微织构球头铣刀铣削钛合金表面粗糙度预测
2017-08-30杨树财周永志张玉华佟欣刘伟伟
杨树财+周永志+张玉华+佟欣+刘伟伟


摘 要:为了研究微织构球头铣刀铣削钛合金加工表面的表面粗糙度,采用正交试验法,进行了微织构球头铣刀铣削钛合金的试验,得出了微坑织构参数与表面粗糙度之间的变化规律并分析了影响机理。利用极差分析法确定了各因素对表面粗糙度影响的主次顺序。通过回归分析原理,建立了表面粗糙度预测模型。统计检验结果表明,所建立的表面粗糙度预测模型是显著的。并对表面粗糙度的预测值与试验观测值进行了对比,证实了模型的可靠性。
关键词:微织构;正交试验法;表面粗糙度;预测模型
DOI:10.15938/j.jhust.2017.03.026
中图分类号: TG506
文献标志码: A
文章编号: 1007-2683(2017)03-0141-06
Abstract:In order to study the surface roughness of titanium alloy by microtextured ballnosed end mill within milling, based on orthogonal test, the experiment of milling titanium alloy with microtextured ball end milling cutter was carried out. The variation regularity between the texture parameters and the surface roughness was obtained and the mechanism was analyzed. The influence of various factors on the surface roughness is determined by the range analysis method. Based on the principle of regression analysis, the predictive model of surface roughness was established. The statistical test results show that the prediction model of surface roughness is significant. The predicted values of the surface roughness were compared with the experimental observations, which confirmed the reliability of the model.
Keywords:microtexture; orthogonal test; surface roughness; predictive model
5 结 论
本文通过微织构球头铣刀铣削钛合金表面粗糙度试验研究,得出如下结论:
(1)球头铣刀前刀面置入微坑织构对已加工表面粗糙度具有显著影响。通过正交试验的极差分析结果表明,微坑织构参数对表面粗糙度影响大小的主次顺序为:直径>间距>深度>距切削刃距离。
(2)通过微织构球头铣刀铣削钛合金试验研究,结果发现微坑织构具有储存细小切屑、磨粒以及其它杂质等作用,微织构的置入在一定程度上改变了切屑流动方向,使已加工表面粘结现象明显改善。从而减少杂质对已加工表面的耕犁,有助于改善工件表面质量。
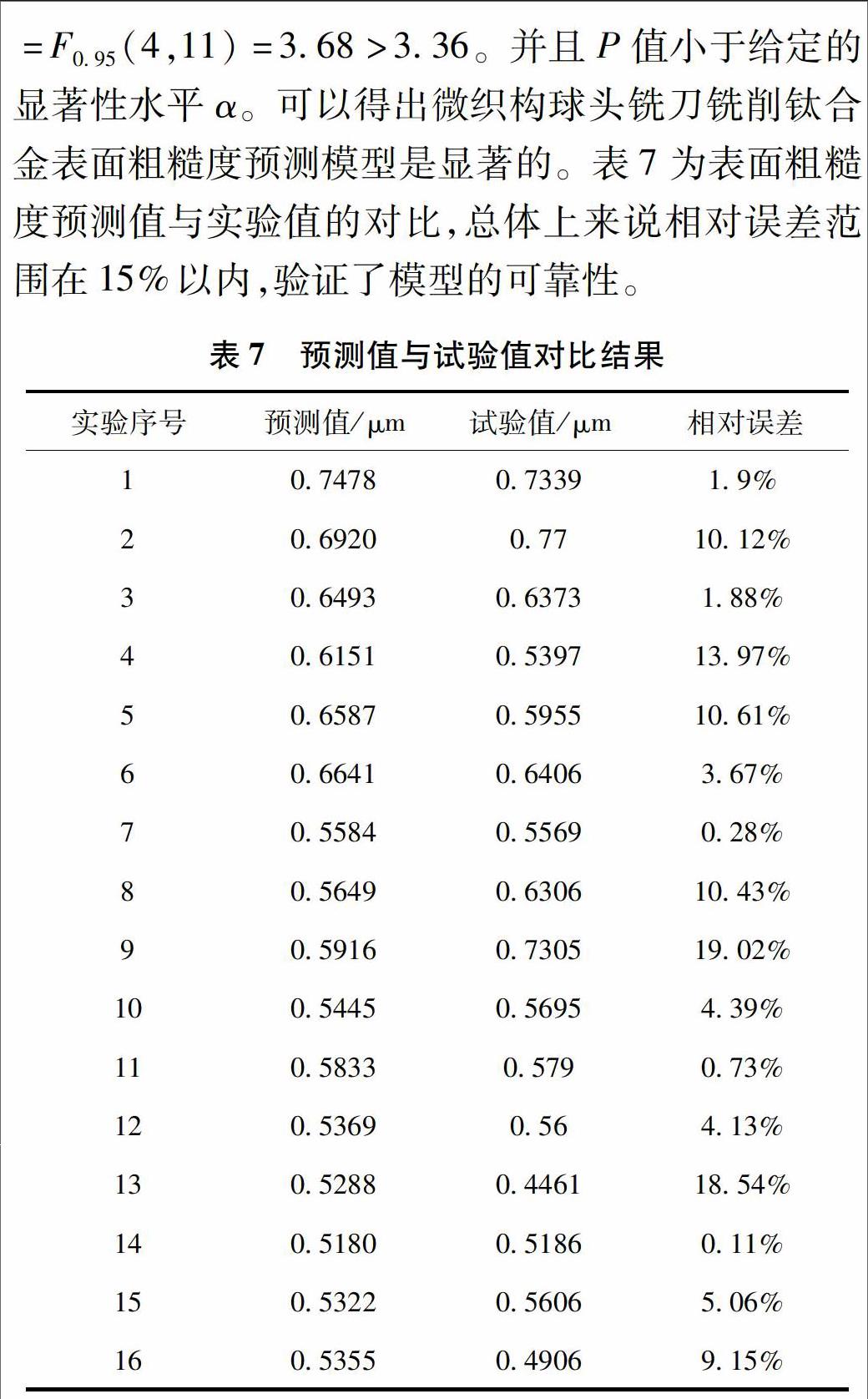
(3)采用正交试验法并对其结果进行回归分析,建立了表面粗糙度预测模型。统计检验结果表明,所建立的表面粗糙度预测模型呈较高显著检验状态。通过试验观测值与预测值的对比分析,证实了模型的可靠性。
参 考 文 献:
[1] ZHANG C, GUO S, ZHANG H, Zhou L (2013) Modeling and Predicting for Surface Topography Considering Tool Wear in Milling Process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 68(9-12):2849-2860.
[2] ZOU B, ZHOU H, HUANG C, et al. Wang J (2015) Tool Damage and Machinedsurface Quality Using Hotpressed Sintering Ti (C7N3)/WC/TaC Cermet Cutting Inserts for Highspeed Turning Stainless Steels. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 79(1-4):197-210.
[3] PETROPOULOS GP, PANDAZARAS CN. Davim JP (2010) Surface Texture Characterization and Evaluation Related to Machining. In: Davim JP (ed) Surface Integrity in Machining. Springer, London, pp 37-66.
[4] EZUGWU EO, WANG ZM (1997) Titanium Alloys and Their Machinability—a Review. J Mater Process Technol 68:262-274.
[5] 楊振朝, 张定华, 姚倡锋,等. TC4钛合金高速铣削参数对表面完整性影响研究[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2009, 27(4).
[6] 戚宝运.基于表面微织构刀具的钛合金绿色切削冷却润滑技术研究.南京航空航天大学博士论文,2011:12-14.
[7] WU Y, ZITELLI J P, TENHUISEN K S, et al. Differential Response of Staphylococci and Osteoblasts to Varying Titanium Surface Roughness.[J]. Biomaterials, 2011, 32(4):951-60.
[8] AMIN AKMN, ISMAILl A F, KHAIRUSSHIMA M K N. Effectiveness of Uncoated WCCo and PCD Inserts iin End Milling of Titanium Alloy—Ti6Al4V[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2007, s 192193(5):147-158.
[9] 杜随更,吕超,任军学,等.钛合金TC4高速铣削表面形貌及表层组织研究[J].航空学报,2008, 29(6):1710-1715.
[10]任军学,姚倡鋒,田卫军,等.球头铣刀结构参数对钛合金铣削表面完整性的影响[J]. 航空制造技术, 2010(1):81-84.
[11]吴泽. 微织构自润滑与振荡热管自冷却双重效用的干切削刀具的研究[D]. 山东大学, 2013.
[12]冯闯.基于钛合金切削的硬质合金球头铣刀磨损研究[D].哈尔滨理工大学,2015.
[13]YANG S C, CUI X Y, ZHANG Y H, et al. Effect of Tool Wear on Surface Qualities in Milling of TC4[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2016, 836-837:132-138.
[14]崔晓雁. 微织构球头铣刀铣削钛合金表面质量研究[D]. 哈尔滨理工大学, 2016.
[15]石英. 高温处理对钛合金物理和机械性能的影响[J]. 中国材料进展, 2000(9):18-19.
[16]Andy.钛合金的特性及其应用[J]. 2010.
[17]JIANG W, HU Y, ZHENG Q, et al. Study of Drilling Temperature on Cortical Bone Based on Microtexture Tool[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2016.
[18]杨树财, 王焕焱, 张玉华,等. 多目标决策的微织构球头铣刀切削性能评价[J]. 哈尔滨理工大学学报, 2016, 21(6):1-5.
[19]杨树财, 王志伟, 张玉华等. 微织构球头铣刀加工钛合金的有限元仿真[J]. 沈阳工业大学学报, 2015, 37(5):530-535.
[20]吴彬, 张登清, 张斌. 基于正交试验法的TC4钛合金铣削参数优化[J]. 机械工程师, 2014(8):93-94.
[21]冯力. 回归分析方法原理及SPSS实际操作[J]. 2004.
(编辑:王 萍)
