基于马田系统的2可加Choquet积分多属性决策方法
2016-10-14常志朋程龙生刘家树
常志朋程龙生刘家树
基于马田系统的2可加Choquet积分多属性决策方法
常志朋1,2,程龙生1,刘家树2
(1.南京理工大学经济管理学院,江苏南京 210094;2.安徽工业大学经济学院,安徽马鞍山 243002)
在实际决策问题中,决策属性间往往存在一定的交互作用,而传统决策方法并不能有效处理。针对这种情况,提出了一种基于马田系统和2可加Choquet积分集成算子的多属性决策方法。2可加Choquet积分集成算子是在2可加模糊测度和Choquet积分算子的基础上推导而得,由单个属性的Shapley值和两两属性间的交互指标构成。为了计算Shapley值,首先提出了一种基于马田系统的属性集重要程度测度方法,并给出了合理性分析,然后根据属性集中的所有属性在决策过程中应表现出积极的合作关系来优化单个属性的全局重要程度,最后将单个属性的相对重要程度和全局重要程度进行融合,得到单个属性的Shapley值;对于交互指标的计算,根据无偏好决策方案集在相同约束条件下应平等竞争的原理,构建了基于多目标的交互指标优化模型。最后基于所得到的Shapley值和交互指标对各候选方案的评价信息进行集成。实例验证结果表明该方法是可行的,能够处理属性间存在交互作用的大规模决策问题。
马田系统;2可加Choquet积分;2可加模糊测度
0 引言
在利用基于经典可加测度的线性集成算子处理多属性决策问题时,属性之间需要彼此独立,然而在实际决策问题中,属性间往往存在一定的交互作用或关联作用,因此传统的线性集成算子并不能有效的处理实际决策问题。Choquet积分[1]是定义在模糊测度基础上的非线性集成算子[2, 3],能够有效处理决策属性间存在的交互作用。应用Choquet积分的前提是确定模糊测度,但是模糊测度确定起来十分复杂,如果有个属性,那么就需要确定个参数。针对这种情况,1974年Sugeno[4]提出了模糊测度,模糊测度虽然将参数减少到个,但是不能充分描述属性间的交互作用,即要么将属性间的交互作用全部描述为积极的合作关系,要么将属性间的交互作用全部描述为消极的合作关系,或者将属性间的交互作用描述为彼此独立[5]。1996年Grabisch[6]提出了可加模糊测度的概念,并在此基础之上定义了2可加模糊测度。由于在确定2可加模糊测度时,只需要确定单个属性的Shapley值和两两属性间的交互指标,因此不但降低了计算的复杂性,而且在一定程度上提高了属性间的表示能力。在处理多属性决策问题时,为避免计算2可加模糊测度,Grabisch[7]根据2可加模糊测度和Choquet积分算子推导出了2可加Choquet积分算子,2可加Choquet积分算子可以直接利用单个属性的Shapley值和两两属性间的交互指标对决策方案的属性值进行集成。
对于单个属性的Shapley值,目前常用的方法主要有:权重法[8]、菱形成对比较法[9]等。这些方法都能根据决策者的知识、经验和决策偏好,通过两两比较确定单个属性的Shapley值,但是不足之处是这些方法都是从局部考虑单个属性的Shapley值,而Shapley值是全局重要性指标[4],即在确定Shapley值时不仅要从局部考虑单个属性的相对重要程度,而且还要从全局考虑包含单个属性后子集的重要程度变化[4],为此本文提出了一种基于马田系统[10-12](Mahalanobis-Taguchi System, MTS)的单个属性Shapley值计算方法。对于两两属性间的交互指标计算,目前常用的方法主要有菱形成对比较法[9, 13]、决策偏好法[14]等,这些方法在实际应用中都取得了良好的效果,但是这些方法都是主观计算方法,如菱形成对比较法和转换法需要决策者来判断两两属性间存在何种交互关系和交互度的大小,决策偏好法需要决策者来确定部分方案的排序或其他偏好参数。本文根据无偏好决策方案集在相同约束条件下应平等竞争的原理,构建了基于多目标的交互指标优化模型,该方法是一种客观计算方法。最后通过实例验证了本文提出的方法是可行的。
1 马田系统
MTS是由日本著名质量工程学家Taguchi在质量工程学基础上发展起来的一种模式识别技术[10]。该方法的一个重要功能是可以利用基于马氏距离的信噪比测度属性集在分类过程中的重要程度,即属性集对MTS能够正确判断类别的贡献。特别是当属性间存在相关性时,由于马氏距离是一种协方差距离,因此能够很好的测度属性集的重要程度。MTS的分类方法参见文献[15, 16]。本文详细介绍用MTS测度属性集重要程度的方法,具体步骤如下:
步骤1确定基准空间;
选取某类样本,将其在各属性下的均值、标准差和相关系数矩阵作为测度的基准空间,本文选取样本集作为参考样本,计算测度的基准空间。
3)计算属性间的相关系数矩阵,
证明:
2 2可加Choquet积分
定义1[4]设为属性集,是的幂集,集函数满足下面两个条件:
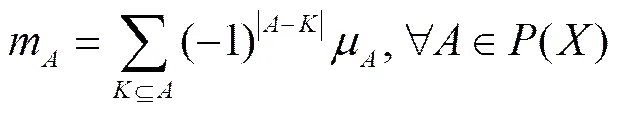
定义2[6]称定义在上模糊测度,如果满足如下条件
因此根据式(8)和定义2可知,2可加模糊测度可以表示为
当利用2可加模糊测度处理多属性决策问题时,为避免决策结果不一致,2可加模糊测度应满足如下单调性和正则性[6]。
基于模糊测度的Choquet积分作为一种非线性集成算子,可以有效处理属性间具有交互作用或关联作用的多属性决策问题。Grabisch[20]利用单个属性的Shapley值和两属性间的交互指标,定义了2可加Choquet积分。
由于2可加Choquet积分算子只涉及单个属性的Shapley值和两个属性的交互指标,特别是Shapley值满足约束条件,可以在一定程度上降低确定的难度。但是要保证利用式(12)所确定的2可加模糊测度具有单调性和正则性。因此当给定的情况下,要满足如下约束条件[6],
3 决策方法
3.1 问题描述
3.2 数据规范化
对于效益型决策属性
对于成本型决策属性
3.3 利用MTS计算单个属性的Shapley值
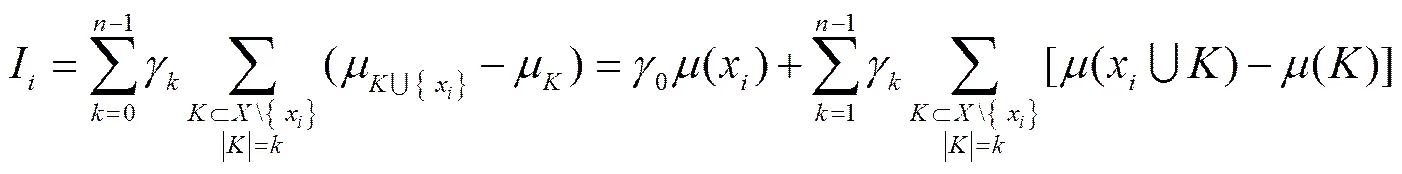
对于一个多属性决策问题为了使决策效果达到最优,应该使属性集(,)中各属性都表现出积极的合作关系,即在决策过程中属性集的重要性不小于中所有属性单独使用时的重要性之和,即

2)由于马氏距离是一种协方差距离,因此用基于马氏距离的信噪比测度属性集在分类过程中的重要程度,能够很好的考虑中所有属性间的交互作用;
3.4 交互性指标的计算
对于式(20)的求解,应使每个决策方案的2可加Choquet积分综合属性值达到最大,但是在相同的约束条件下,不可能使每个决策方案的2可加Choquet积分综合属性值达到最大,需要各方做出适当的妥协,得出唯一的最佳妥协解。最佳妥协解的求解步骤如下:
2)构造单目标优化函数

(22)
3.5 决策步骤
步骤1利用AHP法计算各决策属性的相对重要程度
步骤2 利用MTS计算属性集的重要程度
步骤3 计算单个决策属性的全局重要程度
步骤4 计算单个决策属性的Shapley值
步骤7计算各决策方案的2可加Choquet积分综合属性值。
4 实例计算
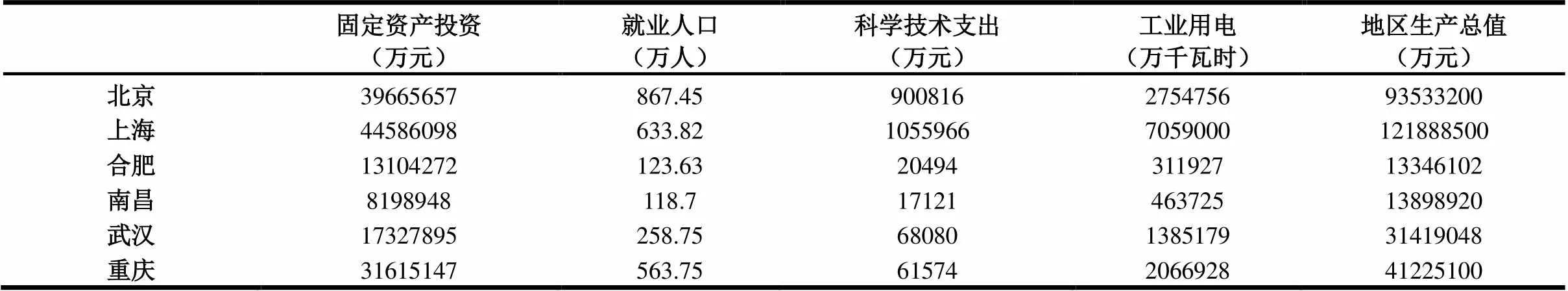
表1 6个城市的数据
步骤1利用AHP法通过两两比较确定各决策属性的相对权重;
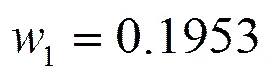
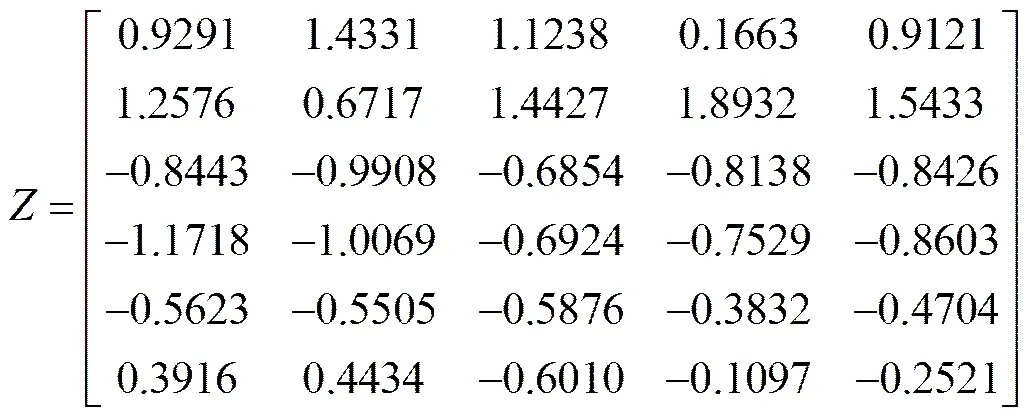
根据表1确定正负理想样本,并利用式(4)对其进行标准化得
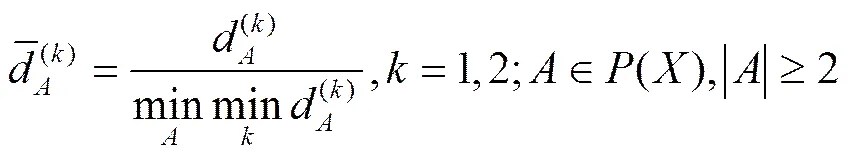

表2 正负理想样本的马氏距离
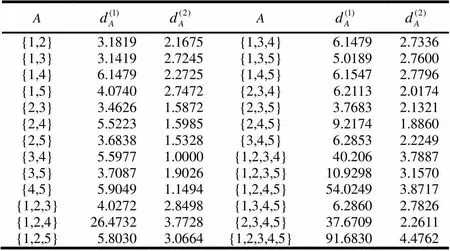
表3 规范化后的正负理想样本马氏距离
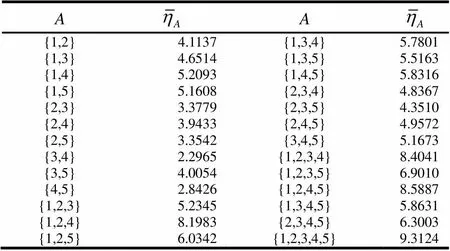
表4 A的重要程度

表5 规范化后的A的重要程度
步骤3利用式(18)构建优化模型,计算单个决策属性的全局重要程度
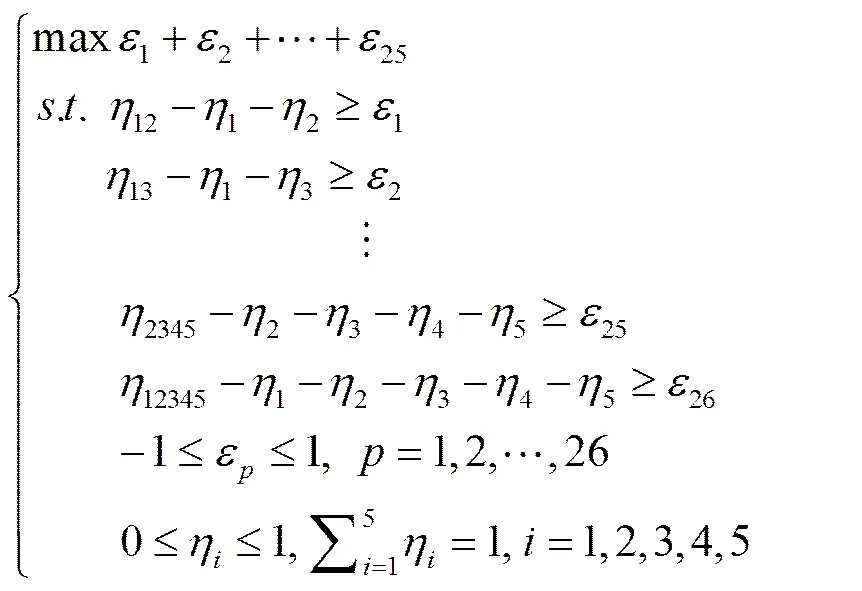
,,,,
步骤4利用式(19)计算单个属性的Shapley值
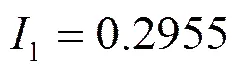
步骤5利用式(20)计算两两属性的交互指标
经过优化得的交互指标值,见表6。

步骤7利用式(12)计算各决策方案的2可加Choque t积分综合评价值如下:

表6 交互指标值
5 结论
2可加Choquet积分算子是定义在2可加模糊测度和Choquet积分基础上的集成算子,由于只涉及单个属性的Shapley值和两两属性间的交互指标,因此利用该算子处理属性间具有交互作用的多属性决策问题,可以大大降低计算的复杂性。为计算该算子中的Shapley值,本文利用广泛应用在质量工程学领域中的马田系统测度属性集的重要程度,并在此基础上给出了一种计算Shapley值的方法。对于该算子中的交互指标,本文根据无偏好决策方案集在相同约束条件下应平等竞争的原理以及2可加模糊测度的约束条件,构建了交互指标优化模型。实例验证表明本文提出的方法是可行的。但是需要指出的是,马氏距离的计算要求相关系数矩阵可逆,因此本文提出的方法更适合属性间存在交互作用的大规模决策问题。
[1] Choquet G. Theory of capacities [J]. Annales de L'instiut Fourier. 1953, 5: 131-295.
[2] Ishii K, Sugeno M. A model of humanevaluationprocess using fuzzy measure [J]. International Journal of Man-Machine Studies. 1985, 22: 19-38.
[3] Grabisch M. Fuzzy integral in multicriteria decision making [J]. Fuzzy sets and systems. 1995, 69(3): 279-298.
[4] Sugeno M. Theory of fuzzy integral and its applications [D]. Tokyo: Tokyo Institute of Technology, 1974.
[5] Grabisch M. The representation of importance and interaction of features by fuzzy measures [J]. Pattern Recognition. 1996, 17(6): 567-575.
[6] Grabisch M. k-order additive discrete fuzzy measures and their representation [J]. Fuzzy sets and systems. 1997, 92(2): 167-189.
[7] Mayag B, Grabisch M, Labreuche C. A characterization of the 2-additive Choquet integral through cardinal information [J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems. 2011, 184(1): 84-105.
[8] Takahagi E. On identification methods of λ-fuzzy measures using weights and λ[J]. Japanese Journal of fuzzy sets and systems. 2000, 12(5): 665-676.
[9] Takahagi E. A fuzzy measure identification method by diamond pairwise comparisons and Φs transformation [J]. Fuzzy Optimization and Decision Making. 2008, 7(3): 219-232.
[10] Taguchi G, Jugulum R. The Mahalanobis-Taguchi strategy: A pattern technology system [M]. John Wiley & Sons, 2002.
[11] Taguchi G, Chowdhury S, Wu Y. The Mahalanobis-Taguchi System [M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2000.
[12] Rajesh J, Taguchi G, Taguchi S. A review and analysis of the Mahalanobis-Taguchi system [J]. Technometrics. 2003, 45(1): 16-21.
[13] 武建章,张强. 基于2-可加模糊测度的多准则决策方法[J]. 系统工程理论与实践. 2010, 30(7): 1229-1237.
[14] Marichal J L. Determination of weights of interacting criteria from a reference set [J]. European Journal of Operational Research. 2000, 124(3): 641-650.
[15] 郑称德,韩之俊. MTS原理及其设计模型[J]. 管理工程学报. 2000, 14(03): 43-47.
[16] 牛俊磊,程龙生. 一种基于改进马田系统的不平衡数据分类方法[J]. 管理工程学报. 2012, 26(2): 85-93.
[17] Grabisch M, Labreuche C, Vansnick J C. On the Extension of Pseudo-Boolean Functions for the Aggregation of Interacting Criteria [J]. European Journal of operational Research. 2003, 148(1): 28-47.
[18] Chateauneuf A, Jaffray J Y. Some Characterizations of Lower Probabilities and Other Monotone Capacities through the use of Mobius Inversion [J]. Mathematical Social Sciences. 1989, 17: 263-283.
[19] 王熙照. 模糊测度和模糊积分及在分类技术中的应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008.
[20] Grabisch M, Labreuche C. A decade of application of the Choquet and Sugeno integrals in multi-criteria decision aid[J]. Annals of Operations Research. 2010, 175(1): 247-286.
Multi-Attribute Decision Making Method Based on Mahalanobis-Taguchi System and 2-additive Choquet integral
CHANG Zhi-peng1,2,CHENG Long-sheng1,LIU Jia-shu2
(1. School of Economics &Management, Nanjing University of Science &Technology, Nanjing 219004, China;2. School of Economics, Anhui University of Technology, Maanshan 243002, China)
The interaction between attributes often exists in real decision-making problems. However, the traditional multiple attributive decision making method (MADM) assumes that all attributes are mutually independent. Therefore, traditional MADM cannot effectively deal with the interaction between attributes.
To solve the problem, a new MADM based on 2-additive Choquet integral aggregation operator and Mahalanobis-Taguchi system (MTS) is proposed. In the new MADM, 2-additive Choquet integral aggregation operator is composed of Shapley value and interaction index. The operator is derived from 2-additive fuzzy measure and Choquet integral. The 2-additive fuzzy measure can be more flexible to represent the interaction between attributes. Choquet integral is a nonlinear function and it can be taken as an integrated operator to deal with MADM. Choquet integral integrated operator doesn’t need to meet with the assumption that attributes are mutually independent. Therefore, it can effectively deal with the interaction between attributes. MTS is a pattern recognition technology based on quality engineering and it is proposed by the famous Japanese quality engineer Dr. Taguchi. MTS has three key tools, including Orthogonal Arrays, Mahalanobis Distance and Signal to Noise Ratio. MTS can not only distinguish the category of a given sample, but also measure the importance of attributes that describe the sample. In MTS, the function of measuring the importance of attribute is based on the orthogonal experiment principle.
In the new MADM, to calculate the Shapley value the Mahalanobis-Taguchi system is firstly used to measure the important degree of attribute set and the rationality of the measure method. The global important degree of a single attribute is optimized on the basis of the principle that all attributes should have positive cooperation in the decision-making process. Finally, the Shapley value is calculated with the degree of globalization and the relative degree of a single attribute. The multi-objective optimization model of the interaction index is proposed on the basis of the principle that all decision-making projects should have equal competition in the decision-making process.
In order to verify the feasibility and validity of the new MADM, we select the best economic vitality cities from Beijing, Shanghai, Hefei, Nanchang, Wuhan, and Chongqing. Five evaluation indices are “fixed-asset investment”, “employed population”, “science and technology spending”, “industrial electricity”, and “gross regional domestic product”. Decision-making data is collected from “Chinese city statistics yearbook 2008”. The result shows that the feasibility of the new MADM and the new MADM can effectively handle real decision making problems.
However, it should be pointed out that Mahalanobis distance is calculated with the inverse of correlation coefficient matrix. Thus, the new MADM is suitable for solving large-scale decision-making problems that deal with the interaction between attributes.
Mahalanobis-Taguchi System; 2-additive Choquet integral; 2-additive fuzzy measures
中文编辑:杜 健;英文编辑:Charlie C. Chen
C934
A
1004-6062(2016)01-0133-07
10.13587/j.cnki.jieem.2016.01.016
2013-02-28
2013-10-14
国家自然科学基金资助项目(71271114);教育部人文社会科学规划基金资助项目(10YJA630020);国家社会科学基金资助项目(12CGL013)
常志朋(1978—),男,吉林榆树人,安徽工业大学经济学院讲师,博士研究生,主要从事多准则决策,管理综合评价、优化算法等研究。
