The Injury Mechanisms of Fracture due to Domestic Violence:A Case Study
2017-05-13LIUDongmeiGAODongXIAWentaoLIZhengdongZHOUShuPENGShuyaInstituteofShanghaiHuayiForensicScienceShanghai00335ChinaShanghaiKeyLaboratoryofForensicMedicineInstituteofForensicScienceMinistryofJusticePRCShanghai00063China
LIU Dong-mei,GAO Dong,XIA Wen-tao,LI Zheng-dong,ZHOU Shu,PENG Shu-ya(.Institute of Shanghai Huayi Forensic Science,Shanghai 00335,China;.Shanghai Key Laboratory of Forensic Medicine,Institute of Forensic Science,Ministry of Justice,PRC,Shanghai 00063,China;3.Linyi Xinguang Institute of Judical Expertise,Linyi 7607,China)
The Injury Mechanisms of Fracture due to Domestic Violence:A Case Study
LIU Dong-mei1,GAO Dong2,XIA Wen-tao2,LI Zheng-dong2,ZHOU Shu2,PENG Shu-ya2
(1.Institute of Shanghai Huayi Forensic Science,Shanghai 200335,China;2.Shanghai Key Laboratory of Forensic Medicine,Institute of Forensic Science,Ministry of Justice,PRC,Shanghai 200063,China;3.Linyi Xinguang Institute of Judical Expertise,Linyi 276017,China)
This article reported a 37-year-old woman who was physically attacked by her husband,which caused her leg injuries.In the hospital a diagnosis was made of fractures of the right patella and left tibia before she underwent an operation of open reduction and internal fixation.Because the husband refused to adm it his fam ily violence comm itted against this woman;instead he claimed that her lower lim b fractures belonged to the falling injuries caused by a traffic accident.The police assigned forensic experts to judicially judge the woman’s injuries.And the identification results of X-ray and CT showed that the transverse fracture of patella had been caused by muscular violence,and that both direct and indirect force resulted in the injuries of left tibia,and the fracture of left medial orbital wall might have been formed during the violence.This article expounded the identification between the injuries of fam ily violence and traffic accident by the applications of imaging,which emphasized the application value of imaging techniques in clinic forensic science.
forensic medicine;domestic violence;injury mechanism;tibial fracture;medial orbital wall fracture
Introduction
Domestic violence,which mainly occurs between fam ily members,is a severe social problem in both the developing and developed countries.In order to safeguard women’s rights,a legal document named The Convention on the Elim ination of All Forms of Discrim ination against Women(CEADW)was passed by the United Nations in 1979.However, the domestic violence involving women still exists. In North America,40%-51%of women tolerated some type of violence in their lifetime[1].As reported,Indian women were at higher risk of domestic violence than non-Indian women[2].In China,it was also reported that 90%of the domestic violence was from husband to w ife[3].It is well recognized that women suffer physical and psychological trauma from domestic violence w ith the feelings of depression,helplessness and hopelessness.Besides traditional forms of violence,e.g.physical assault,the concept of violence has been expanded to such non-traditional types as sexual harassment,breaches of fiduciary trust and stalking[1].In most cases,the husband refuses to adm it the fact and the w ife ex-perienced the oppressive encounter,which may explain why domestic violence continues.In the current case study,the forensic experts helped the police find the bona fide cause of the fractures using the theory of injury mechanism.
Case report
A Chinese woman aged 37 alarmed that her husband beat her repeatedly.On January 17,2013, her husband assaulted her w ith a steel tube and pickaxe on their way to the local Civil A ffairs Bureau,resulting in the injuries of her both legs.Afterwards,she was sent to the hospital for treatment. The X-ray imaging indicated the fractures of her right patella and left tibia,which rendered a surgery of open reduction and internal fixation performed on January 22,2013.A fter the proper treatment in the hospital,she was taken home by his husband. During the recovery period when she was unable to walk,her husband repeatedly whipped her body w ith a rubber stick,causing soft tissue contusion, and even worse,he burnt her face and perineum w ith cigarette butts.
On February 5,2013,she escaped from the house while her husband was sleeping,because she couldn’t bear her husband’s maltreatment any more.The problem,however,the husband refused to admit that it was his violence that caused the fractures,claim ing that on their way to the local Civil A ffairs Bureau she jumped from a moving m inibus,which led to the leg injuries.
The police turned to the lie detector to explore the truth.The injured woman passed the test on June 4,2013,while her husband refused the test. His reaction created a dilemma for the police. Moreover,the CT scanning imaging of the injured woman,made on June 8,2013,showed the signs of the dated fracture of left medial orbital wall.To find the truth of the case,the police requested forensic experts to address the following two questions of whether the factures were caused by stick beating or by the jump from the moving m inibus, and of whether the fracture of left medial orbital wall was formed during the domestic violence.
Clinical presentation
On January 17,2013,the injured woman was sent to the local hospital,where the X-ray imaging showed fractures of right patella and left tibia.Because the hospital didn’t have the capacity for such a patient,she was transferred to the province-level hospital.On January 18,2013,the record of her physical examination stated swelling over the right tibia,tenderness,percussion pain over the right patella w ith palpable bone fricative,hemorrhage in the right knee joint,apparent lim ited movement of the right knee,normal activities and perceptions of the right ankle w ith arteria dorsalis pedis palpated, malformation,swelling and tenderness in the m iddle of the left leg w ith abnormal activity,visible ecchymosis over the left tibia area,and normal perceptions and peripheral blood circulation.According to the X-ray imaging,the surgeon made a diagnosis of fractures of right patella and left tibia.
An operation of open reduction and internal fixation was performed on the injured woman on January 22,2013.When the hematoma and bone fragments were cleared away,steel plate and w ire were used for fracture reduction.Thanks to the successful surgery,the C-arm X-ray imaging indicated that the fracture healed perfectly with the steel plate and w ire well located.
Forensic investigation
On July 31,2013,the forensic experts started to be engaged in the case,producing the results as follows:The X-ray imaging dated January 18,2013 showed that the right patella had a transverse fracture;that the patella was separated into the upper and lower pieces apparently(Fig.1A);and a piece of bone was observed in the inner side of the proximal tibial fracture.Morphologically,the proximal tibial fracture belonged to a short oblique fracture.The consequence of distal tibia injury was a classical spiral fracture.Additionally,the X-ray imaging presented the subluxation of the left talocrural joint(Fig.1B).

Fig.1 Radiographs of lower lim bs
The X-ray imaging dated February 6,2013 showed the signs of the woman’s internal fixation.
Taken on February 6,2013,the colour pictures of the face and legs showed skin ecchymosis on the upper and lower eyelids.There was a sutured wound over the skin of the right knee joint,the length of which was about one centimeter.
The CT scanning imaging dated June 8,2013showed the depression of the left lam ina papyracea of the ethmoid w ith slight swelling of the left medial rectus.No exudation and gas were observed in the orbital,indicating the dated fractures of the left medial orbital wall(Fig.2).
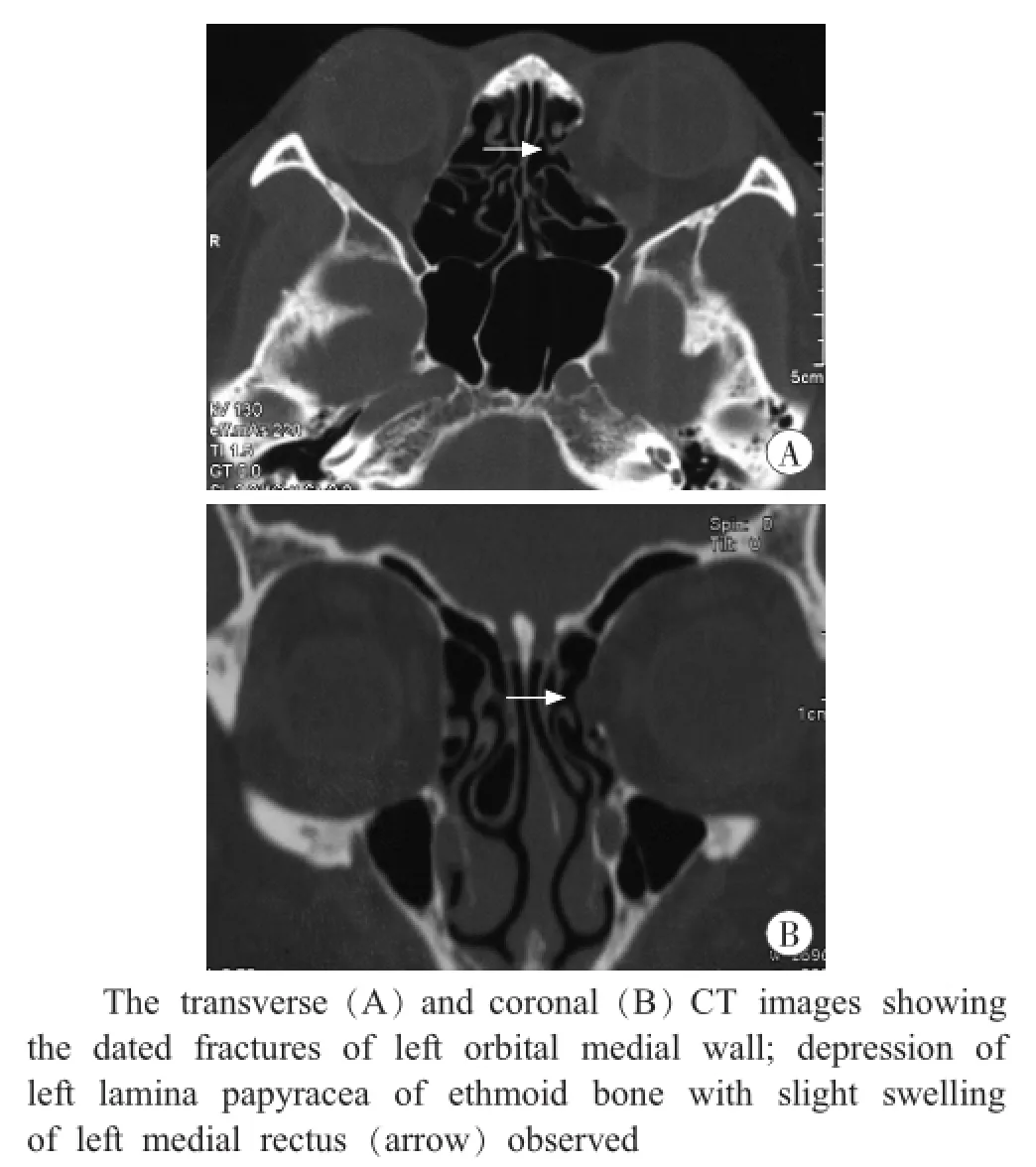
Fig.2 CT scanning images of obit
Expert opinion
Based on a rigorous study,the forensic experts concluded that the transverse fracture of the right patella was caused by muscular violence,and the injuries of the left leg could have been due to both direct and indirect force.The proximal tibial fracture was caused by direct force,while the distal tibia fracture was the result of indirect force.According to the results of the police investigation, the proximal tibial fracture m ight have been caused by stick beating,while weak evidence could prove that the fractures of the distal tibia and right patella were caused in the same injury manner.It couldn’t be ruled out that the fractures of the right patella and distal tibia were formed in the process of falling after proximal tibia injury.If it was verified that the woman’s left eye didn’t receive another external force after February 5,2013,the fracture of the left medial orbital wall could be formed during the husband’s domestic violence.
Discussion
The injured woman alarmed the maltreatment from her husband,causing the fractures of her right patella and left tibia.In a rebuttal,the husband stated that she had jumped from a speeding m inibus, causing her leg injuries.Having reviewed the X-ray imaging,the forensic experts inferred that direct force was responsible for the proximal tibial fracture(e.g.stick beating),while indirect force led to the distal tibia and right patella fractures.
Analysis of fractures
As a common injury,fracture is often caused by traffic accidents or falling incidents.The formation mechanisms of fracture are multiple;different fracture patterns may result from different injury manners.Adm ittedly,the radiographic image plays a significant role in show ing a fracture precisely so that proper and prompt clinical diagnosis and treatment can be made.In the current case,the radiographic images of the injured woman served as the essential evidence for the forensic experts to pursue the true formation mechanism of her tibia and patella fractures and injured orbital wall.
Patella,the largest human sesamoid bone,is an important functional component of the knee joint. Its subcutaneous location makes it likely to be injured at direct or indirect trauma.Patellar fracture accounts for approximately 0.5%-1.5%of all bone fractures[4],which are commonly caused by muscular violence or direct blows.Patellar fracture can be classified into transverse(undisplaced and displaced)and comm inuted forms[5].Transverse is the most common type of patella fracture appearing mostly in young patients w ith good bone quality.In the cases of sudden stumble or jumping from a height, transverse patella fracture is likely to occur when the quadriceps contract abruptly to avoid kneeling. When the quadriceps contract powerfully,the contacted surface between quadriceps and patella acts as a fulcrum.W ith the flexion degree of the knee joint increasing,the compressive force on the patellofemoral articulation enhances subsequently. Patella suffers an indirect force when the extensor mechanism of the knee exceeds the strength of the bone,resulting in a transverse fracture or the avulsion of the inferior pole[6].The compressive forces are dim inished ow ing to the division of the upper and lower poles.In the current case,both the man and injured woman adm itted the fact of falling.To complete the action,the woman’s quadriceps must have contracted violently and aggressively.In the case of exceeding strength of the bone,a transverse patella fracture would occur.From the X-ray imaging,the upper and lower fractured pieces of patella were present,which conformed to the characteristics of muscular or indirect force effect.
As the body’s load-bearing bone,tibial fracture is one of the most common types of long bone fracture for its poor coverage of soft tissue.In 36.7%of bicyclists,both bones of the lower leg, tibia and fibula,were fractured;in 21.5%,the tibiawas fractured and in 41.5%,the fibula,exclusively[7]. According to Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Osteosynthesefragen/Association for the Study of Internal Fixation(AO/ASIF)tibia shaft fractures can be classified into simple fractures,wedge fractures and complex fractures.The groups of single fractures are transverse,oblique and spiral[8].Both direct and indirect force can result in tibial fractures.Direct force, such as heavy impact or serious blows,often causes transverse,short oblique or comm inuted tibial fractures.The fracture often occurs in the site of being hit.The fracture can be angled,which is coincident w ith the external force direction.Differently,indirect force,such as falling and tumble,can cause long oblique or spiral fractures,which are multiply accompanied by the dislocation or subluxation of the talocrural joint.It was reported that fracture caused by a fall combining bending and torsional force was more common in women[9].In the current case,the morphology of proximal tibial fracture was short oblique.Moreover,a piece of bone could be seen in the inner side of the proximal tibia, which conformed to the effect of direct force.Differently,the morphology of distal tibia was a spiral fracture.Subluxation of the left talocrural joint was also presented,which indicated that the woman m ight have suffered torsional forces when the distal tibial fracture occurred.Analyzed synthetically,the current case was highly possible to experience a distal tibial fracture when the bone was in a weight-bearing condition.In other words,the fracture of distal tibia was due to the effect of indirect force.Since its crucial function is load-bearing,the sequelae of the tibial fractures must have caused inconvenience to the woman’s daily activities.
App lications of FEM and CT scanning
In recent years,the finite elementmodel(FEM)has been applied to determ ining injury mechanism, making it possible to duplicate the moment of an injury occurrence.FEM research on liver showed that,among three impact directions,a lateral impact was most likely to cause liver injury w ith a m inimum punch speed of 5m/s[10].It was demonstrated that the simulation method could potentially be effective in identifying forensic cases and in exploring the injury mechanisms of lower limb fractures due to inflicted lesions[11].Wong and his colleagues had successfully established a tibial fracture simulation, showing that the distribution of Von M ises stress of the torsional load was located in the distal third of the lower leg[12].In the current case,we verified the injury mechanisms of the left leg by conducting FEM research,but the result was not positive. However,it was not disheartening that the location of the spiral tibial fracture coincided with Wong’s results,which also could serve as a powerful evidence for the interpretation of the fractures.
The medial wall,formed by the frontal process of the maxilla,the lacrimal bone,the lam ina papyracea of the ethmoid bone and the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone,is likely to be fractured in maxillofacial trauma.Technically,high resolution CT scanning is the first choice for the diagnosis of orbital fracture.The depression of lam ina papyracea of the ethmoid bone,the swelling of medial rectus and exudation and the gas in the orbital often can be observed in CT images of fresh orbital fracture. Blowout fractures in the medial orbital wall may lead to enophthalmos,diplopia and ocular dysmotility[13].In the current case,the orbital CT image dated June 8,2013,showed the depression of lam ina papyracea of the ethmoid bone without exudation and gas in the orbital.Moreover,the colour pictures taken on February 6,2013,showed ecchymosis of the upper and lower eyelids,indicating that the left eye had encountered external forces several days before.The forensic experts inferred that if the woman didn’t have dated injuries or congenital lesions in the left eye before January 8 and her left eye didn’t experience any other external forces after February 5,it was certain that the fracture of the left orbital wall could have been formed during the husband’s domestic violence.
Conclusion
At the hearing of the investigation results,the police adopted the forensic experts’conclusion on the injury mechanisms.The truth was that the husband assaulted his w ife w ith a blunt instrument, leading to a proximal fracture of her left tibia.The fall to the ground w ith an instable center of gravity,led to the fractures of distal tibia and patella. The dated fracture of orbital medial wall m ight have been formed by her husband’s domestic violence.The husband was convicted of the crime for his illegal actions to his w ife.
Acknow ledgment
This study was not supported by any foundation.
[1]Robinson GE.Violence againstwomen in North America[J].Arch Women Ment Hlth,2003,6(3):185-191.
[2]Oetzel J,Duran B.Intimate partner violence in American Indian and/or A laska Native communities:A social ecological framework of determinants and interventions[J].Am Indian A lsk Native Ment Health Res,2004,11(3):49-68.
[3]Zhang KC,Ye DQ.The current situation of fam ily violence against women[J].Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2004,8:570-572.
[4]Weber M J,Janecki CJ,McLeod P,et al.Efficacy of various forms of fixation of transverse fractures of the patella[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,1980,62(2): 215-220.
[5]Graham W.Betts-Symonds.Fracture:Care and management for students[M].London:Macm illan publishers, 1984.
[6]Rodrìguez-Merchán EC.Traumatic injuries of the knee[M].M ilan:Springer-Verlag Italia,2013.
[7]Otte D,Haasper C.Characteristics on fractures of tibia and fibula in car impacts to pedestrians and bicyclists-influences of car bumper height and shape[J]. Annu Proc Assoc Adv Automot Med,2007,51:63-79.
[8]Müller ME,Koch P,Nazarian S,et al.The comprehensive classification of fractures of long bones[M]. Berlin:Springer-Verlag,1990.
[9]Madadi F,Farahmandi MV,Eajazi A,et al.Epidem iology of adult tibial shaft fractures:a 7-year study in a major referral orthopedic center in Iran[J]. Med Sci Monit,2010,16(5):217-221.
[10]Shao Y,Zou DH,Li ZD,et al.Blunt liver injury w ith intact ribs under impacts on the abdomen:a biomechanical investigation[J].PloS One,2013,8(1): e52366.
[11]Li ZD,Zou DH,Liu NG,et al.Finite element analysis of pedestrian lower limb fractures by direct force:The result of being run over or impact?[J]. Forensic Sci Int,2013,229(1-3):43-51.
[12]Wong C,M ikkelsen P,Hansen LB,et al.Finite element analysis of tibial fractures[J].Dan Med Bull, 2010,57(5):A4148.
[13]Saiepour D,Messo E,Hedlund AJ,et al.Radiologic and long-term clinical outcome from treatment of isolated medial orbital wall blowout fractures[J].J Craniofac Surg,2012,23(5):1252-1255.
(Received date:2014-07-24)
(Editor:CHEN Jie-min)
家庭暴力致骨折损伤机制分析1 例(英文)
刘冬梅1,高东2,夏文涛2,李正东2,周姝2,彭书雅3
(1.上海华医司法鉴定所,上海 200335;2.司法部司法鉴定科学技术研究所上海市法医学重点实验室上海司法鉴定专业技术服务平台,上海 200063;3.临沂新光法医司法鉴定所,山东临沂 276017)
本文报道了一名37岁女性遭受丈夫殴打,造成下肢受伤。医院诊断为右髌骨和左胫骨骨折,伤者遂接受了切开复位内固定术。由于丈夫否认对其实施家庭暴力,声称其下肢骨折系交通事故坠落伤。警方遂委托对该女性的损伤进行法医学鉴定。经过审阅X线和CT检查资料,结果为伤者右侧髌骨骨折、左胫骨骨折,以及左眶内侧壁骨折。鉴定意见为髌骨的横向骨折系由肌肉的牵拉暴力引起,左胫骨损伤符合直接和间接外力所致,左眶内侧壁骨折在施暴期间形成的可能性较大。本文阐述了运用影像学技术对家庭暴力案件与交通事故损伤进行鉴别,强调了影像学技术在法医临床鉴定中的应用价值。
法医学;家庭暴力;损伤机制;胫骨骨折;眶内侧壁骨折
DF795.4
:B
1004-5619(2017)02-0209-05
Author:LIU Dong-mei(1987—),M.D,majored in clinical forensic medicine;E-mail:l_dm1987@163.com
XIA Wen-tao,M.D,research fellow, postgraduate tutor in clinical forensic medicine;E-mail:xiawentao629@163.com
10.3969/j.issn.1004-5619.2017.02.029
