血管性痴呆患者血清Hcy hs-CRP与D-二聚体临床研究
2017-01-17袁丽品马建军徐长水
袁丽品 冯 艳 李 学 马建军 徐长水 李 燕
河南省人民医院神经内科 郑州 450003
血管性痴呆患者血清Hcy hs-CRP与D-二聚体临床研究
袁丽品 冯 艳*李 学 马建军 徐长水 李 燕
河南省人民医院神经内科 郑州 450003
目的 研究血管性痴呆(VaD)患者痴呆程度与血清同型半胱氨酸(Hcy)、高敏C反应蛋白(hs-CRP)和D-二聚体相关性,探讨Hcy、hs-CRP和D-二聚体在血管性痴呆中的作用机制。方法 实验分为2组,正常对照组和血管性痴呆组,用散射比浊法检测每份样本中C反应蛋白及D-二聚体含量,采用荧光标记免疫检测法检测血清Hcy水平。结果 与正常对照组相比,血管性痴呆组Hcy、hs-CRP、D-二聚体浓度显著增高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。直线相关分析结果提示,Hs-CRP、Hcy与MMSE评分之间呈负相关性。D-二聚体水平与MMSE评分无相关性。结论 同型半胱氨酸、高敏C反应蛋白和D-二聚体参与了VaD的发病机制。血管性痴呆严重程度与Hcy和Hs-CRP呈显著相关性。
血管性痴呆;同型半胱氨酸;D-二聚体;高敏C反应蛋白
研究[1]表明,血浆同型半胱氨酸(Hcy)水平增高是导致动脉粥样硬化和血栓形成的独立危险因素。超敏C反应蛋白(hs-CRP)在动脉硬化的形成和发展过程中起关键作用,也是重要的炎症标志物之一[2]。血浆D-二聚体水平是纤溶亢进和高凝状态的特异性标志物,其增高提示纤溶活性增加。D-二聚体参与了急性脑梗死的发生发展,在动脉粥样硬化的起始及发展阶段发挥极其重要的作用。动脉粥样硬化与脑血管病的发生、发展、预后密切相关。血管性痴呆(VaD)作为脑血管疾病引起的后天性获得性智能障碍,脑血管疾病危险因素也参与了其发病机制。本文探讨Hcy、hs-CRP和D-二聚体在VaD发病机制中的关系和作用,为VaD的预防和治疗提供线索。
1 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象 选取河南省人民医院2012-01—2014-12血管性痴呆患者60例,男30例,女30例;51~79(65.5±7.5)岁;轻度痴呆28例,重度痴呆32例。并于同期筛选健康人60例作为对照组,男30例,女30例,年龄50~80(平均66.5±7.6)岁。VaD入选标准:依据世界卫生组织国际疾病分类第10版(ICD-10)中血管性痴呆的诊断标准同时符合下列条件:(1)简易智能状态量表(MMSE)评分:13~23分为轻度痴呆,5~12分为中度痴呆,<5分为重度痴呆;(2)改良Hachinski缺血量表评分>4分;(3)符合美国精神病学会DSM-Ⅳ制订的VD标准[3];(4)既往有脑血管疾病史。排除标准:(1)AD及心理疾病患者;(2)近1个月内服用影响Hcy水平的药物(如避孕药、抗癫痫药、多巴胺、叶酸和VitB12);(3)存在营养及代谢性疾病,如甲状腺疾病、严重贫血及营养不良、叶酸和VitB12缺乏、严重肝肾和其他脏器疾病。
1.2 方法 分别抽取2组清晨空腹肘静脉血,检测血清Hcy、Hs-CRP和D-二聚体,室温放置1~2 h,以2 000 r/min离心15 min,提取血清200 μL,置-70℃冰箱保存。采用散射比浊法检测C反应蛋白及D-二聚体含量,采用荧光标记免疫检测法检测血清Hcy水平。

2 结果
2.1 2组Hcy、Hs-CRP和D-二聚体检测结果比较 研究组Hs-CRP、Hcy和D-二聚体检测结果均明显高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。见表1。
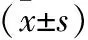
表1 2组Hcy、Hs-CRP和D-二聚体检测结果比较
2.2 不同程度痴呆患者Hcy、Hs-CRP和D-二聚体检测结果比较 直线相关分析结果提示,Hs-CRP、Hcy与MMSE评分之间呈负相关性(r=-0.461、-0.625,P<0.01)。即随着VaD患者MMSE评分的增加,痴呆严重程度降低,血浆Hs-CRP和Hcy水平呈下降趋势。D-二聚体水平与MMSE评分不存在相关性(r=-0.216,P=0.325)。轻度痴呆Hcy和Hs-CRP值明显低于中重度痴呆患者,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01);D-二聚体比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表2。

表2 不同程度痴呆患者Hcy、Hs-CRP和D-二聚体 检测结果比较±s)
3 讨论
随着人口老龄化,痴呆已成为当今世界关注的重要问题。脑血管疾病直接导致认知功能障碍,脑血管疾病危险因素直接参与VaD的病理生理机制。动脉粥样硬化、糖尿病、高血压、高Hcy血症等血管性危险因素可能是血管性痴呆的直接原因。Hcy为甲硫氨酸的中间代谢产物,是一种含硫氨基酸,能促进氧化低密度脂蛋白(LDL)形成、导致血管内皮损害和血小板集聚,是心脑血管疾病的独立危险因素。CRP是炎症反应的标志物,通过免疫应答产生抗炎作用[4]。动脉粥样硬化斑块内的炎症与血清炎性因子水平增高有关,CRP增高程度与脑动脉硬化程度密切相关[5-7]。研究显示,炎症因子,特别是CRP增加能预测认知功能下降[8-9]。血浆D-二聚体水平是纤溶亢进和高凝状态的特异性标志物,其增高提示纤溶活性增加。血浆D-二聚体的水平在缺血性脑卒中急性期明显提高,在恢复期有所下降。D-二聚体参与了急性脑梗死的发生发展,在动脉粥样硬化的起始及发展阶段发挥极其重要的作用,其血浆水平和斑块纤维帽厚度成反比。因此,异常升高的纤维蛋白原会引起患者斑块破裂和血栓形成[10-11]。Carcaillon等[12]研究发现,D-二聚体增加明显增加了血管性痴呆发病率。
本试验结果显示,VaD组血浆Hcy、Hs-CRP和D-二聚体水平较正常对照组明显上升,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01),与以前的研究结果一致[13-16],提示Hcy、Hs-CRP和D-二聚体参与了VaD的发病过程。本试验结果还显示,VaD组血浆Hcy、Hs-CRP与MMSE评分呈负相关,轻度痴呆与中重度痴呆D-二聚体相比差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),说明D-二聚体可能参与了血管性痴呆的发病过程,而与血管性痴呆的进展无关。总之,Hcy、Hs-CRP和D-二聚体可能与血管性痴呆的发生发展密切相关,对血浆Hcy、Hs-CRP和D-二聚体干预可能对血管性痴呆的发生和进展有作用,为脑血管病的二级预防提供一个有益的思路。
[1] Hassan A,Hunt BJ,O'Sullivan M,et al.Homocysteine is a risk factor for cerebral small vessel disease,acting via endothelial dysfunction[J].Brain,2004,127(Pt 1):212-219.
[2] Heringa SM,Berg EVD,Reijmer YD,et al.Markers of low-grade inflammation and endothelial dysfunction are related to reduced information processing speed and executive functioning in an older population-the Hoorn Study[J].Psychoneuroendocrinology,2014,40:108-118.
[3] Fratiglioni L,Grut M,Forsell Y,et al.Clinical Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease and Other Dementias in a Population Survey:Agreement and Causes of Disagreement in Applying Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders,Revised Third Edition,Criteria[J].Arch Neurol,1992,49(9):927-932.
[4] Juma WM,Lira A,Marzuk A,et al.C-reactive protein expression in a rodent model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion[J].Brain Res,2011,1414:85-93.
[5] Kettunen T,Eklund C,Kähönen M,et al.Polymorphism in the C-reactive protein (CRP)gene affects CRP levels in plasma and one early marker of atherosclerosis in men:The Health 2000 Survey[J].Scan J Clin Lab Invest,2011,71(5):353-361.
[6] Nordestgaard BG,Zacho J.Lipids,atherosclerosis and CVD risk:is CRP an innocent bystander?[J].Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis,2009,19(8):521-524.
[7] Alizadeh Dehnavi R,de Roos A,Rabelink TJ,et al.Elevated CRP levels are associated with increased carotid atherosclerosis independent of visceral obesity[J].Atherosclerosis,2008,200(2):417-423.
[8] Singh-Manoux A,Dugravot A,Brunner E,et al.Interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein as predictors of cognitive decline in late midlife[J].Neurology,2014,83(6):486-493.
[9] Silverman JM,Schmeidler J,Beeri MS,et al.C-reactive protein and familial risk for dementia:a phenotype for successful cognitive aging[J].Neurology,2012,79(11):1 116-1 123.
[10] Heijboer H,Ginsberg JS,Büller HR,et al.The use of the D-dimer test in combination with non-invasive testing versus serial non-invasive testing alone for the diagnosis of deep-vein thrombosis[J].Thromb Haemost,1992,67(5):510-513.
[11] Kario K,Matsuo T,Kabayashi H,et al.Rapid quantitative evaluation of plasma D-dimer levels in thrombotic states using an automated latex photometric immunoassay[J].Thromb Res,1992,66(2/3):179-189.
[12] Carcaillon L,Gaussem P,Ducimetière P,et al.Elevated plasma fibrin D-dimer as a risk factor for vascular dementia:the Three-City cohort study[J].J Thromb Haemost,2009,7(12):1 972-1 978.
[13] Liu LB,Li M,Zhuo WY,et al.The role of hs-CRP,D-dimer and fibrinogen in differentiating etiological subtypes of ischemic stroke[J].PloS One,2015,10(2):e0 118 301.
[14] Krarup LH,Sandset EC,Sandset PM,et al.D-dimer levels and stroke progression in patients with acute ischemic stroke and atrial fibrillation[J].Acta Neurol Scand,2011,124(1):40-44.
[15] Kong KH,Chua SG.Deep vein thrombosis based on D-dimer screening in ischaemic stroke patients undergoing rehabilitation[J].Singapore Med J,2009,50(10):971-975.
[16] Barber M,Langhorne P,Rumley A,et al.D-dimer predicts early clinical progression in ischemic stroke:confirmation using routine clinical assays[J].Stroke,2006,37(4):1 113-1 115.
(收稿2016-07-11)
Clinical research of serum homocysteine,high-sensitive C-reactive protein and D-Dimer in patients with vascular dementia
YuanLipin,FengYan,LiXue,MaJianjun,XuChangshui,LiYan
DepartmentofNeurology,thePeople’sHospitalofHenanProvince,Zhengzhou450003,China
Objective To study the relationships between levels of serum homocysteine (Hcy),high-sensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP),D-Dimer and vascular dementia (VaD),and to investigate the mechanism of Hcy,hs-CRP and D-dimer in the vascular dementia.Methods Subjects were divided into normal control group and vascular dementia group.CRP and D-Dimer content were detected by scattering turbidimetry,and the serum Hcy level was detected by fluorescence labeling immunoassay.Results Compared with the normal control group,Hcy,hs-CRP and D-Dimer were significantly higher in the vascular dementia group,and the differences were statistically significant.Linear correlation analysis showed negative correlations between Hs-CRP,Hcy and MMSE scores.There was no correlation between the level of D-Dimer and the MMSE scores.Conclusion Hcy,hs-CRP and D-Dimer are involved in the pathogenesis of vascular dementia (VAD)and there are significant correlations between the severity of vascular dementia and the levels of Hcy and Hs-CRP.
Vascular dementia;Homocysteine;D-Dimer;High-sensitive C-reactive protein
河南省科技攻关项目资助,编号122102310160
R749.1+3
A
1673-5110(2016)24-0037-03
*通讯作者:冯艳,女,1974年10月,硕士,副主任医师
