不同宽度冲刷槽对崩岗崩积体产流产沙的影响
2016-12-19李学增黄炎和林金石蒋芳市郝福星关家椿许煌基杨丹丹王振红
李学增,黄炎和,林金石,蒋芳市,郝福星,关家椿,许煌基,杨丹丹,王振红
(福建农林大学资源与环境学院,福州 350002)
不同宽度冲刷槽对崩岗崩积体产流产沙的影响
李学增,黄炎和※,林金石,蒋芳市,郝福星,关家椿,许煌基,杨丹丹,王振红
(福建农林大学资源与环境学院,福州 350002)
为了解不同宽度冲刷槽对坡面冲刷侵蚀过程中产流产沙的影响,该研究以崩岗崩积体为对象,通过不同冲刷槽宽度(10、20、30、40、50 cm)和不同单宽流量(1.2×10-2、2.4×10-2、3.6×10-2、4.8×10-2m2/min)相结合的室内模拟冲刷试验,研究不同宽度冲刷槽对崩积体产流产沙的影响。结果表明:1)单宽流量为1.2×10-2,2.4×10-2,3.6×10-2m2/min时,不同冲刷槽宽度之间径流率、产沙率存在显著差异(P<0.05);单宽流量为4.8×10-2m2/min时,不同冲刷槽宽度之间径流率、产沙率差异不显著。2)单宽流量一定,不同冲刷槽宽度下径流率随时间变化趋势相同;单宽流量为1.2×10-2m2/min时,不同冲刷槽宽度条件下产沙率和含沙量随时间变化趋势不同,其他单宽流量下产沙率和含沙量随时间变化趋势相同。3)单宽流量相同,不同冲刷槽宽度下累积径流量差异不显著;单宽流量为1.2×10-2,2.4×10-2,3.6×10-2m2/min条件下,不同冲刷槽宽度下累积产沙量和平均含沙量差异显著(P<0.05)。该研究揭示了冲刷槽宽度对崩积体产流产沙的影响,为今后试验冲刷槽宽度的选择提供参考。
冲刷;沙;径流;崩岗;崩积体;冲刷槽宽度;单宽流量
0 引言
崩岗是中国南方红壤区典型且严重的水土流失类型[1-2],爆发性强、侵蚀量大、危害严重[3-4]。崩积体是由原山体坡面、崩壁物质在水力和重力的作用下崩塌滑落而堆积在崩壁下方的物质[5-7],是崩岗侵蚀泥沙的重要来源,具有土质疏松、结构性差,易侵蚀等特点[5]。坡面土壤侵蚀的发生是降雨、植被、土壤、地形等各因素相互影响和作用的综合结果[8],研究坡面土壤侵蚀过程中各要素对侵蚀产流产沙的影响对揭示坡面侵蚀机理具有重要意义。湿周是计算坡面径流水力学参数的重要指标,被证明对水分入渗和产流产沙具有重要指示作用,而冲刷槽宽度对湿周有重要影响,但当前有关冲刷槽宽度对坡面侵蚀的影响研究较少。
研究坡面侵蚀过程可分为室外和室内两种,通常根据试验条件选择不同的冲刷槽宽度。在野外试验方面,要求能够完整地反映地形地貌特征,设置小区宽度在1~3 m之间。郭军权等[9]在研究上方来水对浅沟侵蚀产沙的野外放水冲刷试验时采用宽度为1 m的冲刷槽,结果表明,浅沟径流率和产沙率均随流量的增大而增大;汪邦稳等[10]在研究南方红壤区不同利用土地产流产沙特征时采用3 m宽径流小区。在室内模拟冲刷方面,冲刷槽的宽度多在0.1~0.5 m之间。Wang等[11]在研究土壤表面不同结构对冲刷过程中土壤分离速率的影响中采用0.1 m宽的冲刷槽;王军光等[12]在定量研究坡面冲刷过程中红壤分离速率时采用宽度为0.2 m宽的冲刷槽进行模拟冲刷;Dong等[13]提出一种测量细沟流速的新方法,其研究中采用的冲刷槽宽度为0.2 m;赵纯清等[14]在设计进行土壤侵蚀模拟试验的小型水槽时,设计水槽宽度为0.3 m,并通过研究坡面薄层水流的水力特性等试验验证了装置的可靠性和实用性;Zhang等[15]在研究陡坡条件下泥沙输移能力时采用的冲刷槽宽度为0.4 m;Zhang等[16]用冲刷试验量化细沟侵蚀和浅沟侵蚀分离速率时采用0.5 m宽的冲刷槽。这些研究分别利用不同宽度的冲刷槽进行研究,但对于冲刷槽宽度的选择并没有明确的规定,且实际试验中冲刷槽宽度是否会影响湿周的大小和细沟的发育,进而对坡面侵蚀产生影响,还未见研究报道。此外,稳态条件下单宽流量的大小也会影响细沟的发育,不同冲刷槽宽度是否会因流量的不同对细沟形态产生影响也缺乏理论支持。鉴于以上现状,本文将崩岗崩积体与不同宽度冲刷槽对坡面侵蚀的影响研究结合起来,通过室内模拟冲刷,分析不同冲刷槽宽度和单宽流量条件下崩积体侵蚀产流产沙特征,为坡面土壤侵蚀机理研究提供一定依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
试验所用土壤2014年10月采集于福建省安溪县龙门镇洋坑村(24°57′N,118°03′E)。该位置地处南亚热带气候区,雨量充沛,气候温和,年平均气温18℃,年降水量1 800 mm。采集土体为花岗岩发育的崩岗崩积土,自然状态下土壤平均容重为1.35 g/cm3,土壤含水率在25.22%~28.55%之间,平均含水率为26.50%。将采集土壤混匀分析后得出采集土壤理化性质如下:土壤pH值为5.24;有机质质量分数为2.09 g/kg;砂粒含量高,可达到50.25%;黏粒含量低,石砾、粉粒和黏粒所占百分比分别为36.32%、12.00%和1.43%。土壤质地疏松,结构性差。
1.2 试验装置
试验所用土槽为固定式变坡钢槽,设计为5个不同宽度的冲刷槽,宽度分别为10,20,30,40,50 cm,长3 m,深1 m。试验土槽上方分别放置相应宽度溢流槽,用于保证试验用水均匀平稳溢出。采用河北保定兰格恒流泵有限公司生产的WT600-4F-C型蠕动泵控制流量,可调整误差小于20 mL/min。模拟冲刷试验于2015年7-10月在福建农林大学金山水土保持科教园人工降雨大厅内进行。
1.3 试验设计和试验过程
本试验采用双因素试验设计。通过野外调查,选定崩岗崩积体冲刷试验坡度为15°,冲刷槽宽度分别为10,20,30,40,50 cm。结合研究区常年的降雨数据,经多次室内冲刷试验对单宽流量进行标定后,设定单宽流量分别为1.2×10-2,2.4×10-2,3.6×10-2,4.8×10-2m2/min,每个试验均设置3个重复,共计60场次。试验前将采集土壤自然风干后过10 mm筛,去除根系、石块等杂物。填土时先在土槽底部填入60 cm厚沙石,并铺设透水纱布,保证试验过程中水分可以自由下渗。然后在纱布上装填30 cm厚的试验用土,为求土体尽可能接近野外崩积体,严格控制容重在1.30~1.40 g/cm3,平均容重1.35 g/cm3,并采取分层装填、压实的方法,每次填土厚度为10 cm。试验前采用30 mm/h的雨强降雨,使供试土壤达到充分饱和,用塑料布覆盖后放置18 h,使水分自由运动渗透,保证试验时土壤含水量保持一致并尽可能接近自然状态下土壤水分分布状况。试验开始前,用蠕动泵自带校正功能校正流量至误差小于20 mL/min,试验开始后,水流经蠕动泵进入溢流槽,稳流后流经防渗布,使水流在坡面上完全分散。用秒表记录初始产流时间,并在产流后每分钟接取一次径流和泥沙混合样,单场次试验持续冲刷20 min。试验后用量筒测量采集样品体积,泥沙经105℃烘干后称其质量,并通过计算得出每分钟含沙量数据。
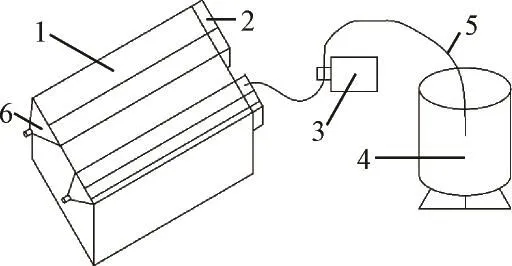
图1 冲刷试验设备示意图Fig.1 Scouring test equipment
1.4 数据分析与处理
试验数据采用Excel2007和SPSS18.0进行处理和分析,绘图和方差分析通过Excel2007进行,多重比较分析通过SPSS18.0进行。
2 结果与分析
2.1 坡面产流特征
图2为不同冲刷槽宽度和单宽流量条件下径流率随时间变化过程。当单宽流量为1.2×10-2m2/min时,整个冲刷过程中不同冲刷槽宽度条件下径流率均逐渐增大,当单宽流量为2.4×10-2和3.6×10-2m2/min时,不同冲刷槽宽度径流率随时间的延长均先增加后趋于稳定,可能是因为在此流量时,各个冲刷槽宽度下水分入渗一段时间后,径流率达到设定值,此后径流率基本稳定,入渗进入稳渗阶段[17-18]。当单宽流量达到4.8×10-2m2/min时,随着时间的延长,各个冲刷槽宽度下径流率逐渐增大至设定径流率后缓慢减小,原因可能是在此单宽流量下,径流的强烈冲刷作用导致坡面土壤质地发生变化,细颗粒被搬运,粗颗粒富集,坡面粗糙度增大,而土壤质地对水分入渗影响显著,土壤质地越轻,土壤入渗能力越强,径流率减小[19]。
对不同单宽流量和冲刷槽宽度下径流率进行方差分析结果表明,单宽流量为1.2×10-2,2.4×10-2和3.6×10-2m2/min时,不同冲刷槽宽度下径流率差异达到显著水平(P<0.05);单宽流量为4.8×10-2m2/min时,不同冲刷槽宽度下径流率差异不显著。进一步进行多重比较分析可知,单宽流量为1.2×10-2m2/min时,冲刷槽宽度10 cm时的径流率与30,40 cm时的径流率差异显著(P<0.05),50 cm的径流率与20 cm时的径流率差异显著(P<0.05),与30,40 cm情况下径流率差异极显著(P<0.01);单宽流量为2.4×10-2m2/min时,冲刷槽10 cm宽度下的径流率与20,50 cm情况下径流率差异显著(P<0.05),与30 cm情况下径流率差异极显著(P<0.01),30与40 cm情况下的径流率差异显著(P<0.05);单宽流量为3.6×10-2m2/min时,冲刷槽10 cm宽度时径流率与30 cm情况下径流率差异显著(P<0.05),与40 cm情况下径流率差异极显著(P<0.01);单宽流量为4.8×10-2m2/min时,不同冲刷槽宽度下径流率差异都不显著。原因可能是当单宽流量为1.2×10-2,2.4×10-2和3.6×10-2m2/min时,细沟发育较缓,片蚀和沟蚀并存,由于不同冲刷槽宽度下细沟发育程度不同而导致径流率存在差异;当单宽流量为4.8×10-2m2/min时,流量较大,细沟发育迅速,很快进入沟蚀阶段,不同冲刷槽宽度下入渗速率相近。

图2 不同冲刷槽宽度和单宽流量条件下径流率变化过程Fig.2 Changes in runoff rate under different width of scouring flumes and discharge per unit width conditions
2.2 坡面产沙特征
不同冲刷槽宽度和单宽流量条件下产沙率变化过程如图3所示。不同冲刷槽宽度和单宽流量条件下含沙量变化趋势与产沙量变化趋势一致。当单宽流量为1.2×10-2m2/min,冲刷槽宽度为10、20和30 cm时,产沙率和含沙量呈先增大后稳定波动变化,而当冲刷槽宽度为40和50 cm时,整个过程产沙率和含沙量都是逐步递增的,未到达平稳波动阶段,这与细沟的发育状况有关,冲刷槽宽度为10、20和30 cm时,细沟发育明显,而冲刷槽宽度为40和50 cm时,细沟数量、宽度、长度和深度都较小,径流分散,片蚀为主要侵蚀方式,产沙率和含沙量较小,当侵蚀方式以片蚀为主转变到细沟侵蚀为主时,产沙量增大[17]。进一步分析可知,单宽流量为1.2×10-2m2/min时,冲刷槽宽度可能会影响径流的动能和汇集,导致细沟发育状况和沟床粗糙度的差异,不同冲刷槽宽度下产沙量和含沙量因此产生差异。单宽流量为2.4×10-2,3.6×10-2,4.8×10-2m2/min时,不同冲刷槽宽度条件下产沙率和含沙量随时间呈现出相同的变化趋势,大致分为3个阶段,分别是逐步递增阶段、平稳波动阶段和递减阶段。首先,径流冲刷破坏土体表面,逐渐产生细沟,产流初期产沙率和含沙量不断增加,在第二分钟时产沙率有所减小,主要是因为冲刷第一分钟时,径流搬运土体表面的松散物质;其次,在细沟发育过程中,产沙率呈平稳波动,这主要因为此时径流率达到设定值;最后,随着冲刷时间的延长,细沟逐渐发育稳定,土壤细颗粒被搬运,土体表面粗颗粒富集,这时径流搬运粗颗粒能力较弱,含沙量和产沙率下降。彭怡等[20]研究表明,土壤中粉粒和黏粒等细颗粒物质容易被优先搬运,而粒径较大的颗粒不易被搬运。在整个过程中,由于径流对沟壁的冲刷作用,加之沟壁水分长期处于饱和状态,会产生崩塌,因此会呈现出波动变化[21]。与赵淦等[22]的研究相比,本研究多了产沙量递减阶段,可能是由于坡度和冲刷槽宽度不同导致的,赵淦等[22]是在坡度为20°~40°,冲刷槽宽度为1 m的条件下进行,而本研究是在坡度为15°的情况下进行的,坡度较小,径流动能也较小,加之冲刷槽宽度较小,导致单宽流量相同条件下汇入细沟的径流较少,冲刷试验后期径流难以搬运粗颗粒,因此产沙率递减。

图3 不同冲刷槽宽度和单宽流量条件下产沙率变化过程Fig.3 Changes in sediment yield rate under different width of scouring flumes and discharge per unit width conditions
对不同冲刷槽宽度和单宽流量条件下产沙率进行多重比较分析,结果发现,单宽流量为1.2×10-2m2/min时,冲刷槽宽度30 cm情况下产沙率与20 cm下产沙率差异显著(P<0.05),与10,40,50 cm下产沙率差异达到极显著水平(P<0.01)。通过对单宽流量1.2×10-2m2/min时的细沟发育状况统计发现,冲刷槽宽度为30 cm时,细沟平均沟宽和平均沟深均明显较其他宽度下大,因而产沙率较大。张科利等[23]研究发现,当坡面进入细沟侵蚀阶段后,产沙量会增加几倍到几十倍,因此细沟的发育状况对产沙量有极其明显的影响。单宽流量为2.4×10-2m2/min时,冲刷槽宽度10 cm情况下产沙率与其他冲刷槽宽度下产沙率差异均达到极显著水平(P<0.01)。单宽流量为3.6×10-2m2/min时,冲刷槽宽度10 cm情况下产沙率与50 cm下产沙率差异显著(P<0.05),与冲刷槽宽度30,40 cm下产沙率差异极显著(P<0.01)。单宽流量为4.8×10-2m2/min时,不同冲刷槽宽度下产沙率差异均不显著。原因是单宽流量为2.4×10-2,3.6×10-2m2/min,冲刷槽宽度为10 cm时,由于冲刷槽宽度较小,能够汇入细沟中的径流有限,细沟发育不明显,因此产沙率较小[23];当单宽流量为4.8×10-2m2/min时,径流量大,携沙能力强,径流对土体的冲刷作用掩盖了不同冲刷槽宽度对产沙率的影响,因此不同冲刷槽宽度条件下产沙率差异不显著。尤其体现在细沟开始发育阶段,不同冲刷槽宽度之间特征曲线重合度较高。
2.3 累积径流量和累积产沙量特征
对不同冲刷槽宽度条件下累积径流量、累积产沙量和平均含沙量进行多重比较分析,结果表明,单宽流量相同时,不同冲刷槽宽度之间累积径流量没有显著差异,3次重复试验数据标准差也较小,表明冲刷槽宽度对累积径流量影响不显著。从图4a和图4b可以看出,单宽流量为1.2×10-2m2/min时,冲刷槽宽度30 cm下累积产沙量和平均含沙量显著高于冲刷槽宽度10,50 cm下累积产沙量和平均含沙量(P<0.05),其他冲刷槽宽度下累积产沙量和平均含沙量差异不显著。冲刷槽宽度为30和50 cm时差异达到最大,累积产沙量分别为3163.02和955.74 kg/m2,平均含沙量分别为0.134和0.047 g/mL;单宽流量为2.4×10-2m2/min时,冲刷槽宽度为10 cm情况下累计产沙量和平均含沙量与其他宽度情况下差异显著(P<0.05),其他冲刷槽宽度下累积产沙量和平均含沙量差异不显著,冲刷槽宽度为10和30 cm时差异达到最大,累积产沙量分别为5 250.90和13 110.55 kg/m2,平均含沙量分别为0.112和0.245 g/mL;单宽流量为3.6×10-2m2/min时,冲刷槽为10 cm情况下平均含沙量显著低于冲刷槽宽度30、40 cm下平均含沙量(P<0.05),冲刷槽宽度为10和40 cm时平均含沙量差异达到最大,分别为0.165和0.252 g/mL;单宽流量为4.8×10-2m2/min时,不同冲刷槽宽度之间累积产沙量和平均含沙量均没有显著差异。

图4 累积产沙量和平均含沙量特征Fig.4 Characteristics of cumulative sediment yield and average sediment concentration
3 结论
本研究表明在坡度为15°条件下,单宽流量为1.2×10-2,2.4×10-2,3.6×10-2m2/min时,不同冲刷槽宽度之间径流率、产沙率存在显著差异(P<0.05);单宽流量为4.8×10-2m2/min时,不同冲刷槽宽度之间径流率、产沙率差异不显著。单宽流量一定,不同冲刷槽宽度下径流率随时间变化趋势相同。单宽流量为1.2×10-2m2/min时,不同冲刷槽宽度条件下产沙率和含沙量随时间变化趋势不同,冲刷槽宽度为10、20和30 cm时,产沙率和含沙量呈先增大后稳定波动变化,而当冲刷槽宽度为40 和50 cm时,产沙率和含沙量逐步递增,其他单宽流量下产沙率和含沙量随时间变化趋势相同,均呈增大-稳定-减小趋势。
总体来讲,当单宽流量为1.2×10-2,2.4×10-2,3.6×10-2m2/min时,不同冲刷槽宽度对崩积体侵蚀产流产沙特征影响达到显著水平(P<0.05),单宽流量为4.8×10-2m2/min时冲刷槽宽度对崩积体侵蚀产流产沙影响不显著。本试验以崩岗崩积体为对象进行研究,由于崩积体具有含沙量高、结构性差、易侵蚀等特点,与其他土壤差异较大,因此今后还需针对其他土壤类型研究冲刷槽宽度对侵蚀产流产沙特征的影响。
[1] 王礼先,孙保平,余新晓. 中国水利百科全书: 水土保持分册[M]. 中国水利水电出版社,2004:48-49.
[2] 林金石,庄雅婷,黄炎和,等. 不同剪切方式下崩岗红土层抗剪特征随水分变化规律[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(24):106-110. Lin Jinshi, Zhuang Yating, Huang Yanhe, et al. Shear strengths of collapsing hill in red soil as affected by soil moisture under different experimental methods[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(24): 106-110. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 梁音,宁堆虎,潘贤章,等. 南方红壤区崩岗侵蚀的特点与治理[J]. 中国水土保持,2009,30(1):31-34. Liang Yin, Ning Duihu, Pan Xianzhang, et al. The characteristics and govemance of collapsing hills in southern red soil erosion area[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China, 2009, 30(1): 31-34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 刘希林,唐川,张大林. 野外模拟崩岗崩积体坡面产流过程及水分分布[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(11):179-185. Liu Xilin, Tang Chuan, Zhang Dalin. Simulated runoff processes on colluvial deposits of Liantanggang Benggang and their water distributions[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(11): 179-185. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] Jiang Fangshi, Huang Yanhe, Wang Mingkuang, et al. Effects of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on steep colluvial deposit erosion in Southeast China[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2014, 78(5): 1741-1752.
[6] 蒋芳市,黄炎和,林金石,等. 坡面水流分离崩岗崩积体土壤的动力学特征[J]. 水土保持学报,2013,27(1):86-89,229. Jiang Fangshi, Huang Yanhe, Lin Jinshi, et al. The dynamic characteristics of soil detachment of slumping deposit by surface runoff in benggang[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013, 27(1): 86-89, 229. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 蒋芳市,黄炎和,林金石,等. 坡度和雨强对花岗岩崩岗崩积体细沟侵蚀的影响[J]. 水土保持研究,2014,21(1):1-5. Jiang Fangshi, Huang Yanhe, Lin Jinshi, et al. Effects of different rainfall intensities and slope gradients on rill erosion of colluvial deposits in granite Benggang[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 21(1): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 赖奕卡. 坡面土壤侵蚀影响因子研究进展[J]. 亚热带水土保持,2008,20(1):12-16. Lai Yika. Research progress of slope soil erosion factors[J]. Subtropical Soil and Water Conservation, 2008, 20(1): 12-16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 郭军权,刘敏,王文龙. 上方来水对浅沟侵蚀产沙的野外放水冲刷试验研究[J]. 水土保持学报,2012,26(3):49-52. Guo Junquan, Liu min, Wang Wenlong. Experimental study on upslope runoff effects on ephemeral gully erosion process[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2012, 26(3): 49-52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 汪邦稳,肖胜生,张光辉,等. 南方红壤区不同利用土地产流产沙特征试验研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(2):239-243. Wang Bangwen, Xiao Shengsheng, Zhang Guanghui, et al. Study on runoff and sediment yield characteristics under different land uses in red soil area of southern China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(2): 239-243. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] Wang Bing, Zhang Guanghui, Zhang X C, et al. Effects of near soil surface characteristics on soil detachment by overland flow in a natural succession grassland[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2014, 78(2): 589-597.
[12] 王军光,李朝霞,蔡崇法,等. 坡面冲刷过程中红壤分离速率定量研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境,2011,20(1):96-100. Wang Junguang, Li Zhaoxia, Cai Chongfa, et al. Quantitative research of red soil detachment rate in the slope scouring processResources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2011, 20(1): 96-100. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] Dong Yuequn, Zhuang Xiaohui, Lei Tingwu, et al. A method for measuring erosive flow velocity with simulated rill[J]. Geoderma, 2014, 232: 556-562.
[14] 赵纯清,蔡崇法,丁树文,等. 土壤侵蚀模拟试验的小型水槽设计[J]. 农业工程,2012,2(1):64-66. Zhao Chunqing, Cai Chongfa, Ding Shuwen, et al. Design of minitype flume for simulation experiment on soil erosion[J]. Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 2(1): 64-66. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] Zhang Guanghui, Liu Yumei, Han Yanfeng, et al. Sediment transport and soil detachment on steep slopes: I. Transport capacity estimation[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2009, 73(4): 1291-1297.
[16] Zhang Qingwen, Dong Yuequn, Li Fang, et al. Quantifying detachment rate of eroding rill or ephemeral gully for WEPP with flume experiments[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2014, 519: 2012-2019.
[17] 蒋芳市. 花岗岩崩岗崩积体侵蚀机理研究[D]. 福州:福建农林大学,2013. Jiang Fangshi. Erosion Mechanism of Colluvial Deposits in Granite Benggang[D]. Fuzhou:Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 蔡雄飞,王济,雷丽,等. 不同雨强对我国西南喀斯特山区土壤侵蚀影响的模拟研究[J]. 水土保持学报,2009,23(6):5-8. Cai Xiongfei, Wang Ji, Lei Li, et al. Laboratorial simulation of different rainfall intensity influence on soil erosion in southwest karst area, China[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2009, 23(6): 5-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 解文艳,樊贵盛. 土壤质地对土壤入渗能力的影响[J]. 太原理工大学学报,2004,35(5):537-540. Xie wenyan, Fan guisheng. Influence of soil structure on infiltration characteristics in field soils[J]. Journal of Taiyuan university of technology , 2004, 35(5): 537-540. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 彭怡,王玉宽,傅斌,等. 紫色土流失土壤的颗粒特征及影响因素[J]. 水土保持通报,2010,30(2):142-144. Peng Yi, Wang Yukuan, Fu Bin, et al. Particle characteristics and influencing factors of eroded purple soil[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2010, 30(2): 142-144. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 朱智勇,解建仓,李占斌,等. 坡面径流侵蚀产沙机理试验研究[J]. 水土保持学报,2011,25(5):1-7. Zhu Zhiyong, Xie Jiancang, Li Zhanbin, et al. Experimental study on mechanism of slope runoff-erosion-sediment yield[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2011, 25(5): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 赵淦,黄炎和,林金石,等. 流量及坡度对崩岗崩积体侵蚀的影响[J]. 水土保持研究,2014,21(2):11-16. Zhao Gan, Huang Yanhe, Lin Jinshi, et al. Effect of discharge and slope gradient on colluvial deposits erosion in Benggang[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 21(2): 11-16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 张科利. 黄土坡面侵蚀产沙分配及其与降雨特征关系的研究[J]. 泥沙研究,1991,36(4):39-46. Zhang Keli. A study on the distribution of erosion and sediment yield on loess slope and the relationship between the distribution and rain characteristics[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 1991, 36(4): 39-46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Effects of different width of scouring flumes on runoff and sediment yield of colluvial deposits of collapsing hill
Li Xuezeng, Huang Yanhe※, Lin Jinshi, Jiang Fangshi, Hao Fuxing, Guan Jiachun, Xu Huangji, Yang Dandan, Wang Zhenhong
(College of Resources and Environment, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou 350002, China)
Collapsing hill is the typical and serious erosion phenomenon in the red soil area of southern China. The colluvial deposit erosion is the main sediment source of collapsing hill, which has the characteristics of loose texture, bad structure, and high erodibility. Study of the influence of elements on erosion sediment in the process of slope erosion is of great significance for revealing the mechanism of slope erosion. The width of scouring flumes is one of the factors that affect the characteristics of erosion and yield of runoff and sediment in the process of slope scouring erosion but now has fewer research achievements. With the colluvial deposits of collapsing hill as the research object, and through the simulated scouring in laboratory, this study intended to disclose the impacts of different width of scouring flumes (10, 20, 30, 40 and 50 cm) and discharge per unit width (1.2×10-2, 2.4×10-2, 3.6×10-2and 4.8×10-2m2/min) on the slope scouring erosion and runoff and sediment yield of colluvial deposits. Soil samples were collected from the Longmen Town, Anxi County, Fujian Province in southeast China, and preprocessed according to the experimental standards. Results showed that: 1) The width of scouring flumes had significant effects on the runoff rate and sediment yield rate when the discharge per unit width was 1.2×10-2, 2.4×10-2and 3.6×10-2m2/min (P<0.05), while had no significant effects when the discharge per unit width was 4.8×10-2m2/min; 2) When the discharge per unit width was 1.2×10-2m2/min, the runoff rate increased gradually with the increase in time, when the discharge per unit width was 2.4×10-2and 3.6×10-2m2/min, the runoff rate increased at first and then became stable with the increase in time, and when the discharge per unit width was 4.8×10-2m2/min, the runoff rate increased at first and then decreased with the increase in time; when the discharge per unit width was 1.2×10-2m2/min, the trends of sediment yield rate and sediment concentration over time under different width of scouring flumes were different, and when the width of scouring flumes was 10, 20 and 30 cm, the sediment yield rate and sediment concentration increased at first and then became fluctuant, but increased with time all the way while the width of scouring flumes was 40 and 50 cm; when the discharge per unit width was 2.4×10-2, 3.6×10-2and 4.8×10-2m2/min, the sediment yield rate and sediment concentration under each width of scouring flumes showed an increase-stability-decrease trend with the increase in time; 3) When the discharge per unit width was constant, the difference of the cumulative runoff yield under different width of scouring flumes was not significant, and that of the cumulative sediment yield and the average sediment concentration were significant (P<0.05) while the discharge per unit width was 1.2×10-2, 2.4×10-2and 3.6×10-2m2/min; when the discharge per unit width was 4.8×10-2m2/min, the width of scouring flumes had no significant effects on the cumulative sediment yield and the average sediment concentration; 4) The width of scouring flumes had no effects on slope erosion and characteristics of runoff and sediment yield when the discharge per unit width was 4.8×10-2m2/min, and thus, faculative width of scouring flumes could be chosen while the discharge per unit width was 4.8×10-2m2/min. This research has used the colluvial deposits of collapsing hill as the research object and carried out the experiments under the condition of 15° slope, but colluvial deposits’ characteristics (loose texture, bad structure, high erodibility) are obviously different from other soil types, and thus, more studies aiming at other soil types about the effects of different width of scouring flumes on erosion and yield of runoff and sediment are needed, and further researches can also be conducted with other slope gradients.
scour; sand; runoff; collapsing hill; colluvial deposits; width of scouring flumes; discharge per unit width
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.09.019
S157.1
A
1002-6819(2016)-09-0136-06
李学增,黄炎和,林金石,蒋芳市,郝福星,关家椿,许煌基,杨丹丹,王振红. 不同宽度冲刷槽对崩岗崩积体产流产沙的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(9):136-141.
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.09.019 http://www.tcsae.org
Li Xuezeng, Huang Yanhe, Lin Jinshi, Jiang Fangshi, Hao Fuxing, Guan Jiachun, Xu Huangji, Yang Dandan, Wang Zhenhong. Effects of different width of scouring flumes on runoff and sediment yield of colluvial deposits of collapsing hill[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(9): 136-141. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.09.019 http://www.tcsae.org
2015-12-29
2016-03-14
国家自然科学基金项目(41001169;41571272);国家科技支撑计划项目(2014BAD15B0303)
李学增,男,河南林州人,研究方向为土壤侵蚀与治理。福州 福建农林大学资源与环境学院,350002。Email:xuezeng_li@163.com
※通信作者:黄炎和,男,广东饶平人,教授,博士,博士生导师,研究方向:土壤侵蚀与治理。福州 福建农林大学资源与环境学院,350002。Email:yanhehuang@163.com
·农业信息与电气技术·
