知识库中的信息测度
2016-10-14黄卫华
黄卫华
(文山学院 数学学院,云南 文山 663099)
知识库中的信息测度
黄卫华
(文山学院 数学学院,云南 文山 663099)
在粗糙集理论中,基于度量决策表中属性重要性大小的需要,有学者提出了互补信息熵的概念。在此基础上,定义了条件熵和互信息等概念,并验证了三者之间的关系,即互补信息熵是条件熵与互信息的和;类似于互补信息熵,互信息同样具有单调性。
信息测度;互补信息熵; 条件熵;互信息
1948年美国数学家ShannonC.E在《贝尔系统技术》杂志上发表了一篇“通信的数学理论”的论文,该论文的发表标志一门新的学科──信息论的诞生。在这篇论文中,Shannon定义了信息熵,给出了关于信息系统实际结构的不确定性度量,并成功应用于许多不同的研究领域。一些学者利用Shannon熵的定义以及Shannon熵的变式度量了粗糙集理论的不确定性[1-7]。梁吉业[8]等定义了粗糙集理论的互补信息熵,并验证该信息熵具有单调性,本文在此基础上定义了条件熵和互信息,给出了三者之间的关系。
1 预备知识
定义1[9]设K=(U, R)是一个近似空间,U是一个非空有限论域,R是U上的一个等价关系,U/R={X1, X2…Xm}表示R的所有等价类构成的集合,[x]R表示包含元素x∈U的R等价类。特别地,U的划分(U)={{x}|x∈U}称为恒等关系,划分Ř(U)={U}称为全域关系。一个近似空间K=(U, R)可以看作是一个关于U的知识库。
定义2[9]给定知识库K=(U, R),对于每一个KU,一个等价关系R,定义两个子集
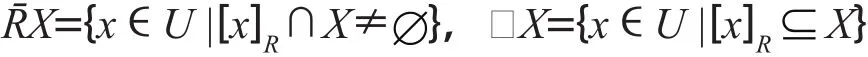
分别称它们为X的R上近似集和R下近似集。
定义3[10]设K=(U, R)是一个近似空间,P, Q是U的两个划分,U/P={P1, P2…, Pm},U/Q={Q1, Q2…, Qn},如果对于任意的Xi∈U/P,均有Yj∈U/Q,使得XiYj,称U/P是U/Q的加细,记作U/PU/Q。
定义4[8]设K=(U, R)是一个近似空间,U是一个非空有限论域,U/R={X1, X2…Xm}是U上的一个等价关系,粗糙集的互补信息熵定义为
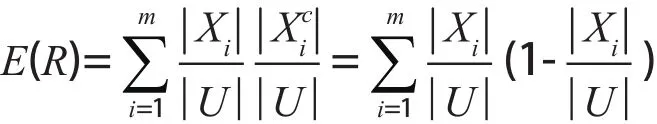
定义5设U是一个非空有限论域,K1=(U, P)和K2=(U, Q)是关于U的两个知识库,其中U/P={P1, P2, …, Pm},U/Q={Q1, Q, …, Qn},Q关于P的条件熵E(Q/P)定义如下
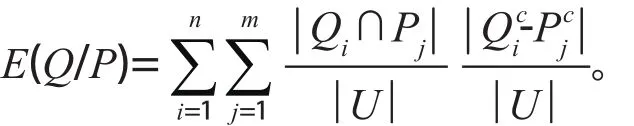
定义6设U是一个非空有限论域,K1=(U, P)和K2=(U, Q)是关于U的两个知识库,其中U/P={P1, P2, …, Pm},U/Q={Q1, Q, …, Qn},Q和P的互信息E(Q; P)定义如下

2 主要结论
定理1设U是一个非空有限论域,K1=(U, P)和K2=(U, Q)是关于U的两个知识库,那么E(Q; P)=E(Q)-E(Q/P)。
证明:设U/P={P1, P2, …, Pm},U/Q={Q1, Q, …, Qn},由集合论知,所以

所以E(Q; P)=E(Q)-E(Q/P)。
定理2设U是一个非空有限论域,K1=(U, P)和K2=(U, Q)是关于U的两个知识库,D是U的决策属性集,如果U/PU/Q,那么E(D; P)≥E(D; Q)。
证明:设U/P={P1, P2, …, Pm},U/Q={Q1, Q2, …, Qn},U/D={d1, d2, …, dr}。因为U/PU/Q,所以m>n且存在集合{1, 2, …, m}的一个划分C={C1, C2, …, Cn},满足因此
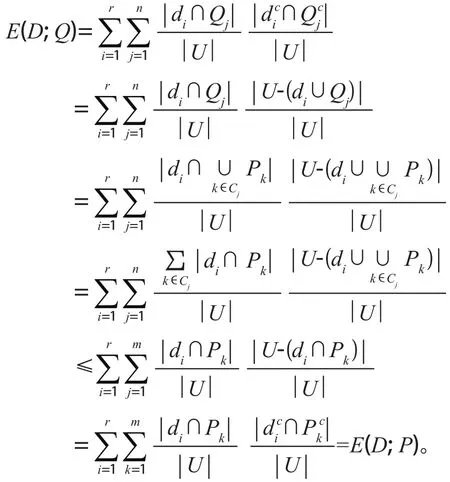
定理2表明随着划分的加细,信息粒度的互信息单调增加。定理2的逆命题一般情况下不成立。
例1设U={1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 },U/Q={{1, 5}{2, 3, 4, 6, 7}{8, 9, 10 }},U/P={{1, 3, 4}{2, 5, 6}{7, 8, 9, 10 }},U/D={{1, 3, 5, 8, 9}{2, 4, 6, 7, 10 }}。
计算

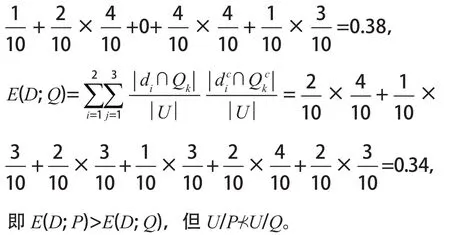
定理3设U是一个非空有限论域,K1=(U, P)和K2=(U, Q)是关于U的两个知识库,则U/PU/Q成立的充要条件是E(Q/P)=0。
证明:设U/P={P1, P2, …, Pm},U/Q={Q1, Q2, …, Qn}。


3 结论
[1] Shannon C E. The mathematical theory of communication[J]. Bell Syst Technol J, 1948(3, 4): 373-423, 623-656.
[2] Beaubouef, T., Petry, F.E. and Arora, G. Information-theoretic measures of uncertainty for rough sets and rough relational databases[J]. Information Sciences, 1998 (59):185-195.
[3] De Luca, A. and Termini, S. A definition of a nonprobabilistic entropy in the setting of fuzzy theory[J].Information and Control,1972(6):301-312.
[4] Liang, J.Y., Xu, Z.B. Uncertainty measures of roughness of knowledge and rough sets in incomplete information systems[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation (Press of University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei),2000(2):2526-2529.
[5] Liang, J.Y., Xu, Z.B. and Miao, D.Q. Reduction of knowledge in incomplete information systems[C]//Proceedings of Conference on Intelligent Information Processing in 16th World Computer Congress (Publishing House of Electronics Industry, Beijing) ,2000(7):528-532.
[6] Wierman, M.J.Measuring uncertainty in rough set theory[J]. International Journal of General Systems, 1999(4):283-297.
[7] Düntsch, I. , Gediga, G. Uncertainty measures of rough set prediction[J].Artificial Intelligence,1998, 106:109-137.
[8] Liang J Y, Chin K S, Dang C Y, et al. A new method for measuring uncertainty and fuzziness in rough set theory[J].Int J Gen Syst, 2002(4):331-342.
[9] 张文修,吴伟志,梁吉业,等.粗糙集理论与方法[M].北京:科学出版社,2001:151-152.
[10] Pawlak Z. Rough sets[J]. International Journal of Computer and Information Sciences, 1982(5):341-356.
The Information Measure in Knowledge Library
HUANG Weihua
(School of Mathematics, Wenshan University, Wenshan Yunnan 663099, China)
The concept of complementary information entropy based on the needs of the importance of attributes in measuring decision table is proposed in rough set theory. On this basis, condition entropy and mutual information are defi ned and the relationship among the three is verifi ed, i.e. the sum of condition entropy and mutual information is complementary information entropy; Mutual information also has the monotonicity similar to complementary information entropy.
information measure; complementary information entropy; conditional entropy; mutual information
TP18
A
1674 - 9200(2016)03 - 0042 - 03
(责任编辑刘常福)
2016 - 03- 03
云南省教育厅科研基金项目“基于粗糙集的数据挖掘算法研究”( 2015Y470 )。
黄卫华,女,河南中牟人,文山学院数学学院讲师,硕士,主要从事信息代数和粗糙集理论研究。
