熊去氧胆酸衍生物及其生物活性研究进展
2016-07-10胡祥正臧臻臻
胡祥正,臧臻臻
(1.天津科技大学 食品工程与生物技术学院,天津 300457;2.天津科技大学 化工与材料学院,天津 300457)
熊去氧胆酸衍生物及其生物活性研究进展
胡祥正1,2Δ,臧臻臻1
(1.天津科技大学 食品工程与生物技术学院,天津 300457;2.天津科技大学 化工与材料学院,天津 300457)
熊去氧胆酸是熊体内产生的一种天然甾类物质,具有重要的药用价值。在临床上用于治疗肝胆疾病。熊去氧胆酸衍生物大多具有生物活性,具有潜在的药用价值。本文从熊去氧胆酸衍生物的合成与生物活性方面概述其研究进展,并对熊去氧胆酸衍生物的应用前景做了展望。
熊去氧胆酸衍生物;合成;应用;生物活性
熊去氧胆酸(UDCA, 3α,7β-二羟基-5β-胆甾烷-24-酸,1)(见图1)是熊胆汁中的一种甾类化合物,是治疗胆结石和肝脏疾病的药物[1-4]。熊去氧胆酸分子中羟基、羧基和甾环上的多个位置可以进行化学修饰,合成具有不同生物活性的衍生物。本文根据化学修饰不同位置所得产物,概述熊去氧胆酸衍生物及其生物活性。许多熊去氧胆酸衍生物具有抗菌、抗病毒、抗寄生虫和抗变态反应以及良好的抗肿瘤活性[5-8]。
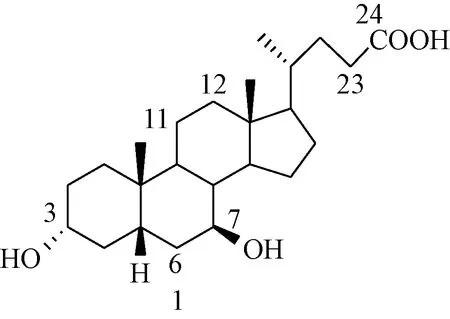
图1 熊去氧胆酸的分子结构Fig.1 Molecule structure of ursodeoxycholic acid
1 不同位置修饰所得的UDCA衍生物及其生物活性
1.1 3位修饰所得的熊去氧胆酸衍生物及其生物活性 3位修饰所得的熊去氧胆酸衍生物数量众多,许多具有生物活性。其中熊去氧胆酸3-硫酸酯(UDCA 3-Suls)是口服UDCA的主要尿代谢物[9-10]。健康男性尿液中1d排泄量相当于(131.0±61.2)μg未氨基化UDCA 3-Suls当量[11]。在临床上UDCA 3-Suls被用作UDCA的应变标志物[12]。UDCA的谷胱甘肽聚合物的C-3硫酸酯在临床上用于治疗胆汁淤积疾病[13]。
UDCA 3α-氨基衍生物 (见图2)对转运蛋白具有高度识别力,科学家们应用这个性质研究细胞的相互作用和分布,以及胆汁酸生物学相关问题[14]。

图2 UDCA 3-NBD 的分子结构Fig.2 Molecule structure of UDCA 3-NBD
UDCA的3位-葡萄糖基衍生物 (见图3),具有较强的水溶性,被用于手术后患者及不能口服药物的患者注射[15]。

图3 3-GLG-UDCA 的分子结构Fig.3 Molecule structure of 3-GLG-UDCA
UDCA、牛磺熊去氧胆酸(tauroursodeoxycholic acid,TUDCA)和甘氨熊去氧胆酸(glycoursodeoxycholic acid,GUDCA)的3α-乙酰葡萄糖胺羧酸酯,有希望应用于治疗人体代谢紊乱[16]。分子中同时含有乙酰葡萄糖胺基和磺酸基的UDCA衍生物 (见图4),与C1型尼曼-匹克病(Niemann-Pick type C1,NP-C1)有关[17]。
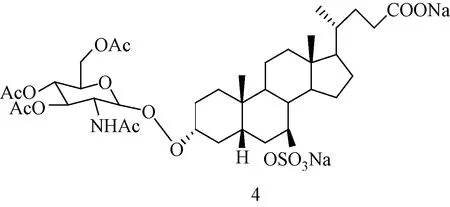
图4 UDCA-3α-N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖-7β-硫酸酯的分子结构 Fig.4 Molecule structure of UDCA-3α-N-acetylglucosamine-7β-sulphate
3-对叔丁基苯甲酰胺基熊去氧胆酸钠盐,在水溶液中呈管状结构,其疏水性对-叔丁基苯基具有增强表面活性剂性能,管状结构的壁为双层结构,内外表面带负电荷,有希望应用于中等尺度主客体化学领域[18-19]。
1.2 6位修饰衍生物 UDCA的6位氟化物6-FUDCA (见图5),能够治疗和预防患者的癌前细胞的形成,防止结肠癌治愈患者病的复发,具有优良的生物活性[20-23]。6位乙基取代的熊去氧胆酸衍生物 (见图6)可作为法尼酯X受体(farnesoid X Receptor, FXR)诱导剂。在临床上作保肝药物,在预防和治疗肝脏及胆汁淤积疾病方面有很好的疗效[24]。

图5 6α-F-UDCA的分子结构Fig.5 Molecule structure of 6α-F-UDCA

图6 6α-烷基-UDCA 的分子结构Fig.6 Molecule structure of 6α-alkyl-UDCA
由6-乙基鹅去氧胆酸(也叫奥贝胆酸,6alpha-ethyl-chenodeoxycholic acid,6-ECDCA)为原料,合成的化合物6-E-23(S)Me-UDCA (见图7),能够增加肠内胰高血糖素样肽1 (glucagon-like protein-1,GLP-1)的转录,增强GP-BAR1效能和专一性,为配体提供潜在的结合位点信息,预计可用于治疗肥胖症、Ⅱ型糖尿病等代谢紊乱引起的疾病[25]。

图7 6α-乙基 -UDCA (7) and 6α-乙基-23(S)-甲基-UDCA(8)的分子结构Fig.7 Molecule structure of 6α-ethyl -UDCA (7) and 6α-ethyl-23(S)-methyl-UDCA(8)
1.3 7位修饰衍生物 UDCA的7位或3、7位引入磺酸基的熊去氧胆酸7-硫酸酯(UDCA 7-Suls)和熊去氧胆酸3,7-二硫酸酯(UDCA 3,7-DSuls),能够防止胆汁淤积和限制肝细胞损害,可用于治疗消化道、肝脏炎症,也可用于改善肝脏疾病或肝功能引起的血清生化性质,增加胆汁流量或降低磷脂或胆固醇的胆汁排泄[12]。在UDCA的7位引入酰基所得的化合物对胆汁结石病、胆管肌能障碍、高甘油三酯血症等疾病具有很好的疗效[26]。UDCA、TUDCA和GUDCA的7位羟基上的氢原子被N-乙酰葡萄糖胺取代后所得的衍生物,具有酶吸附性能,可以利用其在尿液中的含量为诊断原发性肝硬化(Primary Biliary Cirrhosis, PBC)提供有用的信息,是临床上判断肝硬化的诊断指标,期望用于治疗PBC[27]。
UDCA的7位或3、7位引入葡萄糖基得到的UDCA衍生物7-GLG-UDCA和3,7-二GLG-UDCA (见图8),在水中的溶解度都较高,有希望作为利胆药物,用于手术后或不能口服药物的患者注射治疗[15]。

图8 7-GLG-UDCA(9) and 3,7-GLG-UDCA(10)的分子结构Fig.8 Molecule structure of 7-GLG-UDCA(9) and 3,7-GLG-UDCA(10)
图9所示的UDCA 衍生物可抑制钠依赖性胆盐转运体(apical sodium dependent bile acid transporter,ASBT)效力,阻碍Na牛磺胆盐共转运体(Na+/taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide,NTCP)的亲和力。ASBT和NTCP可与多种取代基结合,但是UDCA C-7位修饰得到的类似物大部分不能被ASBT或NTCP聚合转运[28]。

图9 C7,C24位取代的熊去氧胆酸衍生物分子结构Fig.9 Molecule structure of ursodeoxycholic acid derivates at C7,C24
1.4 修饰11位的熊去氧胆酸衍生物 11位和12位同时被氘取代的UDCA衍生物 (见图10)比放射性物质更稳定、安全,且质谱结果与母体不同,口服可用于治疗人的胆汁瘘[29]。

图10 UDCA-d2 的分子结构Fig.10 Molecule structure of UDCA-d2
1.5 23位修饰衍生物 23-甲基熊去氧胆酸(MUDCA)极少分泌到胆汁中,也很少与牛磺酸、甘氨酸结合。在进入消化道后,MUDCA很快进入肝脏,对动物无毒;其硫酸盐化、葡萄苷酸化后能抑制肝脏内二次衍生物的积累,同时也抑制胆汁酸肝肠循环[30]。
细胞表面受体G蛋白偶联胆汁酸受体1(G protein-coupled bile acid receptor 1,GP-BAR1)能够激发胆汁酸活性,刺激人体能量消耗,减少饮食引起的肥胖,临床上用于治疗代谢紊乱,23(S)-MUDCA (见图11)能够与GP-BAR1相互作用,调节其非基因组功能[25]。

图11 23(S)-甲基-UDCA的分子结构Fig.11 Molecule structure of 23(S)-methyl-UDCA
1.6 24位修饰的熊去氧胆酸衍生物
1.6.1 酰胺类衍生物:在生物体内,胆汁酸是胆固醇的代谢产物,它们的作用是促进脂肪和类脂的消化与吸收。在生物体内,胆汁酸通常以游离态和结合态2种状态存在。结合态主要是分别与甘氨酸和牛磺酸结合为甘氨胆汁酸和牛磺胆汁酸。甘氨熊去氧胆酸(GUDCA)和牛磺熊去氧胆酸(TUDCA)是熊体内存在的结合胆汁酸。
与UDCA相比,GUDCA分子毒副作用更小,亲水性更强[31],具有较强的抗氧化作用,在临床上可以作为抗氧化剂,用于治疗高胆红素血症[32]。TUDCA能抑制家族腺瘤息肉病衍生的LT97结肠腺瘤细胞的增长[33];TUDCA以有效地抑制不同类型细胞的凋亡为特征;TUDCA通过调制ER压力对hASCs脂肪形成起决定性作用,被用作减肥药物[34];TUDCA也被用于治疗糖尿病引起的视网膜病变[35]。
如图12所示的UDCA衍生物能够抑制肿瘤细胞增殖,并诱导其凋亡[36-38]。化合物15能抑制前列腺癌细胞PC-3的生长。化合物16能诱导HepG2细胞凋亡,效果比UDCA更好[37],被用作治疗肝癌的特效药[38]。化合物16、17在一定浓度下对MCF-7,MDA-MB-231细胞有抗增殖作用。此外,人们发现新型胆汁酸衍生物对人类胸腺肿瘤细胞的毒性作用可以通过细胞凋亡进行调控[39-40]。
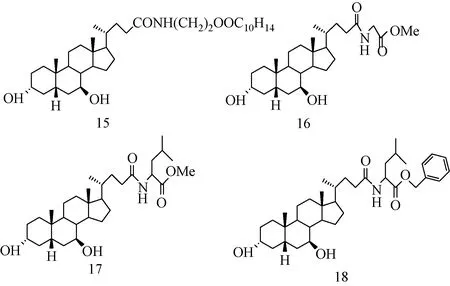
图12 HS-1183(15), HS-1030(16), HS-1133(17), HS-1068(18)的分子结构Fig.12 Molecular structures of HS-1183(15), HS-1030(16), HS-1133(17), HS-1068(18)
磺酰胺类化合物具有较宽的抗菌活性和潜在的抗肿瘤作用[41-43]。图13所示的一系列N-磺酰-3,7-二氧代-5β-胆烷-24-酰胺,对HCT-116、MCF-7、K562呈现良好的选择性细胞毒性。尤其是化合物19对SGC-7901抑制效果较好,化合物20、21、22对人癌细胞系呈现高抑制活性[44]。

图13 N-磺酰-3,7-二氧-5β-胆烷-24-酸的分子结构Fig.13 Molecular structures of N-sulfuryl-3, 7-dioxo-5β-cholane-24-acid
图14所示的UDCA磺酰胺类衍生物,对碳酸酐酶同工酶的抑制效果明显;这些化合物在兔子体内生物利用度比乙酰唑胺(acetazolamide)高[45]。

图14 磺胺类药物衍生物的分子结构Fig.14 Molecular structure of sulfonamide derivatives
图15所示的UDCA脂肪酸衍生物(27),当脂肪酸C链长于14时,此物对模型胆汁溶液胆固醇结晶具有明显的抑制作用,能够溶解小鼠胆结石[46]。

图15 与脂肪酸共轭的熊去氧胆酸衍生物分子结构Fig.15 Molecular structure of fatty acid conjugated with ursodeoxycholic acid
1.6.2 金属配合物:化合物28、29是分子中含有Pt原子的UDCA衍生物(见图16),化合物29能抑制肿瘤细胞生长,抗肿瘤活性强,与母体铂化合物相比,毒副作用低,在临床上被用作治疗肝癌的药物[47-48]。
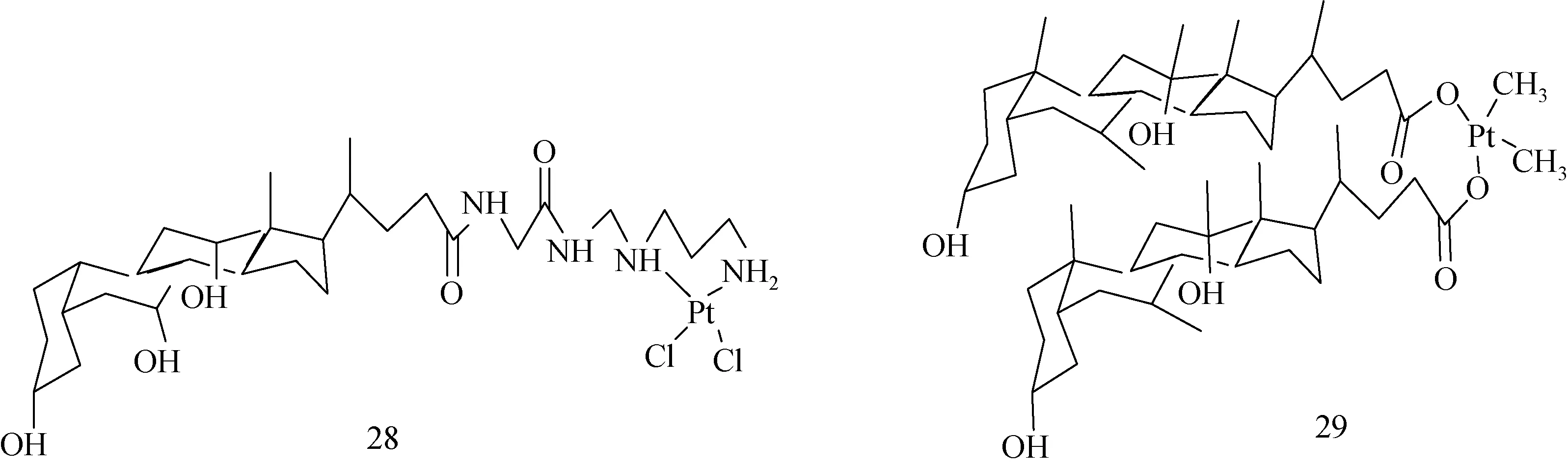
图16 Bamet-D3(28)和Bamet-UD2(29) 的分子结构Fig.16 Molecular structure of Bamet-D3(28), and Bamet-UD2(29)
1.6.3 杂环类:熊去氧胆酸衍生物 (图17)能选择性向肝脏传递NO,显著增加肝脏中cGMP浓度,调节肝脏中血管的扩张和收缩力[49-50]。化合物30比UDCA具有更强的抵抗胺碘酮的毒性作用[51]。能够有效抑制白介素、肿瘤坏死因子等多种炎性因子,对各种原因引起的肝损伤及炎症、门静脉高压、肝硬化及肝纤维化均具有较好的治疗作用[52-53]。

图17 NCX-1000的分子结构Fig.17 Molecular structure of NCX-1000
图18所示的肝靶向一氧化氮释放偶合物对四氯化碳及对乙酰氨基酚诱导的小鼠急性肝损伤具有显著修复作用,除此之外,该偶合物具有良好的肝靶向性,且其肝靶向性优于阳性药化合物30[54]。
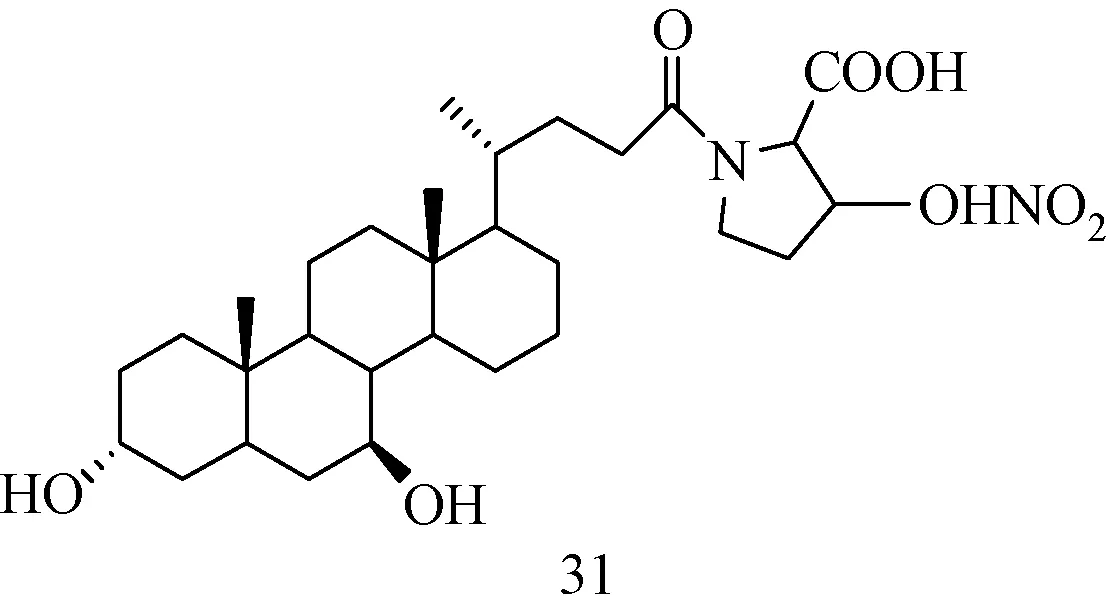
图18 新型肝靶向释放NO药物的分子结构Fig.18 Molecular structure of new liver targeted NO-releasing drugs
图19所示的N-乙酰基-S-(熊去氧胆烷基)半胱氨酸,在兔肝脏内很容易被羧酸酯酶水解[55]。此化合物水解后,能起到UDCA与半胱氨酸的双重药学作用,且更容易吸收[56]。

图19 UDCA-NAC的分子结构Fig.19 Molecular structure of UDCA-NAC
图20所示的哌嗪类胆汁酸衍生物33、34,对骨髓瘤细胞(KMS-11)、恶性胶质癌细胞(GBM)和结肠癌细胞(HCT-116)的生长增殖活性有抑制作用。该杂环固醇类物质有可能成为新型的抗癌药[57]。哌嗪类熊去氧胆酸的酰胺衍生物35、36、37,能够降低对人类结肠癌细胞株DLD-1、HCT-116、HT-29的生存能力[31]。

图20 哌嗪基熊去氧胆酸衍生物的分子结构Fig.20 Molecular structure of piperazinyl ursodeoxycholic acid derivates
熊去氧胆酸葡萄糖衍生物24-GLG-UDCA (见图21),水溶性大约是UDCA的13倍。其可用于注射,极大拓宽了其作为药物的应用途径[15]。

图21 24-GLG-UDCA的分子结构Fig.21 Molecular structure of 24-GLG-UDCA
1.6.4 失碳甾体化合物:24-nor-熊去氧胆酸(nor-UDCA)是UDCA的短侧链衍生物[58],其侧链少一个亚甲基基团,nor-UDCA与UDCA有着不同的物理化学和治疗学的特性。nor-UDCA与UDCA在体内也有不同的代谢机制;2者比较,UDCA对胆总管结扎(common bile duct ligated,CBDL)小鼠毒性比nor-UDCA大,而nor-UDCA能明显改良选择性胆管结扎(selective bile duct ligation,SBDL)小鼠肝脏损伤[59];在治疗肝脏纤维化方面,nor-UDCA比UDCA更有效果[60]。相比UDCA,nor-UDCA在体外直接抑制抗原呈递细胞的性能,激活T细胞。因此,nor-UDCA是治疗肝脏纤维化的潜在药物[61]。
1.6.5 前药类的熊去氧胆酸衍生物:作为内源性天然配基,胆汁酸具有良好的生物兼容性,适合作肝靶向药物载体[62]。图22所示的UDCA的N-烷基酰胺衍生物39、40[63-64],有可能作为前体药成分,应用于治疗多种疾病[65]。
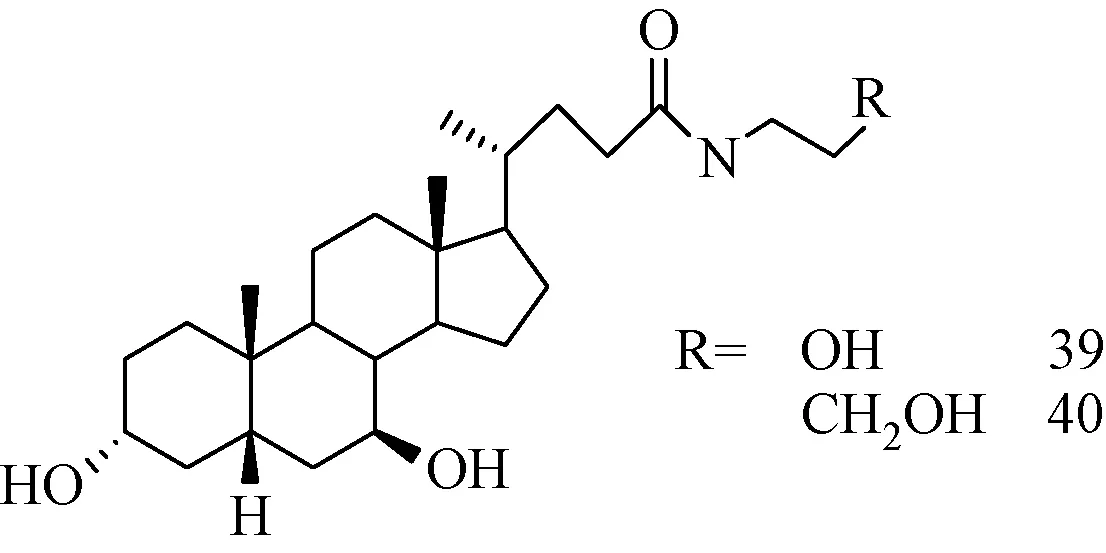
图22 N- 羟烷基3α,7β-二羟基-5β-胆烷-24-酰胺的分子结构Fig.22 Molecular structure of N- Hydroxyalkyl 3α, 7β-dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-amide
Tolle-Sander等[66-67]将阿昔洛韦与熊去氧胆酸24位的羧基通过缬氨酸相连制成前药,即熊去氧胆酸的缬氨酸酯,靶向作用于hAsBT,与单独服用阿昔洛韦相比,该前药的生物利用度显著提高。
UDCA与去氢贝母碱通过酯键结合,形成的熊去氧胆酸去氢贝母碱酯衍生物,在相同剂量下,该衍生物比UDCA或去氢贝母碱的止咳化痰效果都好。该衍生物具有更好的生物活性和较低的毒副作用,可用作止咳化痰药,代替传统中药中的川贝和蛇胆,解决了这2种中药的稀缺问题[68]。
2 结论与展望
UDCA是临床上应用广泛的治疗肝胆疾病的药物,也可以用作药物载体。UDCA衍生物大多具有不同的生物活性,具有潜在的药用价值。随着研究的深入,将会有更多的药用性能更好的UDCA衍生物成为药物,更好地为人类健康服务。
[1] Kitani K.Ursodeoxycholic acid for cholestatic diseases[J].Lancet,1988, 2(332): 8601-8649.
[2]Zhang Y, Lu J, Dai W, et al.Combination Therapy of Ursodeoxycholic Acid and Corticosteroids for Primary Biliary Cirrhosis with Features of Autoimmune Hepatitis: A Meta-Analysis[J].Gastroent Res & Pract, 2013, 2013(3):299-301.
[3]Poupon RE, Balkau B, Eschwtge E.A multicenter, controlled trial of ursodiol for the treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis UDCA-PBC Study Group[J].N Engl J Med, 1991, 324(22): 1548-1554.
[4]Shi J, Wu CY, Chen XY,et al.Long-term effects of mid-dose ursodeoxycholic acid in primary biliary cirrhosis: a metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials[J].Am J Gstroenterol, 2006, 101(7): 1529-1538.
[5]Saksena S, Tandon RK.Ursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of liver diseases[J].Postgrad Med J, 1997, 850(25): 73-75.
[6]Hofmann AF.Pharmacology of ursodeoxycholic acid, An enterohepatic drug[J].Scand J Gastroenterol, 1994, 204(29): 1-15.
[7]Sharma R, Prichard D, Majer F, et al.Ursodeoxycholic acid amides as novel glucocorticoid receptor modulators[J].J Med Chem, 2011, 54(1): 122-130.
[8]Dalpiaz A, Paganetto G, Pavan B, et al.Zidovudine and ursodeoxycholic acid conjugation: design of a new prodrug potentially able to bypass the active ef?ux transport systems of the central nervous system[J].Mol Pharm, 2012, 9(4): 957-968.
[9]Setchell KDR, Watson D, Balistreri WF, et al.A simple, rapid and non-invasive test of compliance to oral ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) therapy-detection of UDCA-sulfate:a specific urinary metabolite[J].Hepatology, 1991(14):261A.
[10]Nakamura K.Investigation of sulfate group position of urinary sulfated ursodeoxycholic acid in patients during ursodeoxycholic acid administration[J].Acta Hepatol Jpn, 1994, 35(11): 814-821.
[11]Kobayashi N, Katsumata H, Katayama H, et al.A monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of ursodeoxycholic acid 3-sulfates in human urine[J].J Steroid Biochem, 2000, 72(5): 265-272.
[12]Setchell KDR.Sulfate conjugates of ursodeoxychloric acid, and their beneficial use in inflammatory disorders and other applications: China, 1211185[P].2009.
[13]李咏梅.熊去氧胆酸联合还原型谷胱甘肽治疗胆汁淤积性肝病疗效观察[J].中国误诊学杂志, 2012, 12(6):1320-1321.
[14]Majer F, Salomon JJ, Sharma R, et al.New fuorescent bile acids: Synthesis, chemical characterization, and disastereoselective uptake by Caco-2 cells of 3-deoxy 3-NBD-amino deoxycholic and ursodeoxycholic acid[J].Bioorgan Med Chem, 2012, 20(5): 1767-1778.
[15]Mandai T, Okumoto H, Nakanishi K, et al.Ursodeoxycholic acid derivatives and methods for producing them.US, 6,075,132[P].2000-6-13.
[16]Niwa T, Koshiyama T, Goto J, et al.Synthesis of N-acetylglucosaminides of unconjugated and conjugated bile acids[J].Steroids, 1992,57(11): 522-529.
[17]Kakiyama G, Muto A, Shimada M, et al.Chemical synthesis of 3β-sulfooxy-7β-hydroxy-24- nor-5-cholenoic acid: An internal standard for mass pectrometric analysis of the abnormal delta5-bile acids occurring in Niemann-Pick disease[J].Steroids, 2009, 74(9): 766-772.
[18]Meijide F, Trillo J V, Frutos S, et al.Formation of tubules by p-tert-butylphenylamide derivatives of chenodeoxycholic and ursodeoxycholic acids in aqueous solution[J].Steroids, 2012, 77(12): 1205-1211.
[19]Tellini VS, Jover A, Meijide F, et al.Supramolecular Structures Generated by a p-tert- Butylphenyl-amide Derivative of Cholic Acid: From Vesicles to Molecular Tubes[J].Adv Mater, 2007, 19(13): 1752-1756.
[20]Gibson JC, Township H, Capuano LR.Prevention and Treatment of Colorectal Cancer by 6-Fluoroursodeoxycholic Acid (6-FUDCA): US, 426340 B1[P].2002-7-30.
[21]Roda A, Pellicciari R, Polimeni C, et al.Metabolism, Pharmacokinetics, and Activity of a New 6-Fluoro Analogue of Ursodeoxycholic Acid in Rats and Hamsters[J].Gastroenterology, 1995, 108(4): 1204-1214.
[22]Pellicciari R, Roda A, Frigerio G.Fluorinated bile acid derivatives, processes for the preparation thereof and pharmaceutical compositions containing them: US, 5166374[P].1992-11-24.
[23]Konigsberger K, Chen GP, Vivelo J, et al.An Expedient Synthesis of 6-Fluoroursodeoxycholic Acid[J].Org Process Res Dev, 2002, 6(5): 665-669.
[24]Ferrari M, Pellicciari R.Process for preparing 3α(β)-7α(β)-dihydroxy-6α(β)-Alkyl-5β-chol acid: US, 7,994,352 B2[P].2011-9-9.
[25]Yu DD, Sousa KM, Mattern DL, Wagner J, et al.Stereoselective synthesis, biological evaluation, and modeling of novel bile acid-derived G-protein coupled Bile acid receptor 1 (GP-BAR1, TGR5) agonists[J].Bioorg Med Chem, 2015, 23(7): 1613-1628.
[26]Scolastico C, Sirtori C, Kritchevsky D.Novel derivatives of ursodeoxycholic acid: US, 4,440,688[P].1984-4-3.
[27]Kobayashi N, Kubota K, Oiwa H, et al.Idiotype-anti-idiotype-based noncompetitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of ursodeoxycholic acid 7-N-acetylglucosaminides in human urine with subfemtomole range sensitivity[J].J Immunol Methods, 2003, 272(1-2): 1-10.
[28]Kolhatkar V, Polli JE.Structural requirements of bile acid transporters: C-3 and C-7 modifcations of steroidal hydroxyl groups[J].Eur J Pharm Sci, 2012, 46(1-2): 86-99.
[29]Tohma M, Nakata Y, Yamada H, et al.Quantitative determination of ursodeoxycholic acid and its deuterated derivative in human bile by gas chromatography-mass fragmentography[J].Chem Pharm Bull, 1981, 29(1): 137-145.
[30]Roda A, Aldini R, Grigolo B, et al.23-Methyl- a,7beta-dihydroxy-5beta-cholan-24-oic Acid: Dose- Response Study of Biliary Secretion in Rat[J].Hepatolcigy, 1988, 8(6): 1571-1576.
[31]Brossard D, Lechevrel M, Kihel LE, et al.Synthesis and biological evaluation of bile carboxamide derivatives with pro-apoptotic effect on human colon adenocarcinoma cell lines[J].Eur J Med Chem, 2014(86):279-290.
[32]Silva SL,Vaz AR, Diogenes MJ, et al.Neuritic growth impairment and cell death by unconjugated bilirubin is mediated by NO and glutamate, modulated by microglia, and prevented by glycoursodeoxycholic acid and interleukin-10[J].Neuropharmacology, 2012, 62(7): 2398-2408.
[33]Heumen BWHV, Roelofs HML, Morsche RHMT, et al.Celecoxib and tauroursodeoxycholic acid cotreatment inhibits cell growth in familial adenomatous polyposis derived LT97 colon adenoma cells[J].Exp Cell Res, 2012, 318(7): 819-827.
[34]Cha BH, Kim JS, Ahn JC, et al.The role of tauroursodeoxycholic acid on adipogenesis of human adipose-derived stem cells by modulation of ER stress[J].Biomaterials, 2014, 35(9): 2851-2858.
[35]Gaspar JM, Martins A, Cruz R, et al.Taurourdeoxycholic acid protects retinal neural cells from cell death induced by prolonged exposure to elevated glucose[J].Neuroscience, 2013, 253(17): 380-388.
[36]Im E, Choi YH, Paik KJ, et al.Novel bile acid derivatives induce apoptosis via a p53-independent pathway in human breast carcinoma cells[J].Cancer Lett, 2001, 163(1): 83-93.
[37]Suh H, Jung EJ, Kim TH, et al.Antiangiogenic activity of ursodeoxycholic acid and its derivatives[J].Cancer Lett, 1997, 113(1-2): 117-122.
[38]Park YH, Kim JA, Baek JH, et al.Induction of apoptosis in hepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by a novel derivative of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA)[J].Arch Pharm Res, 1997, 20(1): 29-33.
[39]Ime EO, Lee S, Suh H, et al.A novel ursodeoxycholic acid derivative induces apoptosis in human MCF-7 breast cancer cells[J].Pharm Pharmacol Commun, 1999, 5(4): 293-298.
[40]Im EO, Choi YH, Paik KJ, et al.Novel bile acid derivatives induce apoptosis via a p53-independent pathway in human breast carcinoma cells[J].Cancer Lett, 2001, 163(1): 83-93.
[41]Winum JY, Rami M, Scozzafava A, et al.Carbonic anhydrase IX: a new druggable target for the design of antitumor agents[J].Med Res Rev, 2008, 28(3): 445-463.
[42]Fournal M, Trachy-bourget MC, Yan PT, et al.Sulfonamide anilides, a novel class of histone deacetylase inhibitors, are antiproliferative against human tumors[J].Cancer Res, 2002, 62(15): 4325-4330.
[43]Mohan R, Banerjee M, Ray A, et al.Antimitotic sulfonamides inhibit microtubule assembly dynamics and cancer cell proliferation[J].Biochemistry, 2006, 45(17): 5440-5449.
[44]Ren J, Wang Y, Wang J, et al.Synthesis and antitumor activity of N-sulfonyl-3,7-dioxo-5beta-cholan 24-amides, ursodeoxycholic acid derivatives[J].Steroids, 2013, 78(1): 53-58.
[45]Temperini C, Scozzafava AL, Supuran CT.Carbonic anhydrase activators: X-ray crystal structure of the adduct of human isozyme II with L-histidine as a platform for the design of stronger activators[J].Bioorg & Med Chem Lett, 2005, 15(23): 5136-5141.
[46]李美英, 刘河, 何新华,等.新型饱和脂肪酸胆酸缀合物的合成及抗胆结石活性研究[J].有机化学, 2009, 3(3): 420-425.
[47]Lafuna M, Martinez-diez, MC, Monte MJ, et al.Liver Organotropism and Biotransformation of a Novel Platinum-Ursodeoxycholate Derivative, Bamet-UD2, with Enhanced Antitumour Activity[J].J Drug Target, 2001, 9(3): 185-200.
[48]Dominguez MF, Macias RIR, Izco-basurko I, et al.Low in Vivo Toxicity of a Novel Cisplatin-Ursodeoxycholic Derivative (Bamet-UD2) with Enhanced Cytostatic Activity versus Liver Tumors.Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics[J].J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2001, 297(3): 1106-1112.
[49]Fiorucci S, Antonelli E, Brancaleone V, et al.NCX-1000, a nitric oxide-releasing derivative of ursodeoxycholic acid,ameliorates portal hypertension and lowers norepinephrine-induced intrahepatic resistance in the isolated and perfused rat liver[J].J Hepatol, 2003, 39(6):932-939.
[50]Fiorucci S, Antonellie E, Morelli A.Nitric oxide and portal hypertension: a nitric oxide-releasing derivative of ursodeoxycholic acid that selectively releases nitric oxide in the liver[J].Digest Liver Dis, 2003, 35(Suppl 2): S61-69.
[51]Amine OC, Aziz E, Allal C, et al.Combining ursodeoxycholic acid or its NO-releasing derivative NCX-1000 with lipophilic antioxidants better protects mouse hepatocytes against amiodarone toxicity[J].Can J Physiol Pharmacol, 2007, 85(2): 233-242.
[52]Fiorucci S, Mencarelli A, Palazzetti B, et al.An NO derivative of ursodeoxycholic acid protects against Fas-mediated liver injury by inhibiting caspase activity[J].P Natl Acad Sci USA, 2001, 98(5): 2652-2657.
[53]Fiorucci S, Antonelli E, Morelli O,et al.NCX-1000, a NO-releasing derivative of ursodeoxycholic acid, selectively delivers NO to the liver and protects against development of portal hypertension[J].P Natl Acad Sci USA, 2001, 98(15): 8897-8902.
[54]李美英, 何新华, 陶林,等.胆汁酸为载体的肝靶向一氧化氮释放药物的设计与合成[J].有机化学, 2008, 28(12):2170-2174.
[55]Mitamura K, Sakai T, Nakai R, et al.Synthesis of the 3-sulfates of N-acetylcysteine conjugated bile acids (BA-NACs) and their transient formation from BA-NACs and subsequent hydrolysis by a rat liver cytosolic fraction as shown by liquid chromatography/ electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry[J].Anal Bioanal Chem, 2011, 400(7): 2061-2072.
[56]Mitamura K, Watanabe S, Sakai T, et al.Chemical synthesis of N-acetylcysteine conjugates of bile acids and in vivo formation in cholestatic rats as shown by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization-linear ion trap mass spectrometry[J].J Chromatogr B, 2009, 877(25): 2630-2638.
[57]Brossard D, Kihel LE, Clement M, et al.Synthesis of bile acid derivatives and in vitro cytotoxic activity with pro-apoptotic process on multiple myeloma(KMS-11), glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), and colonic carcinoma (HCT-116) human cell lines[J].Eur J Med Chem, 2010, 45 (7): 2912-2918.
[58]Trauner M, Halilbasic E, Claudel T.Potential of nor-Ursodeoxycholic Acid in Cholestatic and Metabolic Disorders[J].Dig Dis, 2015, 33:433-439.
[59]Fickert P, Pollheimer MJ, Silbert D, et al.Differential effects of norUDCA and UDCA in obstructive cholestasis in mice[J].J Hepatol, 2013, 58(6): 1201-1208.
[60]Buko VU, Lukivskaya OY, Naruta EE, et al.Protective Effects of Norursodeoxycholic Acid Versus Ursodeoxycholic Acid on Thioacetamide-induced Rat Liver Fibrosis[J].J Clin Exp, Hepatol,2014, 4(4): 293-301.
[61]Sombetzki M, Fuchs CD, Fickert P, et al.24-nor-ursodeoxycholic acid ameliorates inflammatory response and liver fibrosis in a murine model of hepatic schistosomiasis[J].J Hepatol, 2015, 62(4): 871-878.
[62]张盈, 杨硕, 李灵芝.肝靶向给药体系研究进展[J].中国新药杂志, 2013(8): 923-927.
[63]Willemen HM, Vermonden T, Marcelis ATM, et al.N-Cholyl amino acid alkyl esters—a novel class of organogelators[J].Eur J Org Chem, 2001, 2001(12): 2329-2335.
[64]Valkonen A, Lahtinen M, Virtanen E, et al.Bile acid amidoalcohols:
simple organogelators[J].Biosens Bioelectron, 2004, 20(6): 1233-1241.
[65]Valkonen A, Lahtinen M, Kolehmainen E.Synthesis and structural study of bile acid amidoalcohols[J].Steroids, 2008, 73(12): 1228-1241.
[66]Tolle-sander S, Lenta KA, Maeda DY, et al.Increased acyclovir oral bioavailability via a bile acid conjugate[J].Mol Pharm, 2003, 1(1):40-48.
[67]Balakrishnan A, Polli JE.Apical sodium dependent bile acid transporter (ASBT, SLC10A2): a potential prodrug target[J].Mol Pharm, 2006, 3(3): 223-230.
[68]Zhang JL, Wang H, Pi HF, et al.Structural analysis and antitussive evaluation of five novel esters of verticinone and bile acids[J].Steroids, 2009, 74(4-5): 424-434.
(编校:王俨俨)
Progress of ursodeoxycholic acid derivatives and their bioactivities
HU Xiang-zheng1,2Δ, ZANG Zhen-zhen1
(1.College of Food Engineering and Biotechnology, Tianjin University of Science and Technology, Tianjin 300457, China; 2.College of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Tianjin University of Science and Technology, Tianjin 300457, China)
Ursodeoxycholic acid, a kind of natural steroid compound, is synthesized from bear body.It is an important medicine in clinic and can be used to treat liver diseases.Most of ursodeoxycholic acid derivatives have pharmaceutical performance.Research progress of ursodeoxycholic acid derivatives in terms of preparation and bioactivity was described and application prospects were outlooked in this paper.
derivatives of ursodeoxycholic acid; synthesis; application; bioactivities
10.3969/j.issn.1005-1678.2016.07.59
胡祥正,通信作者,男,博士,教授、硕士生导师,研究方向:抗肿瘤药物的开发应用及生物材料的合成,E-mail:huxzh@tust.edu.cn。
O629.21
A
