前列腺癌组织紧密连接蛋白-4表达及与生化复发的关系
2017-06-08张春霆刘全启徐礼臻余谦罗荣利陈良佑杨庆朱再生
张春霆 刘全启 徐礼臻 余谦 罗荣利 陈良佑 杨庆 朱再生
前列腺癌组织紧密连接蛋白-4表达及与生化复发的关系
张春霆 刘全启 徐礼臻 余谦 罗荣利 陈良佑 杨庆 朱再生
目的探讨紧密连接蛋白-4(Claudin-4)在前列腺癌中的表达及与前列腺癌生化复发之间的关系。方法应用S-P法检测79例前列腺癌和45例前列腺增生组织Claudin-4表达状况,分析其与前列腺癌临床病理特点之间的关系,对前列腺癌随诊结果采用Kaplan-Meier生存分析5年前列腺癌患者生化复发与Claudin-4表达之间的关系;结果前列腺癌组织和前列腺增生组织Claudin-4表达阳性率分别为64.56%(51/79)和33.33%(15/45),差异有统计学意义(P均<0.01)。Claudin-4阳性表达在前列腺癌TNM分期Ⅰ~Ⅱ期和Ⅲ~Ⅳ期分别为46.34%和84.21%,在Gleason评分<7分≥7分患者分别为57.14%和72.97%,两者比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。随访60个月内生化复发45例,复发率为56.96%,生化复发的患者中Claudin-4表达阳性39例,Claudin-4表达阴性6例,两组间生化复发率比较差异有统计意义(P<0.01)。前列腺癌患者PSA结果进行Kaplan-Meier生存分析显示Claudin-4阳性患者5年生化复发率高于阴性表达患者。结论前列腺癌组织Claudin-4表达增高,其异常表达与前列腺癌临床分期和Gleason评分及5年生化复发相关,联合检测Claudin-4可能有助于前列腺癌预后评估。
前列腺癌;Claudin-4;免疫组化;生化复发
前列腺癌已成为危害我国男性健康的疾病之一,前列腺癌起病隐匿,病因未明,多种因素参与前列腺癌的发生进展。紧密连接蛋白-4(Claudin-4)在多种肿瘤组织中异常表达[1-4],但在前列腺癌中的表达状况及与前列腺癌生化复发之间的关系报道较少。本研究对Claudin-4在前列腺癌中的表达状况及与前列腺癌临床病理关系和5年生化复发之间的关系进行研究,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料提取2005年1月—2015年8月浙江大学金华医院泌尿外科手术切除或活检证实的前列腺癌患者79例,年龄52~82岁,中位年龄68岁,平均病程(2.0±0.75)年。前列腺癌按照2002年AJCC的TNM分期,Ⅰ~Ⅱ期41例,Ⅲ~Ⅳ期38例。分化程度按照Gleason系统,所有病理标本经有经验的病理医师再次证实。所提取的标本收取前患者无内分泌治疗、放疗及化疗。收集同期前列腺增生患者45例,年龄51~83岁,中位年龄69岁,平均病程(2.0±0.5)年。两组患者年龄、一般资料、病程无明显差异,两组资料有可比性(P>0.05)。
1.2 实验方法采用Claudin-4兔抗人多克隆抗体和DAB显色剂(均购自北京中杉金桥生物有限公司,批号140706)。采用链霉菌抗生物素蛋白-过氧化物酶染色法(S-P法)。严格按试剂盒说明书进行实验,石蜡包埋标本,3μm厚组织连续切片,抗原微波修复,过氧化氢清除内源性过氧化物酶活性。依次加一抗(1:100工作浓度)、生物素标记的二抗和酶标链霉亲和素,37℃孵育20min,DAB显色,显微镜下观察,以PBS液替代一抗作阴性对照,用已知Claudin-4阳性的前列腺癌切片作阳性对照。
1.3 结果判定所有结果均由两位有经验病理医师进行双盲读片显示结果,所有切片进行染色细胞数和染色强度观察,Claudin-4定位于细胞膜,阳性颗粒呈蓝色。高倍镜下染色强度和阳性细胞所占比例进行测定现阳性颗粒数目,5个高倍视野下染色细胞计数所占比例分为5级:<5%为0分,~25%为1分,~50%为2分,~75%为3分,>75%为4分。再按染色强度分为3级:弱染色为1分,中度染色为2分,强染色为3分。每切片得分=染色细胞分数×染色强度分数,<2分为阴性,≥2分为阳性。
1.4 统计学方法应用SPSS19.0统计软件对数据进行处理,计量资料用均数±标准差()表示,计数资料率的比较采用χ2或fish确切概率法,随访临床资料采用Kaplan-Meier生存分析法,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 Claudin-4表达Claudin-4主要分布在前列腺上皮细胞膜,在胞质和胞核上表达少,见图1(封二)。
2.2 Claudin-4蛋白表达与前列腺癌临床病理特征的关系Claudin-4蛋白在前列腺癌中呈现高表达,在79例前列腺癌中Claudin-4蛋白阳性表达51例,阳性表达率为64.56%,在45例前列腺增生组织中阳性表达为15例,阳性率33.33%。Claudin-4蛋白表达阳性率与Gleason分级有关,在Gleason评分≤7分和>7分患者中的阳性表达率分别为57.14%(24/ 42)和72.97%(27/37);在前列腺癌TNM分期Ⅰ~Ⅱ期和Ⅲ~Ⅳ期患者Claudin-4蛋白表达率分别为46.34%(19/41)和84.21%(32/38),Claudin-4蛋白表达随着分化程度加深呈现表达率上升(P<0.05),见表l。
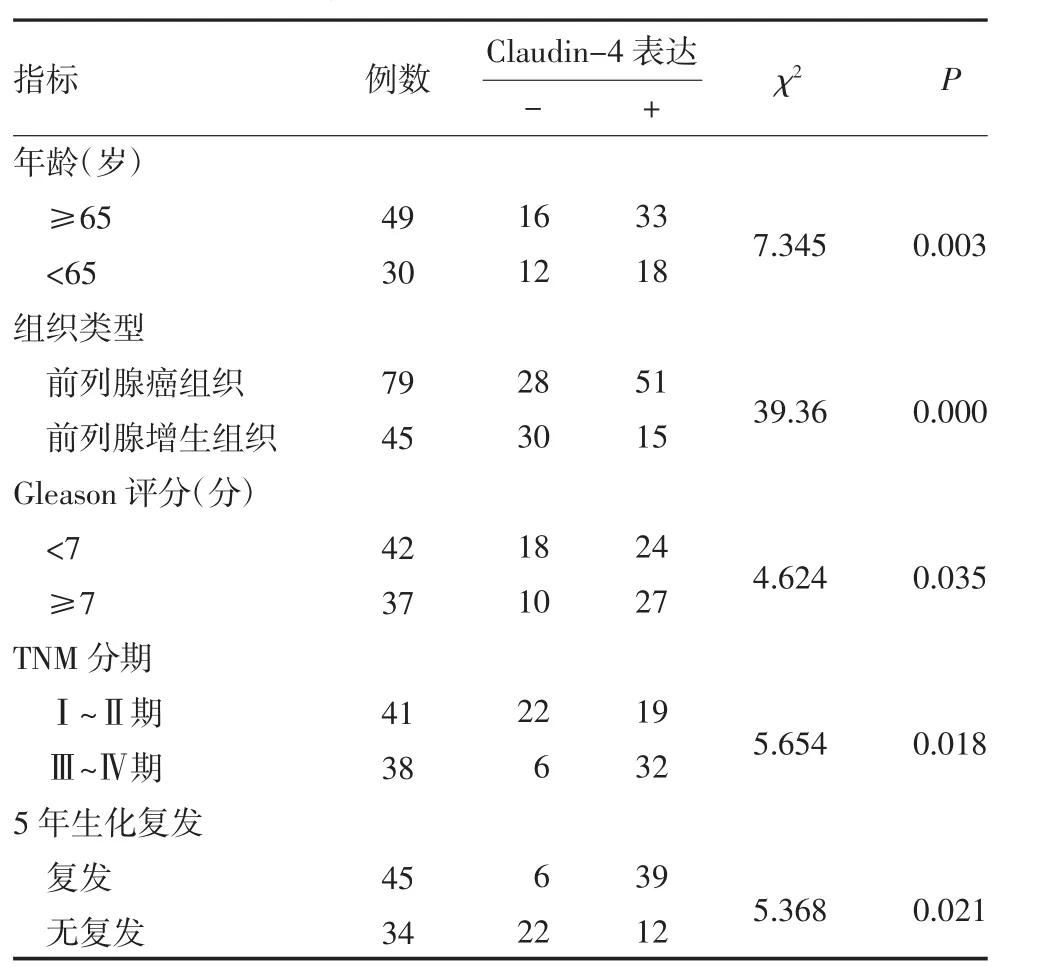
表1 79例前列腺癌患者Claudin-4表达与临床病理及5年生化复发之间的关系(例)
2.3 Claudin-4蛋白表达与随访前列腺癌患者5年生化复发之间的关系79例前列腺癌患者60个月PSA随访中,60个月内生化复发45例,复发率为56.96%,生化复发患者中Claudin-4表达阳性39例;Claudin-4表达阴性28例中60个月生化复发6例,生化复发率为21.43%,见表1。两组间生化复发率比较差异有统计学意义(P=0.007)。Kaplan-Meier生存曲线结果可见Claudin-4阳性表达的前列腺癌患者复发高于Claudin-4表达阴性者,见图2(封二)。
3 讨论
Claudins蛋白是构成紧密连接的重要组成部分。Claudins在多种上皮来源的恶性肿瘤中存在异常表达,并且与这些肿瘤发生和发展以及生存率有关[5-7]。研究显示,Claudins表达存在差异,Claudins家族中与肿瘤有关蛋白在同一组织中有的表达上调,有的则是表达下调或缺失,例如,Claudin-3和Claudin-4在卵巢癌、膀胱癌、胰腺癌中呈现高表达,Claudin-7在乳腺癌和头颈部肿瘤中表达下降,但是在胃癌中高表达[8-10],我们前期基因筛查发现Claudin-4在前列腺癌中表达增高,因此,进一步研究它是否与前列腺癌发生、进展及临床病理相关以及与前列腺癌5年生化复发之间的关系。
本实验中应用免疫组化方法对前列腺癌Claudin-4表达状况进行了研究,结果显示,在前列腺癌中Claudin-4阳性表达率64.56%,在增生的前列腺组织中Claudin-4阳性表达率33.33%,两者相比差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),提示Claudin-4在前列腺癌中异常表达可能与前列腺癌发生有关;国外研究[11]显示,紧密连接蛋白在肿瘤中的作用使E-钙黏蛋白表达减少,引起B-catenin在细胞内聚集,B-catenin/Tif信号通路激活,导致肿瘤细胞黏附力下降,易脱离原发灶,致周围间质、血管、淋巴管及广泛转移。国内张晓波等[12]对雄激素依赖性和非依赖性前列腺癌细胞差异表达膜蛋白表达差异进行了研究,对前列腺癌细胞株LNCaP和PC-3中膜蛋白进行Western印迹检测、串联质谱分析等技术,发现Claudin-4在LNCaP和PC-3细胞存在明显差异,阳性表达率分别为34.3%和72.4%,推测Claudin-4异常表达可能在雄激素非依赖性前列腺癌的发生和发展中发挥重要作用;Meng等[13]对睾酮缺乏后小鼠前列腺内免疫炎症因子变化状况与前列腺疾病进行研究,发现睾酮通过调节前列腺内Claudin-4膜蛋白的表达,进而影响前列腺中炎症因子继发的前列腺疾病,包括前列腺癌;但是在前列腺癌中Claudin-4是否存在上述机制,Claudin-4蛋白表达增高如何参与前列腺癌发生进展以及转移的过程,尚无充分的证据报道。
本研究还对前列腺癌分化程度和临床分期与Claudin-4蛋白阳性表达之间的关系进行比较,发现在Gleason评分<7分和≥7分患者中Claudin-4蛋白阳性表达率分别为57.14%(24/42)和72.97%(27/ 37),在前列腺癌Ⅰ~Ⅱ期和Ⅲ~Ⅳ期Claudin-4蛋白表达率分别为46.34%(19/41)和84.21%(32/38),表明它的异常表达可能参与了前列腺癌的进展和异常分化;文献报道中对卵巢癌研究中发现Claudin-4转录因子通过甲基化调节减低组蛋白酶H3乙酰化作用,可使组蛋白酶H3失活,促进肿瘤进展[14]。Claudin-4也可经蛋白激酶PKC8作用于189苏氨酸/194丝氨酸位点,使其发生磷酸化作用而表达下降,并由细胞膜转至细胞浆。使得紧密连接蛋白出现松散破坏[15]。因此推测前列腺癌进展中Claudin-4异常表达可能经多种调节途径,引起紧密连接骨架蛋白结构破坏,细胞极性和渗透性改变,瘤细胞侵袭力增加,促进肿瘤进展。
本研究发现Claudin-4异常表达与前列腺癌的发生发展相关,随访中C1audin-4阳性表达与前列腺癌5年生化复发之间存在相关性,但是Claudin-4在前列腺癌发生进展中确切的作用机制以及以哪种作用方式参与了前列腺癌的发生进展,尚需要进一步研究。
[1]Kuwada M,Chihara Y,Luo Y,et al.Prochemotherapeutic effects of antibody against extracellular domain of claudin-4 in bladder cancer[J].Cancer Lett,2015,369(1):212-221.
[2]Ma X,Miao H,Jing B,et al.Claudin-4 controls the proliferation,apoptosis,migration and in vivo growth of MCF-7 breast cancer cells[J].Oncol Rep,2015,34(2):681-690.
[3]Cuevas ME,Gaska JM,Gist AC,et al.Estrogen-dependent expression and subcellular localization of the tight junction protein claudin-4 in HEC-1A endometrial cancer cells[J]. Int J Oncol,2015,47(2):650-656.
[4]Alikanoglu AS,Gunduz S,Demirpence O,et al.Expression pattern and prognostic significance of claudin 1,4 and 7 in pancreatic cancer[J].Asian Pac J Cancer Prev,2015,16(10):4387-4392.
[5]Yao Q,Cao S,Li C,et al.Turn a diarrhoea toxin into a receptor-mediated therapy for a plethora of CLDN-4-overexpressing cancers[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2010,398(3):413-419.
[6]Cui YF,Liu AH,An DZ,et al.Claudin-4 is required for vasculogenic mimicry formation in human breast cancer cells[J].Oncotarget,2015,6(13):11087-11097.
[7]Kwon MJ,Kim SH,Jeong HM,et al.Claudin-4 Over-expression is associated with epigeneticderepressionin gastric carcinoma[J].Lab Invest,2011,91(11):1652-1667.
[8]Walther W,Petkov S,Kuvardina ON,et al.Novel Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin suicide gene therapy for selective treatment of claudin-3-and-4-overexpressing tumors[J].Gene Ther,2012,19(5):494-503.
[9]Li JG,Bao GQ,Yang XF,et al.Expression of claudin-4 and KLF-5 in gastric carcinoma and their clinical implication[J].Chin J Diagn Pathol,2014,21(2):94-99.
[10]Wu J,Peng XJ,Wang X.Expression of E-ca-dherin and claudin-4 in gastric carcinoma and its clinical significances[J].Chin J Anatomy,2011,34(1):27-30.
[11]Romanov V,Whyard TC,Waltzer WC,et al.A claudin 3 and claudin 4-targeted Clostridium perfringens protoxin is selectively cytotoxic to PSA-producing prostate cancer cells[J].Cancer Lett,2014,351(2):260-264.
[12]张晓波,唐正严,齐琳,等.雄激素依赖性和雄激素非依赖性前列腺癌差异膜抗原的筛选[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2012,37(8):817-823.
[13]Meng J,Mostaghel EA,Vakar-Lopez F,et al.Testosterone regulates tight junction proteins and influences prostatic autoimmune responses[J].Horm Cancer,2011,2(3):145-156.
[14]Kwon MJ,Kim SS,Choi YL,et al.Derepression of CLDN3 and CLDN4 during ovarian tumorigenesis is associated with loss of repressive histone modifications[J].Carcinogenesis,2010,31(6):974-983.
[15]Hwang TL,Lee LY,Wang CC,et al.Claudin-4 expression is associated with tumor invasion,MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression in gastric cancer[J].Exp Ther Med,2010,1(5):789-797.
(收稿:2016-06-22修回:2016-11-03)
Relationships of Expressionof Claudin-4 and Biochemical Recurrence in Prostate Cancer
ZHANG Chunting, LIU Quanqi,XU Lizhen,YU Qian,LUO Rongli,CHEN Liangyou,YANG Qing,ZHU Zaisheng.Department of Urology,Zhejiang University Jinhua Hospital,Jinhua(321000),China
ObjectiveTo investigate the expression of Claudin-4 in prostate cancer tissue and its relationship with biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer.MethodsS-P method was used to detect the expression of Claudin-4 in 79 cases with prostate cancer and 45 cases with benign prostatic hyperplasia,then the relationship between its expression withthe clinical and pathological features was analyzed.Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was used to analyze 5-year biochemical recurrence in patients and the follow-up results was assessed with the expression of Claudin-4.ResultsThe positive rate of Claudin-4 expression in prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia was64.56%(51/79)and 33.33%(15/45),respectively,with a significant different between them(P<0.01).The positive expression rates of Claudin-4 in tissues at TNM stage I~II and III~IV were 46.34%and 84.21%and intissues from the Gleason score<7 and≥7 were 57.14%and 72.97%,both with a significant difference(P<0.05).In a follow-up of 60 months,45 cases hadbiochemical recurrence,with a recurrence rate of 56.96%;among them,39 cases had positive expression of Claudin-4,4 cases with negative Claudin-4 expression;the difference in recurrence rate was statistically significant(P<0.01).Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that Claudin-4-positive expression patients had a higher 5-year biochemical recurrence rate than patients with Claudin-4 negative expression.Conclusion
Claudin-4 expression was increased in prostate cancer,the increase was related to the clinical stage and Gleason score and biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer.Detection of Claudin-4 may contribute to prognosis of prostate cancer.
prostate cancer;Claudin-4;immunohistochemistry;biochemical recurrence
浙江省金华市科技计划项目(No.2013-3-043)
浙江大学金华医院泌尿外科(金华321000)
朱再生,Tel:18267028028;E-mail:zaishengzhu@126.corn
