PCT、hs-CRP在并发脓毒症的肺炎新生儿中的检测价值
2017-07-31贾凯
贾 凯
(西安市儿童医院检验科,西安 710003)
PCT、hs-CRP在并发脓毒症的肺炎新生儿中的检测价值
贾 凯
(西安市儿童医院检验科,西安 710003)
目的:探析血浆降钙素原(PCT)与高敏C反应蛋白(hs-CRP)在并发脓毒症的肺炎新生儿中的临床检测意义。方法:分析2015年3月至2016年10月在我院接受住院治疗的124例肺炎新生儿的临床资料。根据有无脓毒症及脓毒症病情的严重程度可以将入选者分成A组(轻度脓毒症患儿,52例)、B组(重度脓毒症患儿,34例)和C组(非脓毒症患儿,38)三组。比较三组患儿的一般资料与血浆PCT及hs-CRP的水平、有无脓毒症患儿治疗前后PCT及hs-CRP的水平。分析血浆PCT与hs-CRP在并发脓毒症肺炎患儿中的诊断价值。结果:三组患儿的一般资料无显著差异性。C组、A组、B组患儿血清hs-CRP及PCT水平依次上升,且A、B组显著高于C组,B组显著高于A组。血浆PCT与hs-CRP联合检测的准确性、特异性较单项指标高。合并脓毒症的肺炎患儿治疗后的血浆PCT与hs-CRP水平明显较治疗前低,而无脓毒症的肺炎患儿治疗后的血浆PCT与hs-CRP水平未显著下降。结论:血浆PCT与hs-CRP联合检测有助于早期诊断并发脓毒症的肺炎新生儿,且在其疗效及预后判断中有着较高的预测价值,值得推广。
降钙素原;高敏C反应蛋白;脓毒症;肺炎;新生儿
临床上脓毒症具有较高的致病率与致死率,在新生儿中属于常见疾病之一。肺炎是引发脓毒症的主要病因,故及时治疗并发脓毒症的肺炎患儿对减少新生儿死亡率具有极其重要的作用[1]。最新发现的降钙素原(PCT)与细菌感染有着密切关系,据报道,细菌感染初期,患儿的血浆PCT浓度显著上升[2-3]。大量的研究结果显示,C反应蛋白(CRP)在细菌感染急性期时大幅上升,在病毒感染时则轻度上升或表达正常,故CRP在抗菌药物治疗细菌性感染的新生儿中具有重要的指导价值[3]。由于高敏C反应蛋白(hs-CRP)的精确性、敏感性均较高,故其应用率较CRP高。本研究旨在通过检测并发脓毒症的肺炎新生儿体内血清PCT与hs-CRP的表达水平,探析上述指标对此类患儿病情严重程度及临床疗效的影响,以期给并发脓毒症的肺炎患儿的早期诊断和治疗提供一定的理论参考。
1 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象分析2015年3月~2016年10月在我院接受住院治疗的124例肺炎新生儿的临床资料,其中男64例,女60例,平均年龄(15.7±8.9)d。本研究经我院医学伦理委员会批准,患儿家属知情同意并签署相关知情同意书。入选标准:均合并脓毒血症,由痰培养或血培养证实;病原体全是细菌感染;参照中华医学会儿科学会新生儿组2003年制定的关于新生儿脓毒血症的诊疗方案进行诊断。诊断脓毒症患儿的标准:炎症反应的症状及体征,感染且伴有低温(直肠温度低于35.0℃)或伴有发热(直肠温度超过38.5℃)心动过速的症状;意识变化或者低氧血症或者高乳酸血症或者跳跃的脉搏。而严重脓毒症则为并发器官功能受障的脓毒症。排除标准:肿瘤及自身免疫性疾病患儿;入院前接受过抗感染治疗的患儿。根据有无脓毒症及脓毒症病情的严重程度可以将入选者分成A组(轻度脓毒症患儿,52例)、B组(重度脓毒症患儿,34例)和C组(非脓毒症患儿,38)三组。三组患儿的一般资料无显著差异性(P>0.05),具有可比性,详见表1。
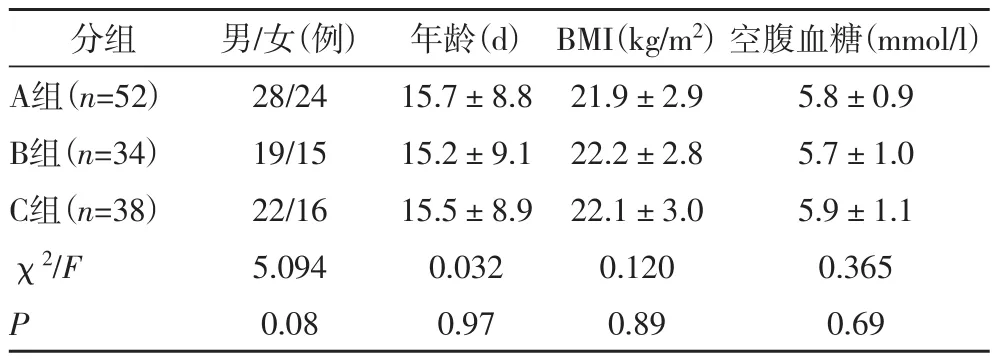
表1 三组患儿的一般资料比较
1.2 研究方法所有入选患儿均在入院当日接受血浆PCT及hs-CRP水平的检测,同时接受相关的辅助检查(包括痰培养及血培养等),另外对脓毒症患儿治疗有效者与非脓毒症的肺炎患儿在治疗1w后实施PCT与hs-CRP水平复检。采用散射比浊法上艾克美全程C-反应蛋白免疫荧光分析仪检测hs-CRP水平,并使用同公司生产的配套试剂,参考标准:0.5-350mg/L。采用酶联免疫荧光法(ELFA)上FIA8100免疫定量分析仪(南京基蛋生物科技有限公司生产)检测血浆PCT,参考标准:0.05~200ng/mL。
1.3 统计学方法本研究中的数据均采用SPSS19.0软件进行分析。数据计量以均数±标准差(±s)形式表示,比较采用t检验和卡方(χ2)检验。我们定义P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 三组患儿血浆PCT及hs-CRP的水平表2结果提示,C组、A组、B组患儿血清hs-CRP及PCT水平依次上升,且A、B组显著高于C组,B组显著高于A组(P<0.01)。
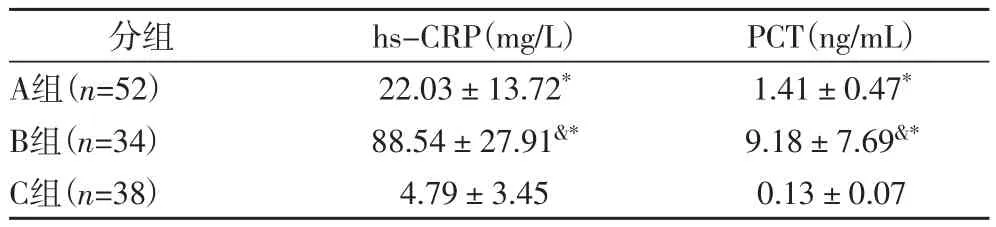
表2 三组患者的血清PCT及hs-CRP水平比较
2.2 血浆PCT与hs-CRP在并发脓毒症肺炎患儿中的诊断价值表3结果提示,血浆PCT与hs-CRP联合检测的准确性、特异性较单项指标高(P<0.05)。

表3 血浆PCT与hs-CRP对并发脓毒症肺炎患儿中的诊断意义
2.3 治疗前后肺炎患儿血浆PCT与hs-CRP水平的变化表4结果提示,合并脓毒症的肺炎患儿治疗后的血浆PCT与hs-CRP水平明显较治疗前低(P<0.05),而无脓毒症的肺炎患儿治疗后的血浆PCT与hs-CRP水平未显著下降(P>0.05)。
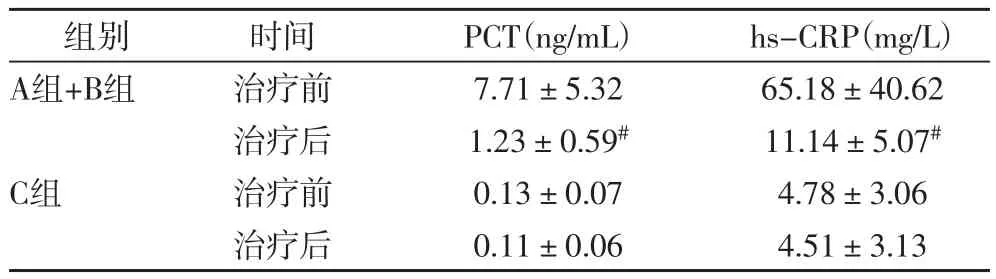
表4 肺炎患儿治疗前后血浆PCT与hs-CRP水平比较
3 讨论
血浆PCT属于无激素活性的一种糖蛋白,在脓毒症患者中可以检测出。当机体未被感染时,血浆PCT诱导途径受抑制,而感染时则可诱发PCT水平显著上升,同时全身肌细胞、脂肪细胞及肝肾等细胞和实体组织中持续释放PCT[4]。在自身免疫性疾病、癌性发热、病毒感染及局部感染等患者血清中,PCT水平只是轻微上升或者基本不升高,但在全身感染严重时PCT水平则显著大幅上升[5]。
血清CRP属于炎症反应的一个重要标志物,在急性时相反应蛋白(APR)中是主要成员,一般少量表达于人体体液内[6]。有研究资料结果显示,健康者血清CRP的参考标准在0.057~8.2mg/L间,而手术、组织受损及炎症反应后其浓度则大幅上升[7]。本文采用的是hs-CRP,其检测灵敏性更高。
本研究发现,并发脓毒症的肺炎新生儿血浆PCT与hs-CRP水平均显著较非脓毒症的肺炎患儿高;且脓毒症新生儿治疗后的血浆PCT与hs-CRP水平显著低于治疗前,有助于临床上疗效的判断;A、B组患儿的血浆PCT与hs-CRP水平分别依次上升,即严重脓毒症肺炎患儿的血浆PCT与hs-CRP水平显著高于轻度脓毒症肺炎患儿。以往有学者认为血清hs-CRP水平无法明显区分脓毒症患儿病情的严重程度[8],与本研究结果略有出入,考虑可能与病例来源不同相关,本研究主要是针对新生儿,而不是成人。新生儿由于肝脏发育及免疫系统均未完善,在被感染或者受严重感染后,新生儿体内产生的血清CRP量可能呈缓慢上升状,与炎症反应相吻合[9]。
血浆PCT与hs-CRP在并发脓毒症的肺炎患儿中具有中等的诊断价值,其中血浆PCT价值略高于血清hs-CRP。血浆PCT的的最佳截点是2ng/m L,血清hs-CRP的最佳截点是55mg/L,且hs-CRP敏感性优于PCT,特异性则相反,而PCT与hs-CRP联合检测的特异性最佳,此结果与以往相关报道结果相吻合[10,11]。
总之,并发脓毒症的肺炎患儿的早期诊断中,血浆PCT与hs-CRP具有一定的临床价值,且操作简单、快速,结果也较客观。血浆PCT与hs-CRP联合检测有助于早期诊断并发脓毒症的肺炎患儿,且在其疗效及预后判断中也具有很好的预测价值,值得推广。
[1] Ertem AG, Efe TH, Yayla, et al. The Association Between Serum Procalcitonin Levels and Severity of Coronary Artery Disease Assessed by SYNTAX Score in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome[J]. Angiology.2016 .3(3): 21-31.
[2] Winkler MS, Nierhaus A, Holzmann M, et al. Decreased serum concentrations of sphingosine-1-phosphate in sepsis[J]. Crit Care.2015.19(1): 1-8.
[3] 段华新, 彭浪, 杨扬, 等. 感染所致104例血小板减少的临床研究[J].湖南师范大学学报 (医学版), 2014, 11(2): 23-26.
[4] Watanabe Y, Oikawa N, Hariu M, et al. Ability of procalcitonin to diagnose bacterial infection and bacteria types compared with blood culture findings[J]. Int J Gen Med.2016.9(9): 325-331.
[5] Mohsen AH, Kamel BA. Predictive values for procalcitonin in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis[J]. Electron Physician.2015.7(4): 1190-1195.
[6] Howman RA, Charles AK, Jacques A, et al. Inflammatory and haematological markers in the maternal, umbilical cord and infant circulation in histological chorioamnionitis[J]. PLoS One.2012.7(12): 51836-51838.
[7] Kweon OJ, Choi JH, Park SK, et al. Usefulness of presepsin (sCD14 subtype) measurements as a new marker for the diagnosis and prediction of disease severity of sepsis in the Korean population[J]. J Crit Care.2014.29(6): 965-970.
[8] Liu YJ, Du P, Rao J. Procalcitonin as a diagnostic and prognostic marker for sepsis caused by intestinal infection: a case report[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.2013.17(10): 1311-1313.
[9] Cotoi OS, Manjer J, Hedblad B, et al. Plasma procalcitonin is associated with all-cause and cancer mortality in apparently healthy men: a prospective population-based study[J]. BMC Med.2013.11(1): 1-9.
[10] Park JH, Wee JH, Choi SP, et al. Serum procalcitonin level for the prediction of severity in women with acute pyelonephritis in the ED: value of procalcitonin in acute pyelonephritis[J]. Am J Emerg Med.2013.31(7): 1092-1097.
[11] Hedegaard SS, Wisborg K, Hvas AM. Diagnostic utility of biomarkers for neonatal sepsis--a systematic review[J]. Infect Dis (Lond).2015.47(3): 117-124.
[12] Vasilcan G, Avasiloaiei A, Moscalu M, et al. Procalcitonine--early marker of neonatal infection[J]. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi.2011.115(4): 1243-1250.
The detective value of PCT and hs-CRP in pneumonia and sepsis newborns
Jia Kai
(Department of clinical laboratory, Xi’an children’s Hospital, Xi’an 710003, China)
Objective Our retrospective study was aimed toanalyze the clinical detective value of the serum PCT and hs-CRP in pneumonia and sepsis newborns. M ethods Clinical data of 124 newborns with pneumonia
treatment at our hospitalfrom March, 2015 to October, 2016 was retrospectivelyanalyzed. Patients included were divided into three groups according to with or without sepsis and the severity of the sepsis condition, group A (children with mild sepsis, 52 cases), group B (children with severe sepsis, 34 cases) and group C (children without sepsis, 38 cases). The general information and the levels of the serum PCT and hs-CRP in three groups and the levels of the serum PCT and hs-CRP before and after treatment in children with sepsis and children without sepsis. The detective value of the serum PCT and hs-CRP in pneumonia and sepsis newborns was analyzed. Results The general information in three groups had no statistical difference. The levels of the serum PCT and hs-CRP in group C, group A and group B increased, and they in group A and group B were obviously higher than those in group C, and they in group B were obviously higher than those in group A. The accuracy and specificityof the combined determination of the serum PCT and hs-CRP were higher than single index. The levels of the serum PCT and hs-CRP in group A and group B after treatment were obviously lower than those in group C, but they in group C had no statistical difference before and after treatment. Conclusion The combined determination of PCT and hs-CRP has high significance for the early diagnosis, observation of curative effect and prognosis on neonatal pneumonia and sepsis. It’s worth promoting
procalcitonin (PCT); high-sensitivity C reactive protein (hs-CRP); sepsis; pneumonia; newborn
R446.62
A
1673-016X(2017)04-0062-03
2017-03-15
贾凯,E-mail:1063513987@qq.com
