贝伐单抗治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌的疗效与安全性临床研究进展*
2017-03-03胡彬彬陈宝清卢铀
胡彬彬 陈宝清 卢铀
·国家基金研究进展综述·
贝伐单抗治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌的疗效与安全性临床研究进展*
胡彬彬①陈宝清①卢铀②
抗血管生成治疗是肿瘤常见的治疗方式之一。贝伐单抗作为抗血管内皮生长因子的单克隆抗体,是目前唯一被批准用于晚期非小细胞肺癌(non-small cell lung cancer,NSCLC)一线治疗的抗血管生成制剂。为了扩大贝伐单抗用于晚期NSCLC的适应证,大量研究继续探索贝伐单抗在一线治疗的联合形式外,还致力于探索其在后线及跨线治疗的疗效和安全性。本文就近年来贝伐单抗用于晚期NSCLC治疗的疗效与安全性临床研究进展进行综述。
非小细胞肺癌 贝伐单抗 化学治疗 靶向治疗 维持治疗 安全性
肺癌是目前世界上导致肿瘤相关死亡的首要原因[1]。非小细胞肺癌(non-small cell lung cancer,NSCLC)约占肺癌的85%[2]。随着近年来抗血管生成治疗手段被验证有效,NSCLC患者的预后有了较大的提升。贝伐单抗通过阻断血管内皮生长因子与其受体结合,能够促使肿瘤血管正常化、减少新生血管的生成,从而有效地发挥抗肿瘤作用[3]。自2006年贝伐单抗被美国食品药品监督管理局(FDA)批准用于晚期NSCLC一线治疗后,大量关于贝伐单抗的临床研究致力于拓展其在NSCLC治疗中的适应证,包括探索新型的药物联合形式、筛选获益的人群以及选择合适的治疗时机等。研究结果显示出贝伐单抗一定的优势性,但同时存在部分争议。本文就贝伐单抗在晚期NSCLC一线、二线及以上治疗和跨线治疗的疗效和安全性临床研究进展进行综述。
1 贝伐单抗用于晚期NSCLC一线治疗
2004年,Johnson等[4]开展的一项Ⅱ期临床试验发现高风险咯血与使用贝伐单抗的肺鳞癌患者密切相关,自此后,贝伐单抗用于NSCLC的临床研究则一致避开纳入病理组织类型为鳞癌或含鳞成分的患者。贝伐单抗联合化疗用于晚期NSCLC一线治疗的疗效与安全已得到不少Ⅲ期临床试验的证实。而探索新的联合形式,如联合靶向治疗及维持治疗的疗效与安全是目前的研究热点(表1)。
1.1 贝伐单抗联合化疗
ECOG 4599是一项878例患者的大型Ⅲ期临床试验。研究将未经过治疗的晚期NSCLC患者随机分配到贝伐单抗联合紫杉醇+卡铂组和安慰剂+紫杉醇+卡铂组中治疗。结果显示,贝伐单抗组和单纯化疗组的客观缓解率(objective response rate,ORR)分别为35%和15%,中位无进展生存时间(median pro⁃gression-free survival,mPFS)分别为6.2和4.5个月,中位总生存时间(median overall survival,mOS)分别为12.3和10.3个月。在安全性方面,贝伐单抗组3级以上不良反应的发生率高于单纯化疗组,主要为中性粒细胞减少、高血压、动静脉血栓、出血事件和蛋白尿[5]。借鉴ECOG 4599的试验设计,国内开展一项Ⅲ期临床试验BEYOND同样验证出贝伐单抗联合紫杉醇+卡铂这一方案在提高ORR、PFS和OS的优势性。此外,研究还针对表皮生长因子受体(epidermal growth factor receptor,EGFR)突变状态进行亚组分析,发现在EGFR突变阳性群中,两组的mPFS分别为12.4和7.9个月,mOS分别为24.3和27.5个月;在EG⁃FR野生型群中,两组的mPFS分别为8.3和5.6个月,mOS分别为20.3和13.8个月[6]。这一研究结果肯定了在EGFR野生型患者中化疗联用贝伐单抗的疗效,而在EGFR突变阳性患者中,化疗联用贝伐单抗的远期疗效还有待进一步证实。基于上述两项临床研究结果,贝伐单抗联合紫杉醇+卡铂已被批准为包括国内患者在内的EGFR野生型晚期NSCLC患者的一线标准治疗。
欧洲开展的一项Ⅲ期临床试验AVAIL则采用吉西他滨+顺铂这一化疗方案,并且设置15mg和7.5mg两个剂量的贝伐单抗组。结果显示,高剂量和低剂量贝伐单抗组较单纯化疗组其mPFS分别延长0.4和0.6个月[7],但未转化为OS的获益[8]。然而,对研究中的105例亚洲患者进一步分析得到低剂量贝伐单抗组存在OS获益,高剂量组仍未得到体现[9]。在安全性方面,高剂量贝伐单抗组的3级以上不良反应的发生率为44%,高于低剂量组(33%)和单纯化疗组(33%),但均可耐受[7]。因此,在临床上治疗方案的选择需考虑人群的不同,对于亚洲患者,采用低剂量的贝伐单抗联合吉西他滨+顺铂或许能获得更好的疗效。
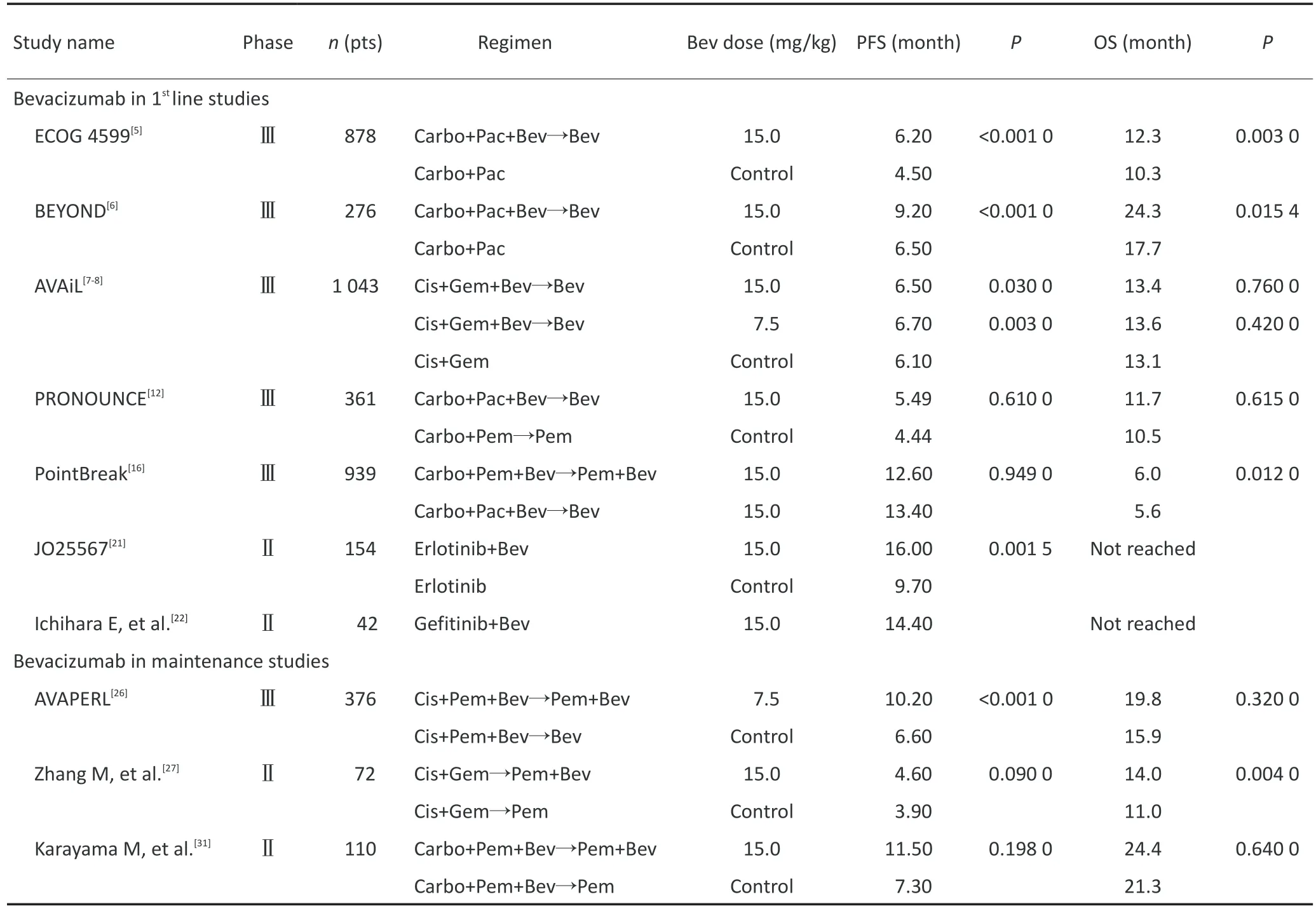
表1 贝伐单抗一线治疗晚期NSCLC的临床研究Table 1 Clinical research of bevacizumab as first-line treatment of advanced NSCLC
培美曲塞联合铂类是治疗晚期NSCLC传统的一线标准化疗方案之一。由于在治疗肺腺癌中的优势性[10-11],诸多研究将贝伐单抗联合铂类为主的化疗方案与之对比[12-15]或将贝伐单抗与之联合。Patel等[16]进行的临床研究PointBreak,则采用贝伐单抗联合培美曲塞+卡铂挑战已成为一线标准治疗方案的贝伐单抗联合紫杉醇+卡铂,是目前唯一将贝伐单抗联合不同化疗方案在一线进行直接对比的Ⅲ期临床试验。研究虽未达到主要终点预设值-培美曲塞组的OS优于紫杉醇组,但是两组的mPFS差异具有统计学意义(6.0个月vs.5.6个月)。在安全性方面,培美曲塞组常见的不良反应为贫血、血小板减少和乏力,而紫杉醇组为中性粒细胞减少、周围神经病变和脱发。虽然贝伐单抗联合培美曲塞+卡铂的疗效优于联合紫杉醇+卡铂未得到证实,但其作为晚期NSCLC一线治疗方案同样是可借鉴的。
此外,新的化疗联合形式也在不断探索中,如贝伐单抗联合多西他赛+铂类[17-18]、贝伐单抗联合长春瑞滨+铂类[19]、贝伐单抗联合替吉奥+铂类[20]均观察到一定的临床疗效。但上述研究均为小样本单臂研究,还需开展更多的大样本Ⅲ期临床试验来证实。
1.2 贝伐单抗联合靶向治疗
在EGFR突变阳性的晚期NSCLC患者中,贝伐单抗联合络氨酸激酶抑制剂(TKI)的研究结果是令人鼓舞的。日本开展的一项Ⅱ期随机对照研究,将EGFR突变阳性的晚期NSCLC患者随机分配到贝伐单抗联合厄洛替尼组和厄洛替尼单药组。结果显示,双药联合组和单药组的mPFS分别为16.0和9.7个月(P=0.001 5),ORR分别为69%和64%(P=0.495 1),疾病控制率(disease control rate,DCR)分别为99%和88%(P=0.017 7)。进一步分析发现,19外显子缺失的患者在两组中的PFS有显著性差异(18.0个月vs.10.3个月),而L858R患者的PFS差异无统计学意义。在安全性方面,双药组和单药组最常见的3级以上不良反应为皮疹(25%vs.19%)、高血压(60%vs.10%)和蛋白尿(8%vs.0)[21]。日本的另一项关于贝伐单抗联合吉非替尼Ⅱ期单臂研究同样得到19外显子缺失的患者其PFS明显优于L858R的患者(18.0个月vs.9.4个月)[22]。上述两项研究结果显示在EGFR突变阳性,特别是在19外显子缺失的晚期NSCLC患者中一线运用贝伐单抗联合TKI的初步优势。此外,两项正在进行的Ⅲ期临床试验(NCT02759614、NCT02633189)将进一步证实贝伐单抗联合厄洛替尼的疗效与安全性。而与之相反的是,在EGFR非选择性的NSCLC患者中,用贝伐单抗联合TKI挑战一线标准治疗的研究则均以失败告终[23-25]。因此,对于EGFR非选择性的NSCLC患者,化疗联合贝伐单抗目前仍是一线标准治疗方案。
探索其他的靶向联合形式也在进行中,如一项贝伐单抗联合塔格瑞斯的Ⅰ/Ⅱ期临床试验(NCT02803203)和一项贝伐单抗联合艾乐替尼的Ⅰ/Ⅱ期临床试验(cNCT02521051)已经注册并开展。上述研究结果将继续拓展贝伐单抗在晚期NSCLC患者一线治疗的适应证。1.3 贝伐单抗维持治疗
贝伐单抗维持治疗的研究结果尚存在争议。一项Ⅲ期临床研究AVAPERL,将患者经过贝伐单抗联合培美曲塞+顺铂治疗后随机分为贝伐单抗联合培美曲塞组和贝伐单抗单药组。结果显示,双药联合组提高患者的PFS(10.2个月vs.6.6个月),但未提高OS。双药联合组3级以上不良反应高于单药组(37.6%vs.21.7%),但无新的不良反应且均可耐受[26]。Zhang等[27]开展的一项小样本研究却得到相反的结果。将72例患者予以吉西他滨+顺铂治疗随机后分为贝伐单抗联合培美曲塞组和培美曲塞单药组。结果显示双药联合组明显提高患者的OS(14.0个月vs. 11.0个月),未提高PFS。此外,部分回顾性分析或Meta分析同样支持其存在OS获益[28-30]。然而,Ka⁃rayama等[31]开展的一项Ⅱ期随机对照研究,将一线经过贝伐单抗联合培美曲塞+卡铂诱导治疗的患者采用与Zhang等[27]相同的维持分组方式进行分组,结果却显示两组的PFS、OS差异均无统计学意义。
正在开展的Ⅲ期临床试验ECOG 5508(NCT011 07626)或许将解决这一疑问。研究在维持阶段将患者分为贝伐单抗组、培美曲塞组和贝伐单抗联合培美曲塞组3种形式进行对比,而诱导阶段采用一线标准治疗方案贝伐单抗联合紫杉醇+卡铂。总之,贝伐单抗用于维持治疗显示出的部分优势,提示医生在临床工作中需结合患者的诱导方案,选择合适的维持形式延长患者PFS或OS。
2 贝伐单抗用于晚期NSCLC二线及以上治疗
培美曲塞、多西他赛和厄洛替尼等作为晚期NSCLC的二线标准治疗,其疗效存在局限性[32-34]。贝伐单抗的联用是否能提升疗效,已有不少研究进行过探讨(表2)。但目前大多为Ⅱ期或回顾性研究,缺乏Ⅲ期临床研究进一步证实。
2.1 贝伐单抗联合化疗
Adjei等[35]开展的一项将贝伐单抗联合培美曲塞作为晚期NSCLC患者二线治疗的单臂研究中,得到mPFS为4.0个月,mOS为8.6个月,DCR为50%。患者未出现新的不良反应,安全性可耐受。Ding等[36]也得到较为相似的结果。国内的一项贝伐单抗联合多西他赛对比多西他赛单药的二线回顾性对照显示,双药联合组的PFS、OS、ORR、DCR分别为6.3个月、10.6个月、54%、86%,单药组则分别为3.5个月、8.2个月、32%、61%,差异均具有统计学意义[37]。Nishino等[38]进行的一项Ⅱ期随机对照研究,将经过化疗联合或不联合贝伐单抗一线治疗失败的患者随机分配至贝伐单抗联合多西他赛组和贝伐单抗联合替吉奥组,虽然多西他赛组未提高患者的PFS、OS,但亚组分析发现,一线未使用贝伐单抗的患者其PFS明显高于使用过贝伐单抗的患者(7.2个月vs.2.9个月),OS、ORR、DCR同样如此。两组不良反应均可耐受。上述研究表明,在晚期NSCLC患者的二线治疗中,贝伐单抗联合培美曲塞或多西他赛是安全并有效的,特别是在一线未使用过贝伐单抗的患者中。
贝伐单抗联合其他化疗方案也有研究报道。如在二线治疗中采用贝伐单抗联合紫杉醇+卡铂,贝伐单抗联合拓扑替康[39-40],黄诚等[41]观察贝伐单抗联合多种化疗方案用于三线及以上治疗的情况,Habib等[42]则观察贝伐单抗联合周给紫杉醇方案在四线及以上治疗的情况。上述方案均显示出一定疗效和安全性,值得继续深入研究。
2.2 贝伐单抗联合靶向治疗
Herbst等[43]开展的一项Ⅱ期随机对照研究,将经过一线含铂化疗方案失败后的患者随机分配至贝伐单抗联合化疗(多西他赛、培美曲塞)组、贝伐单抗联合厄洛替尼组和单纯化疗组。结果显示,3组的mPFS分别为4.8、4.4和3.0个月,mOS分别为12.6、13.7和8.6个月,但差异均无统计学意义。在该研究的安全性方面,相对于厄洛替尼组,化疗组(贝伐单抗联合化疗及单纯化疗)治疗中断和3级以上不良反应的发生率明显更高。为进一步验证贝伐单抗联合厄洛替尼的疗效与安全,研究小组随后进行一项Ⅲ期临床试验BeTa,在二线治疗中采用贝伐单抗联合厄洛替尼挑战厄洛替尼单药。结果显示,两组的OS仍无差异。虽然联合治疗组的PFS有延长倾向性(3.4个月vs.1.7个月),但鉴于对Ⅰ类错误率的控制,研究组未继续对PFS进行统计学意义的验证[44]。Zhang等[45]则对Herbst等[43-44]的两项研究进行Meta分析,得出贝伐单抗联合厄洛替尼相较厄洛替尼单药延长患者的PFS。综合上述研究结果,在现阶段不推荐晚期NSCLC患者二线治疗中使用贝伐单抗联合厄洛替尼。
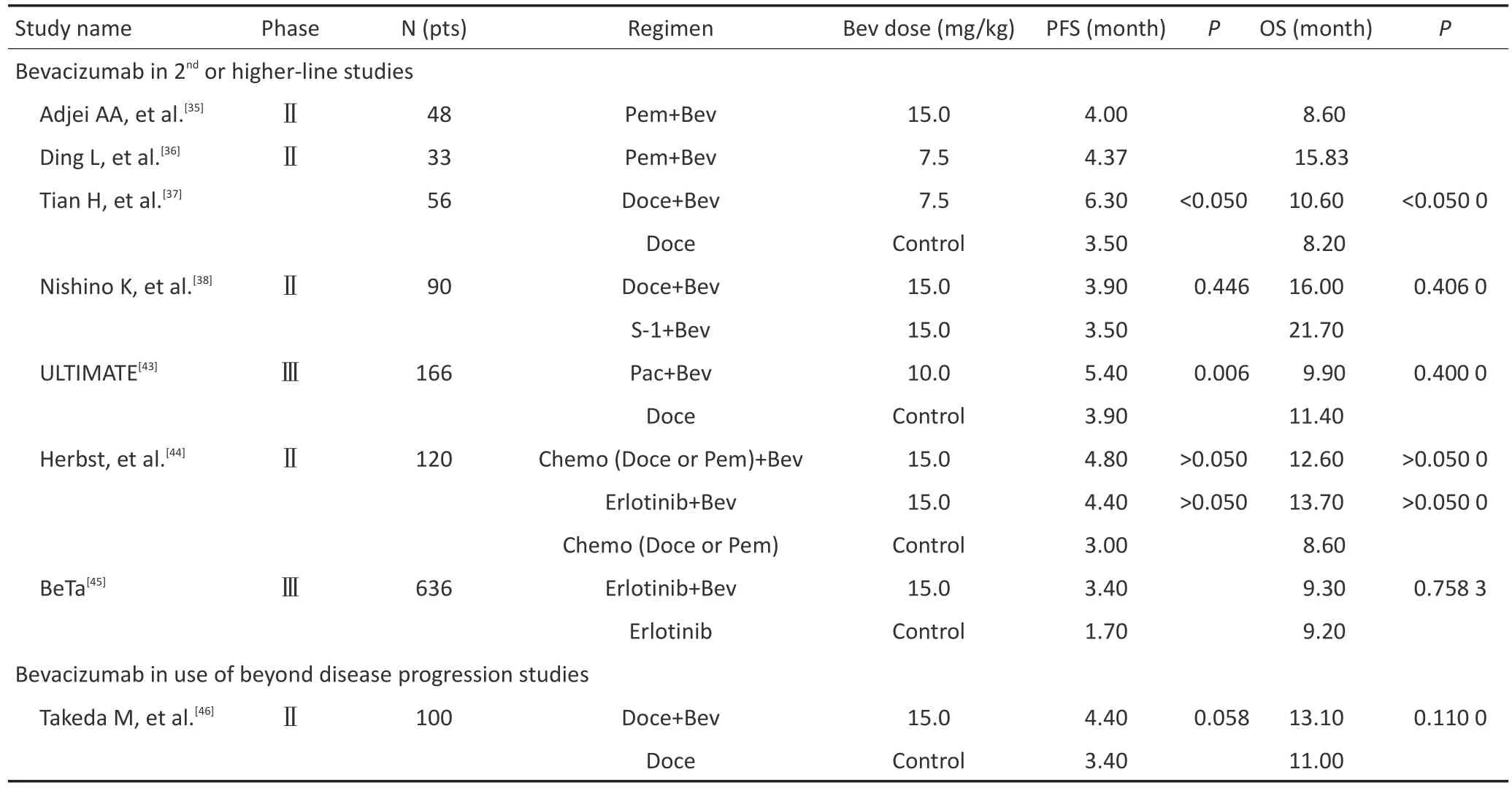
表2 贝伐单抗后线治疗晚期NSCLC的临床研究Table 2 Clinical research of bevacizumab as second-or higher-line treatment of advanced NSCLC
3 贝伐单抗用于晚期NSCLC跨线治疗
近年来,有关贝伐单抗治疗晚期NSCLC的另一项研究热点为贝伐单抗用于跨线治疗是否有效。日本的一项Ⅱ期多中心随机对照研究,将经过一线贝伐单抗联合含铂化疗方案失败的患者随机分配至贝伐单抗联合多西他赛和多西他赛单药组。结果显示,贝伐单抗的继续使用有提高患者的PFS(4.4个月vs.3.4个月)和OS(13.1个月vs.11.0个月)的倾向性,且主要终点PFS的统计学P值达到研究预设值(P<0.2)[46]。为进一步验证其可行性,一项大型Ⅲ期临床研究AvaALL(MO22097;https://clinical trails.gov:NCT01351415)正在开展。研究拟纳入经过一线贝伐单抗联合含铂化疗方案诱导治疗和贝伐单抗维持治疗失败的患者,随机分配至贝伐单抗联合治疗(培美曲塞、多西他赛或厄洛替尼)组和单纯治疗组,同时会对亚洲和非亚洲患者进行亚组分析。该项研究结果将对贝伐单抗能否作为跨线治疗给予直接的答案。
4 小结与展望
贝伐单抗的批准上市是在晚期NSCLC抗血管生成治疗的重大进步。由于其改善肿瘤微血管环境、增强药物通过率的优势,大量研究试图拓展其在NSCLC中的治疗适应证,在探索的过程中存在着肯定与争议。贝伐单抗联合化疗或靶向治疗用于晚期NSCLC一线治疗的疗效与安全得到大部分研究的证实。联合TKI的前期研究和正在开展的Ⅲ期临床试验可能为EGFR突变阳性的晚期NSCLC患者的一线治疗疗效带来新的突破。不足之处在于贝伐单抗的剂量尚无标准及不同的联合方案之间缺乏直接对比。此外,在拓展治疗时机点的探索中,大量关于贝伐单抗用于维持治疗及后线治疗的疗效研究结果并不明确,尤其OS获益存在不确定性。未来关于贝伐单抗用于晚期NSCLC的研究或许会进一步优化剂量和联合方案,以及在后线治疗中开展大样本多中心随机对照试验,包括对跨线治疗疗效与安全性的深入探索。可以预见,随着贝伐单抗适应证的不断扩大与完善,晚期NSCLC患者将有越来越多的治疗选择。而对于临床医生,针对不同的患者群体,把握合适的介入时机并选择适宜的联合方案才能进一步提高患者的整体疗效。
[1]Fitzmaurice C,Dicker D,Pain A,et al.The global burden of cancer 2013[J].JAMA Oncol,2015,1(4):505-527.
[2]Visbal AL,Leighl NB,Feld R,et al.Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Early-Stage Non-small Cell Lung Cancer[J].Chest,2005,128(4):2933-2943.
[3]Bertolini F,Shaked Y,Mancuso P,et al.Tumor angiogenesis[J].N Engl J Med,2008,2008(359):763-764.
[4]Johnson DH,Fehrenbacher L,Novotny W,et al.Randomized phaseⅡ trial comparing bevacizumab plus carboplatin and paclitaxel with carboplatin and paclitaxel alone in previously untreated locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer[J].J Clin Oncol,2004,22(11):2184-2191.
[5]Sandler A,Gray R,Perry MC,et al.Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer[J].N Engl J Med, 2006,355(24):2542-2550.
[6]Zhou C,Wu YL,Chen G,et al.BEYOND:a randomized,doubleblind,placebo-controlled,multicenter,phaseⅢstudy of first-line carboplatin/paclitaxel plus bevacizumab or placebo in Chinese patients with advanced or recurrent nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer[J].J Clin Oncol,2015,33(19):2197-2204.
[7]Reck M,Von PJ,Zatloukal P,et al.PhaseⅢtrial of cisplatin plus gemcitabine with either placebo or bevacizumab as first-line therapy for nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer:AVAil[J].J Clin Oncol,2009,27(8):1227-1234.
[8]Reck M,Von PJ,Zatloukal P,et al.Overall survival with cisplatingemcitabine and bevacizumab or placebo as first-line therapy for nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer:results from a randomised phaseⅢ trial(AVAiL)[J].Ann Oncol,2010,21(9):1804-1809.
[9]Mok TS,Hsia TC,Tsai CM,et al.Efficacy of bevacizumab with cisplatin and gemcitabine in Asian patients with advanced or recurrent non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer who have not received prior chemotherapy:A substudy of the Avastin in Lung trial[J].Asia-Pac J Clin Onco,2011,7(3):4-12.
[10]Scagliotti GV,Parikh P,Von PJ,et al.PhaseⅢstudy comparing cisplatin plus gemcitabine with cisplatin plus pemetrexed in chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer [J].J Clin Oncol,2008,26(21):3543-3551.
[11]Scagliotti G,Hanna N,Fossella F,et al.The differential efficacy of pemetrexed according to NSCLC histology:a review of two PhaseⅢstudies[J].Oncologist,2009,14(3):253-263.
[12]Zinner RG,Obasaju CK,Spigel DR,et al.PRONOUNCE:randomized, open-label,phaseⅢ study of first-line pemetrexed+carboplatin followed by maintenance pemetrexed versus paclitaxel+carboplatin+bevacizumab followed by maintenance bevacizumab in patients with advanced nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer[J].J Thorac Oncol,2015,10(1):134-142.
[13]Nuijten M,Heigener DF,Bischoff HG,et al.Effectiveness of bevacizumab-and pemetrexed-cisplatin treatment for patients with advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer[J].Lung Cancer, 2010,69:S4-10.
[14]Galetta D,Cinieri S,Pisconti S,et al.Cisplatin/pemetrexed followed by maintenance pemetrexed versus carboplatin/paclitaxel/bevacizumab followed by maintenance bevacizumab in advanced nonsquamous lung cancer:the GOIM(gruppo oncologico italia meridionale)ERACLE phaseⅢ randomized trial[J].Clin Lung Cancer, 2015,16(4):262-273.
[15]Chang GC,Ahn MJ,Wright E,et al.Comparative effectiveness of bevacizumab plus cisplatin-based chemotherapy versus pemetrexed plus cisplatin treatment in East Asian non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer patients applying real-life outcomes[J].Asia-Pac J Clin Onco,2011,2:34-40.
[16]Patel JD,Socinski MA,Garon EB,et al.PointBreak:a randomized phaseⅢstudy of pemetrexed plus carboplatin and bevacizumab followed by maintenance pemetrexed and bevacizumab versus paclitaxel plus carboplatin and bevacizumab followed by maintenance bevacizumab in patients with stageⅢB orⅣnonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer[J].J Clin Oncol,2013,31(34):4349-4357.
[17]Kentepozidis N,Kotsakis A,Soultati A,et al.Docetaxel plus cisplatin and bevacizumab for untreated patients with advanced/metastatic non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer:a multicenter phaseⅡstudy of the hellenic oncology research group[J].Cancer Chemoth Pharm,2013,71(3):605-612.
[18]Takiguchi Y,Iwasawa S,Minato K,et al.PhaseⅡstudy of carboplatin,docetaxel and bevacizumab for chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer[J].Int J Clin Oncol,2015,20(4):659-667.
[19]Leon L,Vázquez S,Gracia JM,et al.First-line bevacizumab,cisplatin and vinorelbine plus maintenance bevacizumab in advanced nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer chemo-naïve patients[J].Expert Opin Pharmaco,2012,13(10):1389-1396.
[20]Kaira K,Tomizawa Y,Yoshino R,et al.PhaseⅡstudy of oral S-1 plus cisplatin with bevacizumab for advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer[J].Lung Cancer,2013,82(1):103-108.
[21]Seto T,Kato T,Nishio M,et al.Erlotinib alone or with bevacizumab as first-line therapy in patients with advanced non-squamous nonsmall cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations(JO25567):an open-label,randomised,multicentre,phaseⅡstudy[J].Lancet Oncol,2014,15(11):1236-1244.
[22]Ichihara E,Hotta K,Nogami N,et al.PhaseⅡtrial of gefitinib in combination with bevacizumab as first-line therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer with activating EGFR gene mutations: the okayama lung cancer study group trial 1 001[J].J Thorac Oncol, 2015,10(3):486-491.
[23]Thomas M,Fischer J,Andreas S,et al.Erlotinib and bevacizumab versus cisplatin,gemcitabine and bevacizumab in unselected nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer[J].Eur Respir J,2015,46(1): 219-229.
[24]Ciuleanu T,Tsai CM,Tsao CJ,et al.A phaseⅡstudy of erlotinib in combination with bevacizumab versus chemotherapy plus bevacizumab in the first-line treatment of advanced non-squamous nonsmall cell lung cancer[J].Lung Cancer,2013,82(2):276-281.
[25]Cohen EW,Subramanian J,Gao F,et al.Targeted and cytotoxic therapy in coordinated sequence(TACTICS):erlotinib,bevacizumab,and standard chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer,A PhaseⅡtrial [J].Clin Lung Cancer,2012,13(2):123-128.
[26]Barlesi F,Scherpereel A,Gorbunova V,et al.Maintenance bevacizumab-pemetrexed after first-line cisplatin-pemetrexed-bevacizumab for advanced nonsquamous nonsmall-cell lung cancer:updated survival analysis of the AVAPERL(MO22089)randomized phaseⅢtrial[J].Ann Oncol,2014,25(5):1044-1052.
[27]Zhang YM,Li YQ,Liu ZH,et al.Clinical efficacy of bevacizumab concomitant with pemetrexed in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J].Asian Pac J Cancer Prev,2013,15(8):3447-3450.
[28]Dranitsaris G,Beegle N,Ravelo A,et al.Evaluating the impact of bevacizumab maintenance therapy on overall survival in advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer[J].Clin Lung Cancer,2013,14(2):120-127.
[29]Soria JC,Mauguen A,Reck M,et al.Systematic review and metaanalysis of randomised,phaseⅡ/Ⅲtrials adding bevacizumab to platinum-based chemotherapy as first-line treatment in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J].Ann Oncol,2013,24 (1):20-30.
[30]Kosty MP,Wozniak AJ,Jahanzeb M,et al.Effectiveness and safety of post-induction phase bevacizumab treatment for patients with non-small cell lung cancer:results from the ARIES observational cohort study[J].Target Oncol,2015,10(4):509-516.
[31]Karayama M,Inui N,Fujisawa T,et al.Maintenance therapy with pemetrexed and bevacizumab versus pemetrexed monotherapy after induction therapy with carboplatin,pemetrexed,and bevacizumab in patients with advanced non-squamous non small cell lung cancer[J].Eur J Cancer,2016,58:30-37.
[32]Shepherd FA,Dancey J,Ramlau R,et al.Prospective randomized trial of docetaxel versus best supportive care in patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer previously treated with platinum-based chemotherapy[J].J Clin Oncol,2000,18(10):2095-2103.
[33]Shepherd FA,Rodrigues Pereira J,Ciuleanu T,et al.Erlotinib in previously treated non-small cell lung cancer[J].N Engl J Med,2005,353 (2):123-132.
[34]Hanna N,Shepherd FA,Fossella FV,et al.Randomized phaseⅢtrial of pemetrexed versus docetaxel in patients with non-small cell lung cancer previously treated with chemotherapy[J].J Clin Oncol, 2004,22(9):1589-1597.
[35]Adjei AA,Mandrekar SJ,Dy GK,et al.PhaseⅡtrial of pemetrexed plus bevacizumab for second-line therapy of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer:NCCTG and SWOG study N0426 [J].J Clin Oncol,2010,28(4):614-619.
[36]Ding L,Liu K,Jiang Z,et al.The efficacy and safety of pemetrexed plus bevacizumab in previously treated patients with advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer(ns-NSCLC)[J].Tumor Biol,2015,36(4):2491-2499.
[37]Tian H,Jin E.The efficacy and safety of docetaxel plus bevacizumab versus docetaxel aloneas second-linetreatment for non-small cell lung cancer[J].China Prac Med,2015,10(35):120-121.[田 宏,金 锷.多西他赛联合贝伐珠单抗对比多西他赛单药二线治疗NSCLC的疗效和安全性[J].中国实用医药,2015,10(35):120-121.]
[38]Nishino K,Imamura F,Kumagai T,et al.A randomized phaseⅡstudy of bevacizumab in combination with docetaxel or S-1 in patients with non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer previously treated with platinum based chemotherapy(HANSHIN oncology group 0110)[J].Lung Cancer,2015,89(2):146-153.
[39]Hattori Y,Satouchi M,Shimada T,et al.A phaseⅡstudy of bevacizumab in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel in patients with non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer harboring mutations of epidermal growth factor receptor(EGFR)after failing firstline EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors(HANSHIN oncology group 0109)[J].Lung Cancer,2015,87(2):136-140.
[40]Powell SF,Beitinjaneh A,Tessema M,et al.PhaseⅡstudy of topotecan and bevacizumab in advanced,refractory non-small-cell lung cancer[J].Clin Lung Cancer,2013,14(5):495-501.
[41]Huang C,Zhang J,Ke MY,et al.Clinical observation of combined bevacizumab with chemotherapy in previously treated advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients[J].China Oncol,2012,22(1):47-51. [黄 诚,张 晶,柯明耀,等.贝伐单抗联合化疗治疗晚期多程治疗失败后的非小细胞肺癌临床观察[J].中国癌症杂志,2012,22(1): 47-51.]
[42]Habib S,Delourme J,Dhalluin X,et al.Bevacizumab and weekly paclitaxel for non-squamous non small cell lung cancer patients:a retrospective study[J].Lung Cancer,2013,80(2):197-202.
[43]Herbst RS,O'Neill VJ,Fehrenbacher L,et al.PhaseⅡstudy of efficacy and safety of bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy or erlotinib compared with chemotherapy alone for treatment of recurrent or refractory non-small cell lung cancer[J].J Clin Oncol, 2007,25(30):4743-4750.
[44]Herbst RS,Ansari R,Bustin F,et al.Efficacy of bevacizumab plus erlotinib versus erlotinib alone in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of standard first-line chemotherapy(BeTa):a double-blind,placebo-controlled,phaseⅢtrial[J].Lancet,2011,377 (9780):1846-1854.
[45]Zhang S,Mao X,Wang H,et al.Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab plus erlotinib versus bevacizumab or erlotinib alone in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer:a systematic review and metaanalysis[J].BMJ Open,2016,6(6):e011714.
[46]Takeda M,Yamanaka T,Seto T,et al.Bevacizumab beyond disease progression after first‐line treatment with bevacizumab plus chemotherapy in advanced nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer (west Japan oncology group 5910L):An open‐label,randomized, phaseⅡtrial[J].Cancer,2016,122(7):1050-1059.
(2016-10-13收稿)
(2017-01-03修回)
(编辑:杨红欣 校对:孙喜佳)
Clinical research progress on the efficacy and safety of bevacizumab in treating advanced non-small cell lung cancer
Binbin HU1,Baoqing CHEN1,You LU2
Correspondence to:You LU;E-mail:radyoulu@hotmail.com
1West China School of Medicine,Sichuan University,Chengdu 610041,China;2Department of Thoracic Oncology,West China Hospital, Sichuan University,Chengdu 610041,China
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No.81472196)
Antiangiogenesis therapy is one of the most common anticancer therapies.Bevacizumab is a monoclonal antibody that blocks the binding of the vascular endothelial growth factor to its high-affinity receptors.It is the only antiangiogenic agent approved for the first-line treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer(NSCLC).Many recent studies have attempted to determine the suitable partners of bevacizumab in first-line treatment of NSCLC and evaluate its efficacy and safety as a second-line or beyond and continuous treatment of beyond disease progression in patients with advanced NSCLC.This review summarizes current clinical research about the efficacy and safety of bevacizumab in the treatment of advanced NSCLC.
non-small cell lung cancer,bevacizumab,chemotherapy,target therapy,maintenance therapy,safety

10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.2017.03.191
①四川大学华西临床医学院(成都市610041);②四川大学华西医院胸部肿瘤科
*本文课题受国家自然科学基金项目(编号:81472196)资助
卢铀 radyoulu@hotmail.com
胡彬彬 专业方向为肺癌的化疗与抗血管生成治疗。
E-mail:dr.binbin.hu@outlook.com
