SLE patients and its association with SLE disease activity.
Systemic lupus erythematosus;IL- 34;Activity index
10.3969/j.issn.1000- 484X.2017.08.023
王红旭(1987年-),女,硕士,检验医师,主要从事自身免疫性疾病研究。
及指导教师:赖晓霏(1982年-),女,硕士,主管技师,主要从事自身免疫性疾病的研究,E- mail:87936966@qq.com。
R593.24
A
1000- 484X(2017)08- 1232- 04