基于石墨烯气凝胶的全固态硝酸根离子选择性电极研究
2017-06-05严玉婷毛罕平左志强
严玉婷 毛罕平 王 坤 左志强
(江苏大学农业装备工程学院, 镇江 212013)
基于石墨烯气凝胶的全固态硝酸根离子选择性电极研究
严玉婷 毛罕平 王 坤 左志强
(江苏大学农业装备工程学院, 镇江 212013)
全固态离子选择性电极的结构在许多制备和应用方面具有明显优势。但由于固态界面上缺少有效的离子-电子转化导致其在电位稳定性上表现较差,无法保证各界面电势的稳定性而限制了全固态离子选择性电极的应用。因此,提出使用具有三维结构的石墨烯气凝胶 (GAs) 作为有效的固态转接层材料,用于调节离子载体基选择性聚合膜玻碳电极基底之间的离子-电子转化,基于这一原理制备了高性能全固态硝酸根离子选择性电极。通过透射电子显微镜表征其形貌特征;将其滴涂于玻碳电极表面形成GAs修饰电极,采用循环伏安法表征其电化学行为。在上述修饰电极表面覆上硝酸根离子选择性膜后制备新型的全固态离子选择性电极,通过电位水层测试、电位测量来表征其性能。GAs转接层的离子选择性电极对硝酸根离子展现出良好的能斯特响应和 10-4.2mol/L的检测下限,这为实现硝酸根离子现场即时检测提供了可能。
全固态离子选择性电极; 石墨烯气凝胶; 电位传感; 硝酸根离子检测
引言
目前,我国设施园艺面积已突破380万hm2,居世界第一位,由于其出产量大、需肥量多、土壤肥力消耗高,且不少面积采用无土栽培,有些生产者为了避免缺素问题的发生,往往过量施用氮肥,部分氮肥以硝酸盐形式残留在土壤、地下水和地表水中,不仅造成肥料的浪费和环境的面源污染[1],而且也会引起作物品质的降低,甚至减产。因此,迫切需要在作物生长过程中对硝酸盐进行精确监测和诊断,实现养分的精确管理,这对防治水环境硝酸盐污染起着非常重要的作用。
随着离子选择性膜的研究取得重大突破,产生了现代载基离子选择性电极。但是传统的离子选择性电极易受到跨膜离子流和环境的影响[2], 此外,电极必须浸没在溶液中来保持存放寿命,同时,这类电极无法实现真正的微型化,因此大大限制了离子选择性电极的使用范围[3]。全固态离子选择性电极的出现吸引了广泛关注,由于去除了内接参比液体,增加了电极自身的机械强度,使电极加工具有可操作性,从而再次激发起人们对离子选择性电极的研究兴趣。然而其缺点也非常明显,由于在固态界面上缺少有效的离子-电子转化,电化学信号(离子信号)无法有效和稳定的转变为电信号(电子信号),有电活性的导电聚合物作为固态转接层虽可以减小电位漂移,显著改善电位的稳定性[3-4],但溶解氧以及离子选择性膜与导电聚合物之间界面水层限制了基于导电聚合物的全固态离子选择性电极的应用[5]。最近,以碳材料作为离子-电子转化开始得到人们的关注,例如富勒烯[6]、 三维有序大孔碳[7-8]、碳纳米管[9-10]以及石墨烯[11-13]。
石墨烯气凝胶,作为石墨烯的一种衍生物,是一种自组装多孔碳材料。由于该材料中有石墨烯的成分并且空间上石墨烯相互连接,故其具有超高的表面积以及超强的导电性,而这2个特性是超级电容器电极材料所追求的关键性质,且由于该材料又具有多孔且孔径可调、表面化学结构稳定等优点,被认为是超级电容器的理想电极材料之一[14]。石墨烯气凝胶作为一种热门的碳材料,其在全固态离子选择性电极领域尚未见报道。因此,本文提出使用具有三维结构的石墨烯气凝胶作为有效的离子-电子固态转接层,构建全固态硝酸根离子选择性电极。
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验药品
甲基-N,N,N-三十二烷基铵硝酸根离子、 溴化甲基-三苯基磷酸铵、 2-硝酸苯基-辛烷基乙醚、聚氯乙烯(PVC)、 极性增塑剂邻硝基苯辛醚(NOPE)、硝化纤维素、四氢呋喃皆购自 Sigma-Aldrich 公司,试剂为分析纯等级,液态溶液由去离子水配制。天然石墨(325目)购于青岛天和石墨有限公司。
1.2 氧化石墨(GO)的制备
氧化石墨(GO)采用改进的Hummers法制备[15],具体步骤如下:

1.3 石墨烯气凝胶(GAs)的制备
称取20 mg氧化石墨置于10 mL二次蒸馏水中,超声30 min,制成氧化石墨烯水溶液,将该水溶液移入15 mL玻璃瓶中,再将该15 mL玻璃瓶转移至20 mL聚四氟水热釜中,160℃下反应保持12 h,待反应釜降至室温,得到圆柱状的产物;将上述圆柱状的产物置于-4℃下预冷冻;将预冷冻的材料放入冷冻干燥机中,在-40℃下冷冻干燥过夜,即得到柱状石墨烯气凝胶(GAs)。
1.4 全固态离子选择性电极的制备
玻碳电极(GCE,Φ3.0 mm)使用前,首先在金相砂纸上打磨,再依次用1.0、0.3、0.05 μm Al2O3抛光粉在麂皮上打磨抛光成镜面,再用二次蒸馏水冲洗干净后依次在0.1 mol/L HCl、0.1 mol/L NaOH和无水乙醇中超声清洗1 min,再用二次水超声清洗1 min,室温下晾干备用。


图示意图
1.5 测量方法
循环伏安法:CHI660D 电化学工作站(上海辰华)放置于常规三电极体系电化学池中进行信号采集,工作电极为 GCE/GAs、GCE/RGO 和未修饰的GCE电极,参比电极为 Ag/AgCl/KCl (3 M) 电极,对电极为铂丝电极。在室温下进行,电位扫描范围为-0.6~0.6 V,扫描速度为 0.1 V/s。
2 实验结果与分析
2.1 石墨烯气凝胶的表征
图2分别为还原氧化石墨烯和石墨烯气凝胶的透射电镜图,用于表征两者的形貌。如图 2a所示,单独的片层是透明且非常薄的。从图 2b中可以观察到,该材料是由石墨烯通过自组装的方式堆叠而成的,且空间上石墨烯相互连接,形成多层三维石墨烯结构,图2b是三维石墨烯的宏观形貌,呈现圆柱状,其表面粗糙,布满小孔。

图2 所制备材料的形貌表征Fig.2 Morphology characterization of samples
2.2 不同转接层修饰电极的电化学性能研究
不同转接层修饰电极在 0.1 mol/L NaNO3溶液中的循环伏安测试结果如图3所示。裸玻碳电极在 0.1 V/s 扫描速度下的充放电电流可以忽略不计,而 GCE/RGO展现出独特的电容性电流。有2个区域在-0.6~0.6 V电位范围内可以被区分出来:一个是氧化还原过程(-0.6~0.1 V),这个过程是由于氧气的参与;另一个是电容性过程(0.1~0.6 V)。从图3可以看出,不同修饰材料的循环伏安曲线形状大致一样,但相对石墨烯的修饰电极,石墨烯气凝胶修饰电极的电流明显增大,说明该电极的电容增大。文献[12]报道证实随着石墨烯厚度的增加,其电流也增大。在以石墨烯作为转接层的离子选择性电极中往往都采取多次滴涂的石墨烯层作为传感单元来研究,增加了实验操作的繁琐性。本实验中使用的石墨烯气凝胶由于其自身的三维多层结构,决定了其具有较大的电容且不需要多次修饰,对于固态离子传感器,拥有大的氧化还原电容是至关重要的,因此实验中选择石墨烯气凝胶层作为传感单元来研究。

图3 所制备电极的电化学性能表征Fig.3 Electrochemical properties of GCE/GAs electrode
2.3 修饰不同转接层电极的水层测试


图4 不同修饰电极的水层测试结果
2.4 硝酸根离子的检测

图5 选择性电极用于的检测
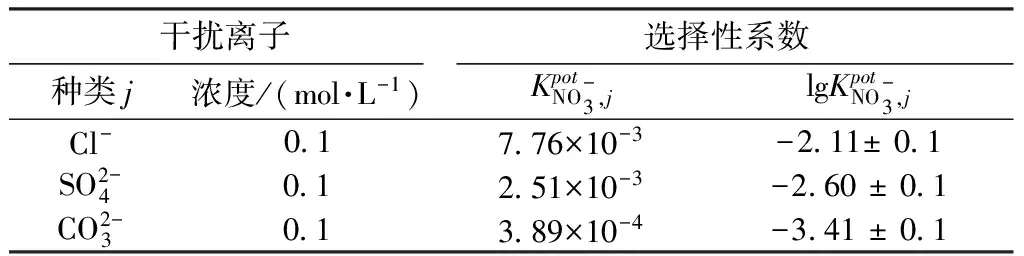
离子选择性电极通常需要在一定范围的干扰离子浓度下使用,超过这个范围,干扰离子就会对电位值产生影响。因此在实际操作中很有必要知道一个传感器的选择性系数。计算式为
(1)

式(1)只有在两种物质的活度已知时才可以计算,更实用的计算方法为
(2)

使用式(2)只需要分别测量传感器对分析离子和干扰离子的标准电位差值,就可以进行活度系数的计算,前提是这两种离子都具有能斯特响应。

干扰离子选择性系数种类j浓度/(mol·L-1)KpotNO-3,jlgKpotNO-3,jCl-0 17 76×10-3-2 11±0 1SO2-40 12 51×10-3-2 60±0 1CO2-30 13 89×10-4-3 41±0 1
2.5 全固态离子选择性电极的稳定性研究

图电极的离子活度电位响应

全固态离子选择性电极的性能主要是由敏感膜所决定的,敏感膜各组分的比例将影响电极电势的响应性能。目前有关全固态硝酸根离子选择性电极检测限一般为10-4~10-5mol/L, 本文的检测限为10-4.2mol/L,属于正常的检测限指标。后期将进一步对敏感膜的配方比例进行优化,以便得到最优性能的全固态离子选择性电极。
3 结束语

1 张维理,田哲旭,张宁,等.我国北方农用氮肥造成地下水硝酸盐污染的调查 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报,1995,1(2):80-87.
2 BAKKER E, BUHLMANN P, PRETSCH E. Carrier-based ion-selective electrodes and bulk optodes: 1. general characteristics [J]. Chemical Reviews, 1997, 97(8): 3083-3132.
3 LINDNER E, GYURCSANYI R E. Quality control criteria for solid-contact, solvent polymeric membrane ion-selective electrodes [J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2009, 13(1): 51-68.
4 BOBACKA J. Conducting polymer-based solid-state ion-selective electrodes [J]. Electroanalysis, 2006, 18(1): 7-18.
5 LINDFORS T. Light sensitivity and potential stability of electrically conducting polymers commonly used in solid contact ion-selective electrodes [J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2009, 13(1): 77-89.
6 FOUSKAKI M, CHANIOTAKIS N. Fullerene-based electrochemical buffer layer for ion-selective electrodes [J]. Analyst, 2008, 133(8): 1072-1075.
7 FIERKE M A, LAI C Z, BUHLMANN P, et al. Effects of architecture and surface chemistry of three-dimensionally ordered macroporous carbon solid contacts on performance of ion-selective electrodes [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2010, 82(2): 680-688.
8 LAI C Z, FIERKE M A, STEIN A, et al. Ion-selective electrodes with three-dimensionally ordered macroporous carbon as the solid contact [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2007, 79(12): 4621-4626.
9 DUEZGUEN A, MAROTO A, MAIRAL T, et al. Solid-contact potentiometric aptasensor based on aptamer functionalized carbon nanotubes for the direct determination of proteins [J]. Analyst, 2010, 135(5): 1037-1041.
10 HEMANDEZ R, RIU J, XAVIER RIUS F. Determination of calcium ion in sap using carbon nanotube-based ion-selective electrodes [J]. Analyst, 2010, 135(8): 1979-1985.
11 HEMANDEZ R, RIU J, BOBACKA J, et al. Reduced graphene oxide films as solid transducers in potentiometric all-solid-state ion-selective electrodes [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(42): 22570-22578.
12 PING J F, WANG Y X, WU J, et al. Development of an all-solid-state potassium ion-selective electrode using graphene as the solid-contact transducer [J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2011, 13(12): 1529-1532.
13 PING J F, WANG Y X, YING Y B, et al. Application of electrochemically reduced graphene oxide on screen-printed ion-selective electrode [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 84(7): 3473-3479.
14 XU Y X, LIN Z Y, HUANG X Q, et al. Functionalized graphene hydrogel-based high-performance supercapacitors[J]. Adranced Materials, 2013, 25(40): 5779-5784.
15 KOVTYUKHOVA N I, OLLIVIER P J, MARTIN B R, et al. Layer-by-layer assembly of ultrathin composite films from micron-sized graphite oxide sheets and polycations [J]. Chemistry Materials, 1999, 11(3): 771-778.
16 FIBBIOLI M, MORF W E, BADERTSCHER M, et al. Potential drifts of solid-contacted ion-selective electrodes due to zero-current ion fluxes through the sensor membrane [J]. Electroanalysis, 2000, 12(16): 1286-1292.
17 TANG W Z, PING J F, FAN K, et al. All-solid-state nitrate-selective electrode and its application in drinking water [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 81: 186-190.
18 BEATA P B. Effects of type of nanosized carbon black on the performance of an all-solid-state potentiometric electrode for nitrate [J]. Microchimica Acta, 2014, 181(9-10):1093-1099.
19 PU P, ZHANG M, LI Y H, et al. Preparation and evaluation of a stable solid state ion selective electrode of polypyrrole/electrochemically reduced graphene/glassy carbon substrate for soil nitrate sensing [J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2016, 11: 4779-4793.
20 LI F H, YE J J, ZHOU M, et al. All-solid-state potassium-selective electrode using graphene as the solid contact [J]. Analyst, 2012, 137: 618-623.
All-solid-state Nitrate-selective Electrodes Based on Graphene Aerogels
YAN Yuting MAO Hanping WANG Kun ZUO Zhiqiang
(SchoolofAgriculturalEquipmentEngineering,JiangsuUniversity,Zhenjiang212013,China)
It is of great advantage for advanced potentiometric detection systems to develop ion-selective electrodes (ISEs) by using solid-state transducer materials. Conducting polymers are the most used solid-state transducing materials. However, their reliability is strongly related to their chemical stability and the formation of internal water films. The ISEs with the implementation of graphene as ion-to-electron transducer were reported. And it was found that the electric current for the graphene modified electrode was decreased with the decrease of thickness of the graphene transducing layer. Thus, a novel all-solid-state nitrate-selective electrode with implementation of 3D multilayer graphene aerogels (GAs) as solid-contact layer was developed. And the as-prepared GAs was characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The GAs films as transducer materials in potentiometric all-solid-state ISEs showed better electrochemical performance in reducing graphene oxide (RGO) films due to its multilayer structure, which was demonstrated by the cyclic voltammetry (CV). As a proof of concept, the performance of the newly developed electrode was evaluated on the basis of nitrate ions. And the hydrophobic nature of the GAs film was characterized via the potentiometric water layer test. The obtained results showed that graphene can significantly facilitate the ion-to-electron transducer and prevent the formation of water layer between the ion-selective membrane and the graphene layer. And the new nitrate-selective electrode displayed a low detection limit of 10-4.2mol/L. GAs offered great promise as a reliable high-performance transducer material for solid-state ISE sensors. Furthermore, the developed electrode exhibited fast response and excellent potential stability, which made it very promising for routine analysis and application.
all-solid-state ion-selective electrode;graphene aerogels;potentiometric sensor;nitrate detection
2016-08-02
2016-12-01
国家自然科学基金项目(31101082、61075036)、“十二五”国家科技支撑计划项目(2014BAD08B03)、江苏高校优势学科建设工程PAPD项目(苏政办发(2011)6号)和农业部农业信息技术重点实验室开放课题项目
严玉婷(1988—),女,博士生,主要从事纳米材料设计和生物传感器应用研究,E-mail: 459979365@qq.com
毛罕平(1961—),男,教授,博士生导师,主要从事现代设施农业及环境自动控制技术研究,E-mail: maohp@ujs.edu.cn
10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2017.05.023
S132; O652.9
A
1000-1298(2017)05-0188-05
