最优冲突回避码的具体构造
2016-06-23黄必昌朱文兴
黄必昌,朱文兴
(1. 百色学院数学与统计学院,广西 百色 533000; 2. 福州大学离散数学与理论计算机科学研究中心,福建 福州 350002)
最优冲突回避码的具体构造
黄必昌1, 2,朱文兴2
(1. 百色学院数学与统计学院,广西 百色533000; 2. 福州大学离散数学与理论计算机科学研究中心,福建 福州350002)
摘要:冲突回避码被应用于多分址冲突信道中,目前对最优冲突回避码的具体构造取得的结果大多是码重k=3, 4, 5, 6, 7的情况,对码重k>7具体构造结果比较少. 为此,利用已有的构造方法结合数论相关知识,进一步构造码重k=8, 9, 10, 11, 12,码长n=(k-1)p时的最优冲突回避码新结果.
关键词:冲突回避码; 码重; 二次剩余; 分圆类
0引言
冲突回避码(conflict-avoiding code, CAC)作为协议序列被应用于无反馈多分址信道(冲突信道)[1-2],多分址信道模型可参看文献[1]. 下面给出冲突回避码的数学描述.

Δ(A)={x-y(modn):x, y∈A, x≠y}
设C是Zn一些k阶子集A⊆Zn的集合,则C被称为长度为n重量为k的冲突回避码, 若其满足:
Δ(A1)∩Δ(A2)=φ, ∀A1, A2∈C, A1≠A2
每个元素A∈C称为一个码字. 对于给定的n和k,符号CAC(n, k)表示所有长度为n重量为k的冲突回避码. 当光正交码互相关性等于1时可看做一种冲突回避码,关于光正交码的定义可参看文献[3].
为了寻求最优码,人们主要考虑一种特殊的码——等差码. 主要原因是这类码的码字差集不同元素的个数比较少,相应地会得到较多的码字.

对于冲突回避码C∈CAC(n, k),码字数量是保证潜在用户数量传输数据的有效性和可靠性. 最优冲突回避码能保证最大数量的潜在用户有效可靠地传输信息. 码字的重量k(汉明码重量)表示用户在每个时段的n个时槽里发送k个数据包[4].
1相关构造及证明
为了方便理解,先介绍一些常用的概念和符号.
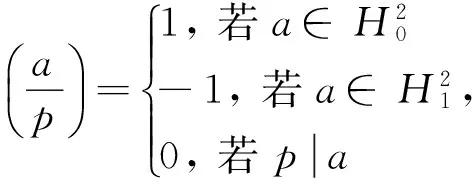
关于勒让德符号,当a=-1, 2, 3, 5, 7时有如下结果,为叙述方便记作引理1.
引理 1[12]若p是奇素数,则
引理2[4]设e≥1和s>1都是整数,p=2em+1是素数且使得每一个(i-es, i-(e-1)s, …, i+(e-1)s), 1≤i≤s-1和(±s, ±2s, …, ±es)都各自形成一个2e阶分圆类代表系. 那么存在一个码C∈CACe(sp, k=es+1)包含m个码字,且满足ZspΔ(C)=pZsp.
引理3[11]若m>s,则引理2构造的码C∈CACe(sp, k=es+1)是最优的.

下面,用引理1和引理2来具体构造等差码.
定理1若p=2m+1是素数且p≡71, 119(mod120),则存在码C∈CACe(7p, 8)包含m个码字.

而当p≡71, 119(mod120)时以上条件满足. 从而命题得证.

证明由定理1,每个pi=2mi+1, 1≤i≤r都是使得Ci∈CACe(7pi, 8)存在的素数,则反复利用引理4递推构造即可.
定理2若p=2m+1是素数且p≡71, 191, 239, 359, 431, 599(mod840),则存在码C∈CACe(8p, 9)包含m个码字.

而当p≡71, 191, 239, 359, 431, 599(mod840)时以上条件满足. 从而命题得证.

证明根据定理2,每个pi=2mi+1, 1≤i≤r都是使得Ci∈CACe(8pi, 9)存在的素数,则反复利用引理4递推构造即可.
定理3若p=2m+1是素数且p≡39, 71, 79, 151, 191, 239(mod280),则存在码C∈CACe(9p, 10)包含m个码字.


证明由定理3,每个pi=2mi+1, 1≤i≤r都是使得Ci∈CACe(7pi, 8)存在的素数,则反复利用引理4递推构造即可.
定理4若p=2m+1是素数且p≡23, 55, 71, 95(mod168),则存在码C∈CACe(10p, 11)包含m个码字.


证明由定理4,每个pi=2mi+1, 1≤i≤r都是使得Ci∈CACe(10pi, 11)存在的素数,反复利用引理4递推构造即可.
定理5若p=2m+1是素数且p≡71, 191, 239, 359, 431, 599(mod840),则存在码C∈CACe(11p, 12)包含m个码字.


证明由定理5,每个pi=2mi+1, 1≤i≤r都是使得Ci∈CACe(11pi, 12)存在的素数,反复利用引理4递推构造即可.
2结论

参考文献:
[1] MASSEY J L, MATHYS P. The collision channel without feedback[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1985, 31(2): 192-204.
[2] GRYORFI N Q A L, MASSEY J L. Constructions of binary constant weight cyclic codes and cyclically permutable codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1992, 38(3): 940-949.
[3] SALEHI J A. Code division multiple-access techniques in optical fiber networks: I. fundamental principles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1989, 37(8): 824-833.
[4] MOMIHARA K, MULLER M, SATOH J,etal. Constant weight conflict avoiding codes[J]. Siam Journal on Discrete Mathematics, 2008, 21(4): 959-979.
[5] FU H L, LI Y H, MISHIMA M. Optimal conflict avoiding codes of even length and weight 3[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2011, 57(8): 5 572-5 572.
[6] JIMBO M, MISHIMA M, JANISZEWSKI S,etal. On conflict avoiding codes of lengthn=4mfor three active users[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2007, 53(8): 2 732-2 742.
[7] LEVENSHTEIN V I. Conflict-avoiding codes for three active users and cyclic triple systems[J]. Problems of Information Transmission, 2007, 43(3): 199-212.
[8] MISHIMA M, FU H L, URUNO S. Optimal conflict avoiding codes of lengthn=(0 mod16) and weight 3[J]. Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 2009, 52(3): 275-291.
[9] Momihara K. Necessary and sufficient conditions for tight equidifference conflict avoiding codes of weight three[J]. Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 2007, 45(3): 379-390.
[10] MA W P, ZHAO C E, SHEN D S. New optimal constructions of conflict-avoiding codes of odd length and weight 3[J]. Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 2014, 73(3): 791-804.
[11] SHUM K W, WONG W S, CHEN C S. A general upper bound on the size of constant weight conflict avoiding codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2010, 56(7): 3 265-3 276.
[12] NATHANSON M B. Elementary methods in number theory[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 2000.
(责任编辑: 郑美莺)
Explicit constructions of optimal conflict-avoiding codes
HUANG Bichang1, 2, ZHU Wenxing2
(1. College of Mathematics and Statistics, Baise University, Baise, Guangxi 533000, China;2. Center for Discrete Mathematics and Theoretical Computer Science, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, Fujian 350002, China)
Abstract:Conflict-avoiding code was applied in multiple-access in the collision channel. Previously, researchers investigate explicit constructions of optimal conflict-avoiding code in the case of k=3, 4, 5, 6, 7. And there is very few results in the case of k>7. In this paper, combing pre-existing constructions with the related knowledge of number theory, a new infinite classes of optimal conflict-avoiding codes with weight k=8, 9, 10, 11, 12 and length n=(k-1)p are obtained.
Keywords:conflict-avoiding code; code weight; quadratic residue; cyclotomic class
DOI:10.7631/issn.1000-2243.2016.03.0390
文章编号:1000-2243(2016)03-0390-04
收稿日期:2015-12-01
通讯作者:朱文兴(1968-),教授,主要从事优化理论与算法研究,wxzhu@fzu.edu.cn
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(61170308); 广西省自然科学基金资助项目(2013GXNSFAA019022); 广西省高校科研项目(2013YB246); 百色学院科研基金资助项目(2012KB01)
中图分类号:O157.4
文献标识码:A
