光电漫反射式联合收割机谷物产量计量系统研发与性能试验
2017-03-04付兴兰张兆国安晓飞赵春江李晨源于佳杨
付兴兰,张兆国,安晓飞,赵春江,李晨源,于佳杨
光电漫反射式联合收割机谷物产量计量系统研发与性能试验
付兴兰1,3,张兆国1※,安晓飞2,3,4,赵春江2,3,5,李晨源1,于佳杨1,3
(1. 昆明理工大学现代农业工程学院,昆明650000;2. 国家农业智能装备工程技术研究中心,北京 100097; 3. 北京农业智能装备技术研究中心,北京 100097;4. 农业智能装备技术北京市重点实验室,北京,100097; 5. 农业部农业信息技术重点实验室,北京,100097)
为了进一步提高联合收割机谷物产量计量系统的精度,自主研发了基于光电漫反射原理的谷物产量计量系统。系统主要由传感器模块、数据处理模块、GPS模块和谷物产量计量显示终端组成。光电式谷物产量计量系统计量作业时,当联合收割机籽粒升运器刮板输送谷物经过漫反射型谷物体积传感器时,会间歇性的阻断光路,从而产生脉宽信号,脉宽信号大小与刮板上谷物厚度成正比,同时升运器转速传感器输出转速信号,谷物产量计量数据处理模块将采集到的2路传感器信号进行放大、滤波和A/D转换后与GPS模块采集的联合收割机行进速度、经纬度信息由RS485总线传输至光电谷物产量计量软件系统,经光电式谷物产量模型处理后,将产量信息、速度信息、位置信息等实时显示在终端上。为了验证光电式谷物产量计量系统的性能,分别开展了室内主要传感器性能台架试验和系统田间动态性能验证试验,试验中谷物喂入量在0.1~6 kg/s范围内,台架试验表明升运器转速传感器测量误差小于2.00%,漫反射型谷物体积传感器测量误差小于3.50%。田间动态性能验证试验结果表明光电式谷物产量计量系统运行稳定,系统检测结果与实际测量结果决定系数R达到0.848 4,测产误差最大为3.51%,满足田间实际测产需要,为精准农业变量作业提供了科学依据。
谷物;光电装置;传感器;联合收割机;产量计量系统
0 引 言
获取谷物作业区域准确的产量信息是评价谷物产量及作业效果的重要指标,产量信息的空间变异性是来年精准变量作业的科学依据[1]。
谷物产量计量在当前精准农业的研究和实践中,是一个必不可少的环节[2]。国外的谷物产量计量相关研究起步较早,谷物产量计量系统已成为联合收割机的标准配件,研究者们也提出了多种谷物计量模型,谷物产量计量系统的测量误差为4.4%[3-6]。研究者对主要产品如John Deere公司开发的Green Star谷物测产系统,Ag Leader公司研制的冲击式PF3000谷物产量监测系统,Raven公司研发的光电对射式Smart Yield Pro系统等进行了试验 研究,结果表明测产系统误差约为5%[7-10]。国内的谷物产量计量研究相较于国外仍处于探索研发阶段。一些大学和研究机构在谷物流量传感器设计方面取得了一些进展[11-13]。张惠莉[14]采用射线的原理设计了一种射线传感器用于谷物流量的实时检测,该方法测试误差在2%以内,但是射线的使用有严格标准且对人体有害。张小超等[15-18]基于称重式的原理设计了一种螺旋输送称重传感装置用于谷物流量检测,台架试验误差小于2%,提高了测产精度,但传感器装置结构复杂。丛秉华等[19-22]对冲量式的谷物流量传感器做出了进一步的优化,提出使用平行梁的方式代替单板冲击式,研制出平行梁谷物流量监测传感器,结果显示传感器的误差小于4%。李新成等[23-27]提出优化采样频率、双阈值滤波等方法消除噪声和机器振动误差的影响,使得测产平均误差为3.27%。在产量计量的研究中,崔笛等[28]提出光电对射式的传感器用于监测谷物流量的方法,小麦流量范围在0.1~1.2 kg/s之间时,测量误差小于3%。有学者将此方法引入到棉花计量系统中[29-32],但到目前为止,还未见采用光电漫反射原理进行谷物产量计量的研究。
本研究的目的是基于光电漫反射原理,研发一种光电式谷物产量计量系统,建立谷物产量光电检测模型,分别开展室内主要传感器台架试验和系统田间动态试验,对系统的稳定性和准确性进行测试,实现谷物产量的快速准确测量。
1 光电式谷物产量计量系统设计
1.1 光电式谷物产量计量系统总体设计
图1是光电式谷物产量计量系统总体结构图。系统主要由传感器模块、数据采集模块、GPS模块和谷物产量计量显示终端组成。传感器模块包括上海迈得豪实业有限公司生产的CHE18-30PA-B710型漫反射型谷物体积传感器,测量精度99%和上海朗鸿自动化工程有限公司生产的JK8002C/PNP型升运器转速传感器,测量精度99%。谷物产量计量显示终端内嵌光电式谷物产量计量软件系统和光电式谷物产量模型。

1. GPS模块2. 谷物产量计量显示终端3. 谷物产量计量数据采集模块 4. 升运器转速传感器5. 漫反射型谷物体积传感器
该系统通过传感器模块获取谷物体积、升运器转速、收割机速度、位置坐标等产量信息,再由数据采集模块将采集到的传感器信息通过解析、处理后由RS485总线传输到计量系统,经过系统和产量模型的处理和计算后将谷物测产作业中的产量、速度、位置等信息实时显示在计量终端上。
1.2 光电式谷物产量计量系统硬件设计
光电式谷物产量计量系统硬件组成如图2a所示。系统主要由多路信息采集单元、数据处理单元、数据显示单元三部分组成。可以实现多路谷物测产信息的采集,数据的A/D转换、滤波等处理,最终在数据显示单元将数据实时显示并存储等功能。其中,信息采集单元的漫反射型谷物体积传感器是测产系统的核心部件。
如图2b所示为漫反射型谷物体积传感器的工作原理。漫反射式谷物体积传感器安装在联合收割机籽粒升运器的侧壁上,传感器光源发射出调制红外光束,当籽粒升运器输送谷物经过漫反射型谷物体积传感器时,红外光束被升运器刮板输送的谷物反射回传感器的光电探测器,经传感器驱动电路处理后输出脉宽电压信号,传感器输出脉宽电压信号大小与刮板谷物厚度成正比,结合刮板的底面积和升运器速度得到谷物的体积,谷物体积与谷物密度计算可得到谷物的质量。
漫反射型谷物体积传感器工作电压为6~36 V,工作电流300 mA,响应时间0.1 ms,检测距离5~30 cm。国内主流的联合收割的刮板侧壁间距为140~200 mm,1/2的侧壁间距大于传感器最小检测距离5 cm,传感器设置有调节旋钮,距离可调,可以有效避免由于升运器侧壁间距太近造成的发射光被侧壁反射回来造成的误差。漫反射型谷物体积传感器设计有保护罩,密封防护等级为IP66,并对安装角度和安装位置进行校正,利用重力原理和刮板橡胶摩擦降低灰尘和谷物浆汁的覆盖,可有效避免灰尘、浆汁等因素干扰。

1. 籽粒升运器 2. 谷物 3. 升运器刮板 4. 传动链条 5. 光源 6. 光电探测器7. 驱动电路 8. 脉宽信号
1. Elevator 2. Grain 3. Scraper of elevator 4. Driving chain 5. Light source 6. Photoelectric detector 7. Driving circuit 8. Pulse signal
注:为刮板上的谷物厚度
Note:: the thickness of grain on scraper
图2 光电漫反射式谷物产量计量系统硬件设计
Fig.2 Hardware design of grain yield monitor based on photoelectric diffuse reflectance
系统中测量升运器转速的传感器选用三线式JK8002C/PNP型霍尔元件,安装在收割机籽粒升运器底部传动轴外侧,并自主研发测速码盘和安装支架,测速码盘设计有2路感应磁铁,以减少系统误差,提高测量精度。数据处理单元选用具有4路计数、测频通道的IPAM7404数据采集模块,最大计数值为32 bits,采样频率为10 Hz,无奇偶校验。谷物产量计量显示终端选用VMC1000嵌入式终端,该终端具有GPS、RS232、RS485、CAN等通讯接口,实现各节点间数据通讯,能运行嵌入式操作系统XPE,完成谷物信号的输入、输出等功能。
1.3 光电式谷物产量计量系统软件设计
光电式谷物产量计量软件系统基于Microsoft Visual Studio 2010平台开发,采用C++语言进行程序编写,实现谷物收获作业时的谷物产量、GPS信息及升运器转速等信息的接收、解析、显示、存储和查看等功能。图3所示为的光电式谷物产量计量软件系统主界面,系统采用RS485总线通讯,采样间隔时间为100 ms,设备地址为1,能够实时显示谷物产量、升运器转速、经纬度和时间等信息,主要由系统设置模块、数据处理模块、数据存储模块、实时显示模块组成。
软件系统各部分的功能如下:1)基本参数设置功能。输入谷物种类、谷物水分、谷物密度、收割区域和收割人等基本信息,实现谷物基本参数设置功能。2)数据处理功能。数据处理功能包括对2路传感器信号和GPS信号的接收与解析,以及光电漫反射谷物产量模型的数据处理与计算。3)数据实时显示功能。实现谷物产量信息、速度信息、基本设置信息实时显示与仪表指示。4)数据存储功能。实现谷物联合收割机谷物田间作业过程中收割时间、谷物流量、升运器转速、收割机行走速度、经度、纬度、收割面积、谷物产量等数据的保存与查看。
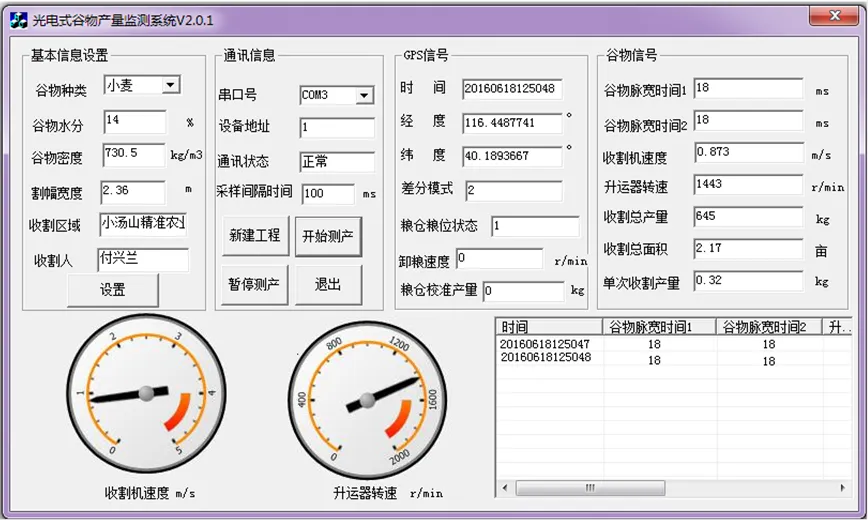
图3 光电式漫反射谷物产量计量软件系统
1.4 光电式谷物产量计量模型
在研究了谷物对光电漫反射作用的光学原理和谷物的运动学原理的基础上,建立了刮板所载谷物近似几何模型。图4是刮板所载谷物近似几何模型图。如图所示谷物堆积形状近似模拟为4个部分,包括下部刮板体积、中部规则长方体体积、上部锲体体积和升运器链条体积。收割机升运器与水平地面的倾角为21º,传感器中心线到刮板前沿的垂直距离为,mm。收割机升运器刮板的长度、宽度和高度,mm。升运器链条的长度和宽度分别为和,mm。对应本研究中的TB60型联合收割机来说都是常量。
a. 传感器安装示意图
a. Diagram for sensor installation

b. 谷堆近似几何模型
b. Approximate geometric model of grain
1. 籽粒升运器 2. 谷物 3. 漫反射型谷物体积传感器 4. 升运器刮板5. 传动链条
1. Elevator of grain 2. Grain 3. Diffuse reflectance grain volume sensor 4. Scraper of elevator 5. Driving chain
注:为刮板间距,mm;为收割机与地面倾角,(°);为传感器中心线到刮板前沿的垂直距离,mm;为刮板长度,mm;为刮板宽度,mm;为刮板高度,mm;x为刮板所载谷物层厚度,mm;ctg为上部锲体中心高度,mm;为链条长度,单位mm;为链条宽度,mm。
Note:: the distance of scraper, mm;: the obliquity of combine harvester and ground, (º);: vertical distance between the sensor centerline and the scraper leading edge, mm;: the length of scraper, mm;: the width of scraper, mm;: the height of scraper mm; x: the thickness of grain on scraper, mm;ctg: the center height of wedge, mm;: the length of chain, mm;: the width of chain, mm.
图4 刮板所载谷物近似几何模型图
Fig.4 Approximation geometric model of grain
根据式(4)将所有的瞬时产量求和,可以求出对应区域的谷物总产量
为了得到更准确的光电式谷物产量模型计算公式,需在收割机田间作业时,通过田间标定试验来获得实际的与的关系式,以进行分析和校正。
2 光电式谷物产量计量系统性能试验
2.1 系统主要传感器性能测试试验
试验采用自主研发设计的谷物测产实验台模拟联合收割机正常工作状况,以三相变频电动机为动力源,测试台架条件下漫反射型谷物体积传感器和升运器转速传感器的准确性和稳定性。图5是谷物测产实验台结构示意图。实验台包括显示器、漫反射型谷物体积传感器、入粮装置、籽粒升运器、升运器转速传感器和调速电动机。
为检验系统主要传感器的准确性和稳定性,通过人工调节自主研发的实验台升运器刮板不输送谷物,以刮板实际厚度12 mm空载运转的条件下,调节电动机速度使升运器转速与田间作业工况相当[25],选定650、750、850、950和1 050 r/min 5个转速水平。记录升运器转速和刮板厚度测量数据。表1为系统主要传感器台架试验数据。
1. 显示器2. 漫反射型谷物体积传感器 3. 入粮装置4. 籽粒升运器 5. 升运器转速传感器 6. 调速电动机
从表1试验数据可以看出升运器转速传感器测量最大误差为1.87%,低于2.00%,具有较好的准确性,各转速水平下,标准差最大为2.33 r/min,离散程度小,具有较好的稳定性。
在升运器转速具有较好的准确性和稳定性的基础上,对表1试验数据进行处理得到刮板空载时在各转速水平下的厚度测量平均值为11.65 mm,与刮板实际厚度12.00 mm最大误差为3.41%,小于3.50%,最大测量值与最小测量值只相差0.18 mm,具有较好的稳定性。
通过调节试验台调速电动机保持升运器转速恒定的条件下,使用与刮板材质相同的黑色橡胶加工制作成若干个长度、宽度相同高度的不同的谷堆模型,通过3 M双面泡棉胶带固定在升运器刮板上运转,用于模拟不同的谷物厚度,分别为23、40、80、120和150 mm,记录刮板谷物厚度测量值。表1数据表明刮板谷物厚度测量值与刮板谷物厚度真实值最大测量误差为2.17%,低于3.00%具有较好的准确性。

表1 系统主要传感器台架试验数据表
注:刮板空载厚度测量值*:在试验台刮板空载时,调节升运器转速,根据脉宽信号计算空载刮板厚度值,与刮板实际厚度12 mm进行误差分析。
Note: Predict without load thickness:Keeping platform work without load, adjusting the elevator speed, according to the pulse width signal without load scraper thickness value is calculated, and the scraper actual thickness is 12 mm for error analysis.
2.2 系统田间动态性能验证试验
光电式谷物产量计量系统田间动态性能验证试验于2016年6月小麦收获季节在北京市小汤山国家精准农业研究示范基地进行,试验地地处116.265 466°~116.270 241°E,40.111 550°~40.111 161°N,小麦种植品种为京冬22,小麦面积为70 hm2。试验现场气象条件良好:晴,气温22~32 ℃。联合收割机试验机型为中国中联重科农业机械责任有限公司设计生产的自走轮式TB60谷物联合收割机,收割机喂入量6 kg/s,割幅宽度2.51 m,发动机功率86.4 kW,收割机行走速度2~4 km/h,外形尺寸6 600 mm×3 000 mm×3 420 mm。田间性能试验分为系统田间空载试验,系统模型标定试验和小麦收割测产试验3个阶段。通过空载试验,对刮板厚度的脉宽信号进行差分滤波,以降低干扰;通过模型标定试验得到标定系数和谷物产量计算模型;通过小麦田间收割测产试验,对光电式谷物产量计量系统测量精度和性能进行 验证。
2.2.1 系统田间空载试验
空载试验在小麦实验田相邻空置实验田进行,实验田地形特征和土壤性能与小麦种植田均相似。在空载试验中,调节收割机的升运器转速在200~1 500 r/min空载运行,对升运器刮板厚度输出脉宽信号进行测试。图6是刮板空载数据输出特性曲线。
从图6可见,随着升运器速度增加,空载刮板脉宽时间逐渐降低。空载特性拟合曲线决定系数2达到0.941 1。根据试验数据处理得到升运器转速为田间工况水平750 r/min和850 r/min时,谷物计量系统测得升运器转速平均值分别为734 r/min和836 r/min,测量误差为2.13%和1.65%,此时升运器刮板厚度测量值分别为11.74 mm和11.65 mm,与刮板实际厚度比较,误差为2.16%和2.91%,光电式谷物产量计量系统在田间动态空载运行时稳定性,测量精度在4.00%以内,满足系统田间测产要求。

图6 系统空载试验输出特性曲线
2.2.2 系统田间标定试验
在谷物实际收获作业中不同型号的谷物联合收割机刮板的厚度及尺寸存在差异,当籽粒升运器刮板转动时,谷物的堆积几何形状和理论形状存在差异,为校正光电式谷物产量计量系统产量模型计算公式,对系统进行了标定试验,得到标定系数,标定不同机型刮板所载谷堆厚度的变化信息,从而得到实际的谷物质量与谷堆厚度的关系式。如图4所示的谷物堆积几何模型,在标定试验中测得试验机型TB60谷物联合收割机的传感器中心线到刮板前沿的垂直距离为为25 mm,,,分别为收割机升运器刮板的长度、宽度和高度,值为 136、65和12 mm。和分别为升运器链条的长度和宽度,值为40和30 mm。根据公式(2)可得到谷物体积公式为:
由式(6)计算得到谷物实时体积,再结合式(7)中谷物密度和标定系数即可计算得到区域面积内的谷物总产量,本次试验中测得的谷物密度为730.5 kg/m3。
2.2.3 系统小麦收割测产试验
标定试验之后进行田间验证试验,验证试验共进行6个车次,试验中每个车次谷物喂入量在0.1~6 kg/s之间,每个车次分别代表不同面积的小麦收割区域,由谷物产量计算模型公式(6)和公式(7)计算获得谷物瞬时体积和质量,将各车次区域面积的体积和质量累加得到谷物总产量值,通过人工采样称量获得谷物实际产量。表2是田间验证试验数据。
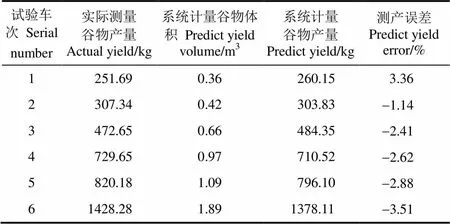
表2 田间验证试验数据表
系统获得的谷物产量和实际测得的谷物产量决定系数R达到0.848 4,误差范围在-3.51%~3.36%,整体小于4.00%,且误差波动较小,说明系统具有较好的准确性和鲁棒性,完全满足田间实际测产需要。试验中最大误差为-3.51%,对收割机田间工作状况和系统实际运行情况分析主要是由于收获区域地面起伏不平、地块不规则导致收割机行走路线变化,割幅未达到2.51 m的正常工作幅宽等所造成的。此外,由于田间试验时谷物水分、温度等参数也存在差异,也会造成误差的产生。
3 结 论
1)基于光电漫反射原理研发设计了谷物产量计量系统,内嵌光电漫反射谷物产量计量模型,可以实现谷物产量、行进速度、位置等信息的实时测量与显示,对谷物喂入量在0.1~6 kg/s范围内均满足要求。
2)系统性能验证试验结果表明,漫反射型谷物体积传感器和升运器转速传感器稳定性和准确性均满足系统要求,田间动态试验表明系统预测值与实测值决定系数2达到0.848 4,系统动态测量误差最大为3.51%,满足田间测产的实际需要。
为了进一步提高光电式谷物产量计量系统的预测模型精度,下一步将考虑谷物水分和温度对模型的影响,仍需开展大量的田间动态试验。
[1] 汪懋华. 精细农业[M]. 北京:中国农业大学出版社, 2011:1-6.
[2] 罗锡文,廖娟,胡炼,等. 提高农业机械化水平促进农业可持续发展[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(1):1—11. Luo Xiwen, Liao Juan, Hu Lian, et al. Improving agricultural mechanization level to promote agricultural sustainable development[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(1): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] Loghavi M, Ehsani R, Reeder R. Development of a portable grain mass flow sensor test rig[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2008, 61(2): 160-168.
[4] Maertens K, Reyns P, De Baerdemaeker J. Double adaptive notch filter for mechanical grain flow sensors[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2003, 266 (3): 645-654.
[5] Reinke R, Dankowicz H, Phelan J, et al. A dynamic grain flow model for a mass flow yield sensor on a combine[J]. Precision Agriculture, 2011, 12(5): 732-749.
[6] Shoji K, Itoh H, Kawamura T. In-situ non-linear calibration of grain-yield sensor–optimization of parameters for flow rate of grain vs. force on the sensor[J]. Engineering in Agriculture, Environment and Food, 2009, 2(3): 78-82.
[7] Shoji K, Miyamoto M. Improving the accuracy of estimating grain weight by discriminating each grain impact on the yield sensor[J]. Precision Agriculture, 2014, 15(1): 31-43.
[8] Burks T F, Shearer S A, Fulton J P, et al. Effects of time- varying inflow rates on combine yield monitor accuracy[J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 2004, 20(3): 269-275.
[9] Fulton P, Sobolik J, Shearer A, et al. Grain yield monitor flow sensor accuracy for simulated varying field slopes[J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 2009, 25(1): 44-48.
[10] An Xiaofei, Meng Zhijun, Wu Guangwei, et al. Development of grain yield monitoring system based on CAN bus technology[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agriculture Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(Supp.2): 262-266. (in English with Chinese abstract)
[11] 刘碧贞,黄华,祝诗平,等. 基于北斗/GPS的谷物收割机作业综合管理系统[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(10): 204-210. Liu Bizhen, Huang Hua, Zhu Shiping, et al. Integrated management system of grain combine harvester based on Beidou& GPS[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(10): 204-210. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 武佳,李民赞,郑立华,等. 谷物联合收获机测产系统性能试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2012,43(增刊1):108-113. Wu Jia, Li Minzan, Zheng Lihua, et, al. Performance test of yield monitor system for grain combine harvester[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(Supp.1): 108-113. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 陈树人,仇华铮,李耀明,等. 谷物流量传感器试验台的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(16):41-46. Chen Shuren, Qiu Huazheng, Li Yaoming, et al. Design and experiment of test-bed for grain flow sensor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(16): 41-46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 张惠莉. 面向康拜因收获过程的谷物流量在线实时测量方法的研究[D]. 北京:中国农业大学,2002. Zhang Huili. The Research of the Methods of Measuring Grain Flow on Real Time for Combines[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2002.
[15] 周俊,苗玉彬,张凤传,等. 平行梁冲量式谷物质量流量传感器田间实验[J]. 农业机械学报,2006,37(6):102-105. Zhou Jun, Miao Yubin, Zhang Fengchuan, et al. Field testing of parallel beam impact-based yield monitor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2006, 37(6): 102-105. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 张小超,胡小安,苑严伟,等. 精准农业智能变量作业装备研究开发[J]. 农业工程,2011,1(3):26-32. Zhang Xiaochao, Hu Xiaoan, Yuan Yanwei, et al. Research and development of intelligent agricultural machinery on precision agriculture[J]. Agricultural Engineering. 2011, 1(3): 26-32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 张小超,胡小安,张爱国,等. 基于称重法的联合收获机测产方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2010,26(3):125-129. Zhang Xiaochao, Hu Xiaoan, Zhang Aiguo, et al. Method of measuring grain-flow of combine harvester based on weighing[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2010, 26(3): 125-129. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 李伟,张小超,胡小安,等. 联合收获机称量式测产系统软件设计[J]. 农业机械学报,2011,42(增刊1):94-99. Li Wei, Zhang Xiaochao, Hu Xiaoan, et al. Design of intelligent yield monitoring software for combine harvester[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2011, 42(Supp.1): 94-99. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 丛秉华,周俊. 双平行梁谷物流量传感器振动噪声消除方法[J]. 传感器技术学报,2013,26(3):377-381. Cong Binghua, Zhou Jun. Vibration noise elimination for a grain flow sensor of dual parallel beam load cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2013, 26(3): 377-381. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 李向东,吕风荣,张德奇,等. 小麦田间测产和实际产量转换系数实证研究[J]. 麦类作物学报,2016,36(1):69-76. Li Xiangdong, LÜFengrong, Zhang Deqi, et al. Empirical study on conversion factors between yield monitoring and actual yield of winter wheat[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops. 2016, 36(1): 69-76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 魏新华,张进敏,但志敏,等. 冲量式谷物流量传感器测产信号处理方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(15):222-228. Wei Xinhua, Zhang Jinmin, Dan Zhimin, et al. Signal processing method of impact-based grain flow sensor for predicted yield[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(15): 222-228.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 郑立华,郭享,李民赞,等. 面向异构平台的谷物测产数据采集及实现[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(9):142-149. Zheng Lihua, Guo Xiang, Li Minzan, et al. Grain yield data collection and service for heterogeneous platforms[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(9): 142-149. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 李新成,李民赞,王锡九,等. 联合收割机远程测产系统开发及降噪试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(2):1-8. Li Xincheng, Li Minzan, Wang Xijiu, et al. Development and denoising test of grain combine with remote yield monitoring system[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(2): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 李新成,李民赞,郑立华,等. 谷物联合收获机测产系统采样频率优化与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2015,46(增刊):74-78. Li Xincheng, Li Minzan, Zheng Lihua, et al. Test and optimization of sampling frequency for yield monitor system of grain combine harvester[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(supp): 74-78.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 李新成,孙茂真,李民赞,等. 谷物联合收获机自动测产系统产量模型[J]. 农业机械学报,2015,46(7):91-96. Li Xincheng, Sun Maozhen, Li Minzan, et al. Modeling algorithm for yield monitor system of grain combine harvester[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(7): 91-96. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 陈进,宁小波,李耀明,等. 联合收获机前进速度的模型参考模糊自适应控制系统[J]. 农业机械学报,2014,45(10):87-91. Chen Jin, Ning Xiaobo, Li Yaoming, et al. Fuzzy adaptive control system of forward speed for combine harvester based on model reference[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(10): 87-91. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 梁学修,陈志,张小超,等. 联合收获机喂入量在线监测系统设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2013,44(增刊):1-6.Liang Xuexiu, Chen Zhi, Zhang Xiaochao, et al. Design and experiment of on-line monitoring system for feed quantity of combine harvester[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(Supp): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 崔笛,李民赞,张俊宁,等. 基于光电原理的容积式谷物流量传感器试验研究[C]//广州:中国农业工程学会2005年学术年会论文集. 2005. Cui Di, Li Minzan, Zhang Junning, et al. Development of a grain volumetric-flow sensor based on photoelectrical principle[C]//GuangZhou: Proceedings of Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering Conference 2005. 2005.
[29] 沈雷. 输棉管籽棉流量光电检测模型建立与优化[D]. 石河子:石河子大学,2014.Shen Lei. The Establishment and Optimization of Photoelectric Detection Model for Seed Cotton Mass Flow in Pipe[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University. 2014.
[30] 林昌建. 基于光电传感器的棉花产量在线监测系统研究[D]. 上海:上海交通大学,2013. Lin Changjian. Study on Cotton Yield Online Monitoring System Based on Photoelectric Sensing[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2013.
[31] 安光辉,马蓉,芦帅,等. 棉纤维质量密度光学检测模型的优化[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(10):253-258. An Guanghui, Ma Rong, Lu Shuai, et al. Optimization of optical measurement model for mass density of cotton fiber[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(10): 253-258. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 周利明,李树君,张小超,等. 基于电容法的棉管籽棉质量流量检测[J]. 农业机械学报,2014,45(6):47-52. Zhou Liming, Li Shujun, Zhang Xiaochao, et al. Detection of seedcotton mass flow based on capacitance approach[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(6): 47-52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Development and performance experiment on grain yield monitoring system of combine harvester based on photoelectric diffuse reflectance
Fu Xinglan1,3, Zhang Zhaoguo1※, An Xiaofei2,3,4, Zhao Chunjiang2,3,5, Li Chenyuan1, Yu Jiayang1,3
(1.650000; 2.100097; 3.100097;4.100097; 5.100097)
Development of remote sensing (RS), geographical information system (GIS) and global positioning system (GPS) has provided new methods for obtaining field grain yield information, which allows better description of spatial variability for grain yield. Monitoring grain yield has become an essential component in precision agriculture, which provides better guidance for grain growth and management such as variable fertilizing, irrigating and spraying. In order to further improve the monitoring accuracy of grain combine harvester, a new real-time grain yield monitoring system based on photoelectric principle was developed in this study. The system was composed of sensor module, grain yield data acquisition module, GPS module and grain yield display terminal. The sensor module included diffuse reflectance grain volume senor as key component of the system and rotating speed sensor of elevator. A model of grain mass on the scraper was established based on optical principle of photoelectric diffuse reflection effect and grain kinematic principle. Prediction model and diffuse reflectance grain yield monitoring software were embedded in the grain yield display terminal. When the elevator scraper of the combine harvester with the grain passed the diffuse reflectance grain volume sensor, the light path would be blocked intermittently. As a result, the corresponding pulse signal would be generated and meanwhile the elevator’s rotating speed sensor would output the rotating speed signal. According to photoelectric principle, the size of pulse signal was proportional to the thickness of grain on the scraper. Subsequently the grain yield data acquisition module converted sensor signals into standard signals, and grain yield information including real-time grain yield and total yield, elevator rotating speed, combine harvester speed, harvest area, and longitude and latitude would be obtained and displayed on the terminal. In order to evaluate the performance of the grain yield monitoring system, both laboratory platform experiment and field dynamic experiment were conducted. For the platform experiment, an experiment platform was designed, which was composed of LED (light-emitting diode) terminal, diffuse reflectance grain volume sensor, grain inlet, elevator, elevator’s rotating speed sensor and motor. The result of platform experiment showed that the rotating speed sensor of elevator had the maximum error of 1.87%, which was less than 2.00%, and the maximum standard deviation of 2.33 r/min, which indicated the sensor had a small discrete degree; the diffuse reflectance grain volume sensor had the maximum error of 3.14%, which was less than 3.50%, and both the accuracy and the stability satisfied the requirements. Field dynamic experiment included 3 parts: field experiment without loading, model calibration experiment and field experiment of wheat yield. The field experiment without loading showed that the pulse signal intensity of diffuse reflectance grain volume sensor decreased with the elevator’s rotating speed increasing, the determination coefficient (2) of output curve was 0.941 1, and the measurement error was within 4.00%. For the model calibration experiment, domestic TB60 type combine harvester was calibrated to obtain the calibration factor of 0.071, and the relationship between grain mass and thickness was gotten. The field wheat yield experiment showed that the grain yield monitoring system based on photoelectric principle was maximum error of 3.51%, which was smaller than the double-plate differential method. The system offered a wide range of grain feeding quantity and satisfied the need of field grain yield monitoring. The research provides a new method to monitor real-time grain yield, and the system is applicable to domestic mainstream models of combine harvester in China.
grain; photoelectric devices; sensors; combine harvester; yield monitor system
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.03.004
S126
A
1002-6819(2017)-03-0024-07
2016-08-29
2016-12-19
北京市农林科学院青年基金(QNJJ201529);国家重点研发计划种行肥行精准拟合与判断关键技术与装备(2016YFD0200605);国家高技术研究发展计划(863计划)农机精准作业协同支撑技术与平台(2013AA102308)
付兴兰,女,云南大理人,主要从事农业信息化技术研究。昆明昆明理工大学现代农业工程学院 650000 Email:1581433861@qq.com
张兆国,男,山东单县人,教授,博士生导师,主要从事农业装备设计与制造研究。昆明昆明理工大学现代农业工程学院 650000。E-mail:zhaoguozhang@163.com
付兴兰,张兆国,安晓飞,赵春江,李晨源,于佳杨.光电漫反射式联合收割机谷物产量计量系统研发与性能试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(3):24-30. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.03.004 http://www.tcsae.org
Fu Xinglan, Zhang zhaoguo, An Xiaofei, Zhao Chunjiang, Li Chenyuan, Yu Jiayang. Development and performance experiment on grain yield monitoring system of combine harvester based on photoelectric diffuse reflectance[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(3): 24-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.03.004 http://www.tcsae.org
