力平衡型多输入齿轮马达的转矩特性分析与试验
2017-07-07闻德生潘为圆石滋洲商旭东马光磊
闻德生,潘为圆,石滋洲,商旭东,马光磊,顾 攀
(燕山大学机械工程学院,秦皇岛 066004)
力平衡型多输入齿轮马达的转矩特性分析与试验
闻德生,潘为圆,石滋洲,商旭东,马光磊,顾 攀
(燕山大学机械工程学院,秦皇岛 066004)
针对传统齿轮马达径向力不平衡、只能输出一种转矩和转矩脉动较高的问题,提出了力平衡型多输入齿轮马达。该马达在一个壳体内有内、外两种马达,可通过不同的连接方式实现4种定转矩和定转速的输出。通过对马达的输出转矩进行理论计算和试验,分析了马达在4种工作方式下的瞬时转矩及转矩脉动,结果表明,单个马达工作时的转矩脉动与啮合齿轮的齿数有关。多个马达同时工作时的转矩脉动与齿轮啮合点的位置及脉动周期有关,当3个内马达共同工作,内、外马达共同工作,内、外马达差动工作时,在内、外马达脉动周期相同的前提下,可调节啮合点的位置,分别使 3个小齿轮的轮齿啮合位置相差1/3,内、外马达轮齿啮合位置相差1/2,内、外马达轮齿啮合位置相同,通过瞬时转矩的叠加,使输出合转矩的脉动最小。试验结果表明,在调节齿轮啮合点的位置后,相同工作方式下的转矩脉动程度明显减少,该研究为多输入马达的进一步研究提供了参考。
齿轮;马达;扭矩控制;力平衡;多输入;差动马达;转矩脉动
闻德生,潘为圆,石滋洲,商旭东,马光磊,顾 攀. 力平衡型多输入齿轮马达的转矩特性分析与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(10):94-101. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.10.012 http://www.tcsae.org
Wen Desheng, Pan Weiyuan, Shi Zizhou, Shang Xudong, Ma Guanglei, Gu Pan. Analysis and test of torque characteristics for force balance and multi input gear motor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(10): 94-101. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.10.012 http://www.tcsae.org
0 引 言
随着液压技术的不断提高和发展,液压传动广泛应用于各个领域,并且由于液压传动具有控制灵活、比功率大的优点,因此在各类农业机械中更是发挥了举足轻重的作用[1-4]。农业机械的工作环境恶劣,对机械传动系统的要求较高,而齿轮马达体积小,质量轻,对恶劣工况的适应性强,符合农业机械的要求,但是齿轮马达由于其转矩波动性比较大、所受径向力不平衡以及困油现象、噪声大等缺点限制了其发展[5]。
目前,国内对液压元件的研究较少,大多集中在对已有液压元件和系统的改善。侯波等[6-8]提出了三从动轮并联齿轮马达,改进了传统齿轮马达的结构,使马达所受径向力平衡,但马达只能输出一种转矩。王志强等[9]改进了大扭矩水压马达的配流副,提高了马达的容积效率。王建利等[10]分析了径向柱塞马达配流轴的疲劳损伤形式,为液压马达配流轴和配流盘结构设计提供了参考。常绿等[11]改造了液压挖掘机自动控制操纵系统,增加了系统稳定性。在液压元件的输出特性方面,李玉堂等[12-17]分析了齿轮泵困油现象对其输出影响及卸荷槽与困油压力的关系。王光明等[18-20]分析了拖拉机液压机械无级变速箱的效率特性,为变速箱的结构优化及动力匹配提供了理论依据。
以上的研究并没有解决现有齿轮马达不能有级变量和减小齿轮马达的转矩脉动的问题,基于双定子原理[21-23],提出了力平衡型多输入齿轮马达,该马达在一个壳体内有内、外两个马达,通过不同的连接方式,可输出四种转矩,液压马达输出转矩脉动是衡量液压马达性能好坏的一个重要指标, 更是衡量以液压马达为执行元件的液压系统稳定性的一个重要指标[24-25],分析马达的转矩脉动,并使转矩脉动达到最小是十分必要的。
1 力平衡型多输入齿轮马达的结构及工作原理
1.1 结构特点
图1为力平衡型多输入齿轮马达的结构图。
力平衡型多输入齿轮马达主要由一个中心大齿轮16,三个小齿轮14,三个共齿轮5,月牙板7和配流盘等零件组成。三个小齿轮与月牙板、共齿轮和前后侧板构成三个内啮合齿轮马达,称为内马达,三个共齿轮与中心大齿轮、壳体和前后侧板构成三个外啮合齿轮马达,称为外马达,其中前后侧板是内马达与外马达的共用零件,各个马达都有独立的配油装置,工作时互不影响。三个共齿轮在中心大齿轮上呈 120°分布,工作时中心大齿轮上的径向力平衡。
1.2 工作原理
与普通的齿轮马达相比,新型的齿轮马达最大的特点就是在一个马达壳体中可以形成排量不同的内、外马达,通过配油可以实现外马达工作、内马达工作、内外马达共同工作、内外马达差动连接4种不同的工作方式。
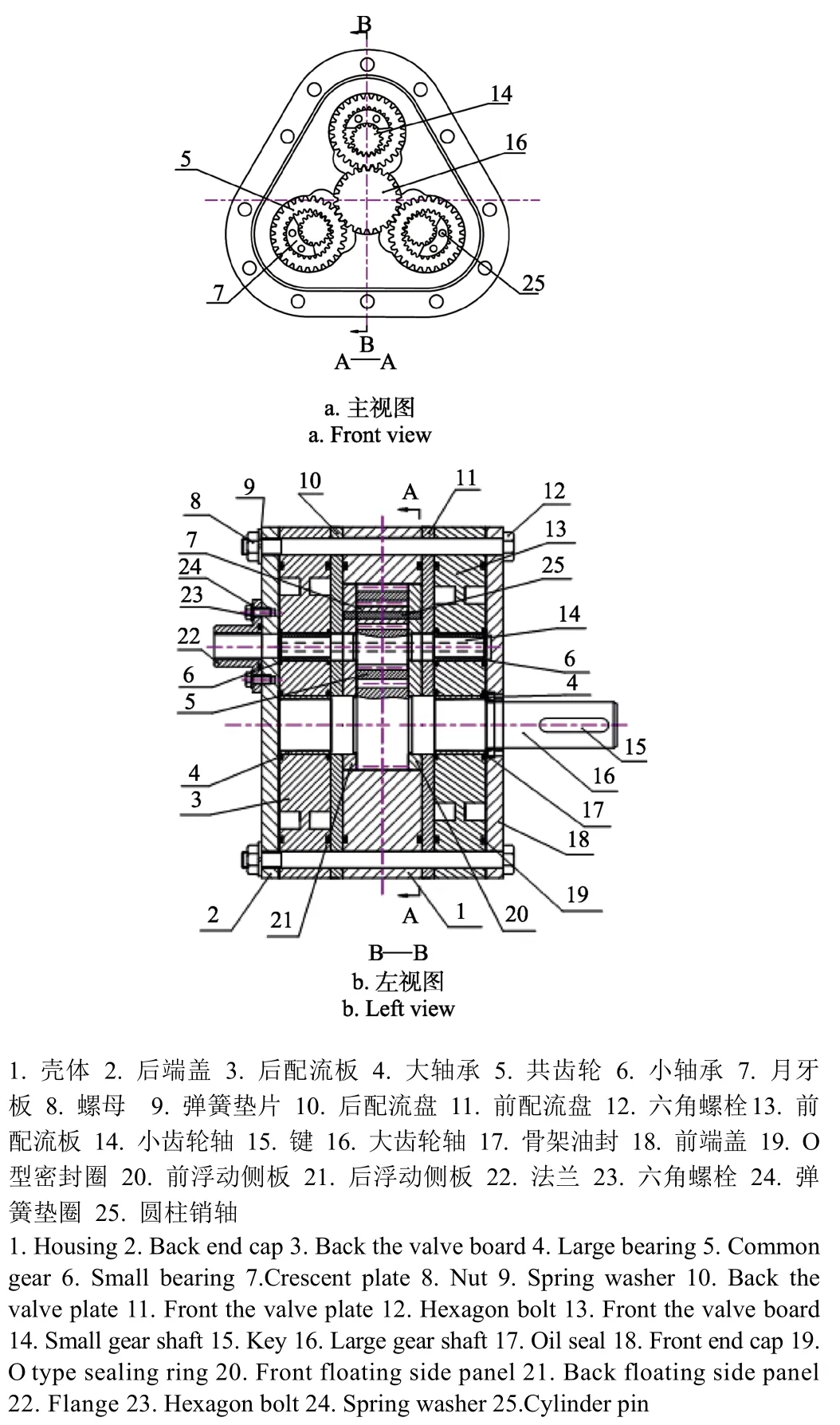
图1力平衡型多输入齿轮马达结构示意图Fig.1 Structure diagram of force balance type multi input gear motor
外马达单独工作的原理如图2a所示,在外马达的配油窗口中通入高压油,内马达与油箱相通时,内马达处于浮动状态,此时外马达工作,内马达不工作,相当于三个外啮合齿轮马达共同作用在中心大齿轮上,形成外马达;内马达的工作原理如图2b所示,在内马达的配油窗口通入高压油,外马达与油箱相通时,外马达处于浮动状态,此时只有内马达输出转矩,相当于三个内啮合齿轮马达通过共齿轮的作用将输出转矩传递给中心大齿轮,由中心大齿轮轴输出转矩;当在内、外马达的配油窗口通入方向相同的高压油时,如图2c所示,内、外马达的转矩方向相同,内、外马达将共同工作,输出合转矩;当反向对内马达和外马达通入高压油时,如图2d所示,由于内马达和外马达的排量不相同,外马达产生的转矩大于内马达产生的转矩,所以会强迫内马达反向旋转,即实现了泵的功能,此时马达输出的转矩方向和外马达单独工作时的转矩方向相同,只是输出转矩相对于外马达单独工作时要小,转速要大[26-27]。
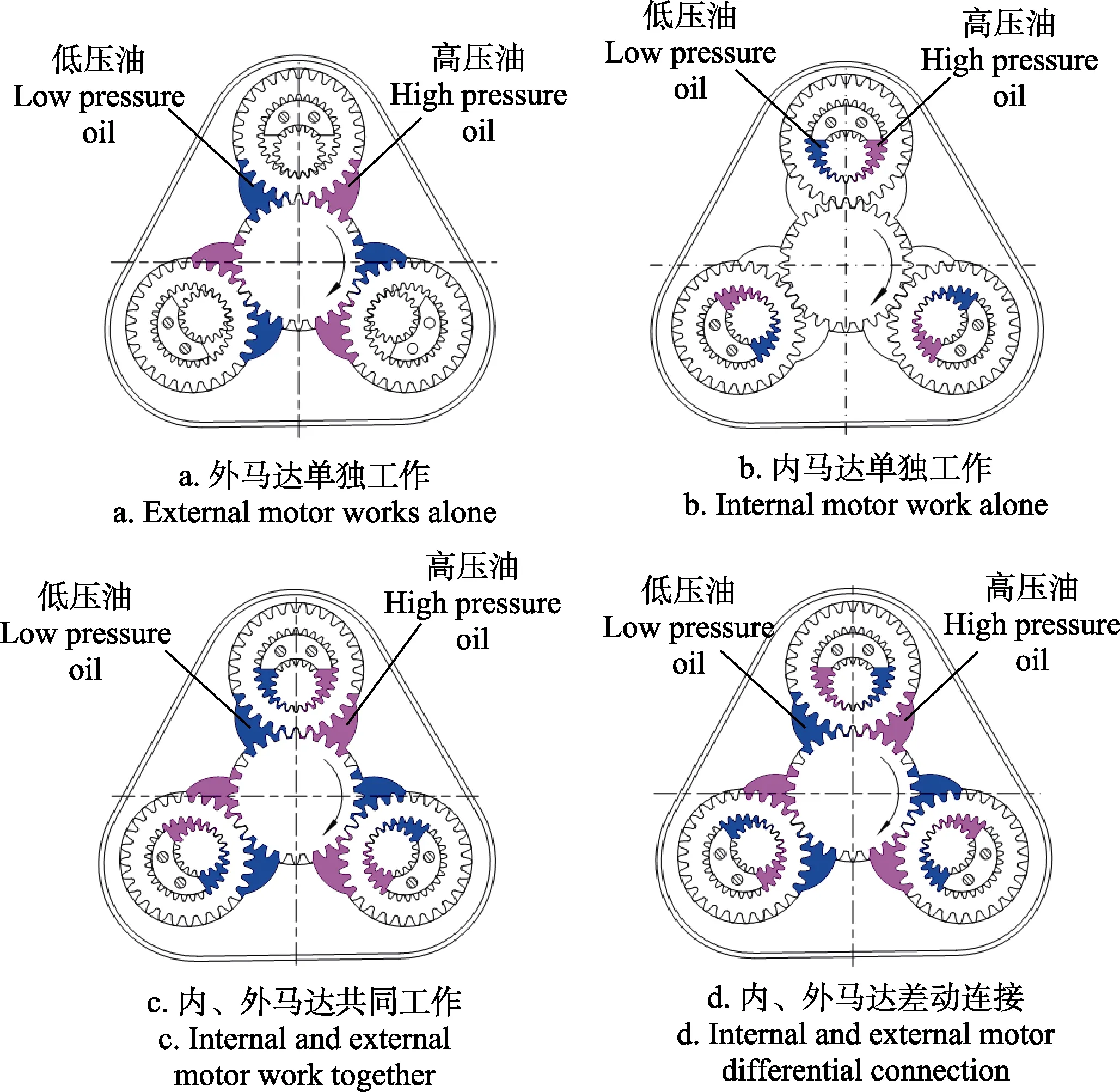
图2 马达的4种工作方式Fig.2 Four working modes of the motor
2 力平衡型多输入齿轮马达的瞬时转矩
转矩与转速以及转矩转速脉动是评价液压马达性能的重要参数[28],力平衡型多输入齿轮马达有四种转矩转速的输出。为了以后在实践的时候有更好的理论依托和参考依据,有必要分析马达每种工作方式的转矩脉动。
2.1 单个内、外啮合齿轮马达的瞬时转矩
为了保证输出齿轮轴的液压力平衡,三个内啮合齿轮马达的设计参数完全相同,因此只需分析一个内啮合齿轮马达的瞬时转矩。马达中所涉及的齿轮均为渐开线标准直齿圆柱齿轮,且按标准中心距安装。设马达在 dt的时间内转过的角度为dφ,体积变化量为dv,内马达的瞬时流量[29]为
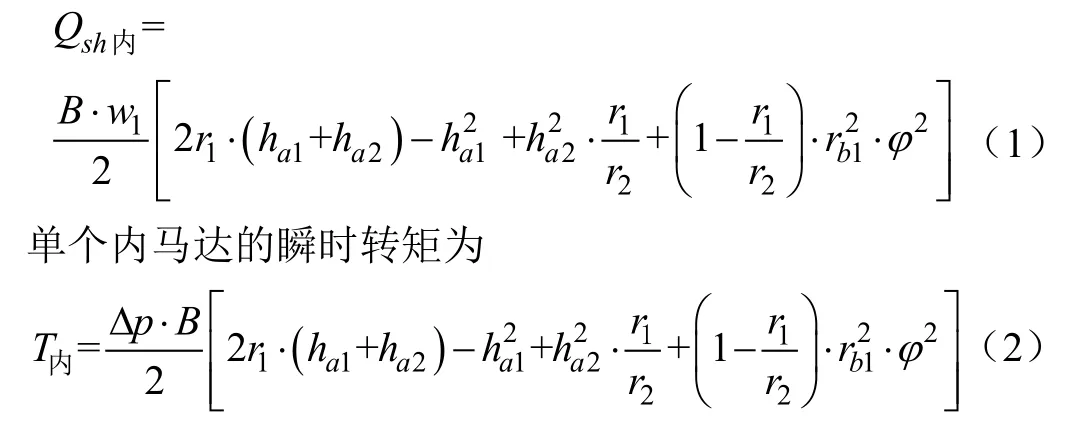
式中 Qsh内为内马达的瞬时流量,L/min;ω1为共齿轮的角速度,rad/s;T内为内马达的瞬时转矩,N·m;Δp为马达进出口压差,MPa;B为齿宽,mm;r1,r2分别为共齿轮内齿和小齿轮的分度圆半径,mm;ha1,ha2分别为共齿轮内齿和小齿轮的齿顶高,mm;rb1为共齿轮内齿的基圆半径,mm;φ为共齿轮随啮合点移动而转过的角度,rad。
同理,可得单个外啮合齿轮马达的瞬时转矩
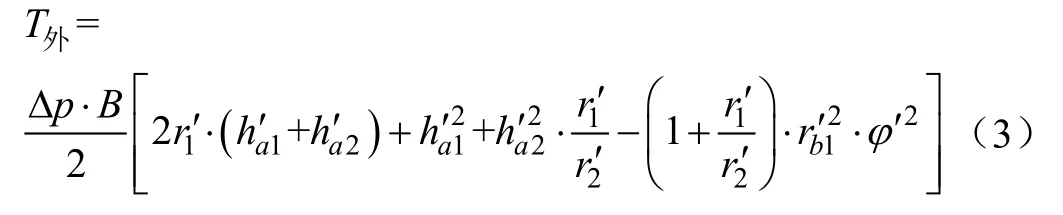
式中T外为外马达的瞬时转矩,N·m;r1′,r2′分别为中心大齿轮和共齿轮外齿的分度圆半径,mm;h′a1,h′a2分别为中心大齿轮和共齿轮外齿的齿顶高,mm;r′b1为中心大齿轮的基圆半径,mm;φ′为中心大齿轮随啮合点移动而转过的角度,rad。
从式(2)和式(3)中可以看出,马达的输出转矩随齿轮啮合点的移动而变化,轮齿刚进入啮合或刚退出啮合时转矩最小,轮齿在节点处啮合时转矩最大,马达每转过一个齿,转矩脉动一次,转矩脉动周期为两个相邻轮齿间的角度。
2.2 内、外马达共同工作时的瞬时转矩
当内、外马达共同工作时,内、外马达都通过中心大齿轮轴输出转矩,将相邻的一个内啮合齿轮马达和一个外啮合齿轮马达的输出转矩换算到中心大齿轮轴上,可得

将式(2)和式(3)代入式(4),得

从式(5)中可以看出,内、外马达共同工作时瞬时合转矩与内、外马达各自的转矩脉动周期及齿轮的转角有关。内、外马达的周期相同时,应满足
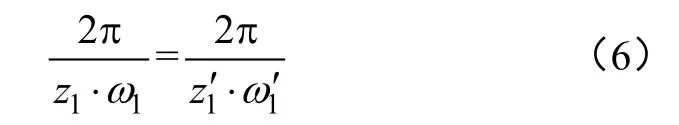
式中T共为内、外马达共同工作时的瞬时转矩,N·m;ω1为共齿轮内齿的角速度,rad/s;ω1′为共齿轮外齿的角速度,rad/s;z1为共齿轮内齿的齿数;z1′为共齿轮外齿的齿数。
由于共齿轮内、外齿的角速度相同

将式(7)代入式(6)可得,当z1=z1′时,即共齿轮内外齿的齿数相同时,内、外马达转过一个齿的时间相同,转矩脉动周期相同。
2.3 内、外马达差动工作时的瞬时转矩
内、外马达差动工作时的瞬时转矩为

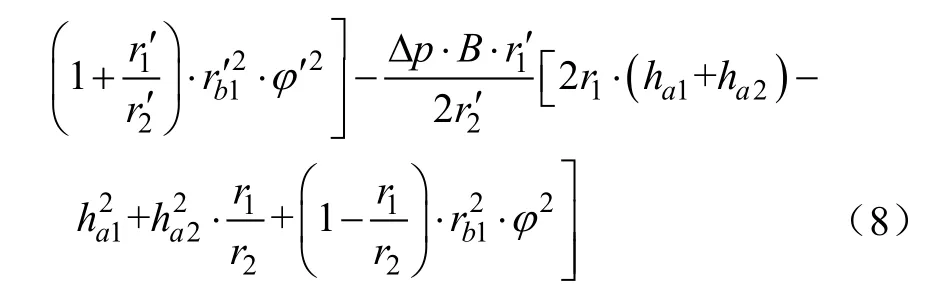
式中T差为内、外马达差动工作时的瞬时转矩,N·m。
3 力平衡型多输入齿轮马达的转矩脉动分析
由前面的分析可知,马达的瞬时转矩会随马达的转动时刻变化,因此马达在工作时会产生一定的转矩脉动,这将对马达的工作产生一定的影响。多输入齿轮马达有4种不同的转矩输出方式,每种工作方式都会有多个马达同时工作,这与单个马达工作产生的转矩脉动不同,应具体分析每种工作方式下的转矩脉动。
3.1 三个内马达共同工作时的转矩脉动
设计内马达中小齿轮的齿数为16,模数为1.5 mm,,共齿轮的内齿的齿数为 24,模数为 1.5 mm,齿宽均为30 mm。通过计算得出内马达的最大瞬时转矩和最小瞬时转矩。3个内啮合齿轮马达共同工作时,合瞬时转矩值将是 3个内马达瞬时转矩值的相加。所设计的三个内马达参数相同,轮齿啮合点的位置相同,瞬时转矩曲线如图3a所示。
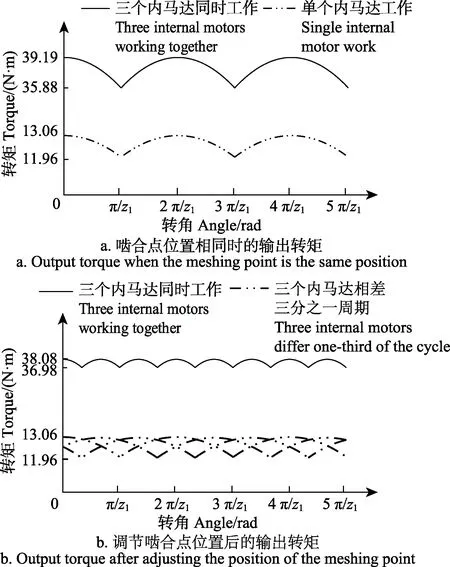
图3 三个内马达共同工作时的输出转矩Fig.3 Output torque of three internal motors working togethter
从图3a中可以看出,当三个内啮合齿轮马达轮齿啮合点的位置相同时,所产生的转矩脉动相当于一个内啮合齿轮马达转矩脉动的三倍,此时马达的转矩不均匀系数为

式中δT为转矩不均匀系数;a为齿轮的压力角,rad;z1,z2分别为共齿轮内齿的齿数和小齿轮的齿数。
图3a中3个内马达共同工作时的转矩脉动是单个内马达转矩脉动的3倍,这是因为3个内马达轮齿啮合点的位置相同,齿数相同,转矩脉动周期相同,使得马达转动时3个内马达在相同转角的瞬时转矩值相同,3个内马达的瞬时转矩值同时达到最大值或最小值,这将使合瞬时转矩值的最大值更大,最小值更小,从而引起了更大的转矩脉动。若使 3个内马达在相同转角的瞬时转矩值不相同,例如当一个内马达的瞬时转矩值达到最大时,另外两个内马达的瞬时转矩值处于最大值和最小值之间(如图 3b所示),这样可以减小合瞬时转矩值中最大值与最小值之间的差值,即减少了转矩脉动。而内马达的瞬时转矩值由轮齿啮合点的位置决定,可通过调节轮齿啮合点的位置,调节瞬时转矩值的大小,因此,多个马达共同工作时的转矩脉动与齿轮齿数和轮齿啮合点的位置有关,齿轮齿数决定了马达的转矩脉动周期,轮齿啮合点的位置决定了瞬时转矩值的大小。由于 3个内马达相互独立,可改变每个内马达共齿轮内齿圈的结构,使3个内马达中共齿轮与小齿轮初始啮合点的位置相差三分之一轮齿,如图4所示。通过将3个内马达的瞬时转矩值相互叠加,可减少马达的转矩脉动,瞬时转矩曲线如图3b所示。
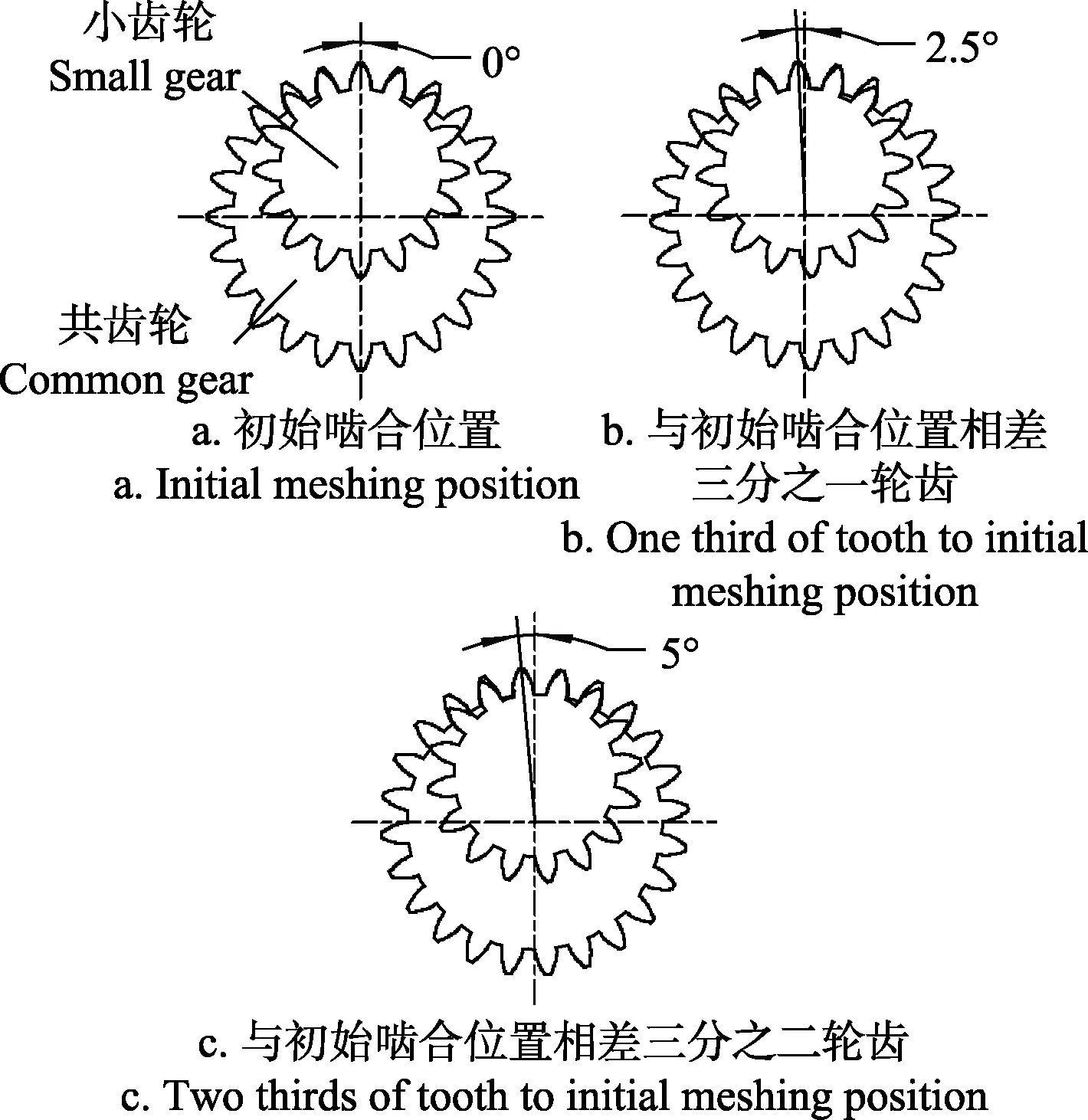
图4 不同轮齿啮合点位置Fig.4 Structure diagram of different meshing positions
从图3b中可以看出,当3个内马达中共齿轮与小齿轮初始啮合点的位置相差三分之一轮齿时,马达的转矩脉动最小,但脉动周期变为原周期的三分之一。此时马达的瞬时转矩为

3.2 三个外马达共同工作时的转矩脉动
三个共齿轮呈 120°角分布且与中心大齿轮外啮合形成三个外马达。当中心大齿轮的齿数是 3的倍数时,三个共齿轮同中心大齿轮啮合点的位置相同,此时 3个外马达的转矩周期相一致,3个外马达在相同的齿轮啮合点处对应相同的瞬时转矩值,即 3个外马达都在相同的时刻达到瞬时转矩的最大值和最小值,3个最大值相加使马达的最大瞬时转矩增大,3个最小值相加使马达达到最小的瞬时转矩,从而转矩脉动最大。当中心大齿轮的齿数不是 3的倍数时,共齿轮与中心大齿轮的三个啮合点的位置不相同,即 3个外马达在相同时刻对应的瞬时转矩值不相同,不会同时出现最大或最小的瞬时转矩,在 3个外马达的瞬时转矩值相加时,可以避免总转矩的最大值和最小值相差过大,降低 3个外马达共同工作时的转矩脉动,因此中心大齿轮的齿数一般不是3的倍数。
3.3 内、外马达共同工作时的转矩脉动
力平衡型多输入齿轮马达有三个相同的内马达和三个相同的外马达,在此只分析一组相邻的内马达和外马达共同工作时的转矩脉动。
由前面的分析可知,内马达和外马达转矩脉动周期分别为 2π/z1ω1和 2π/z1′ω1′,当z1=z1′时,内、外马达的脉动周期相同,若是内、外马达轮齿啮合点的位置相同,内马达瞬时转矩的最大值和外马达瞬时转矩的最大值相互叠加,最小值也相互叠加,转矩脉动将达到最大。若内、外马达啮合点的位置相差半个轮齿,也就是说,当外马达一对啮合的齿轮刚进入啮合或者刚退出啮合时,恰好内马达的一对啮合齿轮的啮合点与节点重合,或者外马达啮合齿轮的啮合点与节点重合时,内马达的啮合轮齿刚进入啮合或者刚退出啮合,此时,内马达转矩的最小值与外马达转矩的最大值叠加,内外马达共同输出的转矩脉动将最小[30],如图5所示。

图5 单组内、外马达共同工作时的输出转矩Fig.5 Output torque of one group of internal and external motor working together
此时,马达的瞬时转矩与时间的关系为
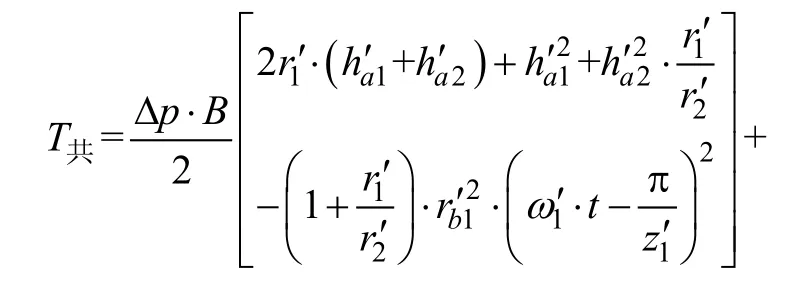

3.4 内、外马达差动工作时的转矩脉动
内、外马达差动工作时,内马达相当于泵,因此当内、外马达的周期相同,轮齿啮合点的位置相同时,内马达与外马达所产生的转矩脉动相互抵消一部分,内、外马达差动工作时的转矩脉动将达到最小,如图6所示。
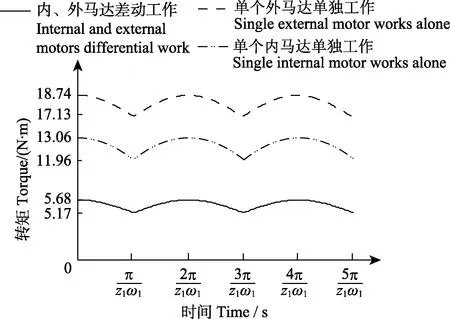
图6 单组内、外马达差动工作时的输出转矩Fig.6 Output torque of one group of internal and external motor differential work
此时,马达的瞬时转矩与时间的关系为

4 试 验
由于所设计的齿轮马达具有新型的结构,所以有必要对其进行原理性试验分析,图7a为马达各个部分的零件图,图7b为试验现场图,图7c为试验系统图。通过换向阀的换向使马达实现4种不同的工作方式。
根据前面的分析,本次试验共制造 3种齿轮马达的试验样机,第一种为 3个内马达轮齿啮合位置相差三分之一轮齿,第二种为每组内、外马达的轮齿啮合位置相差二分之一轮齿,第三种为每组内、外马达的轮齿啮合位置相同。3种马达的排量都相同,外马达排量为54.3 mL/r,内马达的排量为 30.5 mL/r。小齿轮的齿数为16,模数为1.5 mm,共齿轮的内齿的齿数为24,模数为1.5 mm共齿轮外齿圈的齿数为24,模数为2 mm,中心大齿轮的齿数为25,模数为2 mm。
本次试验采用 JN338型转矩测量仪(北京三晶创业科技集团有限公司生产)测量马达工作过程中的瞬时转矩值,设定采样周期为 50 ms,选取马达稳定运转后 1 s内的试验数据,并整理出瞬时转矩的曲线。试验中选用马达的转速范围为150~600 r/min,进油口压力为6 MPa。
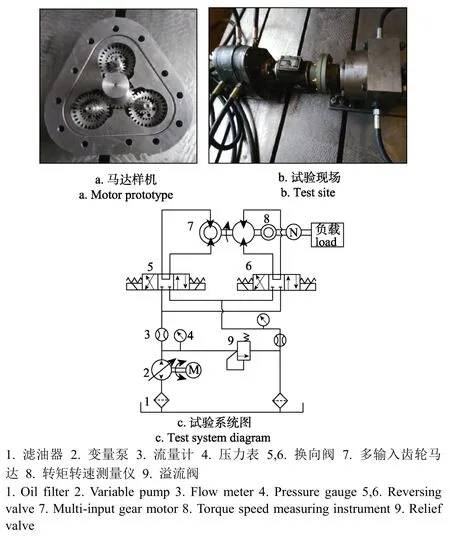
图7 马达样机及试验系统图Fig.7 Motor prototype and test system diagram
通过试验分析并对测量数据进行记录,得到上述 3种马达在不同工作方式下的瞬时转矩,如图8所示。
由图8a可以看出,内马达单独工作的转矩脉动很小,比较图8b和图8c可知,三个内马达的轮齿啮合位置相差三分之一轮齿可明显降低内马达单独工作时的转矩脉动。
由图8b可以看出,内、外马达共同工作时的瞬时转矩曲线波动较小,内、外马达差动工作时的瞬时转矩曲线波动较大,而图8c中恰好出现相反的情况。这说明内、外马达齿轮啮合点的位置影响内、外马达共同工作和差动工作的转矩脉动,但不能使马达在这两种工作方式下的转矩脉动都达到最小。由图 8可知,马达的不同结构影响不同工作方式下的转矩脉动,但无法同时使马达每种工作方式下的转矩脉动都达到最小。
通过试验结果与理论分析对比可知,试验结果基本符合理论分析的结论,但由于试验过程中会受到各种因素的影响,油液本身的品质、液压泵的流量脉动、管路安装、试验样机的精度等都会对试验结果产生一定的影响,因此试验结果与理论分析并不完全一致。
测定了第一种马达在不同压力,不同工作方式下的容积效率和机械效率,整理出曲线如图9所示。
从图9a可以得知,马达在共同工作和差动工作时的容积效率最小,这主要是因为这两种工作方式下马达的所有容腔全都参与工作,增加了马达的泄漏面积,使马达泄漏严重。从图9b可以得知,随着压力的升高马达机械效率提升,这是因为低压时马达的摩擦副没有建立起压力油膜,摩擦力较大,而压力增高时,摩擦副之间形成压力油膜,减少了摩擦力。比较 4种工作方式,马达在共同工作和差动工作时的机械效率较低,这是因为 2种工作方式下作用的摩擦副最多,增大了机械损失。
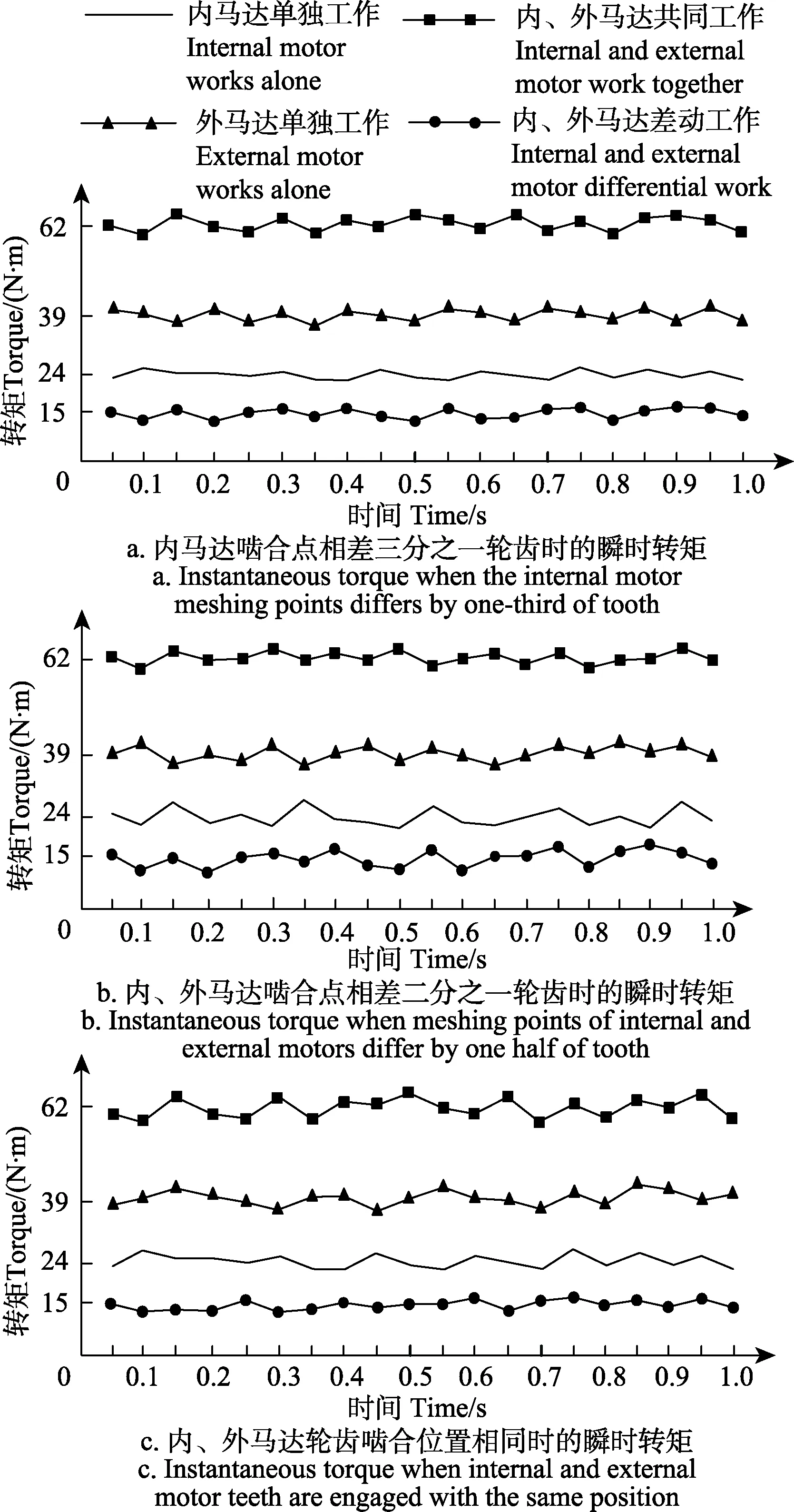
图8 试验马达样机工作时的瞬时转矩Fig.8 Instantaneous torque of test motor prototype

图9 试验马达样机的效率曲线Fig.9 Efficiency curves of test motor prototype
5 结 论
1)提出了力平衡型多输入齿轮马达,新型齿轮马达可输出 4种定转矩和定转速,输出轴径向力平衡,但结构复杂,加工成本高。
2)分析了马达在不同工作方式下的转矩脉动。对马达的瞬时转矩进行理论计算,单个马达工作时的转矩脉动与啮合齿轮的齿数有关。而多个马达同时工作时的转矩脉动已不是几个马达转矩脉动的简单相加,通过调节齿轮啮合点的位置调节马达的瞬时转矩值,调节齿轮的齿数确定马达的脉动周期,在多个马达的相互作用下可以使合转矩的转矩脉动达到最小。因此,多个马达同时工作时的转矩脉动与马达齿轮啮合点的位置及脉动周期有关。
3)通过马达样机的试验得出:改进马达的结构后可以明显减小马达的转矩脉动,但改变一种结构只能减小一种工作方式下的转矩脉动,无法同时使 4种工作方式下的转矩脉动都达到最佳状况。
[1]梁荣庆,坎杂,李成松,等.液压传动技术在收获机械中的应用研究[J].机床与液压,2012,40(20):152-155.Liang Rongqing, Kan Za, Li Chengsong, et al. Applied research of hydraulic drive technology in harvest machinery[J]. Machine Tool & Hydrulics, 2012, 40(20): 152-155. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2]彭熙伟,陈建萍.液压技术的发展动向[J].液压与气动,2007(3):1-5.Peng Xiwei, Chen Jianping. The future trends of hydraulics[J]. Hydraulic & Pneumatics, 2007(3): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3]许仰曾.我国液压工业与技术的发展现状与展望的战略思考[J].液压气动与密封, 2010(8):1-5.Xu Yangzeng. Strategy thinking on development of hydraulic industry and its technology[J]. Hydraulics Pneumatics &Seals, 2010(8): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4]赵武,杜长龙.液压元件的研究现状与发展趋势[J].煤炭科学技术,2004,34(14):71-73.Zhao Wu, Du Changlong. Research status and development trend of hydraulic components[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2004, 34(14): 71-73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5]李壮云.液压元件与系统[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2011:25-26.
[6]侯波.三从动轮并联齿轮马达的理论研究[J].液压与气动,2006(2):18-20.Hou Bo. Research on the paralleled gear motor with 3-idlers[J]. Hydraulic & Pneumatics, 2006(2): 18-20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7]赵连春,宋艳亮,许贤良.三惰轮复合齿轮马达的内部泄漏特性研究[J].安徽理工大学学报:自然科学版,2015(1):14-17.Zhao Lianchun, Song Yanliang, Xu Xianliang. Research on the inner leakage of the compound gear motor with three idlers[J]. Journal of Anhui University of Science and Technology: Natural Science, 2015(1): 14-17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8]侯波,孙全兵,刘传军.三级并联齿轮马达径向液压力分析[J].煤矿机械,2007,28(11):78-80.Hou Bo, Sun Quanbing, Liu Chuanjun. Analysis on radial hydraulic force of parallel gear motor with 3-idlers[J]. Coal Mine Machinery, 2007, 28(11): 78-80. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9]王志强,倪 敬,高殿荣.低速大扭矩水压马达的配流性能分析及试验[J].农业工程学报,2016,32(12):81-87.Wang Zhiqiang, Ni Jing, Gao Dianrong. Distribution performance analysis and test of low speed high torque water hydraulic motor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016,32(12): 81-87. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10]王建利,刘晋浩.液压冲击下五星式径向柱塞马达配流轴疲劳分析[J].农业工程学报,2014,30(19):65-70.Wang Jianli, Liu Jinhao. Fatigue analysis of pintle vale of motor with five-star radial piston under effect of hydraulic shock[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(19): 65-70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11]常绿,王国强,韩云武.液压挖掘机自动控制系统的设计和实现[J].农业工程学报,2007,23(6):140-144.Chang Lv, Wang Guoqiang, Han Yunwu. Design and realization of computer controlled working device system for hydraulic excavator[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE),2007, 23(6): 140-144. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12]李玉龙.基于低速困油模型的外啮合齿轮泵高速困油特性分析[J].农业工程学报,2012,28(9):35-39.Li Yulong. Characteristics analysis of high-speed trapped-oil in external gear pump based on low-speed trapped-oil model[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(9): 35-39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13]李玉龙,孙付春.振动影响齿轮泵困油压力的仿真与理论分析[J].农业工程学报,2012,28(13):77-81.Li Yulong, Sun Fuchun. Simulation and theoretical analysis on trapped oil pressure in external gear pump influenced by vibration[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012,28(13): 77-81. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14]李玉龙,孙付春.齿轮泵齿侧间隙与卸荷槽间距关系的定量分析[J].农业工程学报,2012,28(22):63-68.Li Yulong, Sun Fuchun. Quantitative analysis of relationship between backlash value and distance of two relief grooves in external gear pump[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012,28(22): 63-68. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15]李玉龙,孙付春.基于离心作用的齿轮泵容积效率和困油现象分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2011,27(3):147-151.Li Yulong, Sun Fuchun. Theoretical analysis of volumetric efficiency and phenomenon of trapped oil under centrifugation in external spur-gear pump[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2011, 27(3): 147-151. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16]李玉龙,刘焜.外啮合齿轮泵困油面积和卸荷面积计算式的建立[J].农业机械学报,2009,40(6):203-207.Li Yulong, Liu Kun. Established formulas for trapped-oil area and relief-load area of external spur-gear pump[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2009, 40(6): 203-207. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17]李玉龙,唐茂.困油压力对齿轮泵流量脉动的影响分析[J].农业工程学报,2013,29(20):60-66.Li Yulong, Tang Mao. Influence analysis of trapped oil pressure on flow pulsation in external gear pumps[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(20): 60-66. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18]王光明,朱思洪,史立新,等.拖拉机液压机械无级变速箱效率特性的仿真与试验[J].农业工程学报,2013,29(15):42-48.Wang Guangming, Zhu Sihong, Shi Lixin, et al. Simulation and experiment on efficiency characteristics of hydraulic mechanical continuously variable transmission for tractor[J].Transactions for the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(15): 42-48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19]王光明,朱思洪,王胜红,等.拖拉机液压机械无级变速器的速比控制[J].农业工程学报,2013,29(7):17-23.Wang Guangming, Zhu Sihong, Wang Shenghong, et al.Speed ratio control of tractor hydraulic mechanical CVT [J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(7): 17-23. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20]王光明,朱思洪,史立新,等.拖拉机液压机械无级变速箱换段控制优化与试验[J].农业工程学报,2013,29(18):51-59.Wang Guangming, Zhu Sihong, Shi Lixin, et al.Experimental optimization on shift control of hydraulic mechanical continuously variable transmission for tractor[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(18): 51-59. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21]Wen Desheng, Wang Zhili, Lv Shijun, et al. Slingle-acting double-stator multi-pump sand multi-motors[J]. Journal of Chongqing University (English Edition),2010, 9(4): 208-215.
[22]Wen Desheng, Wang Zhili, Gao Jun, et al. Output speed and flow of double-acting multi-pump and multi-pump and multi-motor[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University-Science A,2011, 12(4): 301-309.
[23]闻德生,张勇,王志力,等.三作用多泵多马达输出转速和转矩的理论分析[J].西安交通大学学报,2011,45(3):81-84.Wen Desheng, Zhang Yong, Wang Zhili, et al. Rotating speed and torque of triple-acting multi-pump and multi-motor[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2011, 45(3): 81-84. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24]闻德生,胡文龙,邱 华,等.多泵单马达传动系统输出转矩特性分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2 0 1 6,47(1):397-402.Wen Desheng, Hu Wenlong, Qiu Hua, et al. Output torque characteristics analysis of multi-pump and single-motor transmission system[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2 0 1 6, 47(1): 397-402. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25]闻德生,王 京,柴伟超,等.单泵多马达传动系统输出转矩特性分析与试验[J].农业工程学报,2016,32(12):88-95.Wen Desheng, Wang Jing, Chai Weichao, et al. Analysis and experiment of output torque characteristics of single-pump multi-motor transmission system[J]. Transaction of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(12): 88-95. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26]闻德生,吕世君,杜孝杰,等.双定子液压马达差动连接理论分析[J].农业机械学报,2011,42(9):219-224.Wen Desheng, Lü Shijun, Du Xiaojie, et al. Theoretical analysis of differential connection of double-stator hydraulic motor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2011, 42(9): 219-224. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27]闻德生,高俊峰,周瑞彬,等.多作用双定子力偶液压马达转矩脉动分析[J].农业机械学报,2014,45(10):319-325.Wen Desheng, Gao Junfeng, Zhou Ruibin, et al. Analysis oftorque pulsation for the multi-acting double-stators couple hydraulic motor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(10): 319-325. (in Chinesewith English abstract)
[28]闻德生,郑珍泉,杨杰,等.双作用双定子凸轮转子叶片电动机转矩脉动分析[J].江苏大学学报:自然科学版,2013,34(5):524-528.Wen Desheng, Zheng Zhenquan, Yang Jie, et al. Torque ripple analysis of double action CAM rotor blade motor with double stator[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University Natural:Science Edition, 2013, 34(5): 524-528. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29]叶清.内啮合齿轮泵几何参数及流里脉动的研究[D].兰州:兰州理工大学,2007.Ye Qing. Research on Geometric Parameters and Pulsating of Internal Gear Pump[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30]刘巧燕,闻德生,高俊峰.内外啮合齿轮马达的转矩脉动分析[J].液压与气动,2015(11),49-53.Liu Qiaoyan, Wen Desheng, Gao Junfeng. Analysis of torque pulsation for internal and external gear motors[J].Hydraulic& Pneumatics, 2015(11), 49-53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Analysis and test of torque characteristics for force balance and multi input gear motor
Wen Desheng, Pan Weiyuan, Shi Zizhou, Shang Xudong, Ma Guanglei, Gu Pan
(College of Mechanical Engineering,Yanshan University,Qinhuangdao066004,China)
With the development of economy, hydraulic transmission is an indispensable part of national economy.Hydraulic actuator is the core part of hydraulic transmission, and the gear motor has the advantages of small size, light weight, and strong adaptability to the harsh working conditions, and has a very important role in hydraulic actuator. But gear motor’s torque fluctuation is larger, and there are unbalanced radial force, trapped oil phenomenon and big noise, so it is difficult to develop. Based on these reasons, in this paper, a force balance type multi input gear motor is proposed,which has 3 internal motors and 3 outer motors in one case, the inner and outer motors are evenly distributed on the output shaft, and the radial force of the output shaft is balanced by the output shaft, which can significantly reduce the total force on the gear shaft and the bearing, and help to improve the service life and the mechanical efficiency of the bearing. Each motor has an independent oil distribution device, their work does not affect each other, and a motor can output 4 kinds of torques and rotational speeds through different connection modes as follows: The internal motor works independently, the outer motor works separately, the internal and external motors work together, and differential connection of internal and external motors. As an actuator, hydraulic motor’s torque and rotational speed can be achieved with the function of the liquid pressure which the hydraulic pump provide, and the hydraulic motor output torque ripple is an important indicator to measure the performance of hydraulic motors. And it is an important index to measure the stability of hydraulic system. The torque ripple of a single gear motor is related to the number of teeth of the meshing gear, and when the motor rotates one tooth, the torque has a pulse. The force balance type multi input gear motor has a plurality of motors at work at the same time, which is different from the torque ripple produced by a single motor working. When the internal motor is working independently, the difference of the position of the initial meshing point for the 3 internal motors is successively one third of tooth. By the superposition of the torque, the torque ripple of the 3 internal motors can be reduced, but the torque pulsation cycle is changed to 1/3. When internal motor and outer motor work together, on the basis of the same pulse period of the internal and external motors, the position of the initial meshing point of the inner and outer motor gear teeth is different from that of the gear teeth, the maximum value and the minimum value are added, and the torque ripple is minimized. For differential connection of internal and external motors,the motor is equivalent to the pump; under the same pulse period, the position of the initial meshing point of the internal and external motor is the same, and the input flow of the internal and outer motor is offset by each other, so as to minimize the torque ripple. Therefore, when working with a single motor, the torque ripple is related to the number of teeth in the meshing gear, and when a plurality of motors work together, the torque ripple is mainly related to the torque pulsation period of the motor and the position of the initial meshing point of the motor.
gears; motors; torque control; force balance; multi-input; differential motor; torque pulsation
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.10.012
TH137.51
A
1002-6819(2017)-10-0012-08
2016-09-29
2017-04-25
国家自然科学基金资助项目(50975246)
闻德生,男,教授,博士生导师,主要从事新型液压元件及液压传动研究。秦皇岛 燕山大学机械工程学院,066004
Email:wendesheng@ysu.Edu.cn
