赛妥珠单抗治疗类风湿性关节炎疗效及不良反应的荟萃分析
2017-02-27唐玥璐尹园园
唐玥璐 白 浩 尹园园
(重庆市肿瘤研究所/医院/癌症中心,沙坪坝400030)
赛妥珠单抗治疗类风湿性关节炎疗效及不良反应的荟萃分析
唐玥璐 白 浩 尹园园①
(重庆市肿瘤研究所/医院/癌症中心,沙坪坝400030)
目的:探究赛妥珠单抗治疗类风湿性关节炎的有效性及安全性。方法:计算机检索Pubmed、Medline、Embase、The Cochrane Library、万方数据库(WANFANG)、中国期刊全文数据库(CNKI)、中国生物医学文献数据库中关于赛妥珠单抗与安慰剂治疗类风湿性关节炎的随机对照研究(Randomized controlled trials,RCTs),检索时限均为建库至2015年3月。采用RevMan5.3软件进行统计分析。结果:共纳入10篇文献、8项研究,纳入文献质量均较高,本meta分析结果显示CZP在改善类风湿患者病情的疗效(ACR20、ACR50、ACR70),关节疾病活动性评分,患者对疾病活动性评价指标(HAQ-DI、关节疼痛、疲劳)方面优于安慰剂组。在轻度、中度、重度不良反应方面两组差异无统计学意义,CZP并未增加不良反应的发生率。结论:CZP能减缓患者关节炎症进展,改善患者关节功能,提高患者生活质量,短期安全性较高,CZP长期疗效及安全性有待于进一步研究证实。
类风湿,关节炎;赛妥珠;安慰剂;meta分析
类风湿性关节炎(Rheumatoid arthritis,RA)是一种病因不明的、以关节滑膜炎为特征的自身免疫性疾病,其发病率约为0.3%~0.4%,多见于30~50岁的女性[1]。传统的改善病情抗风湿药(Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs,DMARDs)虽能有效缓解滑膜炎症进展,但仍不能控制部分RA患者病情进展。肿瘤坏死因子α(Tumor nocrosis factor,TNF-α)抑制剂对控制DMARDs治疗效果不佳的RA患者病情及改善预后有重要作用[2]。目前应用的比较广泛的TNF-α抑制剂主要为依那西普(Etanercept)、英夫利昔单抗(Infliximab)、阿达木单抗(Adalimumab),临床上已证实此3种TNF-α抑制剂能有效减轻RA患者关节炎症,改善关节功能及延缓病情进展[3]。赛妥珠单抗(Certolizumab pegol,CZP)作为一种新型TNF-α抑制剂由聚乙二醇与人源单价体Fab抗体共价结合而形成,其不含Fc片段,不能引起抗体依赖细胞介导的细胞毒作用[4]。CZP多联合甲氨蝶呤(Methotrexate,MTX)治疗RA患者,对于不能耐受DMARDs的患者,则单用CZP治疗。目前临床上已有很多研究对CZP在RA中的有效性和安全性作了评估,本研究拟用meta分析的方法综合目前发表的研究成果,评估CZP治疗RA的有效性和安全性,为DMARDs治疗无效的RA患者的临床治疗提供指导。
1 资料与方法
1.1 纳入和排除标准 (1)研究类型:随机对照研究;(2)纳入对象:18岁以上被确诊为RA的患者;(3)干预措施:CZP联合或不联合MTX与安慰剂治疗RA;(4)评价治疗:美国风湿病学会(ACR)制定的RA缓解标准,ACR20(疗效缓解20%),ACR50,ACR70,以红细胞沉降率(ESR)为基础的28 个关节疾病活动性评分(DAS-28),健康评估问卷功能障碍指数(HAQ-DI),关节疼痛,疲劳评定,不良反应等,对不满足以上标准的研究予以排除。
1.2 检索策略 计算机检索Pubmed、Embase、The Cochrane Library、Medline、万方数据库(WANFA-NG)、中国生物医学文献数据库、中国期刊全文数据库(CNKI)中关于CZP治疗RA的随机对照研究(RCT),检索时限均为建库至2015年3月,检索中文检索词为“赛妥珠”、“类风湿”,英文检索词为“Certolizumab pegol OR CZP”,“rheumatoid arthritis OR RA”,检索语言限定为英文和中文。
1.3 文献筛选及质量评价 由两名研究者独立按纳入和排除标准对文献进行筛选,如遇分歧则通过讨论解决或第三者决定,缺失的资料通过联系研究的作者加以完善。纳入的所有RCT研究采用Jadad评分量表进行文献质量评价,标准包括:(1)随机序列的产生;(2)随机化隐藏;(3)盲法的实施;(4)撤出及退出的理由等4个方面。大于3分则认为是高质量文献。
1.4 数据提取及统计分析 提取纳入文献的一般信息如作者、发表时间,纳入对象的基线资料如性别、年龄、干预措施,统计指标如ACR20、不良反应等数据。应用Cochrane协作网提供的RevMan5.3软件进行统计分析,计量资料如DAS-28(ESR)评分采用加权均数差(WMD)及其95%置信区间(CI)进行评估,计数资料如ACR20、ACR50、ACR70等采用风险比(RR)及其95%置信区间(CI)进行评估。研究间的异质性采用χ2检验(以P= 0.1为异质性阈值)和I2检验(以I2=50%为异质性阈值),若各研究存在异质性,采用随机效应模型,并对其异质性来源进行分析,反之则采用固定效应模型。纳入研究数据信息不全时,本研究只作描述性分析。
2 结果
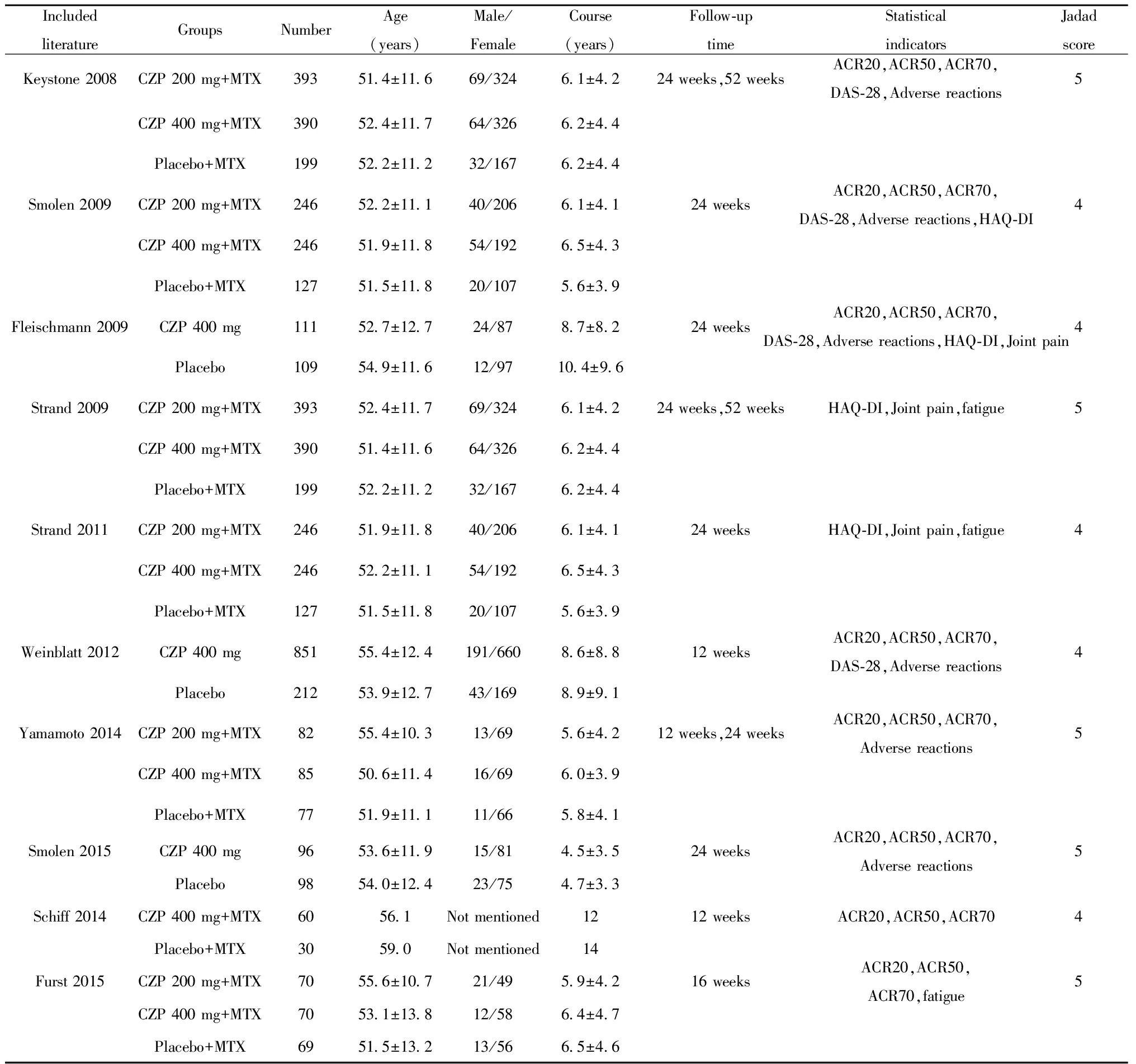
2.1 检索结果 初步检索有关英文文献250篇,未检索到相关中文文献,经全面筛查后最终纳入10篇文献[5-14],8项研究,其中Strand等[10]和Smolen等[11]为同一研究,Strand等[13]和Keystone等[14]为同一研究,因以上文献采用的结局指标不同,故4篇文献均可纳入。共纳入3 621名RA患者,除4篇文献外[5,8,9,12],其余均采用200 mg和400 mg不同剂量的CZP治疗RA患者,3篇文献[5,9,12]单用CZP未联合MTX治疗RA患者,纳入文献均属高质量文献,纳入文献基本特征见表1。
2.2 meta分析结果
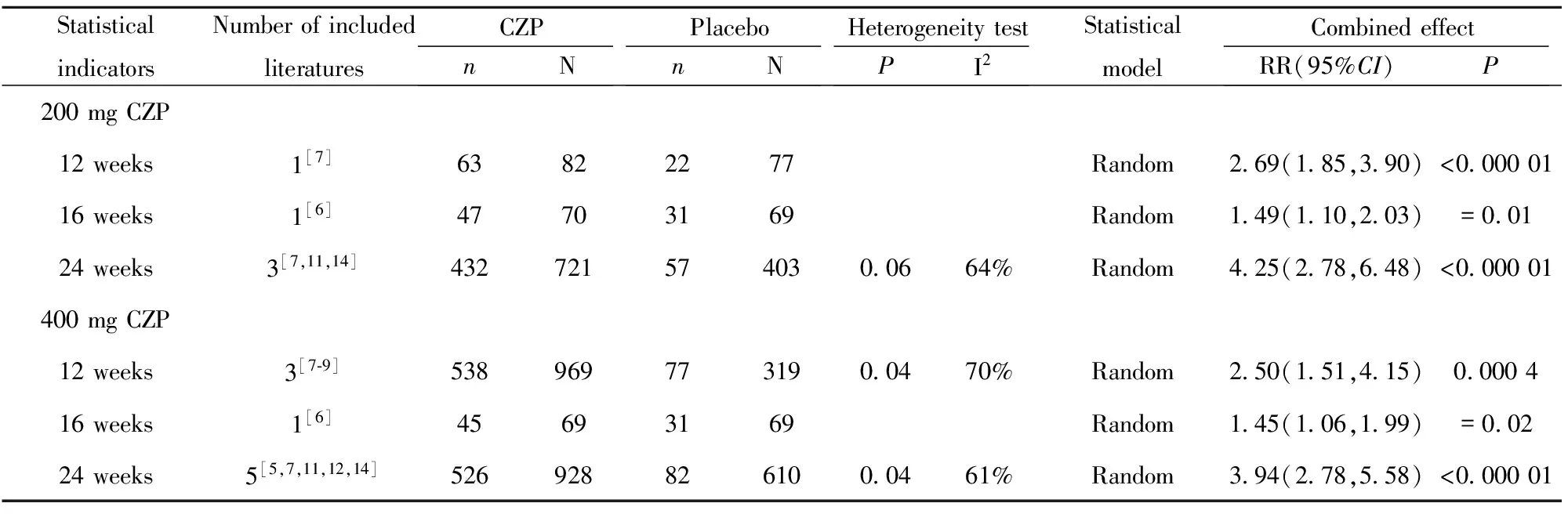
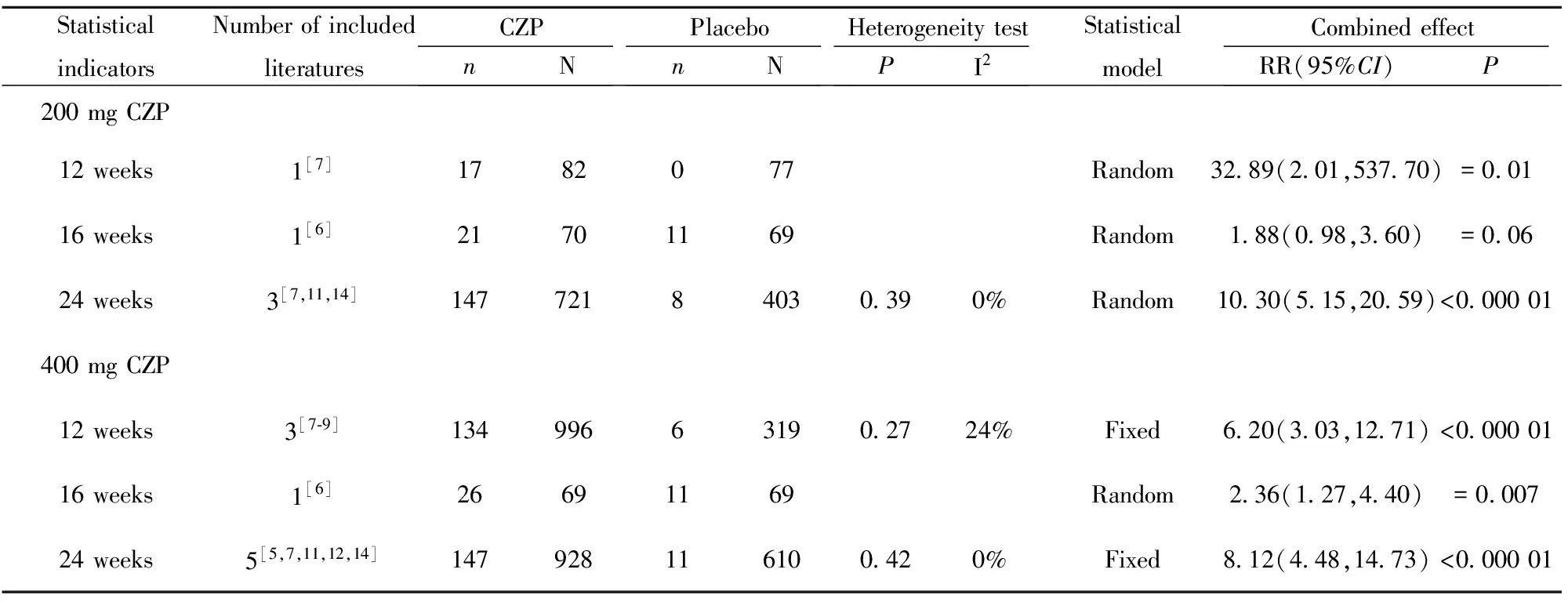
2.2.1 疗效评估 200 mg CZP、400 mg CZP与安慰剂相比,12、16、24周在ACR20方面差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05),详见表2;12、16、24周在ACR50方面差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05),详见表3;除1篇文献外[6],其余文献均显示200 mg CZP、400 mg CZP与安慰剂相比,12周、24周在ACR70方面差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05),详见表4。
2.2.2 DAS-28(ESR)与基线资料变化评估 200 mg CZP、400 mg CZP与安慰剂相比,12、16、24、52周在DAS-28(ESR)变化值方面差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05),详见表5。
2.2.3 患者对疾病活动性评价指标 200 mg CZP、400 mg CZP与安慰剂相比,24、52周在RA患者HAQ-DI改善达到最小临床意义变化值(MCIDs)的患者数量方面差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05),详见表6。除Furst等[6]研究外,其余文献均显示200 mg CZP、400 mg CZP与安慰剂相比, 24、52周在RA患者关节疼痛改善达到最小临床意义变化值(MCIDs)的患者数量方面差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05),详见表7。除Furst等[6]研究外,其余文献均显示200 mg CZP、400 mg CZP与安慰剂相比, 24、52周在RA患者疲劳改善达到最小临床意义变化值(MCIDs)的患者数量方面差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05),详见表8。
2.2.4 安全性评价 200 mg CZP、400 mg CZP与安慰剂在轻度、中度及重度不良反应发生率方面差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05),详见表9。
表1 纳入文献基本特征
Tab.1 Basic characteristics of included literature
IncludedliteratureGroupsNumberAge(years)Male/FemaleCourse(years)Follow⁃uptimeStatisticalindicatorsJadadscoreKeystone2008CZP200mg+MTX393514±11669/32461±4224weeks,52weeksACR20,ACR50,ACR70,DAS⁃28,Adversereactions5CZP400mg+MTX390524±11764/32662±44Placebo+MTX199522±11232/16762±44Smolen2009CZP200mg+MTX246522±11140/20661±4124weeksACR20,ACR50,ACR70,DAS⁃28,Adversereactions,HAQ⁃DI4CZP400mg+MTX246519±11854/19265±43Placebo+MTX127515±11820/10756±39Fleischmann2009CZP400mg111527±12724/8787±8224weeksACR20,ACR50,ACR70,DAS⁃28,Adversereactions,HAQ⁃DI,Jointpain4Placebo109549±11612/97104±96Strand2009CZP200mg+MTX393524±11769/32461±4224weeks,52weeksHAQ⁃DI,Jointpain,fatigue5CZP400mg+MTX390514±11664/32662±44Placebo+MTX199522±11232/16762±44Strand2011CZP200mg+MTX246519±11840/20661±4124weeksHAQ⁃DI,Jointpain,fatigue4CZP400mg+MTX246522±11154/19265±43Placebo+MTX127515±11820/10756±39Weinblatt2012CZP400mg851554±124191/66086±8812weeksACR20,ACR50,ACR70,DAS⁃28,Adversereactions4Placebo212539±12743/16989±91Yamamoto2014CZP200mg+MTX82554±10313/6956±4212weeks,24weeksACR20,ACR50,ACR70,Adversereactions5CZP400mg+MTX85506±11416/6960±39Placebo+MTX77519±11111/6658±41Smolen2015CZP400mg96536±11915/8145±3524weeksACR20,ACR50,ACR70,Adversereactions5Placebo98540±12423/7547±33Schiff2014CZP400mg+MTX60561Notmentioned1212weeksACR20,ACR50,ACR704Placebo+MTX30590Notmentioned14Furst2015CZP200mg+MTX70556±10721/4959±4216weeksACR20,ACR50,ACR70,fatigue5CZP400mg+MTX70531±13812/5864±47Placebo+MTX69515±13213/5665±46
表2 类风湿性关节炎患者ACR20系统评价结果
Tab.2 Systematic review of ACR20 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
StatisticalindicatorsNumberofincludedliteraturesCZPnNPlacebonNHeterogeneitytestPI2StatisticalmodelCombinedeffectRR(95%CI)P200mgCZP12weeks1[7]63822277Random269(185,390)<00000116weeks1[6]47703169Random149(110,203)=00124weeks3[7,11,14]4327215740300664%Random425(278,648)<000001400mgCZP12weeks3[7⁃9]5389697731900470%Random250(151,415)0000416weeks1[6]45693169Random145(106,199)=00224weeks5[5,7,11,12,14]5269288261000461%Random394(278,558)<000001
表3 类风湿性关节炎患者ACR50系统评价结果
Tab.3 Systematic review of ACR50 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis

StatisticalindicatorsNumberofincludedliteraturesCZPnNPlacebonNHeterogeneitytestPI2StatisticalmodelCombinedeffectRR(95%CI)P200mgCZP12weeks1[7]3482677Random532(237,1196)<0000116weeks1[6]35702169Random164(107,252)=00224weeks3[7,11,14]2717213240300958%Random491(279,861)<000001400mgCZP12weeks3[7⁃9]2819692731900958%Random425(191,945)0000416weeks1[6]36692169Random171(112,261)=00124weeks5[5,7,11,12,14]3439285161000363%Random436(269,709)<000001
表4 类风湿性关节炎患者ACR70系统评价结果
Tab.4 Systematic review of ACR70 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
StatisticalindicatorsNumberofincludedliteraturesCZPnNPlacebonNHeterogeneitytestPI2StatisticalmodelCombinedeffectRR(95%CI)P200mgCZP12weeks1[7]1782077Random3289(201,53770)=00116weeks1[6]21701169Random188(098,360)=00624weeks3[7,11,14]14772184030390%Random1030(515,2059)<000001400mgCZP12weeks3[7⁃9]134996631902724%Fixed620(303,1271)<00000116weeks1[6]26691169Random236(127,440)=000724weeks5[5,7,11,12,14]147928116100420%Fixed812(448,1473)<000001
表5 类风湿关节炎患者DAS-28(ESR)变化值系统评价结果
Tab.5 Systematic review of DAS-28(ESR) changein patients with rheumatoid arthritis

StatisticalindicatorsNumberofincludedliteraturesCZPNPlaceboNHeterogeneitytestPI2StatisticalmodelCombinedeffectMD(95%CI)P200mgCZP16weeks1[6]7069Random-088(-134,-042)=0000224weeks1[11]246127Random-177(-202,-152)<00000152weeks1[14]393199Random-090(-112,-068)<000001400mgCZP12weeks1[9]851212Random-094(-150,-038)=000116weeks1[6]6969Random-112(-158,-066)<00000124weeks2[11,12]3572360000492%Random-146(-249,-042)=000652weeks1[14]390199Random-100(-123,-077)<000001
表6 类风湿关节炎患者HAQ-DI系统评价结果
Tab.6 Systematic review of HAQ-DI in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
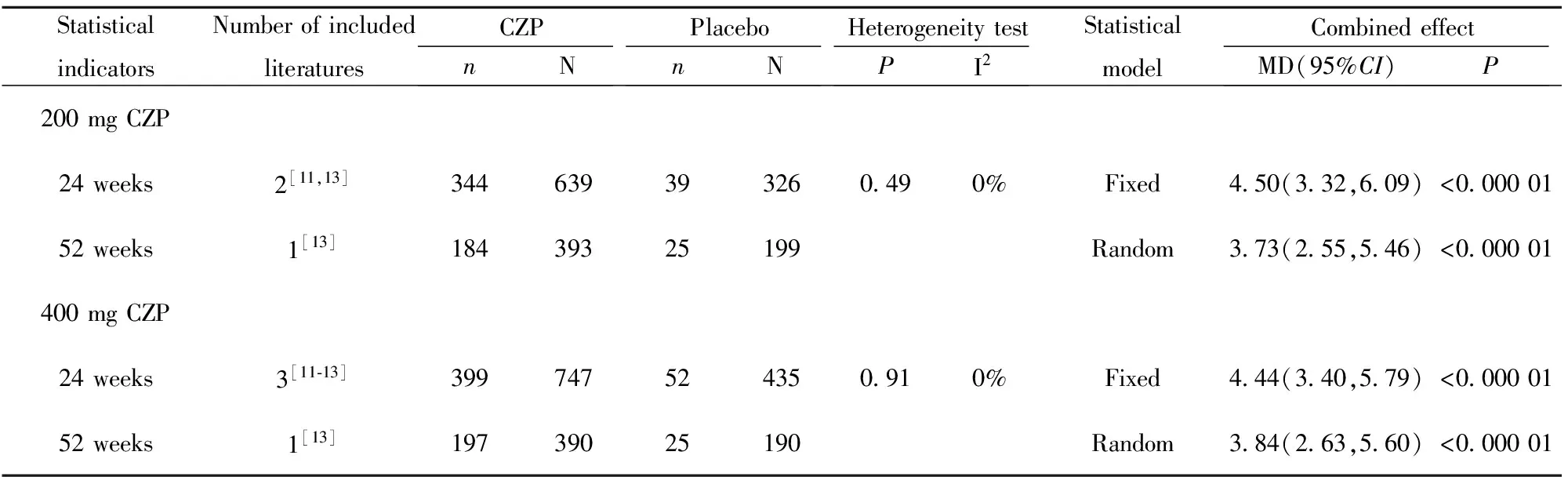
StatisticalindicatorsNumberofincludedliteraturesCZPnNPlacebonNHeterogeneitytestPI2StatisticalmodelCombinedeffectMD(95%CI)P200mgCZP24weeks2[11,13]344639393260490%Fixed450(332,609)<00000152weeks1[13]18439325199Random373(255,546)<000001400mgCZP24weeks3[11⁃13]399747524350910%Fixed444(340,579)<00000152weeks1[13]19739025190Random384(263,560)<000001
表7 类风湿关节炎患者关节疼痛评价
Tab.7 Systematic review of joint pain in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
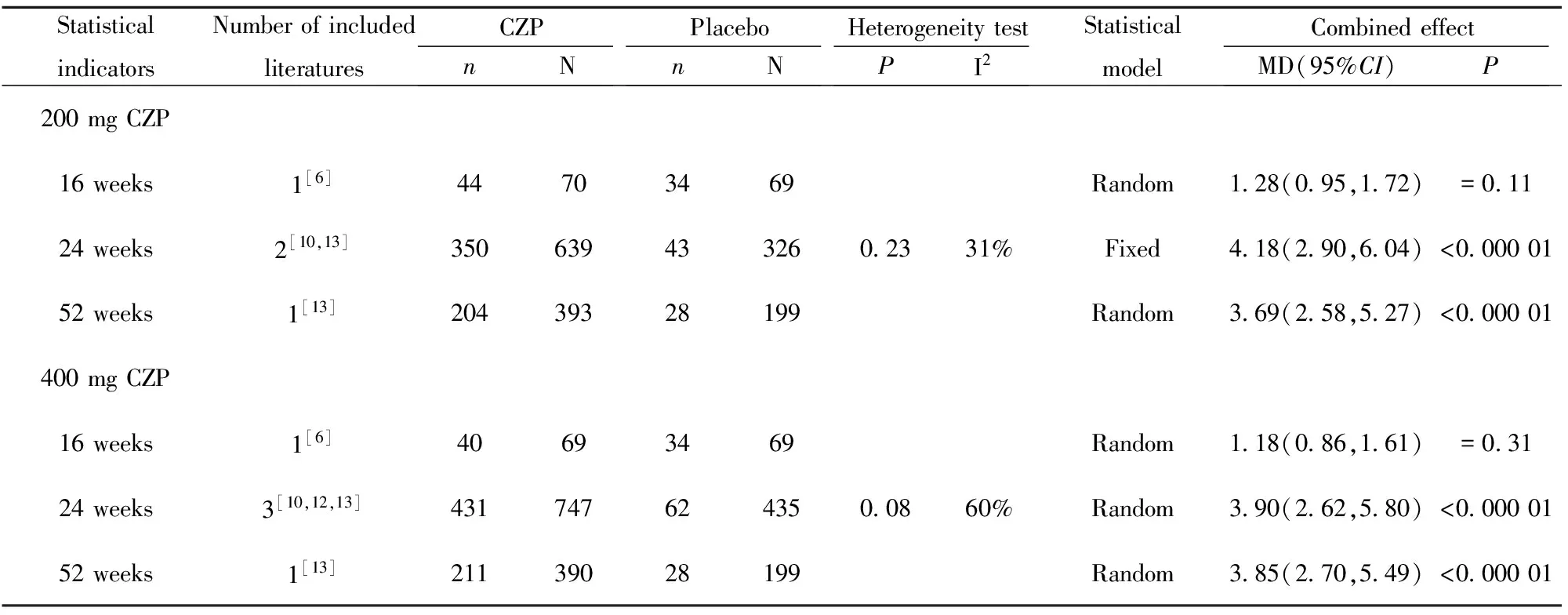
StatisticalindicatorsNumberofincludedliteraturesCZPnNPlacebonNHeterogeneitytestPI2StatisticalmodelCombinedeffectMD(95%CI)P200mgCZP16weeks1[6]44703469Random128(095,172)=01124weeks2[10,13]3506394332602331%Fixed418(290,604)<00000152weeks1[13]20439328199Random369(258,527)<000001400mgCZP16weeks1[6]40693469Random118(086,161)=03124weeks3[10,12,13]4317476243500860%Random390(262,580)<00000152weeks1[13]21139028199Random385(270,549)<000001
表8 类风湿关节炎患者疲劳评定系统评价
Tab.8 Systematic review of fatigue in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
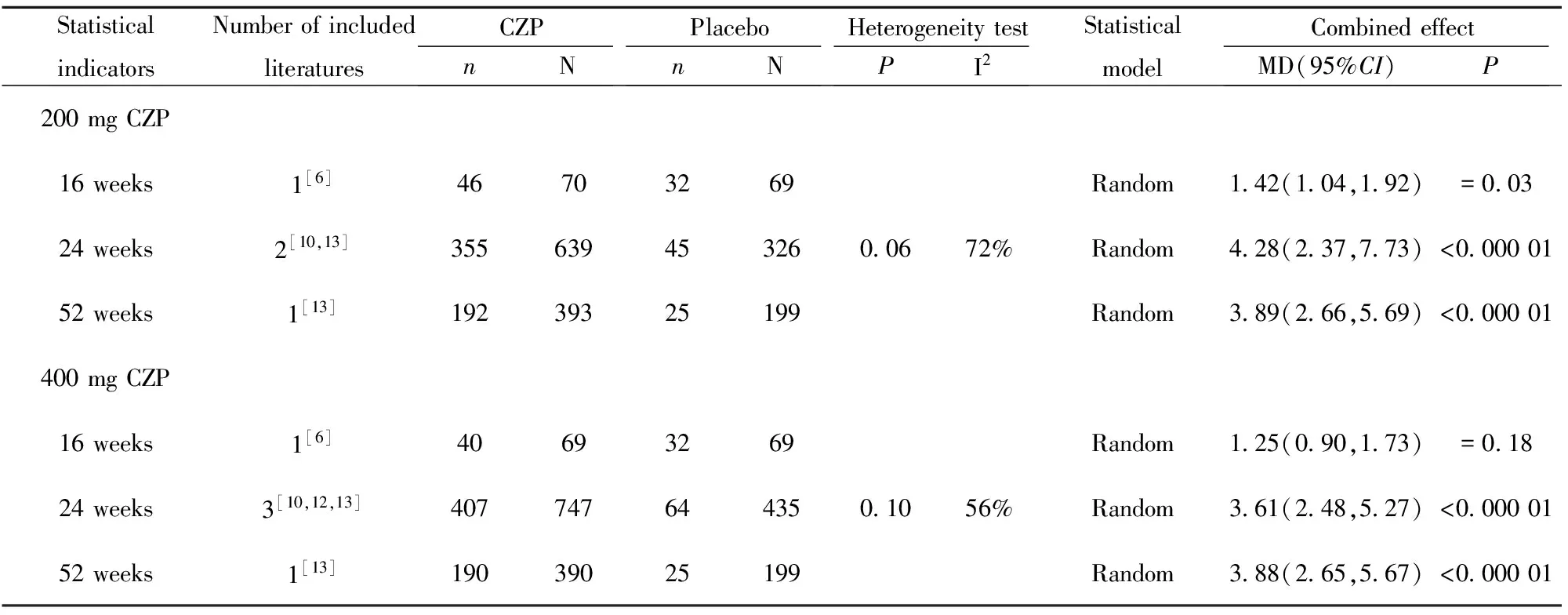
StatisticalindicatorsNumberofincludedliteraturesCZPnNPlacebonNHeterogeneitytestPI2StatisticalmodelCombinedeffectMD(95%CI)P200mgCZP16weeks1[6]46703269Random142(104,192)=00324weeks2[10,13]3556394532600672%Random428(237,773)<00000152weeks1[13]19239325199Random389(266,569)<000001400mgCZP16weeks1[6]40693269Random125(090,173)=01824weeks3[10,12,13]4077476443501056%Random361(248,527)<00000152weeks1[13]19039025199Random388(265,567)<000001
表9 类风湿关节炎患者不良反应系统评价
Tab.9 Systematic review of adverse reactions in patients with rheumatoid arthritis

StatisticalindicatorsNumberofincludedliteraturesCZPnNPlacebonNHeterogeneitytestPI2StatisticalmodelCombinedeffectMD(95%CI)P200mgCZPMildadversereactions3[7,11,14]229722172401<00000196%Random087(039,195)=074200mgCZPModerateadverseeffects3[7,11,14]1387221214010000686%Random068(037,125)=021200mgCZPSevereadversereactions4[6,7,11,14]347922047000270%Random129(035,482)=070400mgCZPMildadversereactions5[7,9,11,12,14]5271677270719<00000192%Random094(060,148)=080400mgCZPModerateadverseeffects5[7,9,11,12,14]4571677225719<00000190%Random089(056,142)=064400mgCZPSevereadversereactions6[6,7,9,11,12,14]10617464678801637%Fixed093(056,155)=079
3 讨论
TNF-α是一种重要的免疫调节细胞因子,RA患者关节腔中的高水平TNF-α在关节滑膜炎性病变及软骨基质降解中有重要作用,研究发现滑膜液中异常高水平的TNF-α在RA的发病中可能起主导作用[15]。赛妥珠单抗是一种新型TNF-α抑制剂,临床已广泛应用于治疗克罗恩病(CD)[16]。本meta分析结果显示200 mg CZP和400 mg CZP在改善类风湿患者病情的疗效(ACR20、ACR50、ACR70),关节疾病活动性评分,患者对疾病活动性评价指标(HAQ-DI、关节疼痛、疲劳)方面优于安慰剂组。在轻度、中度、重度不良反应方面两者差异无统计学意义,CZP并未增加不良反应的发生率。
已有meta分析[17]显示依那西普、英夫利昔单抗、阿达木单抗治疗RA的临床效应,此三类TNF-α抑制剂均含有Fc片段,而CZP为不含Fc片段的TNF-α抑制剂,CZP对RA患者的治疗效应说明了Fc片段可能不是TNF-α抑制剂治疗RA的必要组成部分。在12、24周时,CZP组患者疗效评价指标ACR20、ACR50、ACR70均优于安慰剂组,200 mg CZP组和400 mg CZP组DAS-28(ESR)变化值、病人对活动性评价指标均优于安慰剂组,这均说明了CZP能有效缓解类风湿患者关节炎症进展,减轻患者症状,改善关节功能,提高患者的生活质量。Furst等[6]研究发现在16周时CZP组与安慰剂组RA患者ACR70、疼痛及疲劳评价结果差异均无统计学意义。这主要因为其研究纳入的对象在分组前均有16周的CZP药物服用史,故其CZP的治疗效果不如其他文献报道的明显。本研究显示CZP组和安慰剂组在短期不良反应发生率上差异无统计学意义,这说明了CZP短期安全性较高。Bykerk等[18]对采用CZP治疗的4049例RA患者进行了7.6年的随访调查,发现CZP长期不良反应发生率与安慰剂组差异无统计学意义。CZP长期的安全性有待于更多的、更长随访时间的研究加以验证。
然而本meta分析仍有一定的局限性:(1)纳入研究间异质性较高,会对meta分析的结果产生影响,经分析异质性主要来源于CZP剂量的不同,随访时间不同,是否联合使用MTX等;(2)纳入研究随访时间较短,最长随访时间为52周,CZP长期的疗效和安全性有待于进一步研究;(3)部分结局指标由于数据不足无法进行meta分析,如简化疾病活动指数(SADI)等。
综上所述,本meta分析结果显示CZP单用或联合应用MTX可以作为治疗类风湿性关节炎的方式之一,具有较高的有效性和安全性。鉴于本meta的局限性,建议进一步开展高质量、长时间随访的随机对照研究,加强对CZP长期疗效和安全性的评估,为RA的临床治疗提供指导。
[1] 乔丽君,汪 悦,陈华尧,等.金雀根对类风湿性关节炎动物模型抗炎作用的研究[J].中成药,2009,31(10):1508-1511.
[2] Goldring SR.Pathogenesis of bone and cartilage destruction in rheumatoid arthritis[J].Rheumatology (Oxford),2003,42(Suppl 2):i11-i16.
[3] Liu Y,Fan W,Chen H,etal.Risk of breast cancer and total malignancies in rheumatoid arthritis patients undergoing TNF-alpha antagonist therapy:a meta-analysis of randomized control trials[J].Asian Pac J Cancer Prev,2014,15(8):3403-3410.
[4] Nesbitt A,Fossati G,Bergin M,etal.Mechanism of action of certolizumab pegol (CDP870):in vitro comparison with other anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha agents[J].Inflamm Bowel Dis,2007,13(11):1323-1332.
[5] Smolen JS,Emery P,Ferraccioli GF,etal.Certolizumab pegol in rheumatoid arthritis patients with low to moderate activity:the CERTAIN double-blind,randomised,placebo-controlled trial[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2015,74(5):843-850.
[6] Furst DE,Shaikh SA,Greenwald M,etal.Two dosing regimens of certolizumab pegol in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis[J].Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken),2015,67(2):151-160.
[7] Yamamoto K,Takeuchi T,Yamanaka H,etal.Efficacy and safety of certolizumab pegol plus methotrexate in Japanese rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to methotrexate:the J-RAPID randomized,placebo-controlled trial[J].Mod Rheumatol,2014,24(5):715-724.
[8] Schiff MH,von Kempis J,Goldblum R,etal.Rheumatoid arthritis secondary non-responders to TNF can attain an efficacious and safe response by switching to certolizumab pegol:a phase IV,randomised,multicentre,double-blind,12-week study,followed by a 12-week open-label phase[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2014,73(12):2174-2177.
[9] Weinblatt ME,Fleischmann R,Huizinga TW,etal.Efficacy and safety of certolizumab pegol in a broad population of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis:results from the REALISTIC phase IIIb study[J].Rheumatology (Oxford),2012,51(12):2204-2214.
[10] Strand V,Smolen JS,van Vollenhoven RF,etal.Certolizumab pegol plus methotrexate provides broad relief from the burden of rheumatoid arthritis:analysis of patient-reported outcomes from the RAPID 2 trial[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2011,70(6):996-1002.
[11] Smolen J,Landewe RB,Mease P,etal.Efficacy and safety of certolizumab pegol plus methotrexate in active rheumatoid arthritis:the RAPID 2 study.A randomised controlled trial[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2009,68(6):797-804.
[12] Fleischmann R,Vencovsky J,van Vollenhoven RF,etal.Efficacy and safety of certolizumab pegol monotherapy every 4 weeks in patients with rheumatoid arthritis failing previous disease-modifying antirheumatic therapy:the FAST4WARD study[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2009,68(6):805-811.
[13] Strand V,Mease P,Burmester GR,etal.Rapid and sustained improvements in health-related quality of life,fatigue,and other patient-reported outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with certolizumab pegol plus methotrexate over 1 year:results from the RAPID 1 randomized controlled trial[J].Arthritis Res Ther,2009,11(6):R170.
[14] Keystone E,Heijde D,Mason DJ,etal.Certolizumab pegol plus methotrexate is significantly more effective than placebo plus methotrexate in active rheumatoid arthritis:findings of a fifty-two-week,phase III,multicenter,randomized,double-blind,placebo-controlled,parallel-group study[J].Arthritis Rheum,2008,58(11):3319-3329.
[15] Ohta S,Harigai M,Tanaka M,etal.Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) converting enzyme contributes to production of TNF-alpha in synovial tissues from patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J].J Rheumatol,2001,28(8):1756-1763.
[16] 周 军,张红杰.赛妥珠单抗治疗克罗恩病的临床研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2013,7(24):11717-11720.
[17] Launois R,Avouac B,Berenbaum F,etal.Comparison of certolizumab pegol with other anticytokine agents for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis:a multiple-treatment Bayesian meta analysis[J].J Rheumatol,2011,38(5):835-845.
[18] Bykerk VP,Cush J,Winthrop K,etal.Update on the safety profile of certolizumab pegol in rheumatoid arthritis:an integrated analysis from clinical trials[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2015,74(1):96-103.
[收稿2016-07-24 修回2016-10-10]
(编辑 张晓舟)
欢迎订阅和投稿《中国免疫学杂志》
Efficacy and safety of Certolizumab pegol in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis:a meta-analysis
TANGYue-Lu,BAIHao,YINYuan-Yuan.
ChongqingCancerInstitute&Hospital&CancerCenter,Shapingba400300,China
Objective:To explore the efficacy and safety of Certolizumab pegol in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Methods: Such databases as Pubmed,Medline,Embase,The Cochrane Library,WANFANG,CNKI,Science,CBM and VIP were searched from their establishment to March 2015 for collecting the randomized controlled trials comparing Certolizumab pegol and placebo in the treatment of RA.The meta-analysis was undertaken using RevMan5.3 for Windows.Results: Ten publications and eight researches met the inclusion criteria with high quality.The results revealed CZP significantly improved the ACR20,ACR50,ACR70 response rates,and physical function.CZP was associated with a statistically significant reduction in Disease Activity Score in 28 joints-Erythrocyte sedimentation rate,arthritis pain,and fatigue.There were no significant differences of incidence of treatment-related adverse events between CZP group and placebo group.Conclusion: CZP significantly reduced the RA signs and symptoms,improved physical function and life quality as compared with the placebo in the treatment of RA.More large-scale RCTs are needed to evaluate the long-term efficacy and safety of CZP in the treatment of RA.
Rheumatoid,Arthritis;Certolizumab pegol;Placebo;meta-analysis
10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2017.02.013
唐玥璐(1988年-),女,药师,主要从事免疫抑制剂在肿瘤及自身免疫性疾病中的应用研究。
R979.5
A
1000-484X(2017)02-0226-07
①通讯作者,E-mail:775059475@qq.com。