IL-17A协同GM-CSF和LPS促进骨髓细胞衍生树突状细胞的分化和成熟研究①
2016-11-11刘腾丽郑佞波赵慧丽梁聚友孙丽妲
刘腾丽 乔 赛 郑佞波 唐 莹 赵慧丽 王 悦 梁聚友 孙丽妲 白 虹
(天津医科大学基础医学院免疫学系,天津市细胞和分子免疫学重点实验室,国家教育部免疫微环境与疾病重点实验室,天津300070)
·生物治疗·
IL-17A协同GM-CSF和LPS促进骨髓细胞衍生树突状细胞的分化和成熟研究①
刘腾丽乔赛郑佞波唐莹赵慧丽王悦梁聚友孙丽妲白虹
(天津医科大学基础医学院免疫学系,天津市细胞和分子免疫学重点实验室,国家教育部免疫微环境与疾病重点实验室,天津300070)
目的:探讨IL-17A对小鼠骨髓细胞衍生树突状细胞分化和成熟的影响。方法:分离小鼠骨髓细胞,加入含GM-CSF(20 ng/ml)RPMI1640完全培基培养8 d,诱导小鼠骨髓单个核细胞向DC分化,加入LPS(1 μg/ml)继续培养36 h,进一步诱导DC成熟,同时在骨髓细胞衍生诱导DC分化及成熟的不同阶段加入不同浓度的rmIL-17A(10、100 ng/ml),采用流式细胞术检测DC表面共刺激分子的表达,ELISA方法检测DC培养上清中IL-12p40和IL-10水平。结果:rmIL-17A可促进GM-CSF诱导骨髓细胞衍生DC表面共刺激分子CD40、CD80、CD86和MHCⅡ的表达,且具有剂量依赖性,其中以高浓度rmIL-17A刺激组的CD40及 MHCⅡ表达增加最显著;在LPS诱导DC成熟阶段加入rmIL-17A,骨髓细胞衍生DC共刺激分子CD40、CD80、CD86 和MHCⅡ 的表达均明显增加,并且随着rmIL-17A浓度的增加,CD86 和MHCⅡ的表达水平也随之增高;同时与未加rmIL-17A的对照组相比,低浓度rmIL-17A组LPS刺激骨髓细胞衍生DC 分泌IL-12p40 和IL-10水平均显著增加(P<0.001),高浓度rmIL-17A组IL-12p40水平显著增高(P<0.001),但IL-10水平没有变化。结论:IL-17A可促进GM-CSF诱导的骨髓细胞衍生DC前体细胞表型发展,并能协同LPS诱导骨髓衍生DC的分化和成熟。
IL-17A;粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子;骨髓衍生树突状细胞;脂多糖
树突状细胞(Dendritic cells,DC)是唯一能活化初始T细胞的抗原提呈细胞。成熟DC表达高水平的共刺激分子以及某些黏附分子等,增强DC抗原提呈作用,促进T细胞增殖。成熟DC还能产生IL-12、IL-10、IL-6等细胞因子,影响初始T细胞(Th0)的分化,在机体抗肿瘤、抗感染、移植排斥及自身免疫性疾病的预防与治疗中发挥着重要作用[1-3]。体内DC数量非常少,难于收集,所以建立有效的DC体外扩增方法体系对一些疾病的研究非常重要。Rosenzwaig等[4]运用GM-CSF和TNF-α刺激体外培养的CD34+干细胞,DC比例高达20%~38%。另外,在体外培养DC的后期加入LPS能诱导髓系DC的成熟[5]。
IL-17(又称IL-17A)主要由Th17细胞分泌,作为促炎细胞因子,参与一些疾病相关的炎症病理反应,如牛皮癣和风湿性关节炎等[6]。IL-17A 也被证实在抵抗胞外菌感染中具有重要作用,例如铜绿假单胞菌[7]、肺炎克雷伯氏菌[8],其作用机制主要与其对中性粒细胞的趋化作用有关。但在胞内菌感染中,IL-17A作用机制不同于胞外菌,已有报道显示IL-17A通过调节DC的功能促进CTL对李斯特菌感染的免疫应答[9]。Bai等[10]的研究也显示,在宿主抗衣原体呼吸道感染中,IL-17A通过调节DC功能促进抗衣原体特异性Th1免疫应答而发挥免疫保护作用。虽然一些体内研究已经证实,IL-17A对DC的分化成熟有影响,但是在体外IL-17A对DC分化和成熟的作用鲜有报道。本研究首先建立小鼠骨髓来源的树突状细胞体外扩增模型,在骨髓衍生DC 诱导分化的不同阶段加入不同浓度的rmIL-17A,采用流式细胞术和ELISA方法分别检测不同实验条件下骨髓衍生DC 表面分子的表达以及细胞因子分泌状态,探讨IL-17A对骨髓衍生DC分化和成熟的影响。
1 材料与方法
1.1材料
1.1.1 小鼠骨髓细胞的分离在Lutz方法[11]的基础上加以改进。无菌状态下分离6~8周龄雌性BALB/c小鼠(购自军事医学科学院实验动物中心)胫骨和股骨,用0.45 mm针头的注射器吸取冷RPMI1640(Hyclone,美国)冲出骨髓细胞,离心、弃上清后向沉淀细胞中加ACK(150 mmol/L NH4Cl,10 mmol/L KHCO3,0.1 mmol/L EDTA)破除红细胞,洗去ACK,沉淀细胞用含10%FBS(Hyclone,美国)的RPMI1640完全培基重悬,调节细胞终浓度为2×106ml-1。
1.2方法
1.2.1小鼠骨髓细胞衍生诱导DC的分化和成熟取上述骨髓细胞悬液1 ml放入培养皿中,加入9 ml [含rmGM-CSF(20 ng/ml,Pepro Tech Inc公司)和/或 rmIL-17A(10 ng/ml or 100 ng/ml,Biolegend公司)]RPMI1640完全培基,培养8 d。分别于培养第3天和第6天补充新鲜完全培基[含rmGM-CSF(20 ng/ml)和/或rmIL-17A(10 ng/ml or 100 ng/ml)],于培养第8天收集非贴壁细胞,使用MACS方法分离纯化CD11c+骨髓细胞衍生DC。取纯化后的DC放入24孔培养板中(8×105细胞/孔)继续培养36 h,加入1 μg/ml LPS(Pepro Tech Inc公司)和/或rmIL-17A(10、100 ng/ml)。收获培养上清液检测IL-12p40及IL-10水平,沉淀细胞检测DC表面分子表达。
1.2.2流式细胞术检测骨髓细胞衍生DC表面分子的表达取各组CD11c+骨髓细胞衍生DC,调整细胞浓度为106ml-1,加入1 μl抗鼠APC-CD11c抗体(BD公司),及1 μl FITC标记的抗鼠CD40、MHCⅡ、CD80、CD86抗体(BD公司),4℃避光孵育30 min,用staining buffer洗涤2次,用200 μl 2%多聚甲醛固定后,用流式细胞仪(CantoⅡ,BD公司)检测。采用BD公司的CellQuest 软件分析。
1.2.3ELISA检测骨髓细胞衍生DC细胞因子的分泌用双抗夹心法检测细胞培养上清中细胞因子的水平,用全自动酶标仪(Bio-Rad,美国)读取405 nm OD值。ELISA抗体和标准品均购自eBioscience公司。
1.3统计学分析用SPSS12.0 版的统计软件分析数据,用Student′t检验进行组间比较,以P<0.05为有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1IL-17A可促进GM-CSF诱导骨髓细胞衍生DC前体细胞表型的发展在GM-CSF诱导的骨髓细胞衍生DC分化阶段,加入低浓度rmIL-17A(10 ng/ml)及高浓度rmIL-17A(100 ng/ml),与未加rmIL- 17A对照组相比,骨髓细胞衍生DC表面分子 CD40、CD80、CD86和 MHCⅡ的表达水平均增加,且具有剂量依赖性,以高浓度rmIL-17A刺激组的CD40及 MHCⅡ表达增加最显著,见图1。
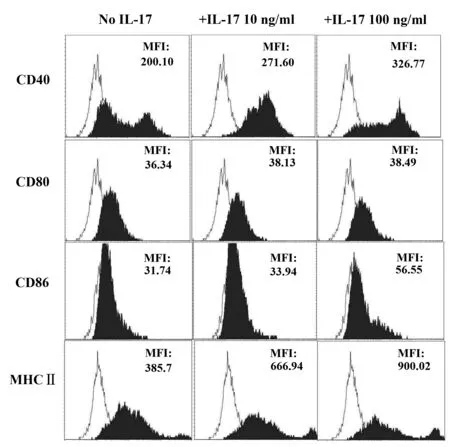
图1 rmIL-17A对GM-CSF诱导的骨髓细胞衍生DC前体细胞表型的影响Fig.1 Effects of rmIL-17A on phenotype of BMDC progenitors propagated in GM-CSF
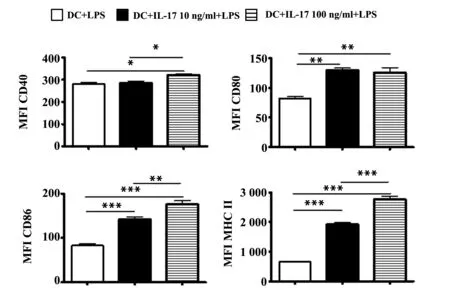
图2 rmIL-17A对LPS诱导的骨髓细胞衍生DC表面分子表达的影响Fig.2 Effects of rmIL-17A on surface molecules expression of BMDC induced by LPSNote: n=4/group,*.P<0.05,**.P<0.01,***.P<0.001.
2.2IL-17A可协同LPS上调骨髓细胞衍生DC表面分子的表达骨髓细胞衍生DC 经GM-CSF刺激培养8 d后,加入含LPS(1 μg/ml)和/或rmIL-17A(10、100 ng/ml)的RPMI1640完全培基中继续培养36 h,与诱导成熟过程中不加rmIL-17A的对照组比较,低浓度rmIL-17A刺激组骨髓细胞衍生DC共刺激分子CD80、CD86 和MHCⅡ的表达水平均明显增加(P<0.01,P<0.001,P<0.001),并且随着rmIL-17A浓度的增加,CD86和MHCⅡ的表达水平也随之增高(P<0.01,P<0.001),但CD40的表达水平只有在高浓度rmIL-17A刺激组显著增加(P<0.05),见图2。

图3 rmIL-17A对LPS刺激的骨髓细胞衍生DC细胞因子分泌的影响Fig.3 Effects of rmIL-17A on cytokines secreted by BMDC with stimulation of LPSNote: n=4/group,**.P<0.01,***.P<0.001.
2.3IL-17A可协同LPS上调骨髓细胞衍生DC细胞因子IL-12p40 和IL-10的分泌用LPS诱导DC发育成熟过程中,与未加rmIL-17A的对照组相比,低浓度rmIL-17A(10 ng/ml)组LPS刺激骨髓细胞衍生DC分泌IL-12p40和IL-10水平均显著增加(P<0.001);高浓度rmIL-17A(100 ng/ml)组DC 分泌IL-12p40水平显著增高(P<0.001),但IL-10没有变化,见图3。
3 讨论
IL-17A作为炎症介质,与炎症反应、自身免疫性疾病及移植排斥反应的发生和发展密切相关,主要通过刺激靶细胞释放前炎症细胞因子及动员中性粒细胞发挥作用[12]。我们先前的研究结果显示,IL-17A通过直接调节DC的功能促进Th1细胞在小鼠衣原体感染中的免疫应答[10],本研究通过体外实验进一步阐述了IL-17A对DC不同分化阶段的影响。首先,探讨了IL-17A对骨髓细胞衍生DC前体表型的影响,用含rmIL-17A及GM-CSF的完全培基联合培养小鼠骨髓细胞衍生DC 前体细胞,结果显示,IL-17A可促进GM-CSF诱导的骨髓细胞衍生DC前体表面分子CD40、CD86和MHCⅡ的表达。其次,探讨了IL-17A对培养后期LPS刺激骨髓细胞衍生DC成熟的影响。骨髓细胞经GM-CSF诱导分化后,加入LPS,联合或者不联合rmIL-17A(10、100 ng/ml)刺激骨髓衍生DC, IL-17A上调了LPS刺激的骨髓细胞衍生DC 共刺激分子的表达,同时也增加了骨髓衍生DC IL-12p40和IL-10产生水平。
作为专职APC,DC除具有提呈抗原,激发机体产生免疫应答的重要功能外,成熟DC还能产生大量的细胞因子,调节免疫应答。DC分泌的细胞因子作为T细胞活化的第三信号在很大程度上决定了免疫反应的类型,如DC通过分泌IL-12和IFN-γ等诱导Th0向Th1细胞分化,通过分泌IL-10抑制抗原特异性T细胞增殖,诱导Treg和CD8+T细胞分化,在维护机体免疫平衡中发挥了重要作用[13]。本文结果显示,在体外IL-17A能够促进LPS诱导的骨髓细胞衍生DC 分泌高水平IL-12p40和IL-10,提示IL-17A可能对Th1以及Treg分化有影响。Duan等[14]体内研究结果证实,在同种异体器官移植排斥反应中IL-17通过调节DC的功能促进Th1细胞应答。以上研究结果为进一步开展对DC的深入探讨以及临床应用奠定了基础。
Lubberts等[15]使用表达IL-17R的BM嵌合体小鼠,证明在诱导关节炎模型的佐剂中,非造血细胞上IL-17R信号对慢性破坏性滑膜炎的形成非常重要,该研究结果提示,IL-17通过与受体特异性结合,激活相应的信号通路,发挥促进炎症发展、免疫排斥、造血等功能。Mary等[16]研究结果显示,20%的骨髓细胞衍生DC前体细胞表达IL-17R,但是,充分分化的骨髓衍生DC上IL-17R表达较少。这与本文结果中IL-17A促进骨髓衍生DC前体细胞表型发育,但对充分分化的骨髓细胞衍生DC的成熟无影响(数据未显示)相符。
总之,本次体外实验不仅成功构建了骨髓细胞衍生DC体外扩增模型,还揭示了在体外IL-17A可通过协同GM-CSF和LPS影响骨髓细胞衍生DC的发育和成熟,但具体机制还需要进一步的研究。
[1]Chuang L,Wu KG,Pai C,etal.Heat-killed cells of lactobacilli skew the immune response toward T helper 1 polarization in mouse splenocytes and dendritic cell-treated T cells[J].J Agric Food Chem,2007,55(26):11080-11086.
[2]Wilson NJ,Boniface K,Chan JR,etal.Development cytokine profile and function of human interleukin 17-producing helper T cells[J].Nat Immunol,2007,8(9):950-957.
[3]Acosta-Rodriguez EV,Napolitani G,Lanzavecchia A,etal.Interleukins 1β and 6 but not transfor ming growth factor-β are essential for the differentiation of interleukin 17-producinghumanT helper cells[J].Nat Immunol,2007,8(9):942-949.
[4]Rosenzwajg M,Camus S,Guigon M,etal.The influence of interleukin-4,IL-13,and Flt-3 ligand on human dendritic cell differentiation from cord blood CD34+progenitor cells[J].Exp Hematol,1998,26(1):63-72.
[5]Manfred B,Lutz NA,Kukutsch MM,etal.Culture of bone marrow cells in GM-CSF plus high doses of lipopolysaccharide generates exclusively immature dendritic cells which induce alloantigen-specific CD4 T cell anergy in vitro[J].Eur J Immunol,2000,30(4):1048-1052.
[6]Kirkham BW,Kavanaugh A,Reich K.Interleukin-17A:a unique pathway in immune-mediated diseases:psoriasis,psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis[J].Immunology,2014,141(2):133-142.
[7]Dubin PJ,Kolls JK.IL-23 mediates inflammatory responses to mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in mice[J].Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physio,2007,292(2):519-528.
[8]Daniel E,Dulek DC,Newcomb KG,etal.Allergic airway inflammation decreases lung bacterial burden following acute klebsiella pneumoniae infection in a neutrophil-and CCL8-dependent manner[J].Infect Immun,2014,82(9):3723-3739.
[9]Xu S,Han Y,Xu X,etal.IL-17A-producing gammadeltaT cells promote CTL responses against Listeria monocytogenes infection by enhancing dendritic cell cross-presentation[J].J Immunol,2010,185(10):5879-5887.
[10]Bai H,Cheng J,Gao X,etal.IL-17/Th17 promotes type 1 T cell immunity against pulmonary intracellular bacterial infection through modulating dendritic cell function[J].J Immunol,2009,183(9):5886-5895.
[11]Lutz MB,Kukutsch N,Ogilvie AL,etal.An advanced culture method for generating large quantities of highly pure dendritic cells from mouse bone marrow[J].J Immunol Methods,1999,223(1):77-92.
[12]Marcal JR,Samuel RO,Fernandes D,etal.T-helper cell type 17/regulatory T-cell immunoregulatory balance in human radicular cysts and periapical granulomas [J].J Endod,2010,36(6):995-999.
[13]Sakaguchi S.Regulatory T cells:key controllers of immunologic self-tolerance[J].Cell,2000,101(5):455-458.
[14]Duan L,Chen J,Xia Q,etal.IL-17 promotes Type I T cell response through modulating dendritic cell function in acute allograft rejection[J].Int Immunopharmacol,2014,20(2):290-297.
[15]Lubberts E,Schwarzenberger P,Huang W,etal.Requirement of IL-17 receptor signaling in radiation-resistant cells in the joint for full progression of destructive synovitis[J].J Immunol,2005,175(5):3360-3368.
[16]Mary A,Antonysamy WC,Fanslow FF,etal.Evidence for a role of IL-17 in organ allograft rejection:IL-17 promotes the functional differentiation of dendritic cell progenitors[J].J Immunol,1999,162(1):577-584.
[收稿2015-11-11修回2015-12-11]
(编辑倪鹏)
IL-17A promotes differentiation and maturation of bone marrow-derived dendritic cells by cooperating with GM-CSF and LPS
LIU Teng-Li,QIAO Sai,ZHENG Ning-Bo,TANG Ying,ZHAO Hui-Li,WANG Yue,LIANG Ju-You,SUN Li-Da,BAI Hong.
Key Laboratory of Cellular and Molecular Immunology of Tianjin,Department of Immunology,School of Basic Medical Science,Tianjin Medical University,Tianjin 300070,China
Objective:To investigate the effect of IL-17A on the differentiation and maturation of murine bone marrow-derived dendritic cells(BMDCs).Methods: Murine bone marrow cells were isolated and cultured in RPMI1640 complete medium in the presence of GM-CSF(20 ng/ml) for 8 days to induce differentiation of murine bone marrow cells to DC progenitors.Then these cells were treated with LPS(1 μg/ml) for 36 h which polarized immature DCs into mature DCs.Different concentrations of rmIL-17A(10 or 100 ng/ml) was added to the culture medium at different stages of BMDC differentiation and maturation.Co-stimulatory molecules expression on BMDC were analyzed by flow cytometry,and the culture supernatants were analyzed for IL-12p40 and IL-10 level by ELISA.Results: rmIL-17 could promote co-stimulatory molecules( CD40,CD80,CD86 and MHCⅡ) expression on BMDCs in a does-dependent manner,especially,the expression of CD40 and MHCⅡ had a significant increase in high concentration of rmIL-17A group;rmIL-17A was added while LPS induced maturation of BMDCs.CD40,CD80,CD86 and MHCⅡ expression on BMDC increased sharply in LPS plus rmIL-17A stimulation group,besides,CD86,MHCⅡ showed a higher level expression on BMDC with the increase of concentration of rmIL-17A.Furthermore,secretion of IL-12p40 and IL-10 increased significantly in the group of DCs treated with LPS plus low concentration of rmIL-17 compared with the group without rmIL-17(P<0.001).However,high concentration of rmIL-17A group showed significantly higher levels of IL-12p40(P<0.001),but there was no difference in IL-10.Conclusion: IL-17A promotes the phenotypic development of BMDC progenitors propagated in GM-CSF and cooperate with LPS to induce BMDC differentiation and maturation.
IL-17A;GM-CSF;BMDC;LPS
10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2016.10.015
①本文受国家自然科学基金(31070797)、天津市应用基础及前沿技术研究计划重点项目基金(15JCZDJC34900,11JCZDJC16200)及教育部博士点基金(20121202110012)资助。
刘腾丽(1990年-),女,硕士,主要从事感染免疫方面的研究,E-mail:liutengli_27@126.com。
及指导教师:白虹(1962年-),女,教授,博士生导师,主要从事感染免疫方面的研究,E-mail:hongbai25@163.com。
R392.12
A
1000-484X(2016)10-1477-04