肽组学在食源性活性肽研究中应用的进展
2016-09-14于志鹏薛如阳赵文竹张宏阳励建荣刘静波渤海大学食品科学与工程学院生鲜农产品贮藏加工及安全控制技术国家地方联合工程研究中心辽宁锦州203吉林大学营养与功能食品研究室吉林长春30062
于志鹏,薛如阳,赵文竹,*,张宏阳,吴 雨,张 霜,励建荣,刘静波(.渤海大学食品科学与工程学院,生鲜农产品贮藏加工及安全控制技术国家地方联合工程研究中心,辽宁锦州203;2.吉林大学营养与功能食品研究室,吉林长春30062)
肽组学在食源性活性肽研究中应用的进展
于志鹏1,薛如阳1,赵文竹1,*,张宏阳1,吴雨1,张霜1,励建荣1,刘静波2,*(1.渤海大学食品科学与工程学院,生鲜农产品贮藏加工及安全控制技术国家地方联合工程研究中心,
辽宁锦州121013;
2.吉林大学营养与功能食品研究室,吉林长春130062)
肽组学作为食品科学技术领域一个新兴的重要研究方法,正逐渐应用到生物活性肽制备、纯化、结构鉴定以及构效关系研究中,涉及活性肽的定性与定量的各个方面的内容。本文综述了肽组学在食源性活性肽制备工艺优化、特定功能活性的活性肽筛选、活性肽与受体的作用机制以及构效关系等研究的国内外进展,以期为肽组学在活性肽中广泛深入地应用提供参考。
活性肽,肽组学,纯化,结构表征,构效关系
活性肽是一类易于机体吸收并具多种生物活性的物质,其主要来源于动植物蛋白水解[1-4]或微生物发酵[5-6],并可被进一步化学修饰。食源性活性肽以其安全无副作用等优点,吸引了越来越多的食品科学、生物学、化学及其交叉领域研究人员的研究兴趣[7-8],并已被应用于食品和保健品行业。目前对于食源性活性肽的研究主要集中在酶解制备、纯化和结构鉴定方面:对于制备方法多采用外源蛋白酶进行酶解[9-10],通过优化设计等手段获得最优酶解条件。近年来对于利用内源性蛋白酶进行酶解制备活性肽的研究逐渐兴起,利用内源性蛋白酶和外源性蛋白酶协同酶解制备活性肽的研究也有报道[9-12],但对于内源性和外源性酶解所制备的活性肽的生理活性的差异对比研究鲜有报道;对于食源性活性肽的纯化与结构鉴定,主要通过膜过滤、色谱过滤进行逐级纯化,多维色谱纯化手段的应用显著提高了活性肽的纯化效率[13-15]。多维色谱纯化为获得高纯度的单一肽组分及结构鉴定发挥了重要作用,但是由于食源性蛋白酶解产物组分复杂,含有成百甚至上千条肽段,而且分子量相近或电荷相等的肽段难以进行分离纯化,给后续的结构鉴定带来了巨大的难题。目前肽结构鉴定的方法主要为质谱法和化学法,提供单一肽的纯化组分是结构鉴定的前提[16-20]。采用逐级分离纯化辅以活性跟踪手段经过多次分离纯化和富集获得单一肽组分最后进行结构鉴定的传统经典研究路线,一方面工作量大、阻碍了活性肽研究的快速发展;更重要的是活性跟踪纯化过程中不可避免的将高活性肽序列遗漏,致使最终获得的活性肽序列仅是最初活性肽复杂体系中活性相对较高的一部分,造成更高活性的活性肽的丢失,因此目前食源性活性肽的高效纯化结构鉴定成为获得完整的高活性活性肽的研究瓶颈,寻求高通量的生物活性肽结构的快速表征方法有助于推进生物活性肽研究的进展。本文综述了肽组学在活性肽研究中应用的进展情况。
1 肽组学
肽组学(peptidomics)是在蛋白质组学基础上发展起来的一个重要分支,是研究低分子量蛋白质和活性肽及其变化规律的科学,是近些年快速发展的一种可大规模表征活性肽的技术[21-24]。目前国际上对于肽组学的研究对象(即低分子量蛋白和活性肽)的分子量还没有明确的规定,多数分子量低于20 ku。肽组(peptidome)为食品原料、产品以及在储藏加工过程中存在或产生的所有活性肽的集合。肽组学研究内容主要涉及活性肽及其前体蛋白质的结构鉴定、特定功能活性肽的水解条件最优化、活性肽结构及其活性的预测以及定量构效关系等[25-26]。肽组学研究对象分为两类:一类为体内自身存在的活性肽;另一类为蛋白质经特殊水解酶产生的酶解产物。因此,肽组学在食源性活性肽的研究中既可以阐明天然存在的活性肽,又可以表征酶解作用后产生的活性肽结构[25-27]。肽组学研究过程包括样品前处理、分离纯化、目标肽定性、目标肽定量和数据分析,其中每一个环节对于获得准确肽信息都起着重要作用。肽组学在活性肽的结构表征研究中,主要通过串联质谱技术快速高效鉴定新的活性肽的序列,并借鉴肽数据库进行检索和构效关系预测[25-29]。肽组学这一新技术在解决活性肽的高效结构表征领域的应用有望能够突破活性肽传统技术所面临的瓶颈问题。借助肽组学快速、高效的特点,将肽组学技术应用于活性肽活性组分的结构表征是活性肽的未来研究发展方向之一。
2 肽组学在活性肽制备优化中的应用
当前对于食源性活性肽的制备主要利用生物酶解技术,通过对原料中蛋白质进行氨基酸全序列分析或通过蛋白质数据库进行检索获得原料蛋白的结构信息后,通过利用不同性质蛋白酶进行酶解并跟踪测定水解度以及目标活性,最终确定所用蛋白酶及所对应的最优酶解制备工艺[28-30]。虽然食源性活性肽的酶解制备技术已经相当成熟,但是在筛选过程中需要花费大量的时间,因此寻找一种更为快捷、周期短且能预测出裂解片段活性肽的氨基酸序列的方法将实现对目前研究现状的突破。肽组学的虚拟酶解数据库在活性肽制备优化中可以发挥更多的作用,在利用虚拟酶解数据库进行特定蛋白酶的水解需要首先通过蛋白质数据库检索出原料蛋白的分子量和氨基酸序列,常用到的蛋白质数据库有UniProt database(http://www.uniprot.org/),ExPASy(http://web. expasy.org/)和world wide protein date bank(http://www. wwpdb.org/)等。在获得原料蛋白质一级结构的基础上,利用肽组学技术根据所使用的蛋白酶种类分别进行虚拟水解,常用的蛋白酶有Arg-C proteinase,Asp-N endopeptidase,Asp-N endopeptidase+N-terminal Glu,Caspase1,Caspase2,Caspase3,Caspase4,Caspase5,Caspase6,Caspase7,Caspase8,Caspase9,Caspase10,Chymotrypsin-high specificity(C-term to[FYW],not before P),Chymotrypsin-low specificity(C-term to [FYWML],not before P),Clostripain(Clostridiopeptidase B),Enterokinase,Glutamyl endopeptidase,GranzymeB,Neutrophil elastase,Pepsin(pH1.3),Pepsin(pH>2),Proline-endopeptidase,Proteinase K,Staphylococcal peptidase I,Tobacco etch virus protease,Thermolysin,Thrombin,Trypsin,这些蛋白酶的选择可根据筛选活性肽结构特性而定,既可以选择一种蛋白酶进行水解也可以选择多种蛋白酶协同水解。虚拟酶解操作中通过录入原蛋白序列信息和选择裂解蛋白酶的种类,便可获得在此条件下酶解产物的结构信息。Raus等[30]利用protein cutter在线虚拟酶解软件对蛋白质进行酶解,并对所获得的肽段分子量、等电点、氨基酸组成以及疏水性进行了分析。计算机虚拟酶解的运用将有利于大规模筛选食源性蛋白质和特定生物活性肽的前体潜在片段,对于节省成本和时间发挥重要作用[31]。
3 肽组学在活性肽结构鉴定中的应用
在过去几年里,生物活性肽的结构鉴定与表征已发展成为食源性活性肽研究中新的研究热点,传统的生物活性肽结构鉴定的研究思路主要是通过色谱技术、膜技术等进行逐级纯化,并在纯化过程中进行目标活性的测定跟踪,不断收集高活性组分后再进行纯化,直到获得单一活性肽组分后进行一级结构和二级结构分析。侧重于研究食品原料中肽的结构组成、相互作用关系和生物活性的肽组学技术在这方面的作用日益突出。高分辨率质谱、计算机模拟水解、构效关系模型、化学计量学和肽数据库管理(表1)等作为肽组学的重要部分在食源性活性肽研究中逐渐被广泛深入地运用[28-29]。这些在线工具的应用以及与当前高灵敏度的生物质谱技术的有机结合为活性肽的结构鉴定提供了解决结构鉴定的难题。目前生物质谱中的液相色谱-飞行时间串联质谱以及四级杆线性离子阱质谱开始逐渐应用到生物活性肽结构分析,并辅以质谱数据解析软件protein pilot极大的缩短了活性肽结构表征的周期[32-36]。
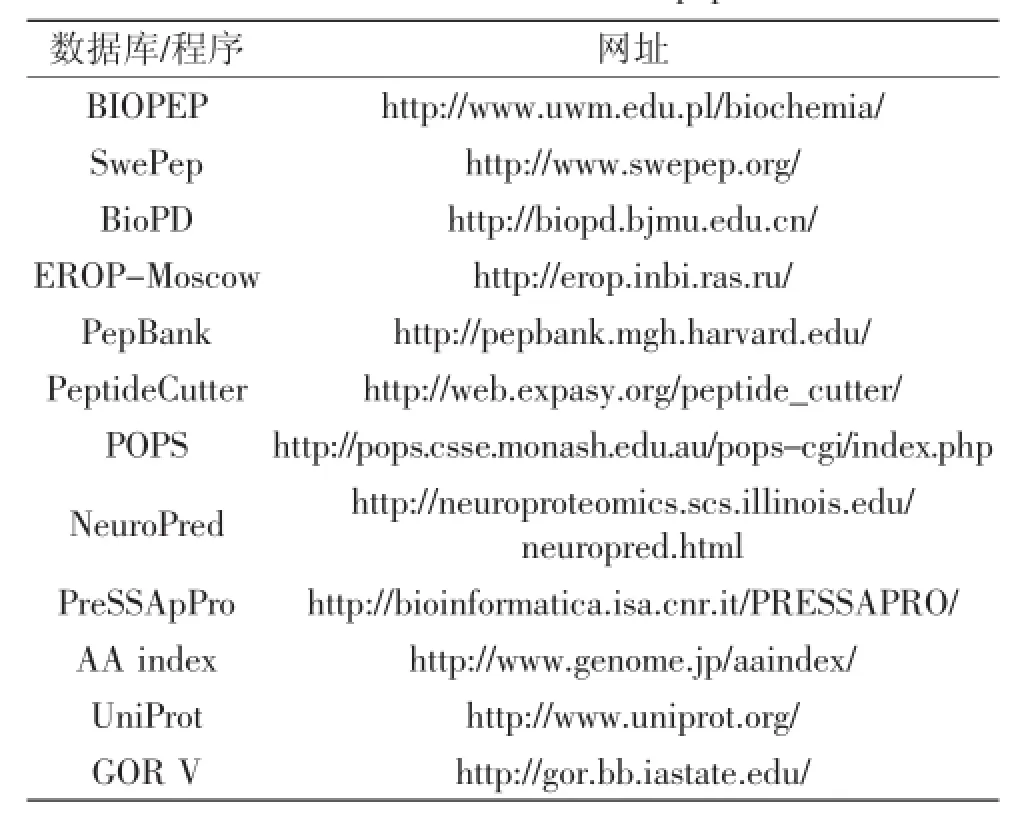
表1 肽组学研究中的主要工具Table 1 Available tools used in peptidomics
生物活性肽的结构鉴定是后续构效关系模型、化学计量学分析和肽数据库管理的研究基础。肽组学作为活性肽结构表征的有效策略,主要通过串联质谱快速鉴定解析食源性蛋白酶解物中活性肽的结构,目前在乳品及蛋清源活性肽结构鉴定中已有运用[28-29],其主要研究思路如下:

肽组学技术目前在食源性活性肽中的应用主要集中在乳源和蛋源活性肽的结构鉴定中,Liu等[37-38]借鉴肽组学技术利用三重四级杆线性离子阱串联质谱从鸡蛋清蛋白酶解产物中高效鉴定出19个活性肽序列,其氨基酸序列分别为RVPSLM,TPSPR,DLQGK,AGLAPY,RVPSL,DHPFLF,HAEIN,QIGLF,HANENIF,VKELY,TNGIIR,KLPGF,EAGVD,EVSGL,NVLQPS,QITKPN,LEPINF,AEAGVD和ANENIF,并通过后续的生物活性筛选获得具有抑制血管紧张素转化酶抑制活性肽RVPSL和抗糖尿病活性肽KLPGF。Wu等[39]利用肽组学中的LC-MS/MS并辅以定量构效关系(QSAR)对大豆蛋白源ACE抑制肽进行了纯化和表征,阐明五条三肽序列分别为IVF,LLF,LNF,LSW和LEF。肽组学尤其在乳源蛋白酶解产物的结构鉴定方面应用更为成熟,Laura等[29]对近年来肽组学在乳源生物活性肽的发现、生物活性筛选以及监测等方面的应用进行了报道,并阐明具有一定生理活性肽的一级结构,质谱分析中主要应用ESI、nano ESI、MALDI以及ESI&MALDI离子源,利用IT、TOF以及IT&TOF质量分析器进行结构分析[33-35],肽组学的一系列应用研究为肽组学在食源性活性肽结构表征中的运用提供了一个成功的参考范例。
4 展望
鉴于食源性生物活性肽已成为功能性食品中重要功效成分且这些化合物的结构和性质的复杂性,科学先进的技术手段对其后续深入研究发挥中决定性作用。肽组学技术将会成为食源性生物活性肽研究领域的一个重要手段,因为生物活性肽的纯化、结构鉴定、体内吸收分布以及代谢等研究均要涉及肽组学技术。肽组学还可应用于活性肽加工和储存过程中的变化研究,而多维液相色谱和毛细管电泳色谱与生物串联质谱技术协同跟踪监测活性肽一级结构变化为产品质量溯源提供技术保障。同时肽组学中的生物信息学工具也逐渐应用于食源性生物活性肽的构效关系研究中,可为阐明生物活性肽发挥生理活性的作用机制提供辅助工具。随着生物活性肽基础研究的深入,体内吸收的生物活性肽的浓度以及在靶器官中分布情况的相关性研究将成为未来生物活性肽研究的热点,肽组学将成为开展这些研究的有效的技术手段,将使感兴趣的生物活性肽发现、优化生产的周期大大缩短,并有助于理解活性肽与受体之间的相互作用机制。
[1]Wang S,Lin L M,Wu Y N,et al.Angiotensin I converting enzyme(ACE)inhibitory activity and antihypertensive effects of grass carp peptides[J].Food Science and Biotechnology,2014,23 (5):1661-1666.
[2]Rafik B,Ali B,Assaâd S,et al.Nine novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme(ACE)inhibitory peptides from cuttlefish(Sepia officinalis)muscle protein hydrolysates and antihypertensive effect of the potent active peptide in spontaneously hypertensive rats[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,170:519-525.
[3]Zou P,Wang J L,He G Q,et al.Purification,identification,and in vivo activity of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide,from ribbonfish(trichiurus haumela)backbone[J].Journal of Food Science,2014,79(1):C1-C7.
[4]Jiang Z M,Wang L Z,Che H X,et al.Effects of temperature and pH on angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity and physicochemical properties of bovine casein peptide in aqueous Maillard reaction system[J].LWT-Food Science and Technology,2014,59:35-42.
[5]Cid G G,Trevor G,Paula J.Novel probiotic-fermented milk withangiotensinI-convertingenzymeinhibitorypeptides produced by Bifidobacterium bifidum MF 20/5[J].International Journal of Food Microbiology,2013,167:131-137.
[6]Jakubczyk A,Karas M,Baraniak B,et al.The impact of fermentation and in vitro digestion on formation angiotensin converting enzyme(ACE)inhibitory peptides from pea proteins [J].Food Chemistry,2013,141:3774-3780.
[7]Young T G.Peptide[J].Nature,1971,232:139.
[8]Korhonen H,Pihlanto A.Bioactive peptides production and functionality[J].International Dairy Journal,2006,16:945-960. 白云,刘莉莉,刘萍,
[9]Asoodeh A,Memarpoor Y M,Chamani J.Purification and characterisation of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from lysozyme hydrolysates[J].Food Chemistry,2012,131:291-295.
[10]Jao C L,Huang S L,Hsu K C.Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides:inhibition mode,bioavailability,and antihypertensive effects[J].Biomedicine(Netherlands),2012,2:130-136.
[11]Lafarga T,Connor P,Hayes M.Identification of novel dipeptidyl peptidase-IV and angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from meat proteins using in silico analysis[J]. Peptides,2014,59:53-62.
[12]Phelan M,Khaldi N,Shields D C,et al.Angiotensin converting enzyme and nitric oxide inhibitory activities of novel milk derived peptides[J].International Dairy Journal,2014,35:38-42.
[13]Li X Y,Li Y,Huang X Z,et al.Identification and characterization of a novel angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptide(ACEIP)from silkworm pupa[J].Food Science and Biotechnology,2014,23(4):1017-1023.
[14]Puchalska P,García M C,Marina M L.Identification of native angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides in commercial soybean based infant formulas using HPLC-Q-ToFMS[J].Food Chemistry,2014,157:62-69.
[15]You L J,Zhao M M,Joe M R.In vitro antioxidant activity and in vivo anti-fatigue effect of loach(Misgurnus anguillicaudatus)peptides prepared by papain digestion[J].Food Chemistry,2011,124(1):188-194.
[16]Asoodeh A,Haghighi L,Chamani J,et al.Potential angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from gluten hydrolysate:Biochemical characterization and molecular docking study[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2014,60:92-98.
[17]Chen H,Muramoto K,Yamauchi F.Structural-analysis of antioxidative peptides from soybean beta-conglycinin[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,1995,43(3):574-578.
[18]Darewicz M,Borawska J,Vegarud G E,et al.Angiotensin I-converting enzyme(ace)inhibitory activity and ace inhibitory peptides of salmon(salmo salar) protein hydrolysates obtained by human and porcine gastrointestinal enzymes[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2014,15,14077-14101.
[19]Barbana C,Boye JI.Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory properties of lentil protein hydrolysates:Determination of the kinetics of inhibition[J].Food Chemistry,2011,127:94-101.
[20]Iwaniak A,Minkiewicz P,Darewicz M.Food-originating ACE inhibitors,including antihypertensive peptides,as preventive food componentsinbloodpressurereduction[J].Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2014,13:114-134.
[21]Janet C C,Alan J H,Cristian J M.Use of proteomics and peptidomics methods in food bioactive peptide science and engineering[J].Food Engineering Review,2012,4:224-243.
[22]侯召华,金春爱,孙晓东,等.蛙类皮肤生物活性肽的研究进展[J].食品科技,2013,38(5):260-264.
[23]靳艳,刘晓艳,邹汉法.基于蛋白质组学、肽组学的中药动物药活性组分的研究[J].世界科学技术:中医药现代化,2011,13(1):162-166.
[24]魏黎明,陆豪杰,杨芃原,等.肽组学样品前处理方法与技术进展[J].色谱,2013,31(7):603-612.
[25]Minkiewicz P,Dziuba J,Darewicz M,et al.Food peptidomics [J].Food Technology and Biotechnology,2008,46(1):1-10.
[26]Nagpal R,Behare P,Rana R,et al.Bioactive peptides derived from milk proteins and their health beneficial potentials:an update [J].Food Function,2011,2:18-27.
[27]Panchaud A,Affolter M,Kussmann M.Mass spectrometry for nutritional peptidomics:how to analyze food bioactives and their health effects[J].Journal of Proteomics,2012,75:3546-3559.
[28]Lahrichi S L,Affolter M,Zolezzi I S,et al.Food Peptidomics:Large scale analysis of small bioactive peptides—A pilot study [J].Journal of Proteomics,2013,88:83-91.
[29]Laura S R,Daniel M M,Elvia C H,et al.Peptidomics for discovery,bioavailabilityandmonitoringofdairybioactive peptides[J].Food Research International,2014,63:170-181.
[30]Raus M,Kopecny D,Sebela M.Program Application for the Prediction of Results of Protein Digestion by Proteolytic Enzymes [J].Chemicke Listy,2013,107(1):44-53.
[31]GasteigerE,HooglandC,GattikerA,etal.Proteinidentification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server[J].Proteomics Protocols,2005,571-607.
[32]Dallas D C,Guerrero A,Khaldi N,et al.Extensive in vivo human milk peptidomics reveals specific proteolysis yielding protective antimicrobial peptides[J].Journal of Proteome Research,2013,12:2295-2304.
[33]Denoni I,Cattaneo S.Occurrence of β-casomorphins 5 and 7 in commercial dairy products and their digests following in vitro simulated gastro-intestinal digestion[J].Food Chemistry,2010,119:560-566.
[34]Martínez-Maqueda D,Hernández-Ledesma B,Amigo L,et al.Extraction/fractionation techniques for proteins and peptides and protein digestion[M].New York:Proteomics in Foods:Principles and Applications,2013:21-50.
[35]Sagardia I,Iloro I,Elortza F,et al.Quantitative structureactivityrelationshipbasedscreeningofbioactivepeptides identified in ripened cheese[J].International Dairy Journal,2013,33:184-190.
[36]Siciliano R A,Mazzeo M F,Arena S,et al.Mass spectrometry for the analysis of protein lactosylation in milk products[J].Food Research International,2013,54,988-1000.
[37]Liu J B,Yu Z P,Zhao W Z,et al.Isolation and identification of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from egg white protein hydrolysates[J].Food Chemistry,2010,122:1159-1163.
[38]Yu Z P,Zhao W Z,Liu J B,et al.QIGLF,a novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme-inhibitory peptide from egg white protein [J].Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2011,91:921-926.
[39]Gu Y C,Wu J P.LC-MS/MS coupled with QSAR modeling in characterising of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from soybean proteins[J].Food Chemistry,2013,141 (3):2682-2690.
Progress on the application of peptidomics methods in food-derived bioactive peptides
YU Zhi-peng1,XUE Ru-yang1,ZHAO Wen-zhu1,*,ZHANG Hong-yang1,WU Yu1,ZHANG Shuang1,LI Jian-rong1,LIU Jing-bo2,*
(1.College of Food Science and Engineering,Bohai University,National&Local Joint Engineering Research Center of Storage Processing and Safety Control Technology for Fresh Agricultural and Aquatic Products,Jinzhou 121013,China;2.Lab of Nutrition and Functional Food,Jilin University,Changchun 130062,China)
Food peptidomics as an emerging field of food science and technology is gradually applied to the biological activity of the peptide preparation,purification,identification,and structure-activity relationship,involved the qualitative and quantitative aspects of bioactive peptides.Objective of this review was to highlight the increasing role of peptidomics as indispensable tool in the fields of production,purification,characterization,and structure-activity relationship of food-derived bioactive peptides,aimed to support extensive application reference of peptidomics in the food-derived peptides field.
bioactive peptide;peptidomics;purification;identification;structure activity relationship
TS201
A
1002-0306(2016)04-0382-04
10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2016.04.069
2015-06-12
于志鹏(1984-),男,博士,讲师,研究方向:蛋白质及活性肽的功能研究与产品开发,E-mail:yuzhipeng20086@sina.com。
赵文竹(1986-),女,博士,讲师,研究方向:植物多糖及糖蛋白,E-mail:zhaowenzhu777@163.com。刘静波(1962-),女,博士,教授,研究方向:营养与功能食品,E-mail:ljb168@sohu.com。
国家自然科学基金面上项目(31271907);国家科技支撑课题-“食源性功能肽生物制备技术研究(2012BAD00B03)”。
