氟喹诺酮类抗生素的表面解吸常压化学电离质谱行为研究
2016-08-02方小伟张兴磊
方小伟,李 婧,李 毅,张兴磊
(1.东华理工大学,江西省质谱科学与仪器重点实验室,江西 南昌 330013;2.东华理工大学分析测试研究中心,江西 南昌 330013)
氟喹诺酮类抗生素的表面解吸常压化学电离质谱行为研究
方小伟1,2,李婧1,2,李毅1,张兴磊1,2
(1.东华理工大学,江西省质谱科学与仪器重点实验室,江西 南昌330013;2.东华理工大学分析测试研究中心,江西 南昌330013)
摘要:采用表面解吸常压化学电离质谱(DAPCI-MS)技术对5种氟喹诺酮类化合物进行多级串联质谱研究,获得了各化合物的多级质谱信息。通过比较各化合物质谱裂解途径的异同,发现在正离子检测模式下,氟喹诺酮类化合物在碰撞诱导解离过程中均产生中性丢失44 u(CO2)、28 u(CO)、20 u(HF)、18 u(H2O)的离子峰。如果结构中含有哌嗪环取代基,脱羧后可观察到哌嗪环的重排反应,生成丢失43 u(C2H3NH2)和57 u(CH3—CH2—NCH2)的碎片离子,这可作为“诊断”其他氟喹诺酮类化合物和结构类似物的特征。该方法无需样品预处理,不使用有机溶剂,分析速度快,是一种无污染、无毒、原位、无损的分析方法,可为痕量药物分析提供新的思路。
关键词:氟喹诺酮类抗生素;表面解吸常压化学电离(DAPCI);质谱
氟喹诺酮类(fluoroquinolones,FQs)药物是在喹诺酮萘啶环的6位处引入氟原子而生成的,属于第三代喹诺酮类(quinolones,QNs)药物。氟喹诺酮类药物是人类在合成抗菌药物方面最重要的突破,因其抗菌谱广、抗菌活性强、毒副作用小、与其他抗菌药物无交叉耐药性等特点,被广泛应用于动物和人类的多种感染性疾病的预防和治疗中。根据国际上非专用药名命名的原则,对此类新药均采用“-oxacin”来命名,而该词在我国音译为“沙星”。目前临床上常用的氟喹诺酮类药物主要有诺氟沙星(norfloxacin)、氧氟沙星(ofloxacin)、左氧氟沙星(levofloxacin)、环丙沙星(ciprofloxacin)、洛美沙星(lomefloxacin)、氟罗沙星(fleroxacin)、培氟沙星(pefloxacin)和依诺沙星(enoxacin)等。随着抗生素的广泛使用,假冒抗生素的问题逐渐引起大家的关注。据世界卫生组织2015年在80个国家发起的新监测和报告项目显示,全球各地假抗生素的问题越来越严重[1]。
传统的抗生素分析方法主要有外观性状观察法[2]和简单试剂识别法[3],这两种方法可对假冒抗生素进行简单的初步筛选。目前,用于抗生素品质鉴定的方法主要有微生物法[4-5]、色谱法[6-9]、毛细管电泳法[10-11]、核磁共振法[12]和电化学法[13]等,但这些方法普遍存在操作步骤复杂、耗时较长等缺点,对于粉状、片状药物,由于其水溶性不强,还需要使用大量的有机溶剂。表面解吸常压化学电离质谱(DAPCI-MS)是近年发展起来的一种新兴质谱技术,具有快速、无损、灵敏度高等优点,可在常温常压下直接对粉状药品中的痕量物质进行分析[14-15]。
本研究拟利用实验室自制的DAPCI电离源,在无需样品预处理的情况下,对5种氟喹诺酮类药物进行串联质谱分析,以获得多级质谱指纹谱图,并分析其在DAPCI-MS正离子模式下的质谱裂解规律,希望为复杂样品中痕量氟喹诺酮类药物的测定提供新的思路和方法,同时也为氟喹诺酮类药物的快速结构解析、定量分析和药代动力学研究提供可靠的理论支持。
1实验部分
1.1主要仪器与装置
LTQ-XL型线性离子阱质谱仪:美国Finnigan 公司产品,配有Xcalibur 型数据处理系统;表面解吸常压化学电离源:实验室自制。
1.2主要材料与试剂
诺氟沙星胶囊:成都天台山制药有限公司产品;氧氟沙星胶囊:上海康普药业有限公司产品;加替沙星片:四川科伦药业股份有限公司产品;氟罗沙星片:河南天方药业股份有限公司产品;盐酸环丙沙星片:广州白云山制药有限公司产品。上述5种药物均购自当地药店,其基本信息列于表1。
1.3实验条件
设置LTQ-MS为正离子检测模式,放电针电压为3.2 kV,离子传输管温度为275 ℃,放电针尖至质谱入口毛细管的直线距离为1.0 cm,样品距放电针尖约1~3 mm,碰撞诱导解离(CID)时间为100 ms,离子选择窗口为1.0 u,碰撞能量为13%~25%,其他参数由LTQ-MS系统自动优化,所得质谱数据扣除背景后导出。
1.4实验方法
对于胶囊类药物,取其内容物,薄薄平铺一层于事先洗净的载玻片上,采用手动方式进样;对于片剂药物,去除其表面糖衣后直接放于载玻片上进样分析。
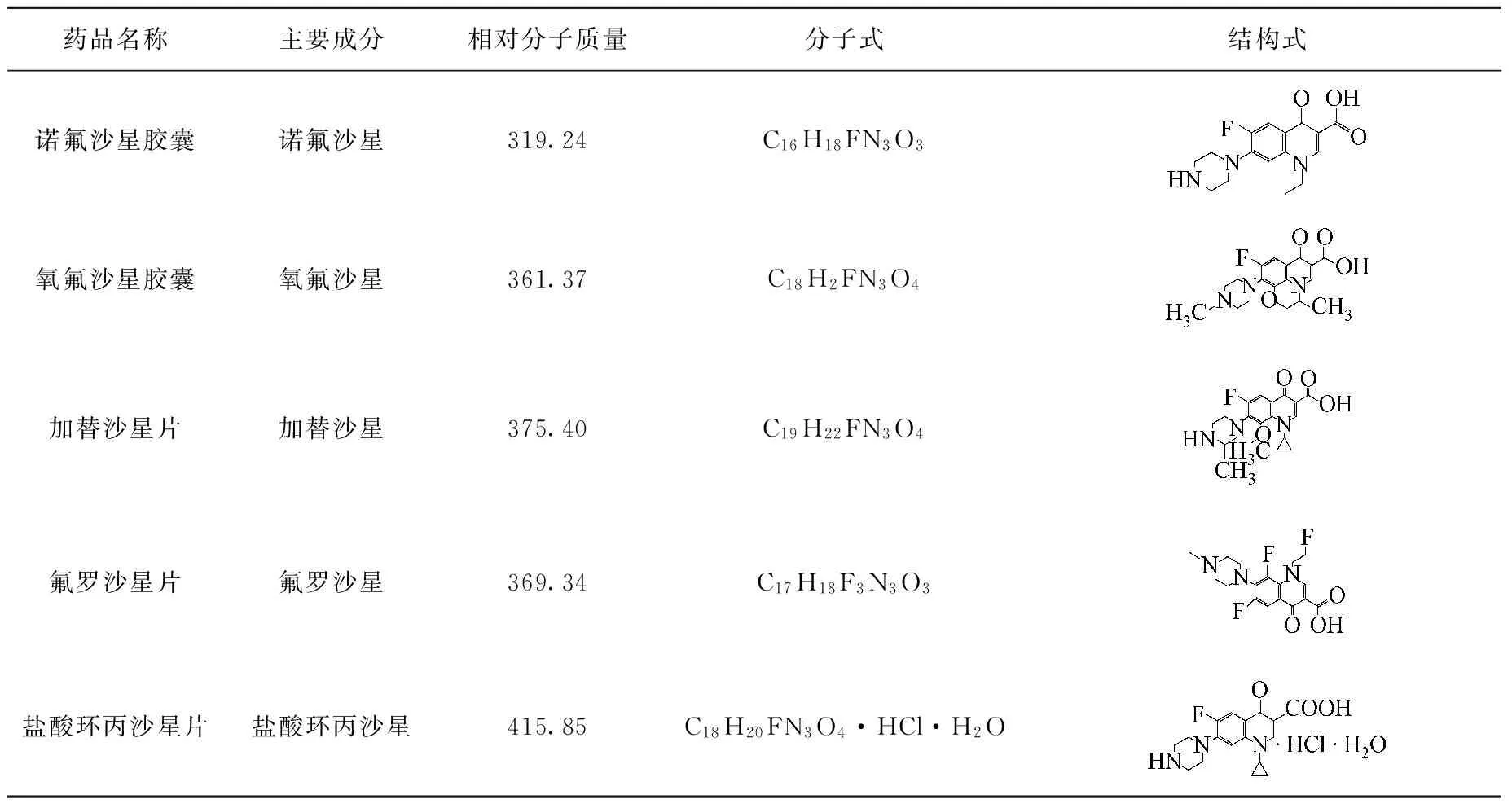
表1 5种氟喹诺酮类药物的基本信息
2结果与讨论

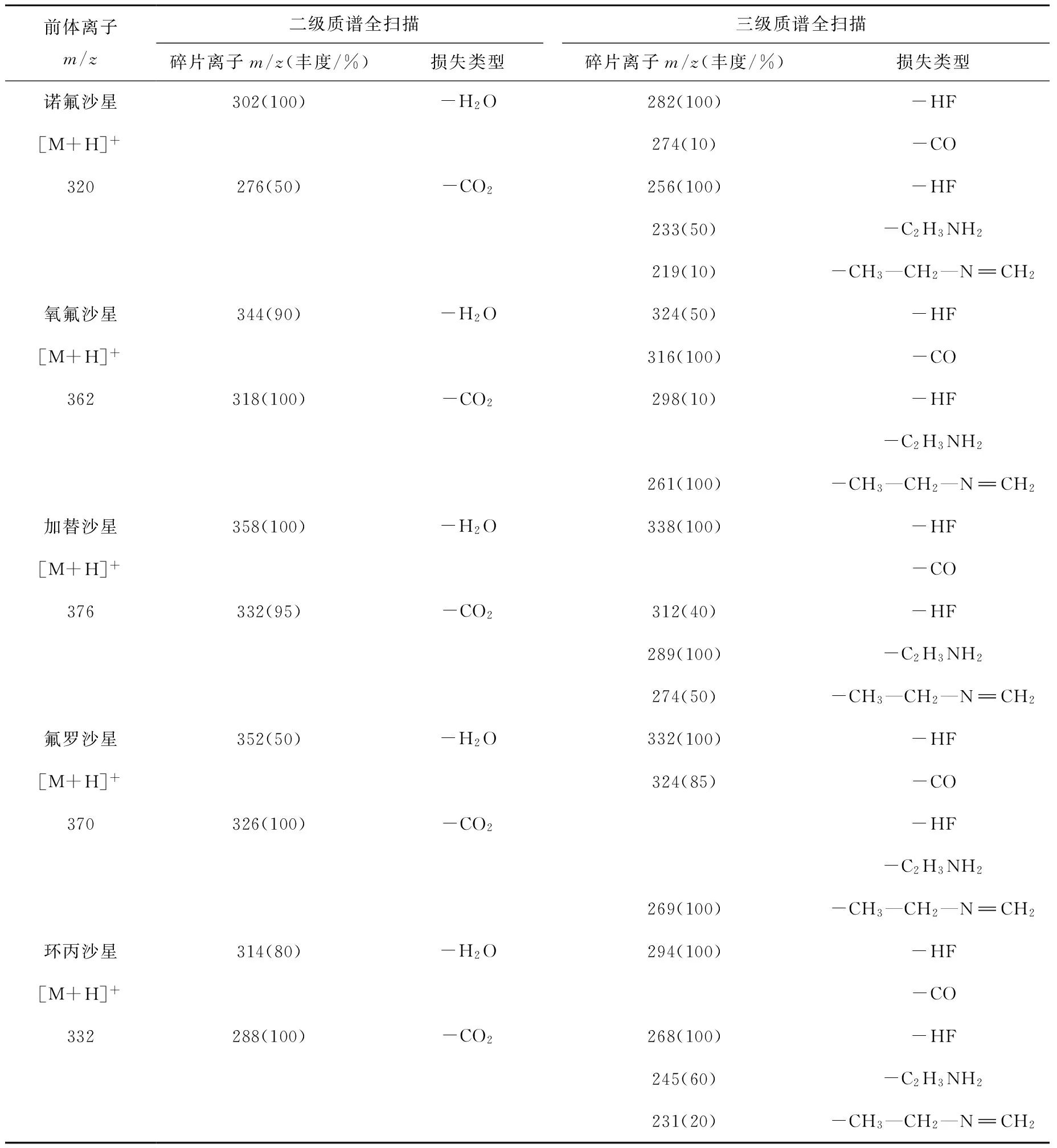
表2 5种氟喹诺酮类化合物的DAPCI-MSn信息(n=1~3)
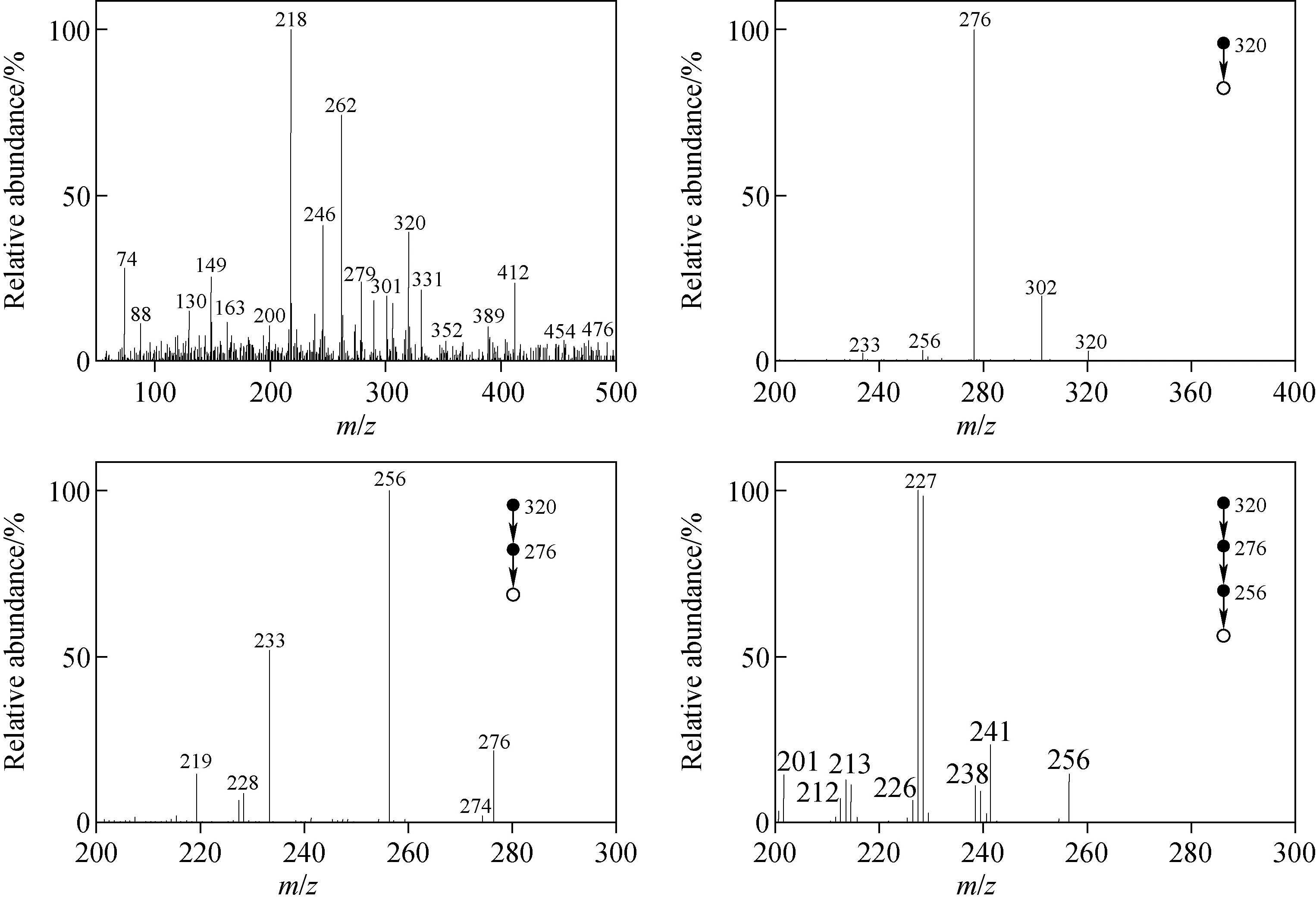
诺氟沙星胶囊的主要成分为诺氟沙星,即1-乙基-6-氟-1,4-二氢-4-氧代-7-(1-哌嗪基)-3-喹啉羧酸,相对分子质量为319。诺氟沙星的串联多级质谱图示于图1,推测的裂解途径示于图2。诺氟沙星呈酸碱两性,在正离子检测模式下可质子化形成准分子离子[M+H]+,从图1a中可明显看到质子化的诺氟沙星准分子离子m/z320。

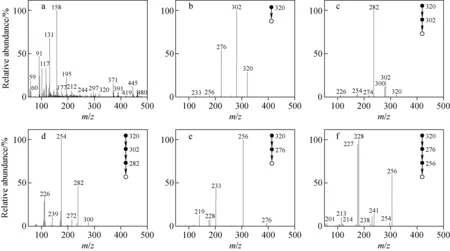
图1 诺氟沙星的串联多级质谱图(n=1~4)
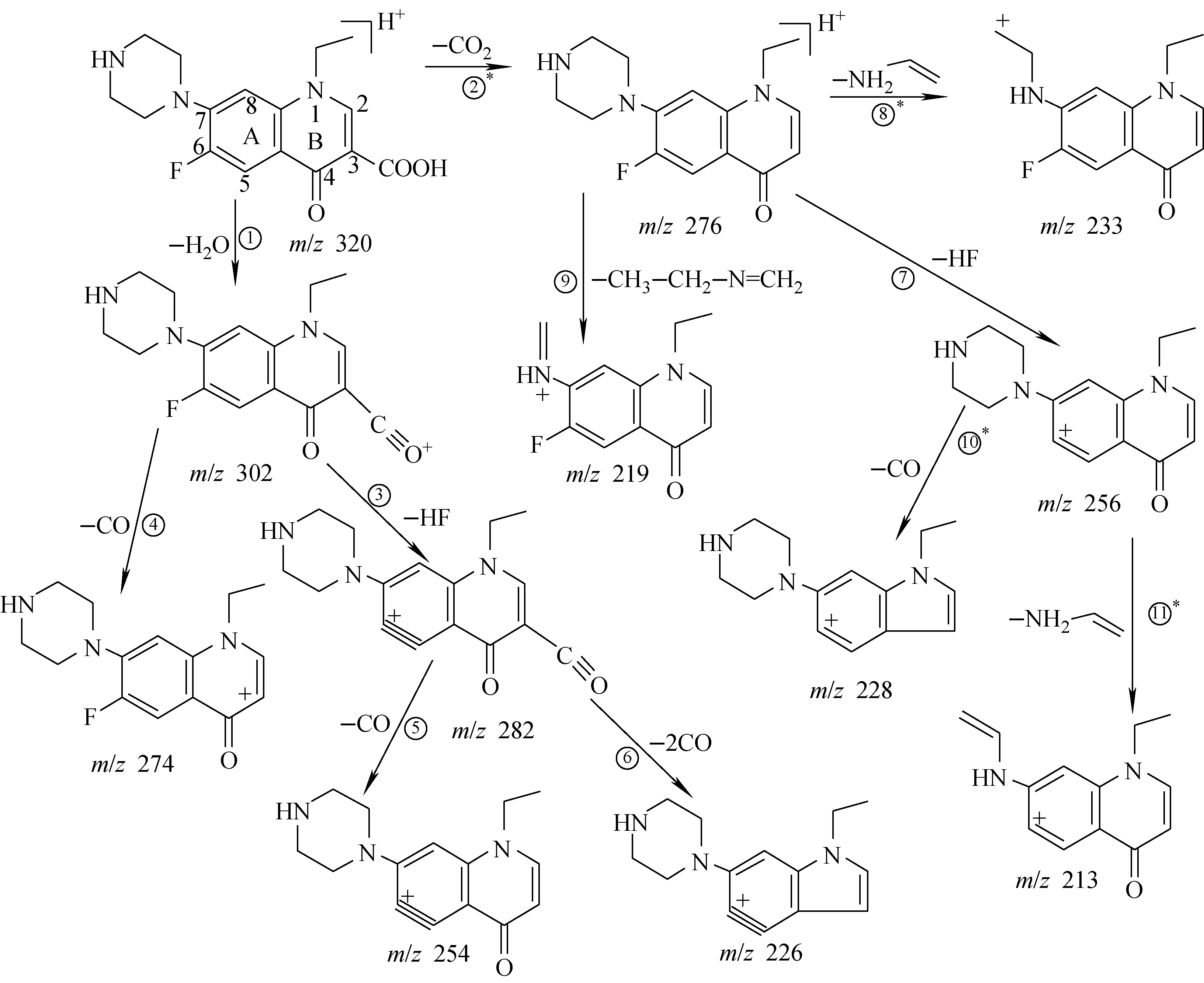
注:图中带*号的裂解途径推测存在分子内重排图2 诺氟沙星的裂解规律
选择二级质谱中的碎片离子m/z302进行CID实验,在三级质谱中,主要得到m/z282碎片离子,以及丰度相对较小的m/z274、254、226碎片离子,示于图1c。其中,m/z282与m/z302相比减少了20 u,推测为中性丢失一分子HF而生成,对应图2中的裂解途径③。m/z274与m/z302相比减少了28 u,推测为中性丢失一分子CO而生成,对应图2中的裂解途径④。m/z254与m/z302相比减少了48 u,推测为母离子中性丢失一分子HF后又失去一分子CO所致,是经过两次断裂后生成的产物,其丰度相对较低。
进一步对m/z282碎片离子进行串联质谱分析,主要得到m/z254和m/z226碎片离子,示于图1d。其中,m/z254与m/z282相比减少了28 u,推测为中性丢失一分子CO而生成,对应图2中的裂解途径⑤。m/z226与m/z282相比减少了56 u,推测为中性丢失两分子CO所致,对应图2中的裂解途径⑥。


3实际样品检测
采用DAPCI-MS法对可能存在抗生素污染的河水样品进行分析,可观察到[M+H]+(m/z320)准分子离子峰,其一级质谱图示于图3a。为排除假阳性,对主要离子峰进行多级串联质谱分析,所得质谱图示于图3b~3d。结果表明,实验所得碎片离子符合推测的诺氟沙星裂解规律,说明该方法可用于实际环境水体中诺氟沙星的快速检测。
4结论

研究表明,DAPCI-MS法可对药物粉末直接进行质谱分析,样品无需任何预处理,每个样品在不足1 min内即可完成质谱分析,且不需要载气,与小型质谱仪联用可用于药品的实时在线分析;该方法不使用任何有机溶剂,是一种无污染、无毒、原位、无损的分析方法,可为痕量药物分析提供新的思路。
注:a.一级质谱图;b.二级质谱图;c.三级质谱图;d.四级质谱图图3 实际河水样品的DAPCI-MSn质谱图
参考文献:
[1]http:∥www.who.int/drugresistance/documents/surveillancereport/en/.
[2]邓姿源. 几种假冒抗生素类药品外观鉴别[J].中国临床医生,2001,29(9):45.
DENG Ziyuan. Exterior of some counterfeit antibiotic drugs to identify[J]. Journal of Chinese Physician, 2001, 29(9): 45(in Chinese).
[3]SINGH B K, PARWATE D V, SHUKLA S K. Rapid color test identification system for screening of counterfeit fluoroquinolone[J]. Journal of Chemistry, 2009, 6(2): 377-384.
[4]杨天赐, 彭宣宪. 微生物比浊法检定抗生素G-418效价[J]. 中国抗生素杂志,2008,33(2):90-92.
YANG Tianci, PENG Xuanxian. Determination of the potency of antibiotic G-418 by microbial turbidimetry[J]. Chinese Journal of Antibiotics, 2008, 33(2): 90-92 (in Chinese).
[5]何作民,申放,黄旺潮. 不同培养基对硫酸庆大霉素注射液含量的影响[J]. 中国药业,2010,19(2):35-36.
HE Zuomin, SHEN Fang, HUANG Wangchao. Effect of different culture mediums on content assay of gentamycin sulfate injection[J]. China Pharmaceuticals, 2010, 19(2): 35-36(in Chinese).
[6]YUAN M R. Determination of the antibiotic oxytetracycline in commercial milk by solid-phase extraction: A high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) experiment for quantitative instrumental analysis[J]. Journal of Chemical Education, 2012, 89(5): 656-659.
[7]BATT A L, KOSTICH M S, LAZORCHAK J M. Analysis of ecologically relevant pharmaceuticals in wastewater and surface water using selective solid-phase extraction and UPLC-MS/MS[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2008, 80(13): 5 021-5 030.
[8]XU P, JIANG S, TAO B, et al. Determination and study on degradation dynamics of fungicide validamycin a residue in soil using pre-column derivatization and capillary gas chromatography[J]. Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2009, 64(8): 818-822.
[9]LIAWRUANGRATH B, LIAWRUANGRATH S. High performance thin layer chromatographic determination of erythromycin in pharmaceutical preparations[J]. Chromatographia, 2001, 54(5): 405-408.
[10]PAJCHEL G, MICHALSKA K, GERMAN R, et al. Assay of the related compounds thiamphenicol, florphenicol, and chloramphenicol by CE[J]. Chromatographia, 2008, 68(7): 587-591.
[11]MICHALSKA K, PAJCHEL G, TYSKI S. Different sample stacking strategies for the determination of ertapenem and its impurities by micellar electrokinetic chromatography in pharmaceutical formulation[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2009, 1 216(14): 2 934-2 942.
[12]施燕红,刘松柏,宋国强. 利用NMR测定盐酸头孢吡肟中杂质的含量[J]. 波谱学杂志,2003,20(3):259-264.
SHI Yanhong, LIU Songbai, SONG Guoqiang. Measurement of the percentage of impurity in cefepime dihydrochloride by NMR[J]. Magnetic Resonance, 2003, 20(3): 259-264(in Chinese).
[14]张燕,沈燕,韩超,等. 表面解吸常压化学电离质谱法直接测定宠物食品中三聚氰胺[J]. 现代科学仪器,2011,(5):86-90.
ZHANG Yan, SHEN Yan, HAN Chao, et al. Surface desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry for direct detection melamine in pet foods[J]. Modern Scientific Instruments, 2011, (5): 86-90(in Chinese).
[15]ZHANG X L, JIA B, HUANG K K, et al. Tracing origins of complex pharmaceutical preparations using surface desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2010, 82(19): 8 060-8 070.
[16]彭涛. 电喷雾串联质谱裂解规律及其在残留分析中的应用研究[D]. 北京:中国农业大学,2007.
[17]马彬,孙玉明,陈笑艳,等. 氟喹诺酮类化合物的电喷雾离子阱质谱分析[J]. 质谱学报,2006,27(3):163-167.
MA Bin, SUN Yuming, CHEN Xiaoyan,et al. Analysis of fluroquinolones by electrospray ion trap mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chinese Mass Spectrometry Society, 2006, 27(3): 163-167(in Chinese).
[18]施冰,张志刚,吴抒怀,等. LC-MS/MS测定水产品中7种氟喹诺酮类抗菌素残留量的方法研究[J]. 检验检疫科学,2004,14(增刊1):25-30.
SHI Bing, ZHANG Zhigang, WU Shuhuai, et al. Determination of 7 kinds of residual fluoroquinolone antibiotics in water by LC-MS/MS[J]. Inspection and Quarantine Science, 2004, 14(Suppl 1): 25-30(in Chinese).
收稿日期:2015-08-28;修回日期:2015-12-17
基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(21305011);国家重大科学仪器设备专项(2011YQ14015008、2011YQ17006702);长江学者和创新团队发展计划项目(IRT13054)资助
作者简介:方小伟(1987—),男(汉族),江西上饶人,助教,分析化学专业。E-mail: fxw273@126.com 通信作者:张兴磊(1986—),男(汉族),山东泰安人,讲师,从事分析化学研究。E-mail: leizi8586@126.com
中图分类号:O657.63
文献标志码:A
文章编号:1004-2997(2016)04-0319-08
doi:10.7538/zpxb.youxian.2016.0032
Analysis of Fluoroquinolones by Surface Desorption Atomospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry
FANG Xiao-wei1,2, LI Jing1,2, LI Yi1, ZHANG Xing-lei1,2
(1.JiangxiKeyLaboratoryforMassSpectrometryandInstrumentation,EastChinaInstituteofTechnology,Nanchang330013,China;2.TheResearchCenterofAnalysisandTesting,EastChinaInstituteofTechnology,Nanchang330013,China)
Abstract:Fluoroquinolones (FQs) are the third generation of quinolones (QNs), which are one of the most important breakthrough in the field of artificially synthesis of antimicrobial agents following sulfa drugs. Because of its wide antimicrobial spectrum, strong antibacterial activity, no cross resistance side effects with other antimicrobial agents, FQs are widely used in small animal and human many kinds of infectious diseases prevention and treatment. However, with the widespread use of antibiotics, the problems of counterfeit antibiotics emerged and proliferated gradually. Therefore, it is need to develope an analytical method with high sensitive and high speed. Mass spectrometry was the development of ambient ionization techniques, which enabled the ionization of samples in their native environment without sample pretreatment. After the emergence of the pioneered technique, desorption electrospray ionization (DESI), including more than 20 direct-ionization techniques, have been developed in the past decades. Among them, desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (DAPCI) is a powerful ionization technique and has been successfully applied to detect trace surface analytes without evidently injuring the sample in food security, forensic science and environmental science. In this study, the DAPCI source coupled with the linear ion trap mass spectrometer was used to investigate the fragmentation mechanism of fluroquinolones. Five compounds of fluroquinolones were analyzed using surface desorption atomospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry (DAPCI-MS) by collision induced dissociation in positive ion detection mode. The mass spectra and structures of the five fluroquinolones were compared with each other, and it was observed that fluroquinolones gave characteristic fragment ions by the neutral loss of 44 u (CO2), 28 u (CO), 20 u (HF) and 18 u (H2O). If compounds have piperazidine substituent, piperazine-link rearrangement can be observed after decarboxyliation, and characteristic fragment ions by the loss of the 43 u (CH2CH—NH2) and 57 u (CH3—CH2—NCH2) were produced. All of them can be used as a “diagnosis” of other fluoroquinolone compounds and structure similar to the characteristics of the ions, which can open a way to fast analyze the FQ drugs.
Key words:fluroquinolones antibiotics; surface desorption atomospheric pressure chemical ionization (DAPCI); mass spectrometry
网络出版时间:2016-07-05;网络出版地址:http:∥www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2979.TH.20160705.1212.012.html
