Evaluation of the water resources carrying capacity of Shandong peninsula, China
2016-12-12WANGKuifeng
WANG Kui-feng
Shandong Key Laboratory of Geological Process and Resource Utilization in Metallic Minerals, Key Laboratory of Gold Mineralization Process and Resource Utilization Subordinate to the Ministry of Land and Resource, Shandong Institute of Geological Sciences, Jinan 250013, China.
Abstract: Research on the carrying capacity and security of water resources is vital for its contribution to implementing sustainable development goals. The limitation of water resources is one of the most important factors that influence the sustainable utilization of resources.Studying the carrying capacity of water resources will not only facilitate monitoring and forecast of national resources and environmental carrying capacity, but also be valuable for building ecological civilization. According to the principles of evaluation system, the carrying capacity of water resources on Shandong peninsula is explored. A comprehensive evaluation model of the carrying capacity of water resources is constructed based on the carrying capacity of water resources index and the composite of water resources index. The results show that the capacity of water resources on Shandong peninsula is generally consistent with overexploitation, and that the development and utilization of water resources has reached a considerable scale under existing economic and technological conditions. The carrying capacity of water resources in this region is relatively small, and the contradiction between supply and demand of water resources is alarming. Relative countermeasures are put forward, to improve the water resources carrying capacity and to provide a basis for future sustainable development and utilization of water resources in this region.
Keywords: Water resources carrying capacity; Shandong peninsula; Evaluation; Water resources carrying capacity index
Introduction
Water is the source of all life on earth. Water is a basic resource and the fundamental element for human survival and underpins social development.However, in modern society, severe water shortage,water pollution, deterioration of water environment and other water supply crises have broken out,with increasing frequency, during social economic development. And water resource has gradually become one of the bottlenecks of regional sustainable development (CAO Jun-kuo et al. 2014;CHENG Guo-dong, 2002; DANG Li-juan and LI-Juan, 2015). Shandong peninsula lies in the middle of the western coast of the Pacific and on the eastern coast of China. The relative lack of water resources on Shandong peninsula, particularly the water supply in urban areas, is a result of excessive mining and the consequent recession of base river flows, factors that endanger the sustainable utilization of water resources (WANG Kui-feng et al. 2014a, b; WANG Kui-feng et al.2015).
Widespread research into water resources carrying capacity began in 1970s, but the output remained low. And it was mainly used as a component of sustainable development theory(Peterson D H, 2002). Study of the water resources carrying capacity on Shandong peninsula began in the mid-1980s, and has focused on the natural and social attributes of water resources, drainage basins,natural features of the region, and economic and social development goals for sustainable development (Theodor J S and Leanne S, 1995; ZHANG Ji and YU Su-jun, 2007; MA Yu-xiang et al. 2015).However, a systematic study and identification of water resources carrying capacity on Shandong Peninsula has not yet been established.
The relationship between the utilization of water resources and social economic development on Shandong peninsula based on previous research,the appropriate evaluation index system and a suitable comprehensive evaluation method are selected for evaluating the water resources carrying capacity, from which suggestions for future water resources utilization can be proposed.
1 Research method
A study on water resources carrying capacity needs to consider both the ability of water resources to maintain supply and demand and the environmental conditions for the water supply to be utilized. Therefore, the carrying capacity of the water resources should be evaluated from two aspects: the water resources loading capacity index,and degree of water resources development advantage. A common method of evaluating environmental quality comprehensively is the composite index of weighted average. And its weighting method is usually the Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP). Using the composite index method based on the weighted value of water resources loading capacity index and the degree of water resources development advantage,a comprehensive evaluation of water resources carrying capacity on Shandong Peninsula is carried out. Both aspects are considered of equal importance, thus both are weighted 0.5. The loading index model was used to evaluate water resources carrying capacity, which does not involve weighting. The degree of advantage for water resources development was calculated using a comprehensive evaluation model, consisting of five factors: Water network density, underground water yield property, groundwater exploitation potential, underground water depth, and water environmental conditions. Weights are assigned to parameters using the AHP method.
1.1 Water resources loading capacity index (C)
In recent years, water resources loading capacity index has gained popularity among researches in China and has been applied to water and soil environmental effects assessments of water resources development in arid regions and to regional ecological and environmental quality assessments. At the same time, as an important index of the overall water supply situation and evaluation of development potential for water resources, the water resources loading capacity index is widely used in rational development of regional water resources, water resources sustainability evaluation, water resources loading capacity evaluation, etc.
The water resources loading capacity index is a main indicator of the potential of water resources for development. It can be expressed with the population size and economic scale of a certain region supported by corresponding water resources,reflecting the relationship between water resources,population and economic growth. The water resources loading capacity index (C) formula is as follows:
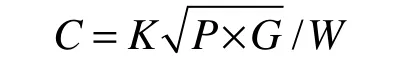
where, C=water resources loading capacity index;P=population (×104people); G=GDP (×108yuan);W=total amount of water resources (×108m³);K=rainfall-related coefficient. The value of K changes in line with the following formula, where R refers to annual rainfall measured in millimetres.

According to the calculated values of the water resources loading capacity index, considering exploitation potential of water resources, regions on Shandong peninsula can be categorized into five levels. The 5 levels are described in Table 1.
The definition of boundary values for the water resources loading index (10, 20, 30, 40) mainly refers to previous studies (FENG Zhi-ming and LIU Deng-wei, 2006; FU Gui-jun et al. 2015;WANG Kui-feng, 2015) and the calculated value of water resources loading index in 5 cities on Shandong Peninsula. Boundary values are used for categorization and distinction.
The next morning, as they passed under the gate, the girl said: Oh! Falada, tis you hang there ;and the head replied: Tis you; pass under, Princess fair: If your mother only knew, Her heart would surely break in two
At the same time, in order to comprehensively evaluate water resources carrying capacity along with the advantage level of water resources development, the water resources loading capacity index was valued as 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 (weak,comparatively weak, average, comparatively strong and strong).

Table 1 Water resources loading capacity index classification standard
1.2 Degree of water resources development advantage (R)
The degree of water resources development advantage mainly refers to the varying degrees of difficulty in water resources development and utilization, due to different hydrogeological conditions and water system characteristics.
According to prevailing hydrological conditions of Shandong peninsula, the elements selected for the comprehensive index method are: Water network density, underground water yield property,groundwater exploitation potential, underground water depth, and environmental conditions of water resources. The factors are weighted using the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) (Table 2).
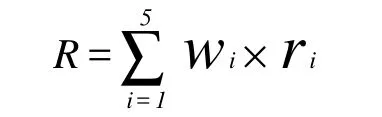
where, R=water resources development advantage value; r=evaluation factor value; w=evaluation factor weight.
Given that the index statistics units consist of natural and administrative units, in order to facilitate the calculation, the data need to be pre-processed and converted into the administrative units. The formula for this transformation is as follows:
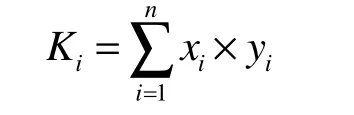
where, x=evaluation index; n=the number of indicators involved in the administrative units;y=weight of the index; K=comprehensive evaluation value of the level of water resources development advantage for indicator x in administrative unit i. Finally, according to five levels of advantage degrees of water resources development, grading standards are evaluated(Table 3).
1.3 Comprehensive evaluation of water resources carrying capacity
The water resources carrying capacity is calculated, using comprehensive weighted average index method. The water resources loading capacity index and index of water resources development advantage both are weighted 0.5. Referring to the evaluation standard of the two comprehensive evaluation indices in the range of 0.75-3.00,regarding each 0.75 value as a grading interval, five grades have been valued as weak, comparatively weak, average, comparatively strong and strong.Grading criteria is demonstrated in Table 4.
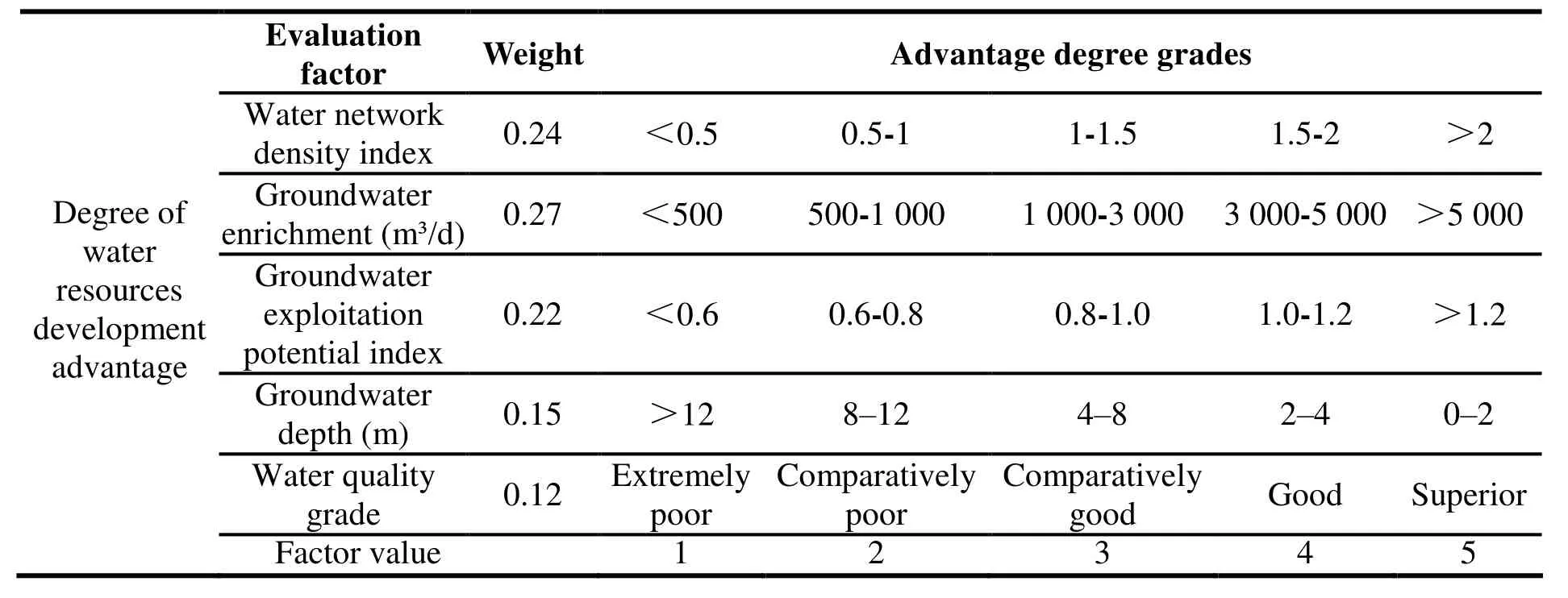
Table 2 Grading standards for degrees of water resources development advantage

Table 3 Degree of advantage in the water resources development scale
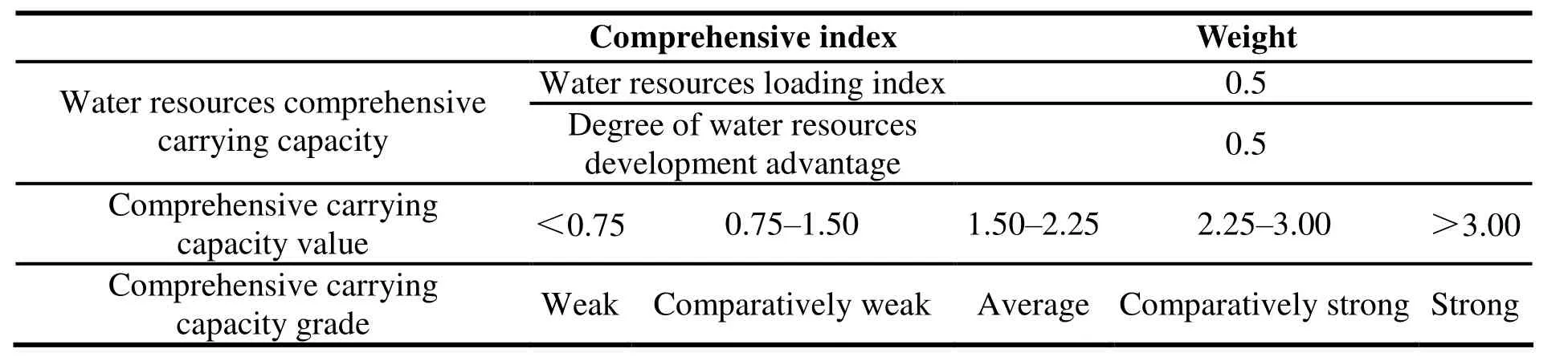
Table 4 Water resources development advantage scale
1.4 Data sources
Obtaining relevant water resources data on a national scale is difficult in China. Therefore, the evaluation unit selected for this study is at city level.Five cities (Qingdao, Yantai, Weifang, Weihai,Rizhao) are set as the case study evaluation units representing the present condition of water resources carrying capacity on Shandong peninsula. The characteristic evaluation indexes for the case study cities are divided into quantitative and qualitative indicators. The main data sources for the quantitative index are the “China City Statistical Yearbook” in 2012, “Statistical Yearbook of Shandong”, the“Shandong Water Resources Bulletin”, “National Economic And Social Development Statistics Bulletin of All Municipal Cities in Shandong”, and“Water Resources Quality Report of All Municipal Cities in Shandong”. Qualitative indicators are mainly from relevant recent research reports and results, such as water density indexes, underground water yield property, and exploitation potential of groundwater resources (HE Ke-qiang et al. 2009;LU Yao-ru et al. 2010). Some initial quantitative data was directly used for water resources evaluation,such as population size, GDP and water quality grades, while other data needed to be quantified through modelled calculation.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Characteristics of water resources loading index
The water resources loading index is calculated for the five city sites selected-Weifgang, Qingdao, Yantai, Rizhao and Weihai(Table 5). Fig. 1 illustrates the results of water resources loading index of each city.
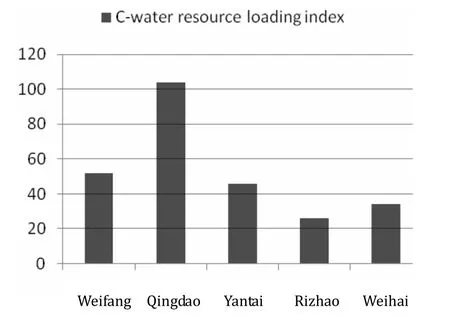
Fig. 1 Water resources loading index graph of five cities on Shandong peninsula, 2013

Table 5 The water resources loading index of five cities on Shandong peninsula, 2013
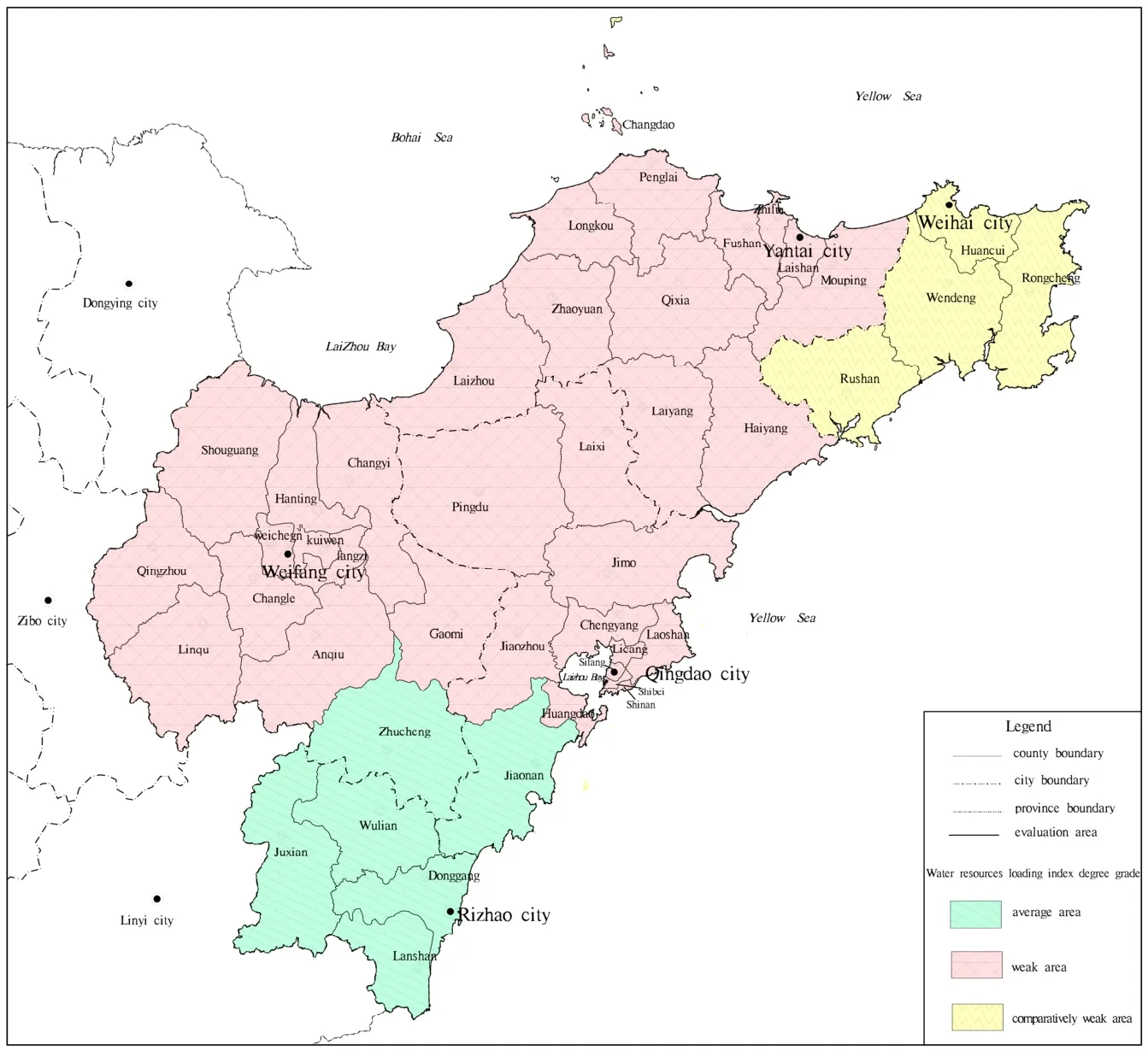
Fig. 2 Shandong peninsula water resources loading capacity index zoning map
The degree of water resources loading capacity across Shandong peninsula was found to be“weak”, “comparatively weak” or “average”, as illustrated in Fig. 2.
Table 5, Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 demonstrate that water resources loading capacity in the five cities of evaluation area is poor on average. In Rizhao City and Weihai City, the levels of water resources development and utilization are relatively low, as are the population densities, and the economic strength is comparatively weak. Consequently, for Rizhao and Weihai, the potential water resources loading capacity is relatively strong. However, the calculated water resources loading capacity for Rizhao and Weihai comes to “average” and“comparatively weak” respectively, due to their limited amount of water resources. Qingdao city has the most concentrated population. It is also the most economically developed city on Shandong peninsula. The water resources loading capacity index for Qingdao is the highest, at 104. A high level development and utilization of water resources in Qingdao has resulted in the lowest potential for further development and utilization.In order to improve regional water resources carrying capacity for Qingdao, further development of water resources will need to shift from traditional to untraditional forms, such as increasing the use of rainwater, desalination, and waste water recycling.
2.2 Degree of water resources development advantage
Collection of indexed statistical data allowed the relevant indicators in various regions to be standardized and unified to a score ranging from one to five according to the grading standards of water resources development advantage levels.Based on the weights of indicators, the composite index is calculated (Table 6, Fig. 3).
Table 6 and Fig. 3 illustrate that the composite index of water resources development advantage is“average” or “strong” in evaluated counties. The areas found to have an “average” level are widely distributed and account for 65% of the total, within which cities take up a large portion of the water resources development advantage levels. The areas with a “comparatively strong” level of water resources development advantage account for 30%.The areas with a “comparatively weak” level are distributed only partly in Qingdao City.
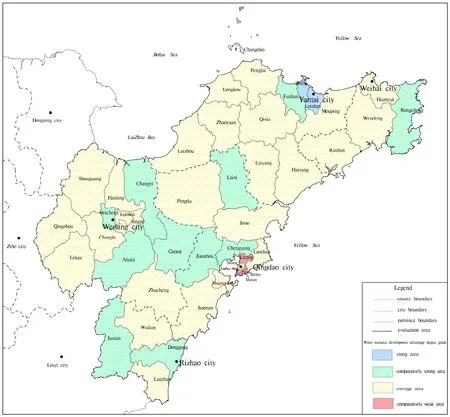
Fig. 3 Water resources development advantage degree evaluation map of Shandong peninsula

Table 6 Degree of water resources development advantage levels on Shandong peninsula
2.3 Comprehensive water resources carrying capacity
The water resources carrying capacity index and the index of water resources development advantage are integrated, both weighting 0.5. The composite weighted index method is used to calculate the comprehensive carrying capacity value for water resources development on Shandong peninsula. The water resources carrying capacity levels and zoning of five cities on Shandong peninsula are categorized into 5 grades:Weak, comparatively weak, average, comparatively strong and strong (Table 7, Fig. 4).
Table 7 illustrates that water resources carrying capacity for the five cities (43 county districts) on Shandong peninsula are mostly at an “average”level. Only two counties exhibit strong levels of water resources carrying capacity (Donggang and Juxian); seven counties are “comparatively strong”;three are “comparatively weak”; and others are“average”. The water resources carrying capacity shows considerable difference among the five cities and 43 counties on Shandong peninsula.
In the cities of Rizhao and Weihai, the overall water resources carrying capacity are “comparatively strong”, thanks to their reasonably well-developed industrial structure, high volume of per capita water resources, reduced levels of economic activities that would consume high levels of energy and water, and their low levels of groundwater exploitation. For Qingdao City, the overall water resources carrying capacity is“average”, with some counties being “comparatively weak”. The overall water resources carrying capacity for Yantai City is “average” The overall water resources carrying capacity for Weifang City is “average”, though some counties' carrying capacity is “comparatively strong”. Weifang's comparatively strong capacity is mainly due to its large population base, less abundant groundwater resources, increasing levels of economic activities that rely on high water consumption, low utilization rate of water resources, reduced availability of water resources per capita, and increasing levels of serious groundwater exploitation with commensurate increasing destruction of groundwater resources.

Fig. 4 Map of water resources comprehensive carrying capacity evaluation by divisions of Shandong peninsula

Table 7 Comprehensive carrying capacity evaluation of water resources by divisions on the Shandong peninsula
3 Conclusions and suggestions
The state of water resources carrying capacity on Shandong peninsula is evaluated using a comprehensive weighted average index method,combined with indexes for the degree of water resources carrying capacity and the degree of water development advantage. It is demonstrated that water resources carrying capacity on Shandong peninsula is, on the whole, currently at an average level. Although parts of Weihai and Rizhao cities are comparatively strong, water resources carrying capacity in Qingdao City is at a comparatively low level because of its large demand for water and high-intensity social and economic development.From the perspective of long-term development,greater water resources carrying capacity is required to guarantee social and economic development of Shandong peninsula. Therefore,the following countermeasures are put forward:
(1) Prioritize the development of deep water resources by shifting the focus of water resources development from a wide range of sources to concentrated deep sources; transform the waterintensive economy into a water-efficient economy;limit the development of water-intensive and high-pollution industries; improve the rate of industrial water use and lower the demand; and encourage innovation and development of water-saving industries.
(2) From a long-term point of view, water resources on Shandong peninsula are far from being sufficient to support the trajectory of economic and social development. Construction of new water sources is necessary, as are increasing investment, optimizing structure and spatial pattern of regional water resources utilization, and increasing the amount of transported water and external artificial introduction.
(3) Sustainable utilization of water resources should be a priority, and efficiency-improving measures should be encouraged. At the same time,planning, management and decision-making concerning water resources development and utilization should be strengthened by the government to ensure adequate clean water resources for all purposes, far into the future.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by Shandong Provincial Bureau of Statistics (No. KT15019&KT13060), and China Geological Survey (No.12120113007200) Scientific Research Funds. We also greatly appreciate the efforts of editors and reviewing experts for their contributions to our research article.
杂志排行
地下水科学与工程(英文版)的其它文章
- Characteristics analysis and model prediction of sea-salt water intrusion in lower reaches of the Weihe River,Shandong Province, China
- Features and evaluation of sea/saltwater intrusion in southern Laizhou Bay
- Distribution characteristics of tritium in the soil in Beishan area of Gansu Province
- Study on ecological and economic effects of land and water resources allocation in Sanjiang Plain
- Research on Pisha-sandstone's anti-erodibility based on grey multi-level comprehensive evaluation method
- Geological environment impact analysis of a landfill by the Yangtze River
