含双(2-二苯基膦苯基)醚的Ag(Ⅰ)配合物的合成和表征
2016-12-20林森李跃崔洋哲张彦茹王梦秦李中峰金琼花
林森 李跃 崔洋哲 张彦茹 王梦秦 李中峰 金琼花
(首都师范大学化学系,北京100048)
含双(2-二苯基膦苯基)醚的Ag(Ⅰ)配合物的合成和表征
林森李跃崔洋哲张彦茹王梦秦李中峰金琼花*
(首都师范大学化学系,北京100048)
合成了2个含有双膦配体的Ag(Ⅰ)配合物,分别是[Ag(DPEphos)(dppe)]2SO4(1)和[Ag(DPEphos)(SCN)]2·CH2Cl2(2)(DPEphos=双(2-二苯基膦苯基)醚,dppe=双(二苯基膦)乙烷),并通过红外光谱,核磁氢谱,元素分析,X射线单晶衍射及荧光光谱表征分析。通过热重分析了2个配合物的热稳定性。结构分析表明配合物1具有简单的单核结构,每个Ag和2个膦配体中的4个P原子螯合配位。配合物2具有双核结构,在配合物2中存在微弱的金属与金属间的作用。在Ag2S2环中,4个原子相互之间形成的内角之和为360°,形成的环[-Ag-S-Ag-S-]是一个平行四边形。荧光光谱显示配合物中的发射峰主要来源于双膦配体中的π-π*跃迁。热重分析结果表明,在340℃附近,2个配合物开始分解,具有良好的稳定性。
双(2-二苯基膦苯基)醚;双(二苯基膦)乙烷;Ag(Ⅰ)配合物;荧光;热重分析
0 Introduction
Currently,an increasing interest in the design and synthesis of mono-and bi-nuclear complexes or clusters with group 11 metals(Cu,Ag,Au)has been attracted,notonly for their fascinating architectures[1-3], but also for the potential applications in antibacterial agents[4],organic lightemitting diodes[5]and catalysis[6-7]. Among these complexes,silver(Ⅰ)complexes with many commercially available bisphosphine ligands have been systematically investigated.
Bis(2-(diphenylphosphino)phenyl)ether(DPEphos, Scheme 1)has been extensively studied by Van Leeuwen and his co-workers[8]due to its good chelating capability and its catalytic utility in a variety of organic transformations[9].The tridentate nature of this ligand produces interesting coordination architectures. In view of this,considerable attention has been paid to the developmentsofthe metal-DPEphos complexes[10]. As closed-shell d10metal complexes,copper-DPEphos complexes have been extensively studied,but few silver complexes containing DPEphos were obtained. Besides,bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane(dppe)is usually used as bridging or chelating ligand in polymeric complex to form various coordination modes[11-12].

Scheme 1 Structures of ligands DPEphos and dppe
Following the earlierstudieson homolepticsilver(Ⅰ)compounds with bisphosphine ligands[10-13],we became naturally interested in extending our investigations to silver(Ⅰ)complexes with two kinds of bi-sphosphine ligands(Scheme 1).In this paper,we report the synthesis,structure characterization and photophysical properties of two silver(Ⅰ)complexes with DPEphos ligands[Ag(DPEphos)(dppe)]2SO4(1)and[Ag(DPEphos) (SCN)]2·CH2Cl2(2)(Scheme 2).They have been isolated and characterized by IR,single crystal X-ray diffraction,fluorescence and1H NMR spectroscopy.In particular,complex 2 shows metallophilic interactions in which metalmetal interactions are atypically shorter than the sum of their van der Waals radii.Sometimes, this may lead to enhanced photophysical properties as wellas stabilization ofmetalcomplexes[14-15].

Scheme 2 Routine of synthesis for complexes 1 and 2
1 Experimental
1.1Materials and measurements
All chemical reagents are commercially available and used without furthermore treatment.FT-IR spectra (KBr pellets)were measured on a Perkin-Elmer Infrared spectrometer.C,H and N elements analysis were carried out on an Elementar Vario MICRO CUBE(Germany)elemental analyzer.Roomtemperature fluorescence spectra were measured on F-4500 FL Spectrophotometer.1H NMR was recorded at room temperature with a Varian VNMRS 600MHz spectrometer.
1.2Synthesis of[Ag(DPEphos)(dppe)]2SO4(1)
Complex 1 was prepared at room temperature, using Ag2SO4(0.031 3 g,0.1 mmol),dppe(0.079 9 g, 0.2 mmol)and DPEphos(0.107 1 g,0.2 mmol)in a mixture of 5 mL CH2Cl2and 5 mL CH3OH.Yield: 65%.1H NMR(600 MHz,DMSO-d6,298 K):δ7.46~6.75(m,CHbenzene),2.47(d,CH2).IR data(KBr pellets, cm-1):3 420s,3 053m,1 638m,1 586w,1 481m,1 460 m,1 434s,1 258w,1 214m,1 095s,998w,871w,803w, 744s,695s,512m,476w.Element analysis Calcd.for C124H104Ag2O6P8S(%):C 68.08,H 4.76;Found(%):C 67.52,H 4.74.
1.3Synthesis of[Ag(DPEphos)(SCN)]2·CH2Cl2(2)
Complex 2 was prepared in a manner similar to thatdescribed for 1,using AgSCN(0.03 4 g,0.2 mmol) and DPEphos(0.107 0 g,0.2 mmol)in a mixture of 5 mL CH2Cl2and 5 mL CH3OH.Yield:18%.1H NMR (600 MHz,DMSO-d6,298 K):δ7.44~6.67(m,CHbenzene). IR data(KBr,cm-1):3 435w,2 090m,2 017w,1 619w, 1 478m,1 460m,1 433s,1 258w,1 222m,1 094w,798w, 745s,694s,541w,506w,471w.Anal.Elementanalysis Calcd.for C75H58Ag2Cl2N2O2P4S2(%):C 60.24,H 3.88, N 1.87;Found(%):C 61.38,H 4.08,N 2.08.
1.4Structure determination
Single crystals of the title complexes were mounted on a Bruker Smart 1000 CCD diffractometer equipped with a graphite-monochromated Mo Kα(λ= 0.071 073 nm)radiation.Semi-empirical absorption corrections were applied using SADABS program[16]. Allthe structures were solved by direct methods using SHELXS program of the SHELXTL-97 package and refined with SHELXL-97[17].Metal atom centers were located from the E-maps and other non-hydrogen atoms were located in successive difference Fourier syntheses.The final refinements were performed by full matrix least-squares methods with anisotropic thermal parameters for non-hydrogen atoms on F2. The hydrogen atoms were generated geometrically and refined with displacement parameters riding on the concerned atoms.Crystallographic data and experimental details for structural analysis are summarized in Table 1.Selected bond lengths and angles of 1~2 are given in Table 2.
CCDC:1416572,1;1416573,2.

Table 1 Crystallographic data for complexes 1~2

Table 2 Selected bond distances(nm)and bond angles(°)for complexes 1~2
2 Results and discussion
2.1Synthesis of the single crystal
Two Ag(Ⅰ)complexes are air-stable,soluble in common polar solvents such as methanol, dichloromethane,acetonitrile.We have synthesized a series of silver(Ⅰ)complexes with DPEphos and dppe ligands including the complex[Ag(DPEphos)(dppe)] BF4[13].In view ofourinterestin the influence ofanions, we have reported a few metal complexes with sulfate or thiocyanate anion.In literature[18-20],there are different coordination modes of sulfate anion,which can influence the structure of the complexes. However,complex 1 with free sulfate anion was obtained by reactions in the mixed solution of CH3OH and CH2Cl2.In addition,thiocyanate can act as a highly versatile bi-dentate ligand with a polarizableπ system to form the coordination mode(μ-NCS)[21].We obtained sulfur-bridged binuclear cluster 2 by the reaction of AgSCN with DPEphos in the same molar ratio in the absence of dppe.Also all the complexes are stable in air and can be stored for long term.
2.2Infrared spectroscopy and1H NMR spectroscopy
The infrared spectra of complexes 1~2 show that the absorption peaks around 1 434 cm-1are due to CC stretch vibration of the phenyl rings and the middle absorption peaks around 3 052 cm-1are caused by CH vibration of the phenyl rings.The absorption of the S-O stretch vibration is around 1 214 cm-1.And the band around 2 090 cm-1for 2 is assigned to thiocyanate(SCN-).
The1H NMR spectra of complexes 1~2 exhibit signals(multiple peaks)atδ7.4~6.7,which can be attributed to protons from the benzene rings of the diphosphine ligands.In complex 1,the triplet signal ofthe methylene group ofdppe is atδ2.47.
2.3Description of the crystal structure
Complex 1 is simple mono-nuclear complex with Ag2SO4,dppe ligand and DPEphos ligand.The molecule structure of complex 1 is shown in Fig.1. Each Ag(Ⅰ)atom is four-coordinated and attached to four phosphorus atoms(two from a chelating dppe ligand and two from a chelating DPEphos ligand). Their bond lengths are close to those in analogous complexes[13].The geometry around each metal center is distorted tetrahedral as is evident from the angles in the range of 81.83(7)°~125.19(6)°.In complex 1, the average bite angle of the DPEphos ligand is 104.17(6)°,which is larger than its natural bite angle (βn)[8].However,they are much smaller than that in [Ag(κ2-P,P′-DPEphos)(2,2′-bpy)][OTf](113.51(7)°)and [Ag(DPEphos)(py2SH)2]NO3(112.20(2)°)[22-23],which is attributed to the influence of co-ligand.The C-H…π (0.262 nm and 0.287 nm)weaker interactions stabilize the complex.

Fig.1 Molecular structure of complex 1
Single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis reveals that complex 2 crystallizes in the triclinic system with space group P1.It consists of inversion symmetric dimers with a diamond-shaped Ag2S2group at the center(Fig.2).Complex 2 is a bi-nuclear cluster of Ag(Ⅰ)where the Ag…Ag distance(0.331(5)nm) exceeds the sum of two covalent radii(four coordinated univalent silver)(0.292 nm)but is shorter than the sum of two van der Waals radius of silver atoms(0.344 nm),to some extent,indicating weak argentophilic interactions.The sum of the internal angles of the four-member ring[-Ag-S-Ag-S-]in the Ag2S2core is 360°,demonstrating that the ring is a parallelogram.Two adjacent[Ag(DPEphos)(SCN)]units are bridged by two S atoms with 50%occupancy to form a dimer,just like Ag2I2(DPEphos)2[24].And the average bite of the DPEphos ligand is 113.24(3)°in complex 2,which is smaller than the same bite in Ag2I2(DPEphos)2.

Fig.2 Molecular structure of complex 2
2.4Thermogravimetric analysis
The complexes 1~2 have been analyzed by TGA. From Fig.3,we can see that the complex 2 decomposes by two steps,and complex 1 decomposes by one step.
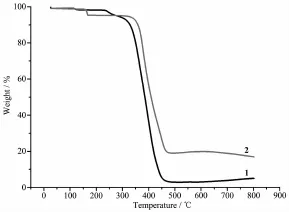
Fig.3 TGA curves of complexes 1~2
The initial weight loss of complex 1 is at 340℃, then complex 1 decomposes to Ag rapidly from 340 to 450℃.Complex 2 starts to decompose at175℃,which is attributed to the weight loss of the dichloromethane molecule from the crystallattice.The low decomposing temperature of 2 is due to the low boiling point of dichloromethane.Complex 2 decomposes into Ag2S rapidly from 400 to 470℃.The finalweightlossdata(%) of the two complexes are listed as following:complex 1:94.99%(Calcd.95.06%);complex 2:83.09%(Calcd. 83.41%).
The order of the stability is as following:complex 1>complex 2.The great stability shown by the two complexes may be caused by the way of chelating through P atoms.
2.5Description of luminescent
The luminescent excitation and emission spectra of complexes 1~2 are measured in the solid state at room temperature(Fig.4).The ligand dppe exhibitsfluorescence signal at 434 nm with an excitation maximum at 310 nm[25].In the solid fluorescence emission spectrum of DPEphos ligand,the emission peak is found at453 nm(λex=317 nm)[13].In the fluorescence emission spectra ofcomplexes 1~2,the emission peaks are found at434 nm(λex=370 nm)for 1,443 nm(λex= 351 nm)for 2,respectively.The similarity of the emission spectra of complexes 1~2 and that of dppe or DPEphos ligand indicates that the origin of these emissions all involves emissive state derived from ligand-centred(π-π*)transition.

Fig.4 Solid-state excitation and emission spectra of 1~2 at 298 K
3 Conclusions
Two new Ag(Ⅰ)complexes ofphosphine-containing ligands(DPEphos or dppe)have been synthesized and characterized by elemental analysis,IR,X-ray diffraction,fluorescence,1H NMR,spectroscopy.Structure analysis shows complex 1 is of simple mono-nuclear structures,each silver atom is chelated by a dppe ligand and a DPEphos ligand.Complex 2 is a binuclear cluster of Ag(Ⅰ),indicating weak argentophilic interactions.The luminescent spectra show that the origin of these emissions involves emissive state derived from ligand-centered(π-π*)transition.The great stability shown by the two complexes may be caused by the way of chelating through phosphine atoms.The great stability can be used in optical materialand other applications.
References:
[1]Yue C Y,Yan C F,Feng R,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2009,48: 2873-2879
[2]Wu J Y,Chao T C,Zhong M S.Cryst.Growth Des.,2013, 13:2953-2964
[3]Li X X,Gong Y Q,Zhao H X,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2014,53: 12127-12134
[4]Pallavicini P,Dacarroa G,Diaz-Fernandez Y A,et al.Coord. Chem.Rev.,2014,275:37-53
[5]Minaev B,Jansson E,Ågren H.J.Chem.Phys.,2006,125: 234704(18 pages)
[6]Wang X X,Liu Y G,Hecke K V,etal.Z.Anorg.Allg.Chem., 2015,641:903-910
[7]Ming C L,Li Y H,Li G Y,et al.Transition Met.Chem., 2014,39:477-485
[8]Kranenburg M,Vander Burgt Y,Kamer P,et al.Organometallics,1995,14:3081-3089
[9]Venkateswaran R,Balakrishna M S,Mobin S M,et al.Inorg. Chem.,2007:720-731
[10]Kaeser A,Moudam O,Accorsi G,etal.Eur.J.Inorg.Chem., 2014:1345-1355
[11]Liu X Q,Liu Y Y,Hao Y J,et al.Inorg.Chem.Commun., 2010,13:511-513
[12]Aslanidis P,Cox P J,Divanidis S,et al.Inorg.Chim.Acta, 2004,357:2677-2686
[13]Gao S,Li Z F,Liu M,et al.Polyhedron,2014,83:10-15
[14]Rajput G,Yadav M K,Drew M G,et al.Inorg.Chem., 2015,54:2572-2579
[15]Young A G,Hanton L R.Coord.Chem.Rev.,2008,252: 1346-1386
[16]SADABS,Siemens AnalyticalX-ray Instrument Inc.,Madison, WI,1996.
[17]Sheldrick G M.SHELXS-97 and SHELXL-97,University of Göttingen,Germany,1997.
[18]Huang X,Lu Z F,Jin Q H,et al.Polyhedron,2013,65:129-135
[19]Bosch E,Matheny J,BrownA E,etal.CrystEngComm,2011, 13:5755-5762
[20]Song L L,Jin Q H,Cui L N,et al.Inorg.Chim.Acta,2010, 363:2425-2429
[21]Qiu Q M,Jin Q H,Sun J J,et al.Polyhedron,2012,44:215-220
[22]Balakrishna M S,Venkateswaran R,Mobin S M.Polyhedron, 2008,27:899-904
[23]Christofidis G,Cox P J,Aslanidis P.Polyhedron,2012,31: 502-505
[24]Freudenmann D,Feldmann C.Inorg.Chim.Acta,2011,375: 311-313
[25]Jin Q H,Yuan Y,Yang Y P,et al.Polyhedron,2015,101: 56-64
Syntheses and Characterization of Silver(Ⅰ)Complexes of Bis(2-(diphenylphosphino)phenyl)ether
LIN Sen LI Yue CUIYang-Zhe ZHANG Yan-Ru WANG Meng-Qin LIZhong-Feng JIN Qiong-Hua*
(Department of Chemistry,Capital Normal University,Beijing 100048,China)
Two novel silver(Ⅰ)complexes[Ag(DPEphos)(dppe)]2SO4(1)and[Ag(DPEphos)(SCN)]2·CH2Cl2(2) (DPEphos=bis(2-(diphenylphosphino)phenyl)ether,dppe=bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane)have been synthesized and characterized by IR,1H NMR spectroscopy,elemental analysis,single-crystal X-ray diffraction and fluorescence spectra.Structure analysis shows that complex 1 has simple mono-nuclear structures,and each silver atom is chelated by four phosphines.Complex 2 has a bi-nuclear cluster of Ag(Ⅰ),showing weak argentophilic interactions.The sum of the internal angles of the four-member ring[-Ag-S-Ag-S-]in the Ag2S2core is 360°, demonstrating that the ring is a parallelogram.The luminescent spectra of 1~2 are studied,which show that the emission peaks are assigned to theπ-π*transitions of the diphosphine ligands.Thermogravimetric analysis shows that two complexes begin to decompose ataround 340℃,indicating their strong stability.CCDC:1416572, 1;1416573,2.
bis(2-(diphenylphosphino)phenyl)ether;bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane;silver(Ⅰ)complex;fluorescence;TGA
O614.122
A
1001-4861(2016)12-2165-07
10.11862/CJIC.2016.273
2016-06-12。收修改稿日期:2016-10-19。
国家自然科学基金(No.21171119,81573832)、863国家高技术研究发展计划(No.2012AA063201)、北京教育委员会基金(No.KM201210028020)、北京市优秀人才项目(No.2010D005016000002)和北京市自然科学基金(No.7122015)资助。
*通信联系人。E-mail:jinqh@cnu.edu.cn;会员登记号:S06N3669M1105。
