蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫区系初步分析
2016-08-23李媛媛德力格尔
李媛媛,石 凯,德力格尔
(内蒙古民族大学农学院,内蒙古通辽,028000)

蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫区系初步分析
李媛媛,石凯*,德力格尔
(内蒙古民族大学农学院,内蒙古通辽,028000)
对蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫标本鉴定和资料整理,共得到5属34种。其中,种类最多的是草盲蝽属Lygus13种(38.24%),占绝对优势。在世界动物地理区划中,蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫以古北界为主,种数占15种(44.12%)。在中国动物地理区划中,草盲蝽复合组单独分布于蒙新区的物种有8种,约占物种总数的1/4(23.54%),其次是蒙新区与华北区共有5种(14.72%),蒙新区与东北区共有3种(8.82%),其它动物区系分布的物种均较少。在蒙新区动物地理区划中,蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫以西部荒漠亚区种数最多,共14种(41.18%),其次为东部草原亚区和西部荒漠亚区共有9种(26.47%)。
草盲蝽复合组;区系;蒙新区
草盲蝽复合组Lyguscomplex在半翅目Hemiptera异翅亚目 Heteroptera的分类中隶属盲蝽科Miridae盲蝽亚科Mirinae盲蝽族Mirini,世界已知360余种,中国已知124种(Schuh,1995;Kerzhner,1999;郑乐怡,2004),绝大多数草盲蝽复合组昆虫与农、林、牧业生产关系密切。蒙新区东西跨度大,自然条件复杂,蕴含着丰富的动物资源,然而关于蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫区系缺乏系统深入研究。学者们对草盲蝽复合组昆虫的报道仅局限于分别对草盲蝽属、丽盲蝽属、新丽盲蝽属、后丽盲蝽属、树丽盲蝽属昆虫的种类进行描述和记载(Aglyamzyanov,1990;郑乐怡等,1992;Josifov,1992;齐宝瑛等,1993;Aglyamzyanov,1994;吕楠等,1994;Schwartz,1996;吕楠等,1997,1998;能乃扎布,1999;吕楠等,2001;Aglyamzyanov,2003,2006)。在近年广泛野外调查的基础上,结合内蒙古师范大学数十年的馆藏标本和内蒙古民族大学标本室积累的标本,通过查阅大量文献资料,本文对蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫进行整理、分类和鉴定,并对其组成和区系进行了系统分析,为了解蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫资源、多样性、害虫防治提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1材料来源
本文所用草盲蝽复合组昆虫标本主要来自近7年作者的采集,以及内蒙古师范大学能乃扎布昆虫研究中心昆虫标本馆数十年的馆藏标本和内蒙古民族大学农学院昆虫标本室标本。
1.2分析方法
物种鉴定依据中国动物志及一些与草盲蝽复合组相关的文献资料(Carvalho,1955;Kelton,1955;Kerzhner,1964;能乃扎布,1987;Kerzhner,1988;郑乐怡等,1990;齐宝瑛等,1997;Yasunaga,2002;郑乐怡,2004)。
动物地理区系参照章士美和张荣祖的划分方法,将世界动物地理区系划分为古北界、东洋界、新北界、新热界、非洲界、澳洲界6个区划;将中国动物地理区系划分为蒙新区、华北区、东北区、青藏区、西南区、华中区、华南区7个部分;将蒙新区又划分为东部草原亚区、西部荒漠亚区和天山山地亚区(章士美,1984;张荣祖,1999)。
2 结果与分析
2.1蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫属种组成
蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫共5属34种,其中草盲蝽属种类最多,共13种,占物种总数的38.24%;其次是丽盲蝽属和后丽盲蝽属各7种;再次是新丽盲蝽属5种;树丽盲蝽属种数最少仅2种。详见表1。
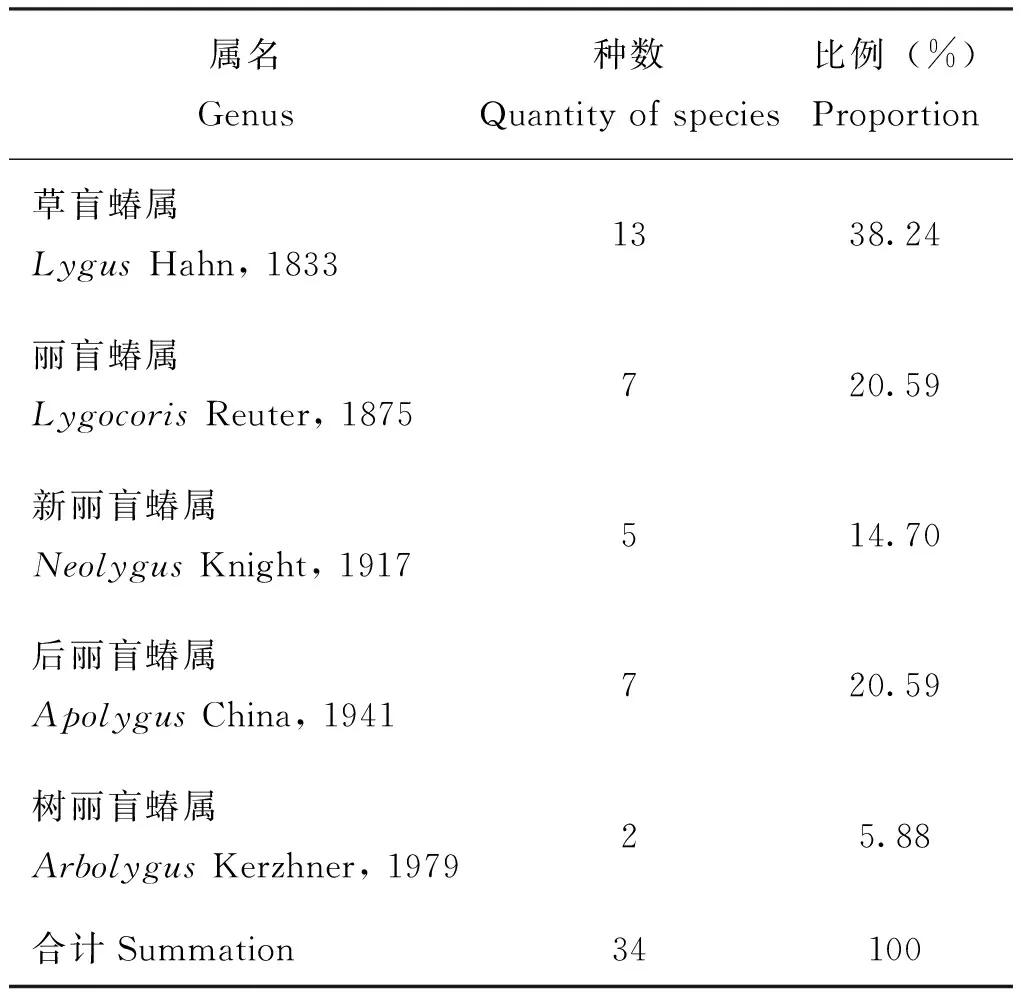
表1 蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫的属种组成
2.2蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫区系特征
2.2.1蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫在世界动物地理区划中的分布特征
由表2可知,蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫在世界动物地理区划中共有4个分布型。其中,单区型(古北界)种数最多,共15种,占草盲蝽复合组昆虫总种数的44.12%;二区型中以古北界+东洋界种数最多,共14种,占总种数的41.18%;三区型(古北界+东洋界+新北界)种数最少,共2种,占总种数的5.88%。属级区系分布类型与种级略有不同,在单区型(古北界)和二区型(古北界+东洋界)中均有5属分布,占草盲蝽复合组昆虫总属数的100%;古北界+新北界和古北界+东洋界+新北界各有2属分布,分别占总属数的40%。
2.2.2蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫在中国动物地理区划中的分布特征
蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫在中国动物地理区划中共有14种分布型,见表3。按各区划分布种类由多到少分别为:蒙新区34种,占100%;华北区18种,占52.94%;青藏区12种,占35.29%;华中区11种,占32.35%;东北区 9种,占26.47%;西南区6种,占17.65%;华南区3种,占8.82%。全国分布种2种,占5.88%。
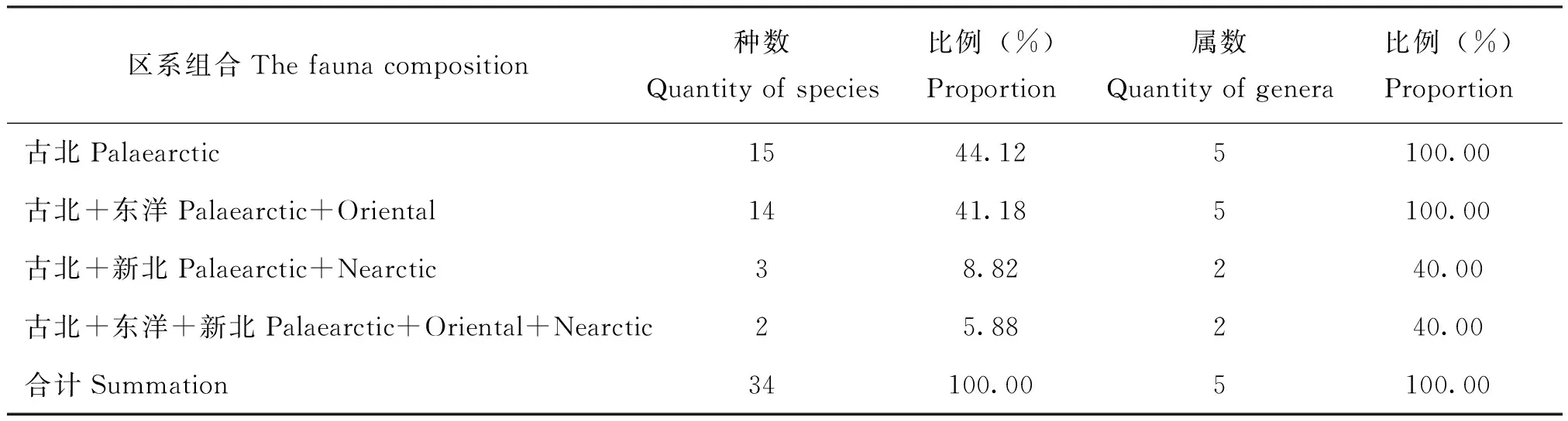
表2 蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫在世界动物地理区划中的分布类型
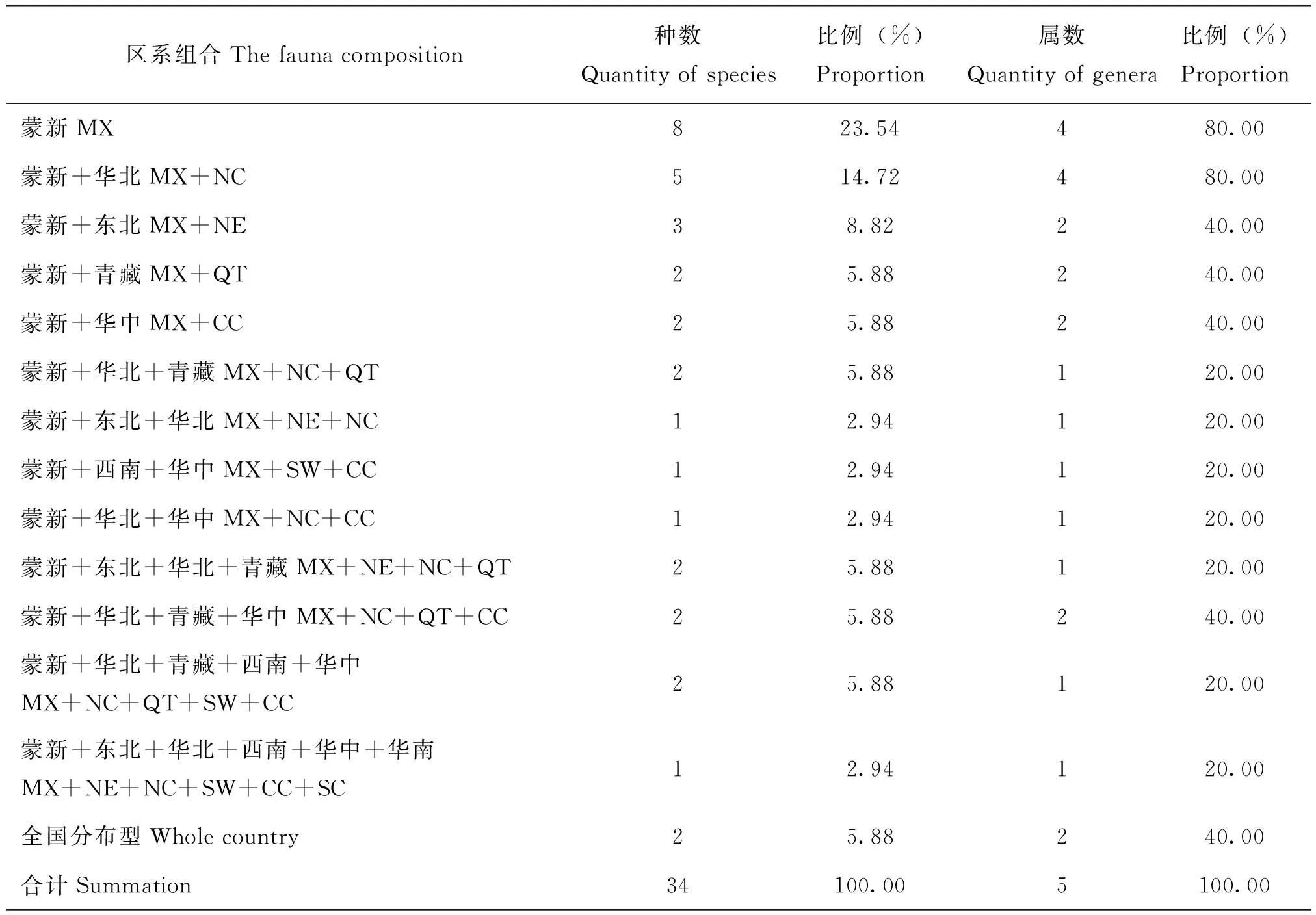
表3 蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫在中国动物地理区划中的分布类型
注:MX,蒙新;NE,东北;NC,华北;QT,青藏;SW,西南;CC,华中;SC,华南。Note:MX,Inner Mongolia-Xinjiang Region; NE,North-East Region; NC,North-China Region; QT,Qingzang-Tibet Region; SW,South-West Region; CC,Central-China Region; SC,South-China Region.
从跨区分布看,种类由多到少分别为:仅分布于蒙新区的种类最多,共8种,占总种数的23.54%;蒙新区+华北区5种,占总种数的14.72%;蒙新区+东北区3种,占总种数的8.82%;其它跨区分布类型种数均低于3种。属级分布类型蒙新区和蒙新区+华北区各4属,分别占总属数的80%;蒙新区+东北区、蒙新区+青藏区、蒙新区+华中区、蒙新区+华北区+青藏区+华中区以及全国分布型为2属,各占总属数的40%;其他分布型均为1属,分别占总属数的20%。从以上数据可以看出,蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫属级、种级区系均以蒙新区成分为主,与古北界中的华北区、青藏区、东北区关系密切。
2.2.3蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫在蒙新区动物地理区划中的分布特征
蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫在蒙新区动物地理区划中共有6种分布型,见表4。其中,西部荒漠亚区种数最多,共14种,占总种数的41.18%;东部草原亚区+西部荒漠亚区种数次之,共9种,占总种数的26.47%;全区分布型种数6种,占总种数的17.65%。属级分布类型与种级基本一致,西部荒漠亚区5属,占总属数的100%;东部草原亚区+西部荒漠亚区共有4属,占总属数的80%。
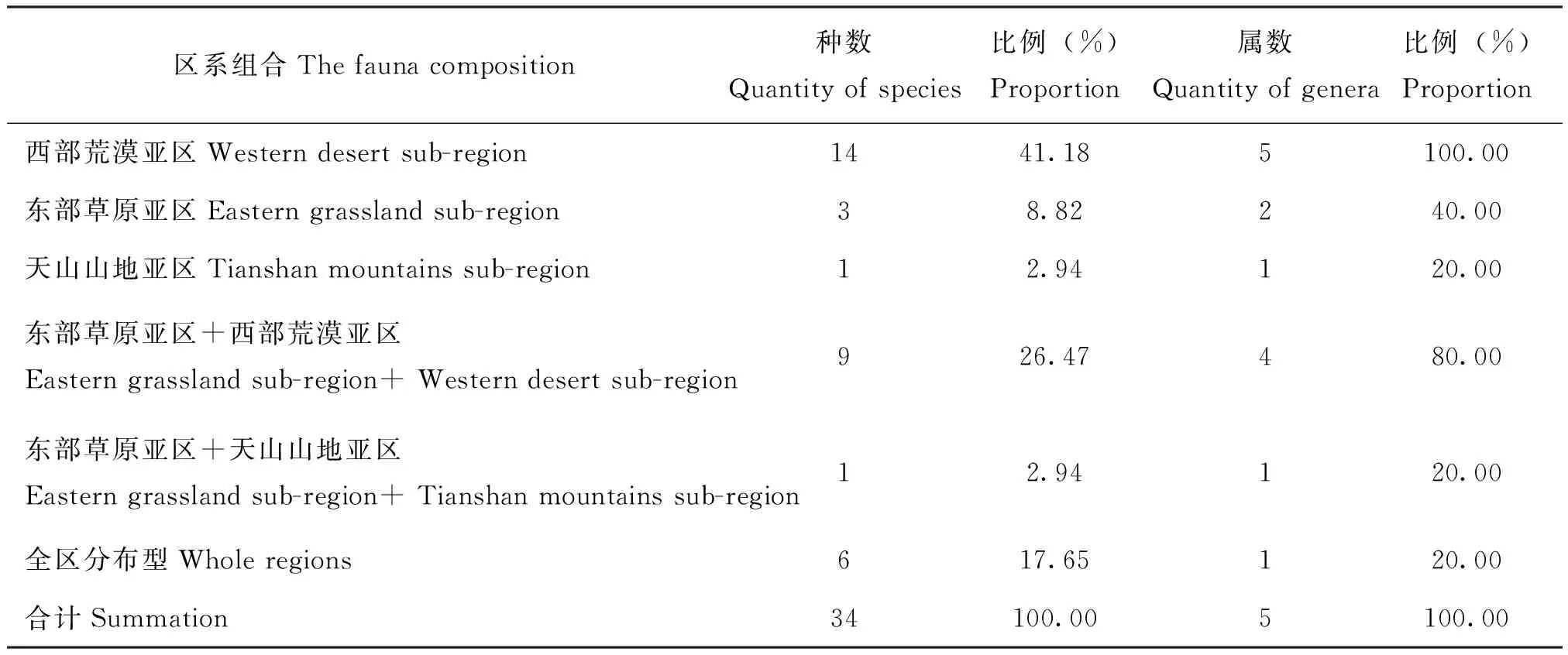
表4 蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫在蒙新区动物地理区划中的分布类型
2.3蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫与邻近国家及地区共有种比较
由表5可知,蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫与俄罗斯和蒙古的共有种最多,共15种,占其物种总数的44.12%;其次是与哈萨克斯坦的共有种11种,占32.35%;而与吉尔吉斯斯坦和塔吉克斯坦地区的共有种较少,仅草盲蝽属和后丽盲蝽属有个别共有种。与陕西、黑龙江、河北、山西、吉林和辽宁地区的共有种分别为11种(32.35%)、9种(26.47%)、7种(20.59%)、6种(17.65%)、3种(8.82%)和1种(2.94%)。
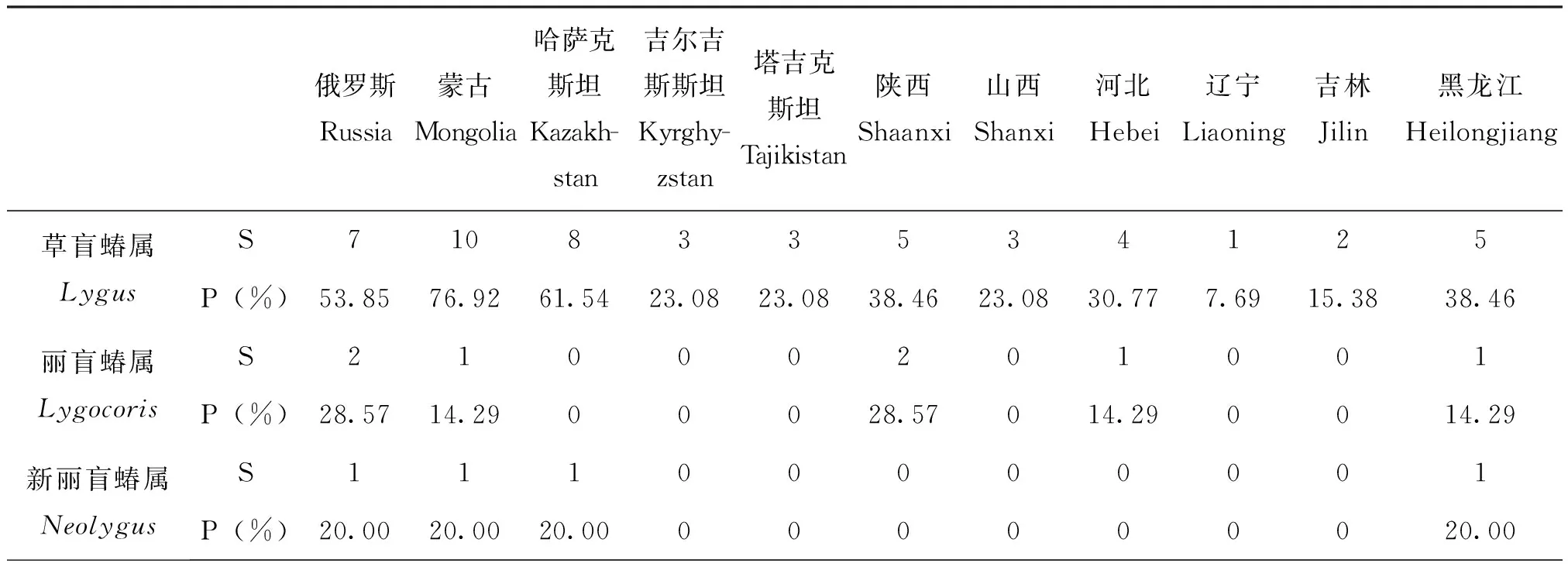
表5 蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫各属与邻近国家及地区共有种及其比例
续上表
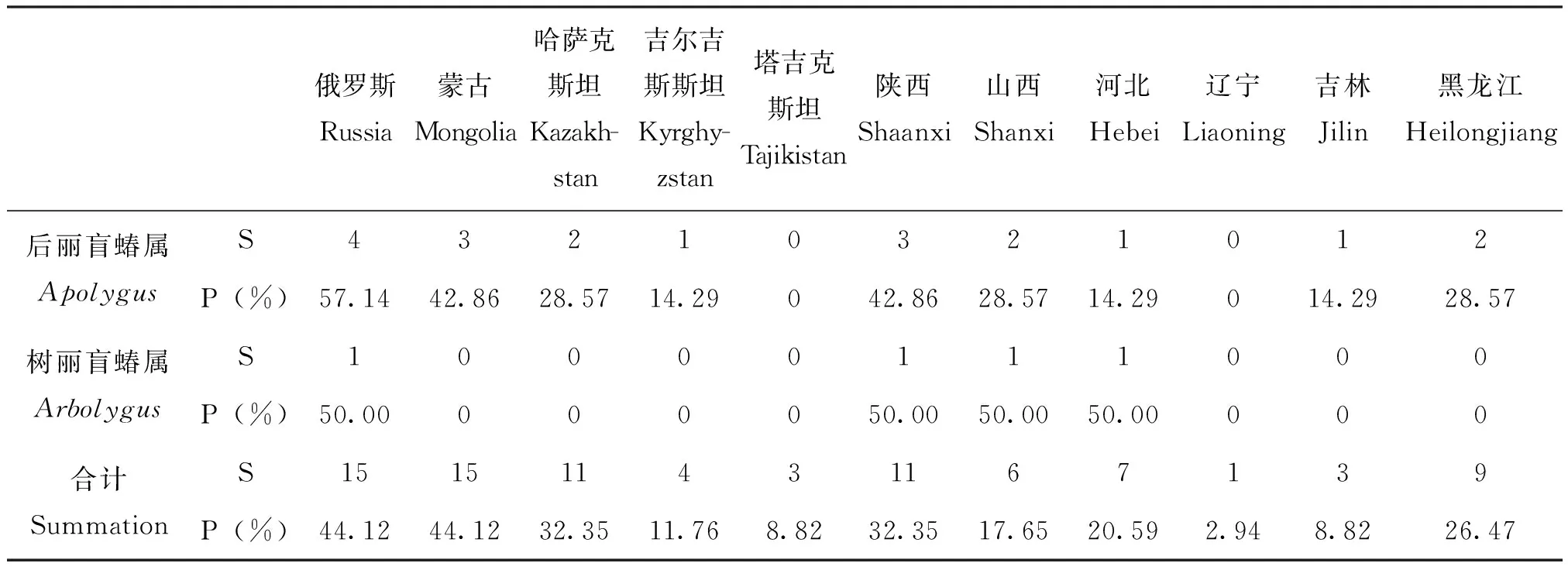
俄罗斯Russia蒙古Mongolia哈萨克斯坦Kazakh-stan吉尔吉斯斯坦Kyrghy-zstan塔吉克斯坦Tajikistan陕西Shaanxi山西Shanxi河北Hebei辽宁Liaoning吉林Jilin黑龙江Heilongjiang后丽盲蝽属ApolygusS43210321012P(%)57.1442.8628.5714.29042.8628.5714.29014.2928.57树丽盲蝽属ArbolygusS10000111000P(%)50.00000050.0050.0050.00000合计SummationS151511431167139P(%)44.1244.1232.3511.768.8232.3517.6520.592.948.8226.47
注:S,物种;P,百分比。Note:S,species; P,proportion.
3 结论与讨论
对蒙新区5属34种草盲蝽复合组昆虫种类组成和区系特征进行了初步分析。其中草盲蝽属Lygus有13种,占绝对优势,其次是丽盲蝽属Lygocoris和后丽盲蝽属Apolygus各有7种,新丽盲蝽属Neolygus5种,树丽盲蝽属Arbolygus2种。在世界动物地理区划中,以单区型古北界分布为主15种(占物种总数的44.12%),其次为古北界和东洋界的共有种14种(占41.18%)。在中国动物地理区划中,单独分布在蒙新区的物种最多,有8种(23.54%),其次是跨蒙新区与华北区分布的物种有5种(14.72%),在其它动物区系分布的草盲蝽复合组昆虫均较少。在蒙新区动物地理区划中,分布于西部荒漠亚区的种数最多,共14种(41.18%),其次为东部草原亚区和西部荒漠亚区共有种9种(26.47%);属级分布类型与种级相同。
蒙新区地处温带、暖温带,境内大部分地区为典型的大陆性气候,有高原、盆地、山地等多种地形,其东部为干草原地带、西部为荒漠与半荒漠地带、天山为山地森林与森林草原地带,其境内多样的地形地貌使得蒙新区内的草盲蝽复合组昆虫的区系分布也较为复杂。本文研究结果表明蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫区系以单区型古北界为主体,充分印证了蒙新区属于古北界;蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫区系拥有鲜明的蒙新区特征且与古北界中的华北区、青藏区、东北区关系密切,该结论与以往学者的研究结论基本一致(范玉香等,2011)。本论文未对蒙新区草盲蝽复合组昆虫区系起源、演化进一步分析,对其与周边地区也未做聚类比较,这些内容将在今后的研究中陆续开展。
致谢:感谢内蒙古师范大学能乃扎布先生的大力帮助,感谢参与标本采集的老师和学生。
References)
Aglyamzyanov RS. Synonymy of twoLygusspecies from Inner Mongolia (Heteroptera: Miridae)[J].ZoosystematicaRossica, 2003,11 (2): 326.
Aglyamzyanov RS. On the taxonomic status ofLygusisraelensis Linnavuori,1962 (Heteroptera: Miridae)[J].ZoosystematicaRossica, 2006,14 (2): 211-212.
Aglyamzyanov RS. Review of species of the genusLygusin the fauna of Mongolia, I [J].InsectsofMongolia, 1990, 11: 25-39.
Aglyamzyanov RS. Review of species of the genusLygusin the fauna of Mongolia, II (Heteroptera: Miridae)[J].ZoosystematicaRossica,1994,3 (1): 69-74.
Aukema B,Rieger C. Catalogue of the Heteroptera of the Palaearctic Region.Vol.3, Cimicomorpha Ⅱ, Miridae[M]. The Netherlands: Entomological Society Press,1999:62-123.
Carvalho JCM. Key to the genuer of Miridae of the World (Hemiptera)[M]. Bol. Mus. Goeldi-Tomo, XI (II),1955:68-78.
Fan YX, Tang GM. Fauna analysis of spiders of the family Gnaphosidae in Mengxin area (Arachnida: Araneae)[J].JournalofInnerMongoliaNormalUniversity(Natural Science Edition),2011,40(5):518-521. [范玉香,唐贵明.蒙新区平腹蛛科蜘蛛区系分析[J]. 内蒙古师范大学学报(自然科学汉文版),2011,40(5):518-521]
Josifov M. Eine neueLygus-Art aus Tadzhikistan (Insecta, Heteroptera: Miridae) [J].Reichenbachia,1992,29: 5-8.
Kelton LA. Genera and subgenera of theLyguscomplex(Heteroptera: Miridae)[J].CanadianEntomologist,1955a,87: 277-301.
Kerzhner M. Key to the Insect of European Part of USSR[M]. Moskow-Leningrad,1964:700-765.
Kerzhner M. Key to insects from Soviet Far East[M]. Leningrad:Nauka publishing House,1988:779-835.
Lu N, Zheng LY. Four new species of the genusApolygusChina from China (Insecta: Hemiptera: Miridae)[J].ActaZootaxonomicaSinica, 1997, 22(2): 162-168.
Lu N, Yasunaga T. Two new species of the subgenusNeolygusknight of the genusLygocorisreuter from China (Heteroptera:Miridae) [J].BulletinoftheBiogeographyicalSocietyofJapan,1994,49(2): 99-103.
Lu N, Zheng LY. A taxonomic study on the genusArbolygus(Heteroptera: Miridae) from China[J].Entomotaxonomia,1998, 20(2): 79-96.
Lu N,Zheng LY. Revision of Chinese species ofLygocoris(subg.Lygocoris) reuter (Hemiptera: Miridae: Mirinae)[J].ActaZootaxonomicaSinica, 2001, 26(2): 121-153.
Neng NZB. Insects of Inner Mongolia China[M]. Huhehaote: Inner Mongolia People’s Press,1999: 58-59. [能乃扎布.内蒙古昆虫[M].呼和浩特:内蒙古人民出版社,1999: 58-59]
Neng NZB, Qi BY. Fauna of pentatomidae of Inner Mongolia[J].JournalofInnerMongoliaNormalUniversity(Natural Science Edition), 1987,14(3): 22-31.[能乃扎布,齐宝瑛.内蒙古蝽科昆虫的区系分析[J].内蒙古师范大学学报(自然科学版), 1987,14(3): 22-31]
Qi BY. Notes on the Characteristics of Genitalia of the bugs of the bugs ofLygushahnfrom Inner Mongolia[J].JournalofInnerMongoliaNormalUniversity(Natural Science Edition),1993,4(Suppl.): 1-6. [齐宝瑛.内蒙古草盲蝽属昆虫的外生殖器特征记要[J].内蒙古师范大学学报(自然科学汉文版),1993,4(增刊): 1-6]
Qi BY, Neng NZB, Zhao RGT,etal. Studies on the diversity and fauna of Heteroptera in western desert of Inner Mongolia[J].JournalofInnerMongoliaNormalUniversity(Natural Science Edition),1997,3:56-64. [齐宝瑛,能乃扎布,照日格图,等.内蒙古西部荒漠半翅目昆虫多样性及区系研究[J].内蒙古师范大学学报(自然科学版),1997,3:56-64]
Schuh RT. Plant Bugs of the World (Insect: Heteroptera: Miridae) Systemetic Catalog, Distributions, Host List, and Bibliography[M]. The New York: Entomological Society Press,1995:685-859.
Schwartz MD, Kerzhner IM. Type specimens and identity of some Chinese species of the “Lyguscomplex” (Heteroptera: Miridae)[J].ZoosystematicaRossica,1996,5(2): 249-256.
Tomohide Y, Michael DS, Frederic C. New genera, species, synonymies, and combinations in the “Lyguscomplex” from Japan, with discussion onPeltidolyguspoppiusandWarrisiacarvalho(Heteroptera: Miridae: Mirinae)[J].AmericanMuseumNovitiates, 2002:1-27.
Zheng LY, Liu GQ, Lu N,etal. Fauna Sinica, Insecta Vol.33.Hemiptera[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004:1-427. [郑乐怡, 刘国卿, 吕楠, 等. 中国动物志(第三十三卷)昆虫纲·半翅目·盲蝽科·盲蝽亚科)[M].北京:科学出版社, 2004:1-427]
Zheng LY, Yu C. Notes on Chinese species ofLygus(S.Str.)hahnwith descriptions of three new species (Hemiptera: Miridae)[J].ActaZoosystematicaRossica, 1992, 17 (3): 352-359.[郑乐怡,于超.草盲蝽属中国种类记要(半翅目:盲蝽科)[J].动物分类学报,1992, 17(3): 352-359]
Zheng LY, Yu C. A new genus of theLyguscomplex from China, with description of six new species (Heteroptera: Miridae)[J].EntomologicaScandinavica,1990,21(2):159-171.
Zhang SM. As to the fauna of insecta[J].JournalofJiangxiArgriculturalUniversity,1984,1:11-19.[章士美. 昆虫的分布区系[J].江西农业大学学报,1984,1:11-19]
Zhang RZ. Zoogeography of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press,1999,1-502.[张荣祖.中国动物地理[M].北京:科学出版社,1999,1-502]
A preliminary study onLyguscomplex fauna in Mongolia-Xinjiang Region
LI Yuan-Yuan, SHI Kai*, DELIGEER
(College of Agronomy, Inner Mongolia University for Nationalities, Tongliao 028000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region,China)
There were 5 genera 34 species ofLyguscomplex distributed in Inner Mongolia-Xinjiang Region by identified the specimens and classified relevant records. Among them, the genera ofLygushad the most species (13 species accounted for 38.24%), having absolute advantage. Faunistic analyses showed that Palaearctic species (15 species about 44.12%) as it principal part at the level of world zoogeographical regions.Lyguscomplex only distributed in Inner Mongolia-Xinjiang Region had 8 species, almost equal to quarter of the total number of species (23.54%), followed by 5 common species (14.72%) distributed in Inner Mongolia-Xinjiang Region and North China region, 3 common species (8.82%) of in Inner Mongolia-Xinjiang region and the northeast region. And there were less species in other fauna. There were 14 species only distributed in the Western desert sub-region, accounting for 41.18% of the total species in Inner Mongolia-Xinjiang zoogeographical regions, the next is the common species (9 species accounting for 26.47%) of Eastern grassland sub-region and Western desert sub region.
Lyguscomplex; fauna; Inner Mongolia-Xinjiang Region
国家自然科学基金(31301922);内蒙古民族大学科学研究项目(NMDYB15014)
李媛媛,女,1982年生,河北唐山人,讲师,硕士,研究方向昆虫分类学,E-mail: liyuanyuan20131128@126.com
Author for correspondence, E-mail: nmshikai@126.com
2016-04-05; 接受日期Accepted:2016-04-23
Q968.2;S433.4
A
1674-0858(2016)04-0792-06
