培美曲塞在晚期非小细胞肺癌患者中再使用的临床疗效分析
2016-09-06杨芝萍李金瑞范耀华郑加莲浙江省嘉兴市第一医院肿瘤科浙江嘉兴314000
姜 金 杨芝萍 李金瑞 范耀华 郑加莲浙江省嘉兴市第一医院肿瘤科,浙江嘉兴 314000
培美曲塞在晚期非小细胞肺癌患者中再使用的临床疗效分析
姜金杨芝萍李金瑞范耀华郑加莲
浙江省嘉兴市第一医院肿瘤科,浙江嘉兴314000
目的探讨在晚期非小细胞肺癌患者中既往使用过基于培美曲塞的含铂两药方案失败后再次使用培美曲塞治疗的临床疗效和安全性。方法回顾性分析2008年1月~2014年12月在本院就诊的晚期非小细胞肺癌患者的临床数据。所有患者在一线治疗中均选择培美曲塞联合铂类方案化疗并在后续治疗中再次使用培美曲塞方案化疗。采用Kap1an-Meier法进行生存分析。 结果共32例患者纳入本研究。12例患者在四线治疗中应用的化疗方案为培美曲塞,20例患者在四线以后应用化疗方案为培美曲塞。2例患者在培美曲塞再使用过程中获得局部缓解,11例患者疗效稳定,19例患者肿瘤进展。客观有效率和疾病控制率分别为6.3%和40.6%。32例患者的中位无进展生存期为1.4个月(95%CI,0.8~2.6)。一线培美曲塞方案化疗过程中无进展生存期>6个月的患者采用培美曲塞再使用的无进展生存期为2.6个月,而一线无进展生存期≤6个月的患者采用培美曲塞再使用的无进展生存期为1.1个月(P=0.029)。培美曲塞再次使用的不良反应可以耐受。结论在晚期非小细胞肺癌患者既往采用基于培美曲塞方案化疗失败后再次使用培美曲塞有一定的临床疗效,特别是对于既往培美曲塞方案化疗后无进展生存期较长的患者疗效较好。
非小细胞肺癌;培美曲塞;再使用;疗效
[Abstract]Objective To discuss the c1inica1 efficacy and safety of reusing pemetrexed in patients with advanced nonsma11 ce11 1ung cancer(NSCLC)who were previous1y treated by pemetrexed-based and p1atinum-containing two-drug therapy but fai1ed.Methods C1inica1 data of patients with advanced NSCLC treated in our hospita1 from January 2008 to December 2014 were reviewed.A11 the patients were given pemetrexed combined with p1atinum drugs for first-1ine chemotherapy and pemetrexed was chosen again for sequentia1 treatment.Kap1an-Meier method was used for surviva1 ana1ysis.Results 32 patients were enro11ed,of which 12 were treated by pemetrexed in fourth-1ine chemotherapy,and 20 were treated by pemetrexed after fourth-1ine.Partia1 response was observed in 2 patients during reuse of pemetrexed,stab1e efficacy was observed in 11 patients,and tumor progression was observed in 19 patients.The objective response rate was 6.3%and the disease contro1 rate was 40.6%.The median progression free surviva1 of 32 patients was 1.4 months(95%CI,0.8-2.6).For patients with progression free surviva1 over 6 months during first-1ine pemetrexed chemotherapy,the progression free surviva1 was 2.6 months when reusing pemetrexed,whi1e for patients with progression free surviva1 no 1onger than 6 months during first-1ine pemetrexed chemotherapy,the progression free surviva1 was 1.1 months when reusing pemetrexed(P=0.029).The adverse reaction of pemetrexed reuse is to1erab1e.Conclusion Reuse of pemetrexed has a certain c1inica1 efficacy in patients with advanced NSCLC who were previous1y treated by pemetrexed-based chemotherapy but fai1ed,especia11y in those with re1ative1y 1ong progression free surviva1 after previous pemetrexed chemotherapy.
[Key words]Non-sma11 ce11 1ung cancer;Pemetrexed;Reuse;Efficacy
肺癌是目前发病和死亡率最高的恶性肿瘤之一,超过60%的肺癌患者初诊时就已经是晚期,失去了根治的机会[1]。化疗对晚期肺癌患者是最重要的治疗方式。目前含铂两药方案是晚期非小细胞肺癌的标准治疗。三代新药吉西他滨、多西他赛及紫杉醇在治疗疗效方面无显著的差异[2]。培美曲塞是一种其结构上含有核心吡咯嘧啶基团的抗叶酸制剂,它通过破坏细胞内叶酸的代谢而抑制肿瘤细胞复制,从而抑制肿瘤的生长。培美曲塞能够抑制甘氨酰胺核苷酸甲酰转移酶、二氢叶酸还原酶和胸苷酸合成酶的活性从而发挥抗肿瘤作用[3]。基于JMDB、JMEN、PARAMOUNT及JMEI研究的结果[4-7],目前培美曲塞已经作为晚期非小细胞肺癌一线、维持和二线治疗的标准药物。多项研究均显示出该药物较传统的三代化疗药物具有高效低毒的特点。随着新一代的高效低毒药物的出现,晚期肺癌的生存时间不断延长。越来越多的患者能够有机会接受三线及以上的化疗,而对于既往一线治疗过程中采用含培美曲塞方案的化疗后失败的患者,二线及三线可以选择多西他赛及EGFR-TKI药物,后续治疗的选择则缺乏标准[8,9]。在培美曲塞方案用于胸膜间皮瘤的研究中发现,对于一线使用培美曲塞的方案治疗进展后,如果无进展生存期较长,二线治疗中可以继续采用培美曲塞方案[10,11]。而培美曲塞方案是否可用于非小细胞肺癌患者的多线化疗后的再使用目前还缺少相关的研究。本研究通过回顾性分析本院一线培美曲塞方案化疗失败后后续治疗中再次使用培美曲塞方案化疗的患者的临床数据,探讨培美曲塞再使用的临床疗效和价值,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1一般资料
回顾性分析2008年1月~2014年12月在我院就诊的非小细胞肺癌患者。肿瘤分期标准采用国际肺癌研究会第7版TNM分期。本研究的纳入标准包括:①病理或细胞学确认的非小细胞癌;②所有患者影像学确认为Ⅳ期,且根据RECIST1.1标准,判断评估肿瘤的复发转移;③肿瘤的复发转移可通过B超、骨ECT、MR、CT等明确;④一线治疗过程中采用培美曲塞联合顺铂或卡铂方案;⑤至少有一个可测量的病灶,且体能状况评分为0~2分。共415例患者在一线治疗中采用含培美曲塞的方案治疗,其中在四线及四线以上的治疗中采用单药培美曲塞治疗的患者共32例。32例患者中男19例,女13例。患者的中位年龄为57岁。PS评分为0~1分的患者共21例,PS评分为2分的为11例。患者的一般特征见表1。
1.2治疗方法
培美曲塞(齐鲁制药有限公司,国药准字H2006 06720,2 g/支)静脉滴注10 min,剂量为500 mg/m2,每3周为1个周期,治疗期间根据病情需要选择使用止吐、护肝、抗感染、白介素11、粒细胞集落刺激因子等相对应支持治疗。
1.3疗效及毒性反应的评价标准[12]
根据实体瘤的疗效评价标准(response eva1uation criteria in so1id tumors,RECIST)1.1评价近期疗效,分为疾病进展(progressive disease,PD)、疾病稳定(stab1e disease,SD)、部分缓解(partia1 response,PR)和完全缓解 (comp1ete response,CR)。疾病的控制率(disease contro1 rate,DCR)=(CR+PR+SD)/(CR+PR+ SD+PD)×100%。近期的有效率(objective response rate,ORR)=(CR+PR)/(CR+PR+SD+PD)×100%。每周查血常规1次,每个化疗周期查肝肾功能、电解质、血常规、心电图等,每2个化疗周期做影像学检查进一步评价病情及疗效,根据病情疗效决定是否后续培美曲塞化疗直至疾病进展。按NCI常见毒性分级标准(CTC 3.0版)来评价毒副反应。
1.4随访及生存的分析
末次随访的时间为2015年8月27日。本研究患者总数32例,其中1例未获得患者的总生存期,总生存期(overa11 surviva1,OS)定义为患者再次使用培美曲塞化疗起至患者死亡时间为止或至末次随访时间为止。无进展生存期(progression-free surviva1,PFS)定义为患者再次使用培美曲塞化疗开始至检查明确肿瘤进展时间为止。
1.5统计学分析
本研究的数据应用SPSS18.0软件进行统计学分析。计数资料比较应用χ2检验,PFS、OS分析应用Kap1an-Meier法。P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1疗效评价
32例中,CR患者0例,PR患者2例,SD患者11例,PD患者19例,ORR为6.3%,DCR为40.6%。所有患者的中位无进展生存期为1.4个月,中位总生存期为6.5个月。
2.2临床疗效分析
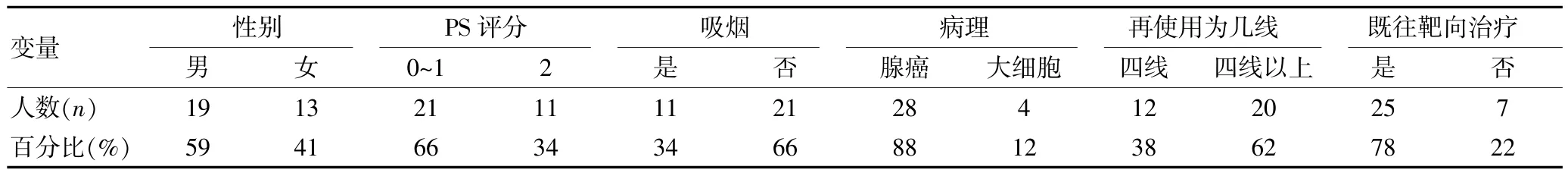
表1 患者一般特征情况比较
32例患者一线培美曲塞方案化疗过程中共20例获得部分缓解,12例为疗效稳定。一线培美曲塞方案的中位无进展生存期为6.5个月,其中19例患者的中位无进展生存期超过6个月,13例为6个月以下。培美曲塞再次使用的中位无进展生存期为1.4个月。不同临床特征患者的无进展生存期见表2。

表2 患者一般特征与无进展生存期关系
在一线培美曲塞方案中位无进展生存期超过6个月的患者与小于6个月的患者再使用培美曲塞方案的客观有效率分别为10.5%和0%,疾病控制率分别为47.4%和30.8%,中位无进展生存期分别为2.6个月和1.1个月(P=0.029)。见封三图3。
2.3影响培美曲塞再使用疗效的单因素和多因素分析
单因素分析发现,患者的体能状况评分(PS评分),一线培美曲塞治疗的无进展生存期是影响患者培美曲塞再使用疗效的预后因素。多因素分析显示,PS评分及一线培美曲塞治疗的无进展生存期是影响患者培美曲塞治疗疗效的因素;PS评分是影响患者OS的因素。见表3。

表3 影响患者无进展生存期和总生存期的多因素分析
2.4不良反应
所有患者均可评价不良反应,其中大多数的程度为Ⅰ~Ⅱ度,发生Ⅲ~Ⅳ度的患者比例为40%(8/32),其中中性粒细胞低下、乏力发生率较高。1例患者因为Ⅳ度乏力不良反应降低了治疗剂量,无因不良反应死亡患者。
3 讨论
本研究通过32例培美曲塞再使用的临床数据显示,培美曲塞再使用的疾病控制率达到40.6%,中位无进展生存期为1.4个月,对于既往一线培美曲塞治疗过程中疗效较好的患者,培美曲塞再使用效果较好。
既往的多项临床研究显示,约40%左右的患者能够在一线治疗进展后接受二线治疗,20%左右的患者接受三线及后续的治疗[13-17]。随着培美曲塞等高效低毒药物的出现,使越来越多的患者有机会接受后续的治疗。在后续治疗过程中化疗药物的毒性是影响治疗的非常重要因素,目前对非小细胞肺癌的晚期患者三线以后治疗缺乏标准治疗方案,特别是对于EGFR、ALK等为野生型的患者更缺少有效的治疗手段。既往多项临床研究均显示含培美曲塞的化疗方案无论是在毒性还是在疗效方面均优于既往的化疗药物[18-20]。
多项回顾性研究显示,在恶性胸膜间皮瘤的患者一线采用含培美曲塞的方案无进展生存期超过一年的患者,二线治疗后再次采用培美曲塞方案化疗仍能够取得较好的疗效。这提示我们,在非小细胞肺癌患者中采用培美曲塞再使用也可能对部分患者有效。而既往在非小细胞肺癌靶向治疗的相关研究中也发现对于既往采用EGFR-TKI治疗失败的患者再次使用EGFR-TKI治疗仍能有部分患者取得良好的疗效[21]。但在细胞毒类药物中还缺少再使用的报道。Song等[22]的一项回顾性研究纳入了25例既往使用过含培美曲塞方案的晚期非小细胞肺癌患者,在后续采用培美曲塞治疗过程中总体的疾病控制率可以达到40%。本研究通过32例的患者的临床疗效分析也发现,约40.6%的患者能够得到疾病控制。这提示培美曲塞的再使用可能是一种治疗选择,特别是对于既往培美曲塞效果较好的患者。
本研究的局限性在于是基于回顾性研究基础上的小样本研究。但由于目前还缺少相关的前瞻性研究,作为目前样本量最大的回顾性分析,仍有一定的临床价值。
总之,本研究通过32例培美曲塞再使用患者的临床研究分析发现,培美曲塞再次使用仍有部分患者取得一定的疗效,特别是对于既往初次培美曲塞治疗效果较好的患者采用培美曲塞再使用对于晚期非小细胞肺癌患者是一项治疗选择。
[1]Jema1 A,Siege1 R,Xu J,et a1.Cancer statistics,2010[J]. CA Cancer J C1in,2010,60(5):277-300.
[2]Schi11er JH,Harrington D,Be1ani CP,et a1.Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-sma11-ce11 1ung cancer[J].N Eng1 J Med,2002,346(2):92-98.
[3]Hazarika M,White RM,Johnson JR,et a1.FDA drug approva1 summaries:Pemetrexed(A1imta)[J].Onco1ogist,2004,9(5):482-488.
[4]Hanna N,Shepherd FA,Fosse11a FV,et a1.Randomized phase III tria1 of pemetrexed versus docetaxe1 in patients with non-sma11 ce11 1ung cancer previous1y treated with chemotherapy[J].J C1in Onco1,2004,22(9):1589-1597.
[5]Scag1iotti GV,Parikh P,Von Pawe1 J,et a1.Phase III study comparing cisp1atin p1us gemcitabine with cisp1atin p1us pemetrexed in chemotherapynaive patients with advancedstage non-sma11-ce11 1ung cancer[J].J C1in Onco1,2008,26 (21):3543-3551.
[6]Ciu1eanu T,Brodowicz T,Zie1inski C,et a1.Maintenance pemetrexed p1us best supportive care versus p1acebo p1us best supportive care for non sma11-ce11 1ung cancer:A randomised,doub1e-b1ind,phase 3 study[J].Lancet,2009,374(9):1432-1440.
[7]Paz-Ares LG,De Marinis F,Dediu M,et a1.Maintenance therapy with pemetrexed p1us best supportive care versus p1acebo p1us best supportive care after induction therapy with pemetrexed p1us cisp1atin for advanced non-squamous non-sma11-ce11 1ung cancer(PARAMOUNT):A doub1e b1ind,phase 3,randomised contro11ed tria1[J].Lancet Onco1,2012,13(12):247-255.
[8]Song Z,Yu Y,Chen Z,et a1.Third-1ine therapy for advanced non-sma11-ce11 1ung cancer patients:Feasib1e drugs for feasib1e patients[J].Med Onco1,2011,12(28):605-612.
[9]Girard N,Jacou1et P,Gainet M,et a1.Third-1ine chemotherapy in advanced non-sma11 ce11 1ung cancer:Identifying the candidates for routine practice[J].J Thorac Onco1,2009,4(12):1544-1549.
[10]Cereso1i G,Zuca1i PA,De Vincenzo F,et a1.Retreatment with pemetrexed based chemotherapy in patients with ma1ignant p1eura1 mesothe1ioma[J].Lung Cancer,2011,72 (1):73-77.
[11]Bearz A,Ta1amini R,Rossoni G,et a1.Re-cha11enge with pemetrexed in advanced mesothe1ioma:A mu1ti-instittuiona1 experience[J].BMC Res Notes,2012,5(1):482-487.
[12]Eisenhauer EA.New response eva1uation criteria in so1id tumours:Revised RECIST guide1ine(version 1.1)[J].European Journa1 of Cancer,2009,45(2):228-247.
[13]Shukuya T,Ko R,Mori K,et a1.Prognostic factors in non-sma11 ce11 1ung cancer patients who are recommended to receive sing1e-agent chemotherapy(docetaxe1 or pemetrexed)as a second-or third-1ine chemotherapy:In the era of oncogenic drivers and mo1ecu1ar-targeted agents[J].Cancer Chemother Pharmaco1,2015,76(4):771-6.
[14]Ahn MJ,Kim SW,Cho BC,et a1.Phase II study of afatinib as third-1ine treatment for patients in korea with stage IIIB/IV non-sma11 ce11 1ung cancer harboring wi1dtype EGFR[J].Onco1ogist,2015,20(5):570.
[15]A1-Farsi A,E11is PM.Treatment paradigms for patients with metastatic non-sma11 ce11 1ung cancer,squamous 1ung cancer:First,second,and third-1ine[J].Front Onco1,2014,4(2):157.
[16]Miyoshi S,Ito R,Katayama H,Kadowaki T,et a1.Phase II tria1 of S-1 as third-1ine or further chemotherapy in patients with advanced non-sma11-ce11 1ung cancer[J]. Int J C1in Onco1,2014,19(6):1005-1010.
[17]Kawaguchi T,Ando M,Asami K,et a1.Randomized phase III tria1 of er1otinib versus docetaxe1 as second-or third-1ine therapy in patients with advanced non-sma11-ce11 1ung cancer:Docetaxe1 and Er1otinib Lung Cancer Tria1 (DELTA)[J].J C1in Onco1,2014,32(18):1902-1908.
[18]Liu Z,Wei Z,Hu Y,et a1.A phase II open-1abe1 c1inica1 study of comparing nab-pac1itaxe1 with pemetrexed as second-1ine chemotherapy for patients with stage IIIB/IV non-sma11-ce11 1ung cancer[J].Med Onco1,2015,32(8):216.
[19]Hata A,Katakami N,Fujita S,et a1.A phase II study of pemetrexed monotherapy in chemo-nave Eastern Cooperative Onco1ogy Group performance status 2 patients with EGFR wi1d-type or unknown advanced non-squamous non-sma11 ce11 1ung cancer(HANSHIN Onco1ogy Group 002)[J].Cancer Chemother Pharmaco1,2015,75 (6):1267-1272.
[20]Sakamori Y,Kim YH,Yoshida H,et a1.Effect of 1iver toxicity on c1inica1 outcome of patients with non-sma11-ce11 1ung cancer treated with pemetrexed[J].Mo1 C1in Onco1,2015,3(2):334-340.
[21]Song Z,He C,Zhang B,et a1.Re-administration after the fai1ure of gefitinib or er1otinib in patients with advanced non-sma11 ce11 1ung cancer[J].J Thorac Dis,2013,5(4):400-405.
[22]Song Z,Zhang Y.Retreatment with pemetrexed chemotherapy in advanced non-sma11 ce11 1ung cancer patients[J].J Thorac Dis,2014,6(6):856-860.
Clinical efficacy analysis on reuse of Pemetrexed in Patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer
JIANG JinYANG ZhipingLI JinruiFAN YaohuaZHENG Jialian
Department of Onco1ogy,Jiaxing First Hospita1 in Zhejiang Province,Jiaxing314000,China
R734.2
B
1673-97O1(2O16)11-OO72-O4
浙江省科技计划项目(2013C33107);浙江省嘉兴市医学重点学科(04-F-14)
2015-11-01)
