非ST抬高型ACS患者窦性心律震荡与ST—T及超敏肌钙蛋白关系分析
2017-08-22王海林王培宁黄庆彬
王海林+王培宁+黄庆彬
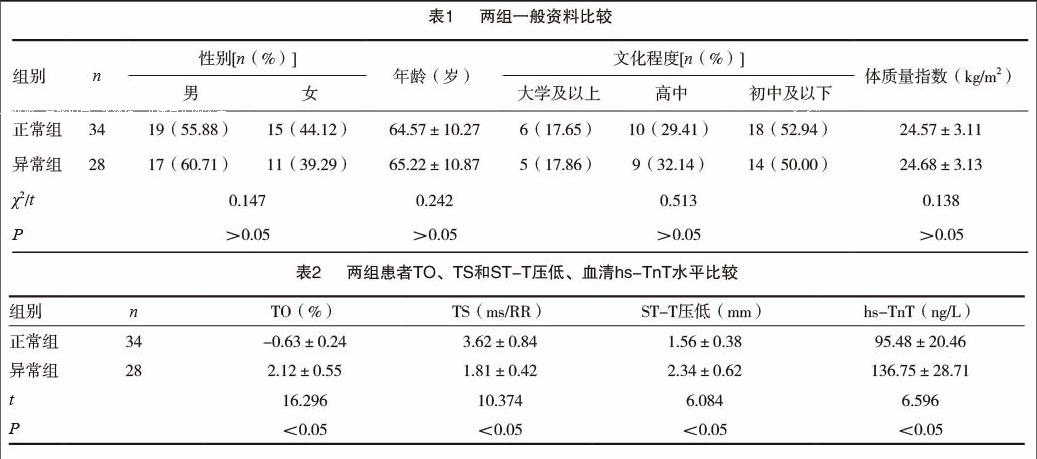
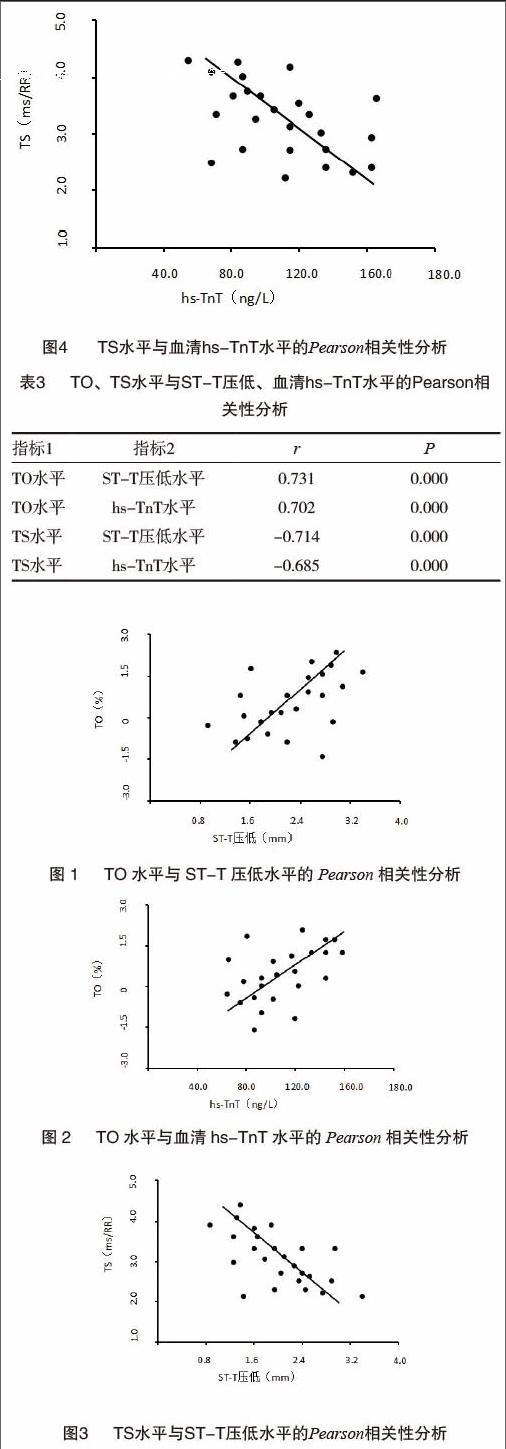
[摘要] 目的 探討非ST抬高型急性冠状动脉综合征(acute coronary syndrome,ACS)患者窦性心律震荡与ST-T及超敏肌钙蛋白关系分析。 方法 回顾性分析2014年9月~2016年5月期间我院及广东省人民医院确诊治疗的非ST抬高型ACS患者62例,依据是否伴有窦性心律震荡异常分为异常组(n=28例)和正常组(n=34例),所有患者均给予经心脏彩超、动态心电图等检查,采用酶联免疫吸附法检测血清超敏肌钙蛋白T(hypersensitive troponin T,hs-TnT)水平,采用Pearson相关性分析法分析震荡初始值(turbulence onset,TO)、震荡斜率(turbulence slope,TS)水平与ST-T压低、血清hs-TnT水平的关系。 结果 异常组患者TO、ST-T压低、血清hs-TnT水平明显高于正常组,前者TS水平明显低于后者,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);Pearson相关性分析法结果显示,TO水平与ST-T压低、血清hs-TnT水平呈正相关(r1=0.731,P<0.05;r2=0.702,P<0.05),TS水平与ST-T压低、血清hs-TnT水平呈负相关(r3=-0.714,P<0.05;r4=-0.685,P<0.05)。 结论 非ST抬高型ACS患者窦性心律震荡中的TO、TS水平与ST-T压低及血清hs-TnT水平有关,提示其也具有有效反映患者病情的作用,可作为患者病情新的心电评估指标之一,值得临床作进一步推广。
[关键词] 非ST抬高型急性冠状动脉综合征;窦性心律震荡;ST-T;超敏肌钙蛋白
[中图分类号] R542.22 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 2095-0616(2017)13-254-04
[Abstract] Objective To explore relationship analysis of sinus rhythm turbulence and ST-t and high-sensitivity troponin of patients with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome(ACS). Methods 62 patients with Non-ST Elevation ACS who were diagnosed and treated in our hospital and Guangdong General Hospital from September 2014 to May 2016 were retrospectively analyzed.According to sinus rhythm turbulence abnormality,all patients were divided into the abnormal group(n=28) and the normal group(n=34).All patients were given heart color ultrasound,dynamic electrocardiogram and other examinations.Hypersensitive troponin T(hs-TnT) level was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.Relationship between turbulence onset (TO) and turbulence slope(TS) and ST–T lowering and serum hs-TnT level was analyzed by Pearson correlation analysis. Results TO,ST-t lowering and serum hs-TnT levels of patients in the abnormal group were significantly higher than those of the normal group while TS was significantly lower than that of the normal group.There were statistical differences(P<0.05).Results of Pearson correlation analysis showed TO level,ST–T lowering and serum hs-TnT level were positively correlated(r1=0.731,P<0.05;r2=0.702,P<0.05).TS level,ST–T lowering and serum hs-TnT level werenegatively correlated (r3=0.714,P<0.05;r4=0.685,P<0.05). Conclusion For patients with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome,TO level and TS level are correlated to ST–T lowering and serum hs-TnT level.It indicates its effect of effectively reflecting diseases of patients and it can be regarded as the new ECG evaluation index,which is worthy of further clinical promotion.
[Key words] Non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome;Sinus rhythm turbulence;ST-T;High-sensitivity troponin
[摘要] 目的 探討非ST抬高型急性冠状动脉综合征(acute coronary syndrome,ACS)患者窦性心律震荡与ST-T及超敏肌钙蛋白关系分析。 方法 回顾性分析2014年9月~2016年5月期间我院及广东省人民医院确诊治疗的非ST抬高型ACS患者62例,依据是否伴有窦性心律震荡异常分为异常组(n=28例)和正常组(n=34例),所有患者均给予经心脏彩超、动态心电图等检查,采用酶联免疫吸附法检测血清超敏肌钙蛋白T(hypersensitive troponin T,hs-TnT)水平,采用Pearson相关性分析法分析震荡初始值(turbulence onset,TO)、震荡斜率(turbulence slope,TS)水平与ST-T压低、血清hs-TnT水平的关系。 结果 异常组患者TO、ST-T压低、血清hs-TnT水平明显高于正常组,前者TS水平明显低于后者,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);Pearson相关性分析法结果显示,TO水平与ST-T压低、血清hs-TnT水平呈正相关(r1=0.731,P<0.05;r2=0.702,P<0.05),TS水平与ST-T压低、血清hs-TnT水平呈负相关(r3=-0.714,P<0.05;r4=-0.685,P<0.05)。 结论 非ST抬高型ACS患者窦性心律震荡中的TO、TS水平与ST-T压低及血清hs-TnT水平有关,提示其也具有有效反映患者病情的作用,可作为患者病情新的心电评估指标之一,值得临床作进一步推广。
[关键词] 非ST抬高型急性冠状动脉综合征;窦性心律震荡;ST-T;超敏肌钙蛋白
[中图分类号] R542.22 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 2095-0616(2017)13-254-04
[Abstract] Objective To explore relationship analysis of sinus rhythm turbulence and ST-t and high-sensitivity troponin of patients with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome(ACS). Methods 62 patients with Non-ST Elevation ACS who were diagnosed and treated in our hospital and Guangdong General Hospital from September 2014 to May 2016 were retrospectively analyzed.According to sinus rhythm turbulence abnormality,all patients were divided into the abnormal group(n=28) and the normal group(n=34).All patients were given heart color ultrasound,dynamic electrocardiogram and other examinations.Hypersensitive troponin T(hs-TnT) level was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.Relationship between turbulence onset (TO) and turbulence slope(TS) and ST–T lowering and serum hs-TnT level was analyzed by Pearson correlation analysis. Results TO,ST-t lowering and serum hs-TnT levels of patients in the abnormal group were significantly higher than those of the normal group while TS was significantly lower than that of the normal group.There were statistical differences(P<0.05).Results of Pearson correlation analysis showed TO level,ST–T lowering and serum hs-TnT level were positively correlated(r1=0.731,P<0.05;r2=0.702,P<0.05).TS level,ST–T lowering and serum hs-TnT level werenegatively correlated (r3=0.714,P<0.05;r4=0.685,P<0.05). Conclusion For patients with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome,TO level and TS level are correlated to ST–T lowering and serum hs-TnT level.It indicates its effect of effectively reflecting diseases of patients and it can be regarded as the new ECG evaluation index,which is worthy of further clinical promotion.
[Key words] Non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome;Sinus rhythm turbulence;ST-T;High-sensitivity troponin
[摘要] 目的 探討非ST抬高型急性冠状动脉综合征(acute coronary syndrome,ACS)患者窦性心律震荡与ST-T及超敏肌钙蛋白关系分析。 方法 回顾性分析2014年9月~2016年5月期间我院及广东省人民医院确诊治疗的非ST抬高型ACS患者62例,依据是否伴有窦性心律震荡异常分为异常组(n=28例)和正常组(n=34例),所有患者均给予经心脏彩超、动态心电图等检查,采用酶联免疫吸附法检测血清超敏肌钙蛋白T(hypersensitive troponin T,hs-TnT)水平,采用Pearson相关性分析法分析震荡初始值(turbulence onset,TO)、震荡斜率(turbulence slope,TS)水平与ST-T压低、血清hs-TnT水平的关系。 结果 异常组患者TO、ST-T压低、血清hs-TnT水平明显高于正常组,前者TS水平明显低于后者,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);Pearson相关性分析法结果显示,TO水平与ST-T压低、血清hs-TnT水平呈正相关(r1=0.731,P<0.05;r2=0.702,P<0.05),TS水平与ST-T压低、血清hs-TnT水平呈负相关(r3=-0.714,P<0.05;r4=-0.685,P<0.05)。 结论 非ST抬高型ACS患者窦性心律震荡中的TO、TS水平与ST-T压低及血清hs-TnT水平有关,提示其也具有有效反映患者病情的作用,可作为患者病情新的心电评估指标之一,值得临床作进一步推广。
[关键词] 非ST抬高型急性冠状动脉综合征;窦性心律震荡;ST-T;超敏肌钙蛋白
[中图分类号] R542.22 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 2095-0616(2017)13-254-04
[Abstract] Objective To explore relationship analysis of sinus rhythm turbulence and ST-t and high-sensitivity troponin of patients with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome(ACS). Methods 62 patients with Non-ST Elevation ACS who were diagnosed and treated in our hospital and Guangdong General Hospital from September 2014 to May 2016 were retrospectively analyzed.According to sinus rhythm turbulence abnormality,all patients were divided into the abnormal group(n=28) and the normal group(n=34).All patients were given heart color ultrasound,dynamic electrocardiogram and other examinations.Hypersensitive troponin T(hs-TnT) level was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.Relationship between turbulence onset (TO) and turbulence slope(TS) and ST–T lowering and serum hs-TnT level was analyzed by Pearson correlation analysis. Results TO,ST-t lowering and serum hs-TnT levels of patients in the abnormal group were significantly higher than those of the normal group while TS was significantly lower than that of the normal group.There were statistical differences(P<0.05).Results of Pearson correlation analysis showed TO level,ST–T lowering and serum hs-TnT level were positively correlated(r1=0.731,P<0.05;r2=0.702,P<0.05).TS level,ST–T lowering and serum hs-TnT level werenegatively correlated (r3=0.714,P<0.05;r4=0.685,P<0.05). Conclusion For patients with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome,TO level and TS level are correlated to ST–T lowering and serum hs-TnT level.It indicates its effect of effectively reflecting diseases of patients and it can be regarded as the new ECG evaluation index,which is worthy of further clinical promotion.
[Key words] Non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome;Sinus rhythm turbulence;ST-T;High-sensitivity troponin
