大肠不耐热肠毒素B亚单位佐剂活性相关蛋白的筛选
2017-01-06周慧聪王秋娟陈思静马永平
刘 林,周慧聪,王秋娟,陈思静,马永平
(重庆医科大学分子医学与肿瘤研究中心,生物化学与分子生物学教研室,重庆 400016)
大肠不耐热肠毒素B亚单位佐剂活性相关蛋白的筛选
刘 林,周慧聪,王秋娟,陈思静,马永平
(重庆医科大学分子医学与肿瘤研究中心,生物化学与分子生物学教研室,重庆 400016)
目的 通过对大肠杆菌不耐热肠毒素B亚单位相互作用蛋白的分析,探讨LTB佐剂活性的分子机制。方法 纯化的LTB蛋白和生理盐水分别处理RAW 264.7细胞,pull-down实验分离与LTB有相互作用的蛋白分子,质谱鉴定这些相互作用蛋白;免疫荧光和Western blot分析验证与LTB相互作用蛋白在细胞内的相互作用。结果 通过质谱鉴定了25种可能与LTB存在相互作用的蛋白分子,并构建了其相互作用网络图,筛选出可能与LTB免疫调节作用相关的蛋白分子;免疫荧光结果显示神经节苷脂能阻断LTB进入RAW 264.7细胞内,LTB在细胞内与GM130存在相互作用,而Vimentin在生理状态下与LTB不存在相互作用;LTB处理RAW 264.7细胞12 h后,β-actin表达上调,Hspd1表达无变化。结论 LTB佐剂活性的发挥是通过与免疫细胞表面GM1结合,引起内吞,并以小泡的形式到达高尔基体,通过高尔基体的加工。最终通过与Jup结合进而作用于TCF/LEF,引起Bcl-2、IL-6、Runx3等基因表达的变化,发挥促进T细胞和B细胞的增殖分化及活化、分泌细胞因子及免疫球蛋白的作用。
LTB;RAW 264.7;相互作用蛋白;免疫;佐剂;内吞
大肠杆菌不耐热肠毒素由产毒型大肠埃希菌(ETEC)产生,因其不耐热,在60℃处理30 min即被破坏,故称作不耐热肠毒素(LT)[1-2]。LT 是一类六聚体大分子,由1个 A 亚基 (LTA) 和5个B亚基 (LTB) 组成,结构和功能与霍乱毒素相似[3]。LTB作为LT的非毒性亚基,能刺激机体产生强烈的黏膜和系统免疫[4]。LTB的免疫调节作用包括促进 Th1 和 Th2 型细胞反应的细胞因子的表达,CD8+T细胞的凋亡和CD4+T细胞的增殖;使B细胞活化的MHCⅡ、ICAM-1、CD25、CD40分子表达增加,影响巨噬细胞[5-6]和B细胞的抗原处理和呈递过程[7,8],以及DC的发育和成熟,使DC细胞更好的发挥抗原递呈的作用[9],从而达到增强机体对抗原的免疫应答[10-12]。然而对于LTB引起这些免疫调节变化的机制尚不清楚,因而本实验选用小鼠单核细胞巨噬细胞白血病细胞株RAW 264.7[13]作为研究对象,研究 LTB 介导的免疫应答的分子机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料 LTB质粒由本实验室构建并保存;E.coliBL21(DE3)由本教研室保存;原核表达载体pET-32a购自Invitrogen公司;RAW 264.7细胞源于本实验室免疫学课题组陈全教授馈赠;胎牛血清、DMEM培养基购自Hyclon公司;Protein Interaction Kit购自Thermo Fisher公司;兔源GM130抗体、兔源Vimentin抗体、兔源Hspd1抗体和兔源β-actin抗体均购自武汉博士德生物技术有限公司,鼠源抗His标签抗体、羊抗兔DY488绿色荧光抗体和羊抗鼠DY549红色荧光抗体购自Santa Cruz公司;Toxin Eraser购自金斯瑞生物科技有限公司;蛋白纯化磁珠购自北京鼎国生物技术有限公司。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 LTB融合蛋白的纯化鉴定 透析袋预处理:依次用10 mmol·L-1Na2CO3溶液和10 mmol·L-1EDTA-Na溶液各煮沸15 min,蒸馏水彻底洗净备用;诱导表达LTB融合蛋白,收集菌体,提取并纯化LTB蛋白,纯化后蛋白经透析复性并浓缩后,用Toxin Eraser Kit去除内毒素,用BCA法测定其浓度,SDS-PAGE检测纯化蛋白纯度及其分子质量大小。
1.2.2 细胞培养及Pull-down实验 RAW 264.7细胞用含10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养,待细胞密度达到60%~70%,用无血清DMEM处理8 h使细胞同步化,实验组加入100 mg·L-1LTB蛋白,对照组加等体积生理盐水,处理12 h后收集细胞,提取细胞蛋白,测蛋白浓度。取等量的纯化的LTB融合蛋白和提取的两组细胞蛋白(保证LTB融合蛋白过量),用Protein Interaction Kit做pull-down实验,分离与LTB有相互作用的蛋白分子,SDS-PAGE检测分离得到蛋白的差异,并将分离得到的相互作用蛋白进行质谱鉴定,对鉴定结果进行分析处理。
1.2.3 免疫荧光验证生理情况下与LTB存在相互作用的蛋白 RAW 264.7细胞于24孔板中爬片,待细胞密度达到50%~60%,分为4个组,每组3个孔,第1组只加生理盐水,第2组和第3组加10 μg LTB融合蛋白,第4组加已用神经节苷脂(GM)封闭30 min的LTB融合蛋白(LTB ∶GM=1 ∶5),分别收集处理时间为5、15、30 min的爬片,快速洗涤后,马上用4%多聚甲醛固定,PBS洗5次,每次5 min;2% triton 100处理10 min,洗3次;加山羊血清于37℃孵箱,封闭30 min;一抗37℃孵育2 h,洗涤5次;二抗避光37℃孵育90 min,荧光显微镜检测结果。
1.2.4 Western blot 检测相互作用蛋白Hspd1和β-actin表达水平 收集LTB融合蛋白处理12 h的RAW 264.7细胞,提取细胞蛋白,采用BCA法测定蛋白浓度。按每孔50 μg蛋白量上样,经12% PAGE胶电泳分离后,将目的蛋白电转于PVDF膜上,5% BSA封闭 2 h,一抗4℃孵育过夜,TBST洗3次,每次15 min,加二抗室温摇床孵育2 h,ECL发光检测结果。
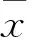
2 结果
2.1 LTB蛋白纯化 SDS-PAGE结果显示,纯化得到的蛋白分子量约为30 ku,与LTB蛋白实际分子量大小一致(Fig 1),表明获得了高纯度的LTB融合蛋白,可以用于后续实验。
2.2 LTB抓取到的相互作用蛋白的SDS-PAGE检测 SDS-PAGE 结果显示,与对照组相比,LTB 处理组有明显多于对照组的条带,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),表明通过pull down捕获到了与LTB有相互作用的蛋白分子(Fig 2)。
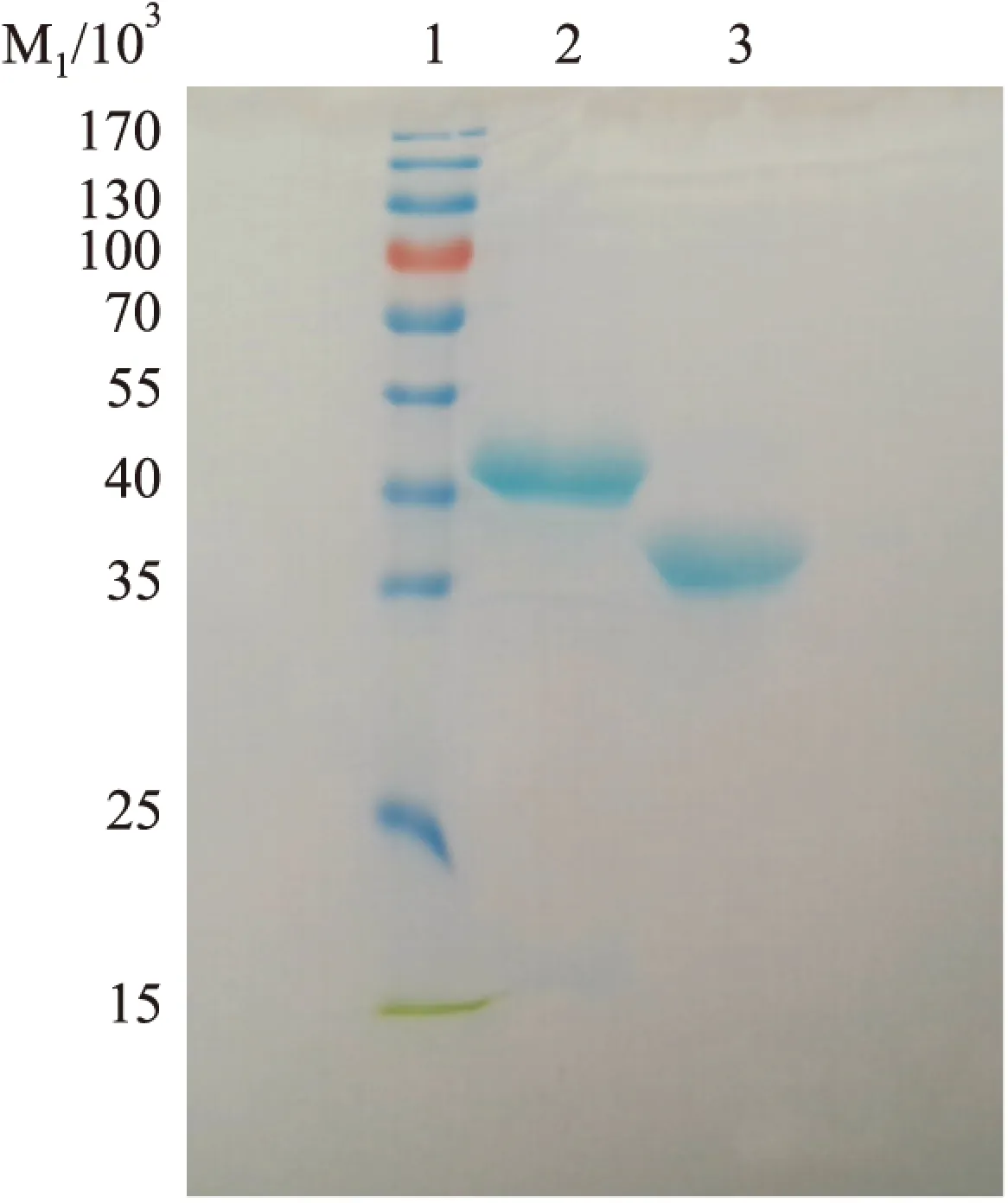
Fig 1 SDS-PAGE analysis of purified VP8 fusion protein and LTB fusion protein
1:Marker;2:VP8 fusion protein;3:LTB fusion protein
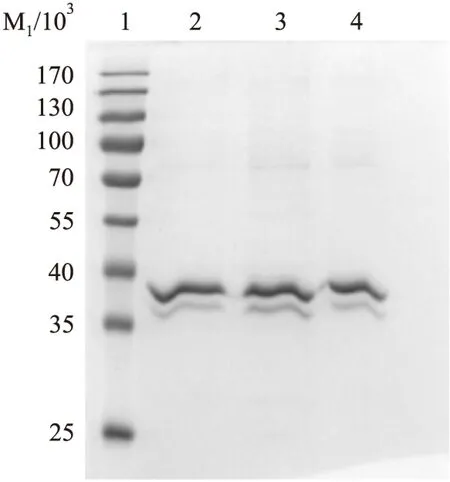
Fig 2 SDS-PAGE analysis of proteins interaction with LTB
1:Marker;2:Control group;3:Experimenal group;4:LTB fusion protein
2.3 LTB pull down蛋白的质谱分析结果
2.3.1 初步筛选得到的相互作用蛋白及其功能性分析 将得到的质谱数据根据筛选标准进行筛选,标准要求鉴定出的蛋白大于阈值可信肽段数大于3,Unused(置信度)值大于 1.3,筛选得到的相互作用蛋白见Tab 2,共25个相互作用蛋白,其中有12个属于Keratin蛋白家族,可信肽段数小于10的蛋白有9个,可信肽段数在10~20之间的共9个,可信肽段数大于20的共7个,并对其进行功能性分析,它们的功能见Tab 3。
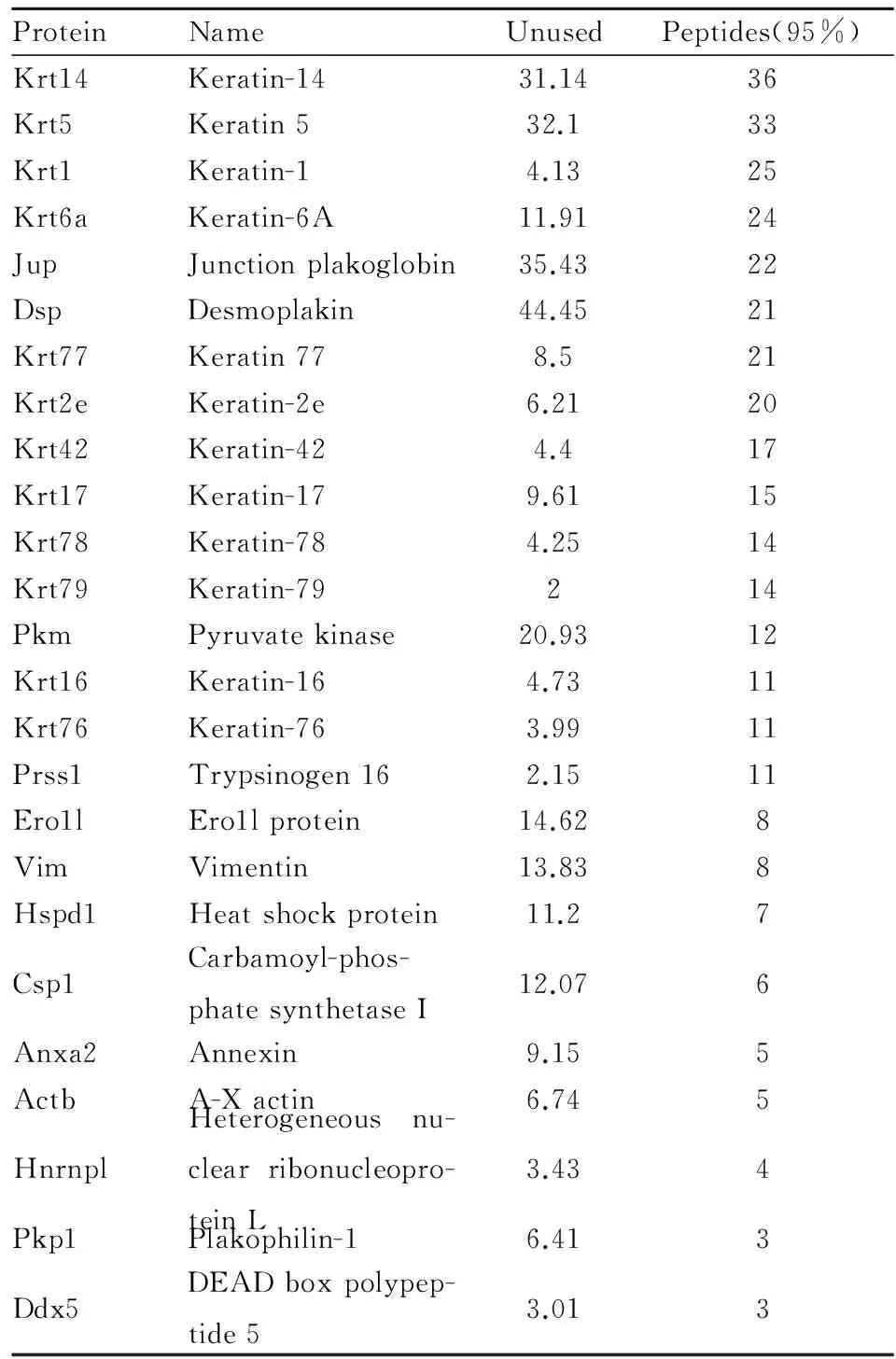
Tab 1 The interacting proteins identified by MS

Tab 2 The analysis of interacting protein′s function
续表

ProteinsFunctionKeratin-78Contributestotheformationofthecytoskeleton,cel-lularcomponents,cytoskeletalintermediatefibersKeratin-79Contributestotheformationofthecytoskeleton,cel-lularcomponents,cytoskeletalintermediatefibers.Vimentinclass-Ⅲintermediatefilamentsfoundinvariousnon-epithelialcells,especiallymesenchymalcells.Vimen-tinisattachedtothenucleus,endoplasmicreticulum,andmitochondria,eitherlaterallyorterminallyDesmoplakinInvolvesintheorganizationofthedesmosomalcad-herin-plakoglobincomplexesintodiscreteplasmamembranedomainsandintheanchoringofintermedi-atefilamentstothedesmosomes.A-XactinContributestotheformationofthecytoskeleton,cel-lular,cytoskeletalintermediatefibers.Plakophilin-1Seemstoplayaroleinjunctionalplaques.Contributestoepidermalmorphogenesis.JupPlaysacentralroleinthestructureandfunctionofsubmembranousplaques.ActsasasubstrateforVE-PTPandisrequiredbyittostimulateVE-cadherinfunctioninendothelialcells.Canreplacebeta-catenininE-cadherin/cateninadhesioncomplexeswhichareproposedtocouplecadherinstotheactincytoskele-ton.PKMPyruvatekinase,oxidativedecompositionofglucoseandgenerationATP.Prss1Serinelikeenzymecatalyticactivity,proteinhydroly-sis.Ero1lproteinRedoxenzymeactivity,electrontransportchain,pro-tein.folding,intracellularproteintransport,endocy-tosisandeffluxHspd160kuheatshockprotein.Mayfacilitatethecorrectfoldingofimportedproteins.Carbamoyl-phosphatesynthetaseIGlutamyltransferaseactivity,hydrolaseactivity,lig-aseactivity,nitrideCompoundmetabolism,synthesisofbasecompounds,biologicalsynthesisofcellulara-minoacids.playsanimportantroleinremovingex-cessammoniafromthecell.AnnexinPlaysimportantrolesintheinnateimmuneresponseaseffectorofglucocorticoid-mediatedresponsesandregulatoroftheinflammatoryprocess.Hasanti-in-flammatoryactivity.Playsaroleinglucocorticoid-mediateddown-regulationoftheearlyphaseofthein-flammatoryresponse.Heterogeneousnu-clearribonucleopro-teinLLikelytoplayaroleinthenuclearmetabolismofhnRNAs,particularlyforpre-mRNAsthatcontaincytidine-richsequences.Canalsobindpoly(C)single-strandedDNA.Playsanimportantroleinp53/TP53responsetoDNAdamage,actingatthelevelofbothtranscriptionactivationandrepression.Ddx5Thetranslationinitiationfactor,translationregula-tion,RNAhelicase.Involvesinthealternativeregu-lationofpre-mRNAsplicing.
2.3.2 相互作用蛋白的相互作用网络图 通过http://string-db.org/ 网站提供的分析工具对这些蛋白的相互作用进行了预测(Fig 3)。根据这些蛋白分子相互作用网络图,发现有4个蛋白分子与其他蛋白分子没有相互作用,因此推测这些蛋白分子与其他蛋白分子的相互作用可能还未被发现,或者是非特异性结合的蛋白分子。剩余的21种蛋白,以Jup为界限分为左右两半,左边的13种蛋白均为细胞骨架蛋白,11种属于Keratin家族,剩下的2个分别是Pkp1,并且发现这些分子间的相互作用都比较强。右边的蛋白以Jup为起始,以Ddx5、PKM、Anxa2 3个分子结束。
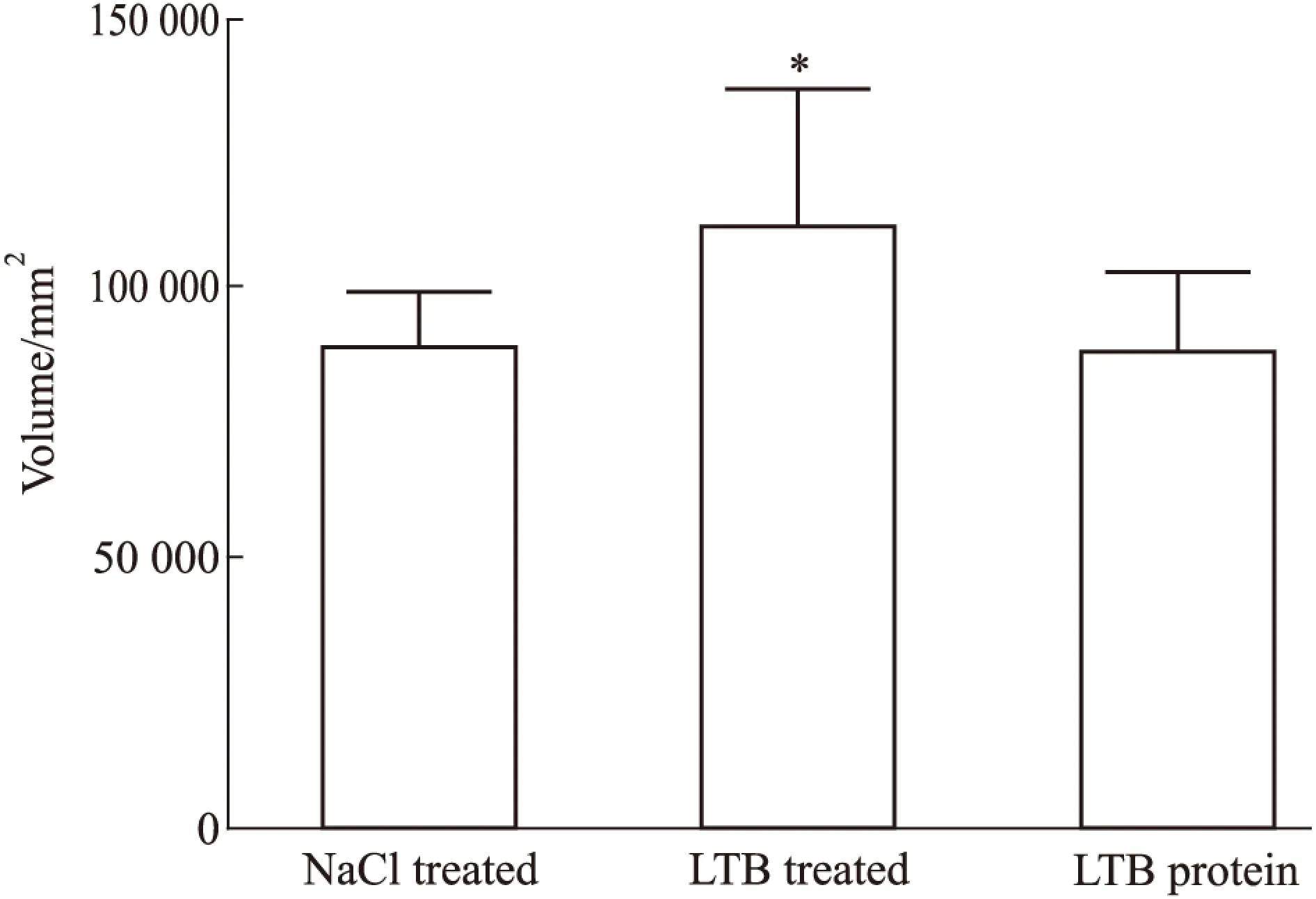
Fig 3 Analysis for volume of proteins captured by LTB fusion protein
*P<0.05vsNaCl
2.4 LTB在RAW 264.7细胞内的免疫荧光定位 免疫荧光结果显示,对照组(NaCl组)未加LTB处理,所以5、15、30 min细胞内均未出现红色荧光信号,而GM130标记组和Vimentin标记组细胞内均有红色荧光信号;Vimentin标记组没有与LTB相互作用的阳性信号,表明LTB在细胞内与Vimentin蛋白不存在相互作用;而GM130标记组有与LTB相互作用的橙色阳性信号(箭头标记),而且随着时间增加阳性信号增强,表明LTB是能够进入巨噬细胞内,且随时间延长,进入细胞内的LTB的量也增加;GM130+GM 组5、15、30 min细胞内均无红色荧光信号,表明神经节苷脂(GM)能够阻断LTB进入巨噬细胞内(Fig 5)。
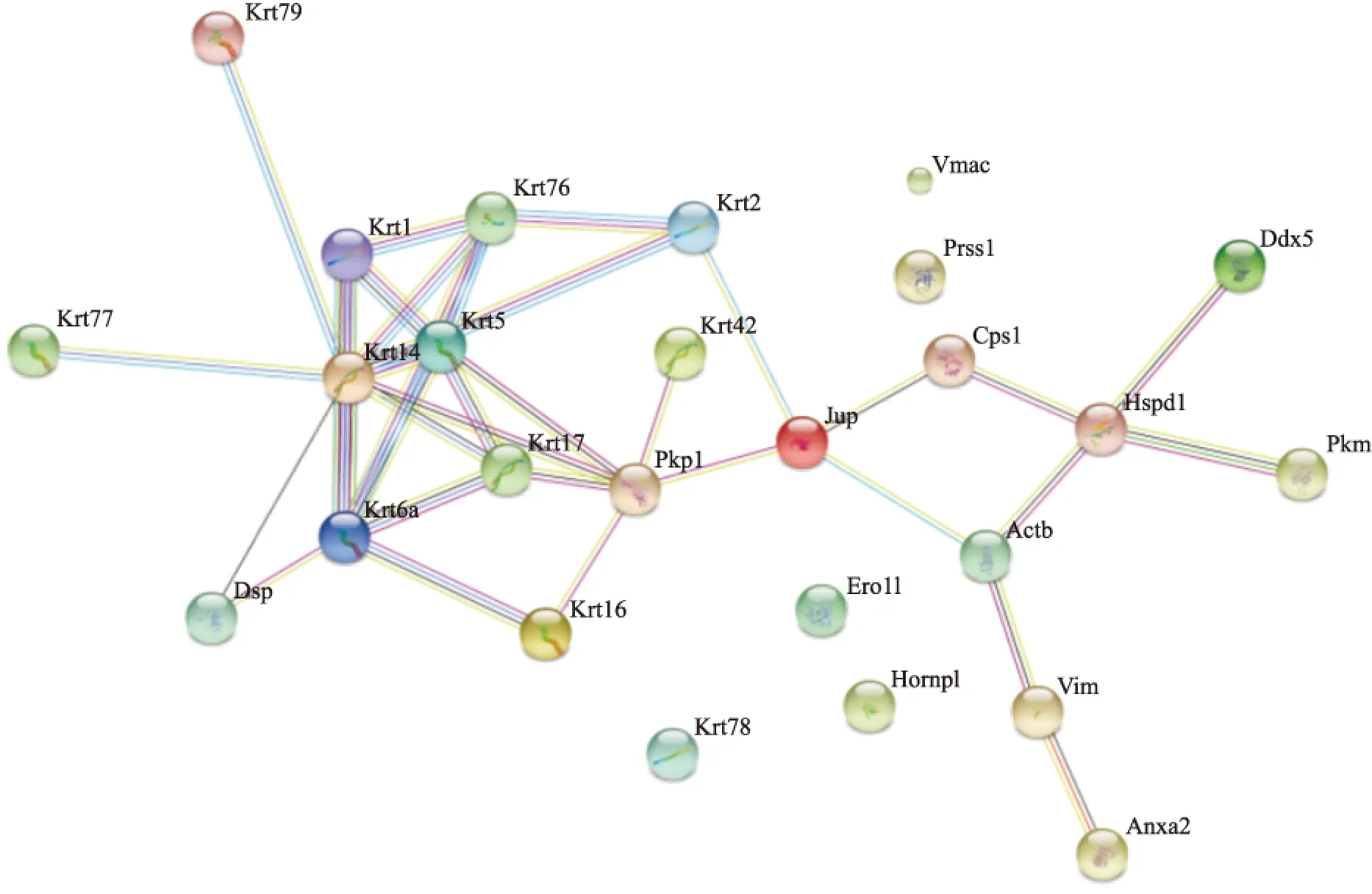
Fig 4 Map of protein-protein interaction
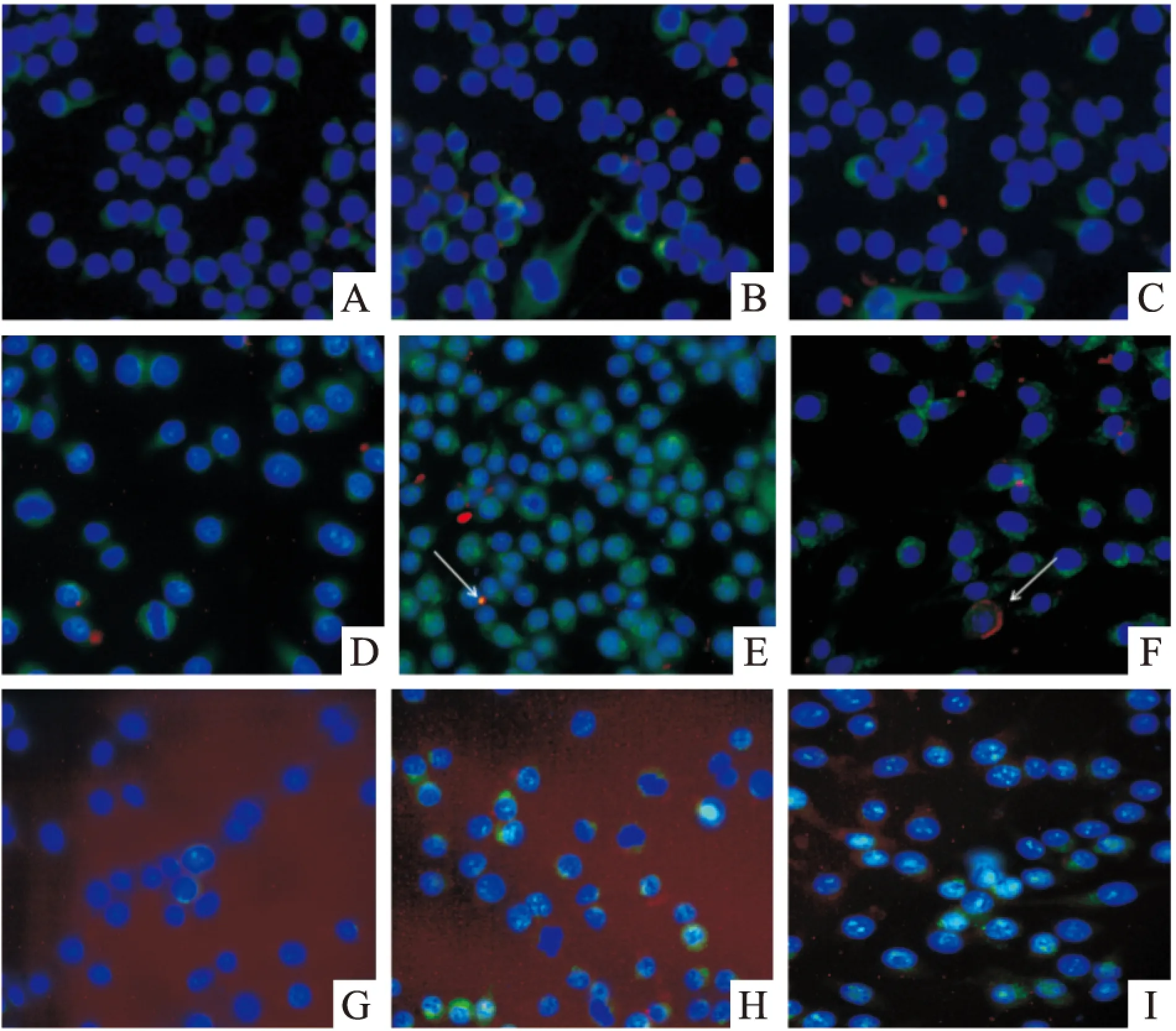
Fig 5 The immunofluorescence analysis of interactions between LTB fusion protein and Vim or GM130
A:Vim 5 min;B:Vim 15 min;C:Vim 30 min;D:GM130 5 min;E:GM130 15 min;F:GM130 30 min;G:GM130+GM 5 min;H:GM130+GM 15 min;I:GM130+GM 30 min
2.5 相互作用蛋白β-actin和Hspd1表达水平检测 LTB处理 RAW 264.7细胞12 h后,与对照组相比,β-actin的表达是上调的,且差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05);Hspd1表达无变化,差异无统计学意义(Fig 6, Fig 7)。
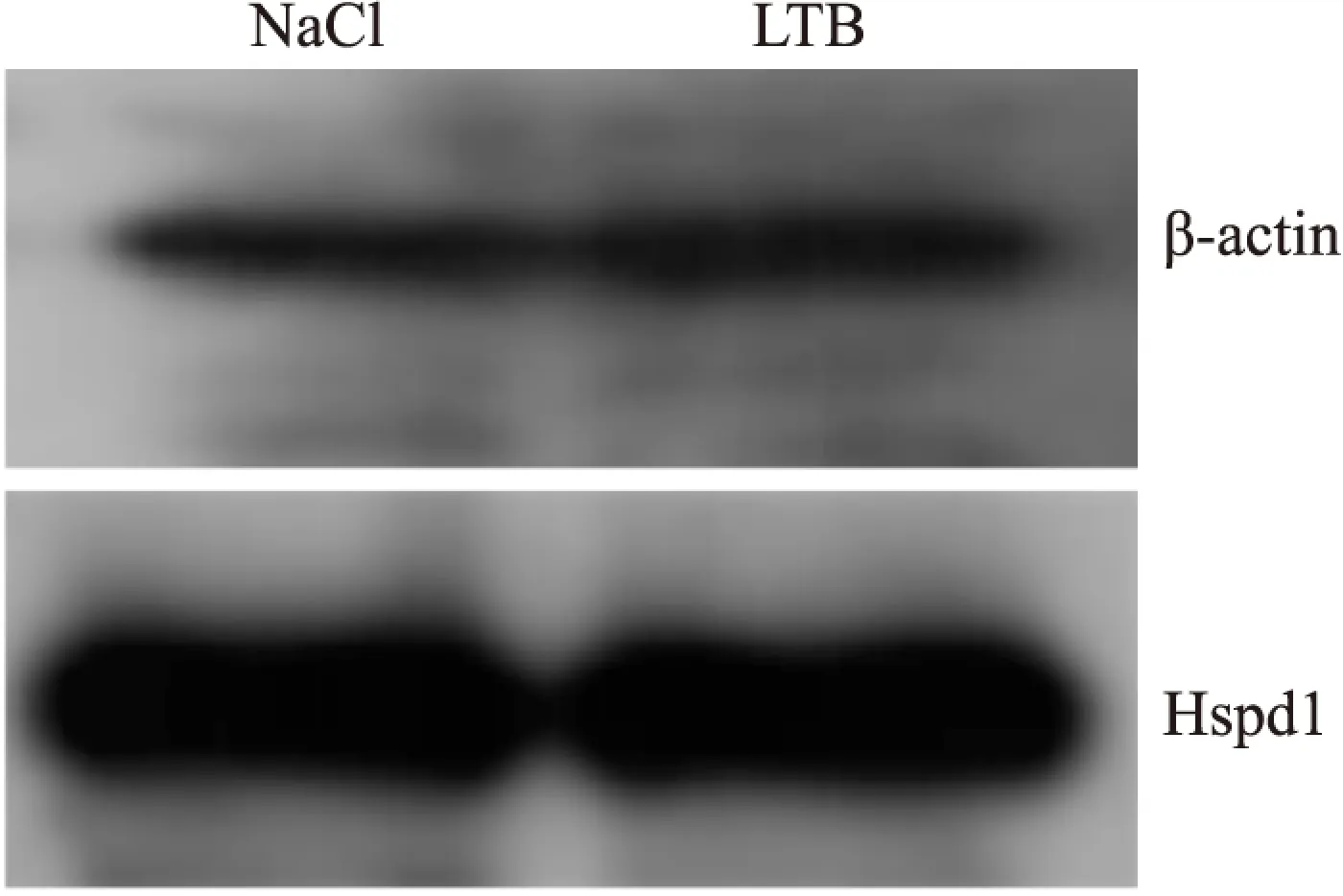
Fig 6 Expression of β-actin and Hspd1 in RAW 264.7 induced by LTB
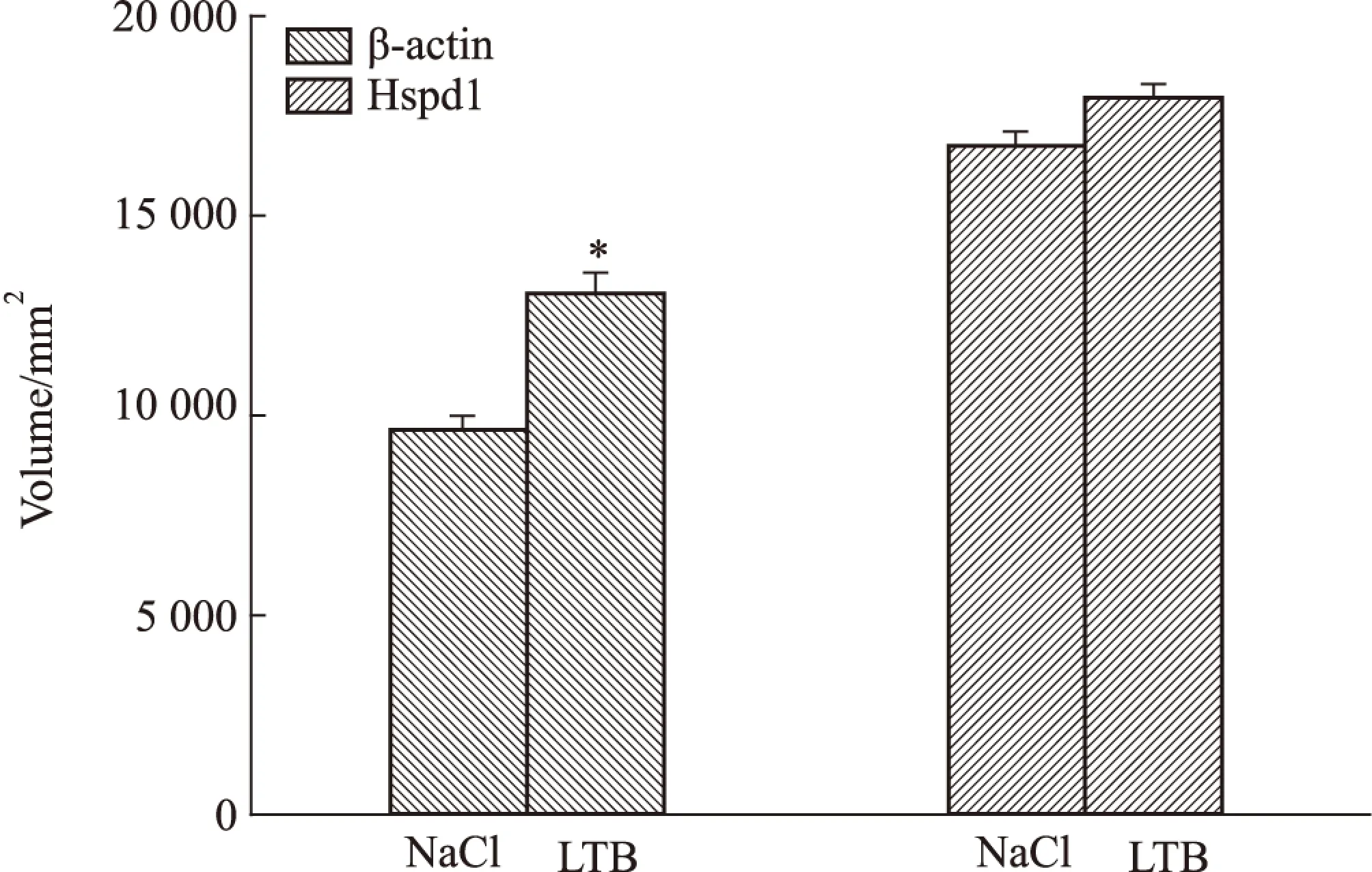
Fig 7 Analysis for volume of interacting proteins of LTB
*P<0.05vsNaCl
3 讨论
大肠杆菌不耐热肠毒素 B 亚单位(LTB)是一种非常有效的黏膜免疫佐剂,它能刺激机体产生强烈的黏膜和系统免疫应答。大量研究表明LTB与GM1的结合对于LT的佐剂活性是必需的[14],并且GM1 是广泛表达于绝大多数细胞表面[15-16],这使得LTB 的佐剂活性的应用范围极广。还有研究表明LT不但能与神经节苷脂结合,还能与缺乏唾液酸的GM1、GD1b以及乳糖神经酰胺等受体结合,然而,这些受体对于LTB的佐剂活性的作用尚不清楚[17]。还有研究表明LTB在某些反应中表现出比LT和CT更好的黏膜佐剂效应[18-20],且LTB几乎没有毒性。LTB通过与细胞表面的GM1结合,不仅能增强机体对抗原的免疫应答效应,还能够改变黏膜免疫应答的类型。一些研究表明LTB并不能促进DC细胞的成熟[9]。LTB对于T细胞的作用也不全是促进作用,LTB除能促进CD4+T细胞的增殖外,还能诱导CD8+T细胞的凋亡[6,8]。因此对于LTB佐剂的活性机制的研究就显得十分必要。为此,本文通过pull-down实验结合质谱,鉴定了与LTB存在相互作用的25种蛋白分子,通过对这些蛋白分子的功能和信号通路查询,发现有4种蛋白未显示出与其他蛋白的相互作用,也未发现与之相关信号通路;11种Keratin家族蛋白主要构成细胞骨架,维持细胞形态功能的稳定,也没有找到它们与免疫调节相关的证据;余下的10种蛋白分子中Pkp1、Anxa2、Hspd1、Ddx5都没有与之相关的信号通路,除Ddx5能够调节Th17细胞的功能同时能促进细胞的增殖外,未见到他们参与免疫调节的报道,Actb参与白细胞的跨内皮细胞转移,它在上皮细胞的表达上调能够影响细胞骨架蛋白的重排,从而促进白细胞由血液透过上皮细胞向组织细胞的转移,但在巨噬细胞中表达增加作用尚不清楚;Vimentin参与人类疱疹病毒第四型的感染的信号通路,但通过免疫荧光实验表明LTB在细胞内与Vimentin不存在相互作用;Dsp能够通过与Jup作用激活TCF/LEF,达到促进cyclin1、c-Myc和PPARy基因的表达从而促进细胞的增殖与活化,研究表明TCF/LEF能够通过影响Bcl-2、IL-6、ICOS影响TFH细胞的活动,从而促进T细胞和B细胞的增殖与分化,以及影响IL-4, IL-21等细胞因子和免疫球蛋白的表达[21-23]。免疫荧光阻断实验验证了LTB内吞进入巨噬细胞内必须依赖于与细胞表面的GM1受体结合,内吞进入细胞内通过与GM130的结合,由高尔基体进行加工转运,LTB本身也是一种抗原,免疫细胞对其加工处理很可能与其他一般抗原加工处理途径是一致的。再与Jup等作用激活TCF/LEF从而引起一系列免疫调节反应,因此推测LTB发挥佐剂活性的信号通路(Fig 8)。
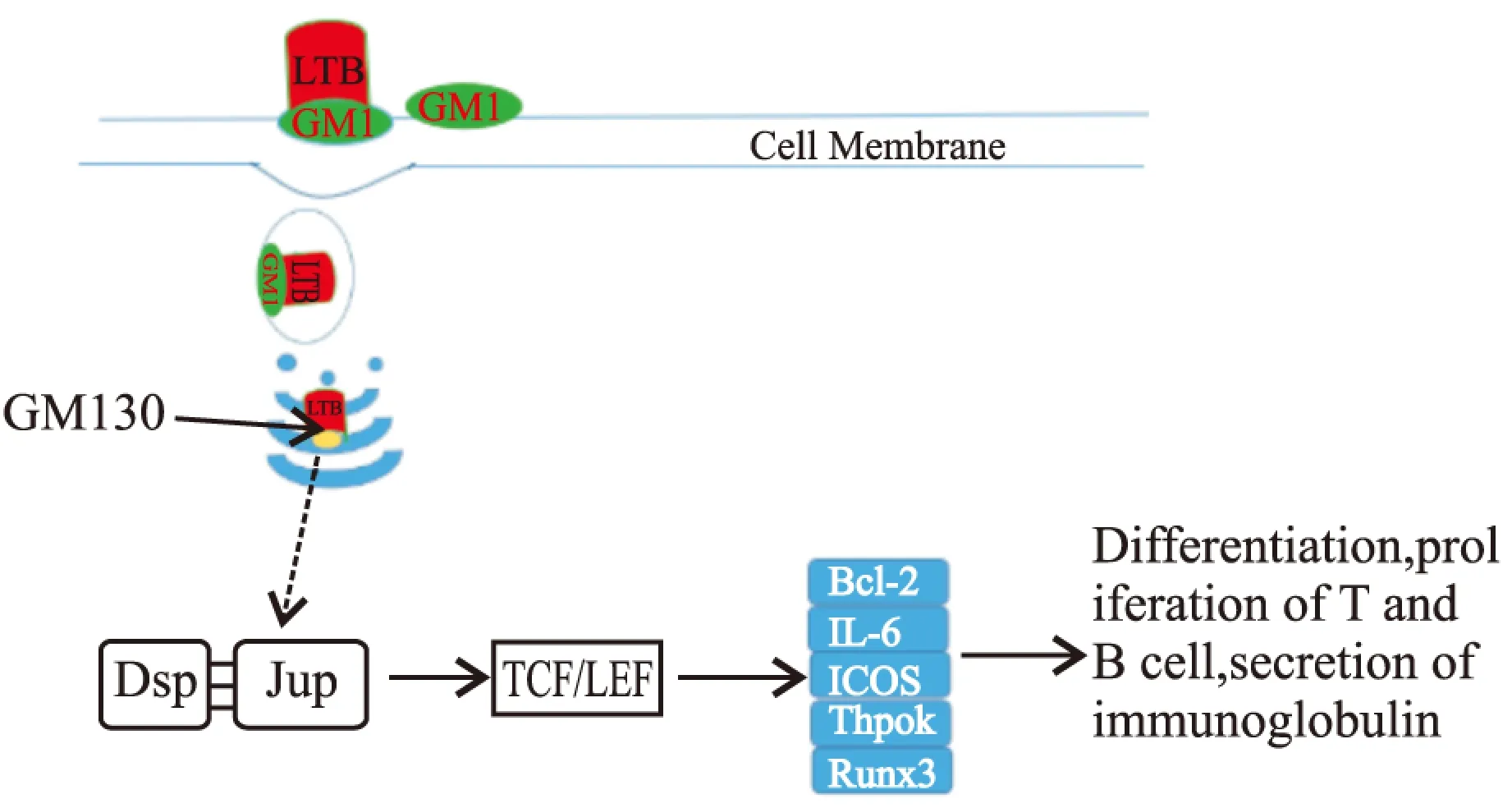
Fig 8 T and B cell differentiation and proliferation: Immunoglobulin and cytokine secretion
LTB作为佐剂的研究由来已久,LTB已被认为是最有潜力的黏膜免疫佐剂,本研究通过蛋白质相互作用与生物信息学预测,推测了LTB发挥佐剂活性可能的信号通路,为LTB的进一步深入研究和临床应用奠定了基础。
(致谢:本实验完成于重庆医科大学分子医学与肿瘤研究中心,在此感谢本实验室的老师及实验管理人员,同时也感谢我的指导老师马永平教授在实验过程的指导及帮助。)
[1] Salimian J, Salmanian A, Khalesi R, et al. Antibody against recombinant heat labile enterotoxin B subunit(rLTB) could block LT binding to ganglioside M1 receptor[J].IranJMicrobiol,2010,2(3):120-7.
[2] De Haan L, Verweij W, Agsteribbe E, et al. The role of ADP-ribosylation and G(M1)-binding activity in the mucosal immunogenicity and adjuvanticity of the Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin and Vibrio cholerae cholera toxin[J].ImmunolCellBiol,1998,76(3):270-9.
[3] De Haan L, Verweij W R, Feil I K,et al. Role of GM1 binding in the mucosal immunogenicity and adjuvant activity of the Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin and its B subunit[J].Immunology,1998,94(3):424-30.
[4] Fraser S A, de Haan L, Hearn A R, et al. Mutant Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin B subunit that separates toxoid-mediated signaling and immunomodulatory action from trafficking and delivery functions[J].InfectImmun,2003,71(3):1527-37.
[5] Fingerut E, Gutter B, Goldway M, et al. B subunit of E. coli enterotoxin as adjuvant and carrier in oral and skin vaccination[J].VetImmunolImmunop,2006,112(3-4):253-63.
[6] Brereton C F, Sutton C E, Ross P J, et al. Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin promotes protective Th17 responses against infection by driving innate IL-1 and IL-23 production[J].JImmunol,2011,186(10):5896-906.
[7] Millar D G, Hirst T R, Snider D P. Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit is a more potent mucosal adjuvant than its vlosely related homologue, the B subunit of cholera toxin[J].InfectImmun,2001,69(5):3476-82.
[8] Ji J, Griffiths K L, Milburn P J, et al. The B subunit of Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin alters the development and antigen-presenting capacity of dendritic cells[J].JCellMolMed,2015,19(8):2019-31.
[9] Nashar T O, Williams N A, Hirst T R. Cross-linking of cell surface ganglioside GM1 induces the selective apoptosis of mature CD8+T lymphocytes[J].IntImmunol,1996,8(5):731-6.
[10]Truitt R L, Hanke C, Radke J, et al. Glycosphingolipids as novel targets for T-cell suppression by the B subunit of recombinant heat-labile enterotoxin[J].InfectImmun,1998,66(4):1299-308.
[11]Yankelevich B, Soldatenkov V A, Hodgson J, et al. Differential induction of programmed cell death in CD8+and CD4+T cells by the B subunit of cholera toxin[J].CellImmunol,1996,168(2):229-34.
[12]袁 琴,袁 丁,周志勇,等. 竹节参齐墩果烷皂苷对RAW 264.7巨噬细胞SIRT1活性影响及抗炎作用研究[J]. 中国药理学通报,2016;32(3):349-54.
[12]Yuan Q, Yuan D,Zhou Z Y,et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of Chikusetsu oleanane saponin on RAW 264.7 cell through regulating SIRT1 activity[J].ChinPharmacolBull,2016,32(3):349-54.
[13]Francis M L,Ryan J, Jobling M G, et al. Cyclic AMP-independent effects of cholera toxin on B cell activation. II. Binding of ganglioside GM1 induces B cell activation[J].JImmunol,1992,148(7):1999-2005.
[14]Moreno-Altamirano M M, Aguilar-CarmonaI, Sanchez-Garcia F J. Expression of GM1, a marker of lipid rafts, defines two subsets ofhuman monocytes with differential endocytic capacity and lipopolysaccharide responsiveness[J].Immunology,2007,120(4): 536-43.
[15]Spangler B D. Structure and function of cholera toxin and the related Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin[J].MicrobiolRev,1992,56(4):622-47.
[16]Bibolini M J, Julia Scerbo M, Peinetti N,et al. The hybrid between the ABC domains of synapsin and the B subunit of Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis[J].CellImmunol,2012,280(1):50-60.
[17]Grassmann A A, Felix S R, dos Santos C X, et al. Protection against lethal leptospirosis after vaccination with LipL32 coupled or coadministered with the B subunit of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin[J].ClinVaccineImmunol,2012,19(5):740-5.
[18]Williams N A. Immune modulation by the cholera-like enterotoxin B-subunits: from adjuvant to immunotherapeutic[J].IntJMedMicrobiol,2000,290(4-5):447-53.
[19]Yang X,Mariuzza R A. Pre-T-cell receptor binds MHC: Implications for thymocyte signaling and selection[J].ProcNatlAcadSciUSA,2015,112(27):8166-7.
[20]陈艳芳,刘培庆. PIP140/PGC-1α在AngⅡ调节心肌能量代谢中的作用研究[J]. 中国药理学通报,2015,31(2):194-8.
[20]Chen Y F, Liu P Q. Role of RIP140 and PGC-1α in angiotensin Ⅱ mediated energy metabolism in cardiomyocytes[J].ChinPharmacolBull, 2015,31(2):194-8.
[21]Steinke F C,Yu S,Zhou X,et al. TCF-1 and LEF-1 act upstream of Th-POK to promote the CD4+T cell fate and interact with Runx3 to silence CD4 in CD8+T cells[J].NatImmunol,2014,15(7):646-56.
[22]Mookerjee-Basu J, Kappes D J. New ingredients for brewing CD4+T(cells):TCF-1 and LEF-1[J].NatImmunol,2014,15(7):593-4.
[23]Masato Kubo.TCF-1 and LEF-1 help launch the T(FH) program[J].NatImmunol,2015,16(9):900-1.
Exploration for interacting protein ofE.coliat-labile enterotoxin B subunit(LTB) as adjuvant
LIU Lin,ZHOU Hui-cong,WANG Qiu-juan,CHEN Si-jing,MA Yong-ping
(DeptofBiochemistryandMolecularBiology,MolecularMedicineandTumorResearchCenter,ChongqingMedicalUniversty,Chongqing400016,China)
Aim To explore the mechanism ofE.coliheat-labile enterotoxin B subunit(LTB) as adjuvant by analysis of cellular proteins interacting with LTB.Methods Whole cell proteins were purified from RAW 264.7 cell after treated with LTB or NaCl 12 h, respectively. The cellular proteins were interacted with LTB and the interacting proteins were purified by pull-down assay and identified by mass spectrography. The LTB interaction proteins were conformed with Western blot and immunofluorescence assay.Results 25 LTB interaction proteins were found, and their interaction network was mapped; four proteins(Jup, Dsp, Ddx5 and Vimentin) were indicated to be related with LTB adjuvant activity; immunofluorescence assay indicated that GM130 interacted with LTB, however, Vimentin had no interaction with LTBinvivo. After treated by LTB, the expression of β-actin was upregulated obviously in RAW 264.7 cell, whereras, Hspd1 did not show any change.Conclusions LTB exerts adjuvant activity through binding to GM1 of immune cells, causing endocytosis and transporting to the Golgi apparatus by vesicles. Then LTB might bind to Jup and affect TCF/LEF activity, regulating the expression of Bcl 2, IL-6, and Runx3. The result is promoted T cell and B cell proliferation, differentiation and activation by secretion of cytokines and immunoglobulins.
LTB; RAW 264.7; interacting protein; immune; adjuvant; endocytosis
时间:2016-12-5 15:14
http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/34.1086.R.20161205.1514.048.html
2016-06-30,
2016-08-20
国家自然科学基金资助项目(No 30972585)
刘 林(1990-),男,硕士,研究方向:肿瘤与基因工程疫苗,E-mail:1137997269@qq.com; 马永平(1968-),男,博士,硕士生导师,研究方向:肿瘤与基因工程疫苗,通讯作者,E-mail:ypmaqq@163.com
10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2016.12.024
A
1001-1978(2016)12-1761-06
R329.24;R341 ;R392.11;R392.12;R378.21;R977.6