Highly selective synthesis for 4,4′-bisphenol F from phenoland formaldehyde catalyzed with[C4mim][HSO4]ionic liquid☆
2016-05-30DanfengWangZhichengHeZhiminWuYingTanYongfeiLiYuejinLiu
Danfeng Wang,Zhicheng He,Zhimin Wu*,Ying Tan,Yongfei Li,Yuejin Liu*
College ofChemicalEngineering,Xiangtan University,Xiangtan 411105,Hunan,China
1.Introduction
Bisphenol F,a mixture of 2,2′-,2,4′-and 4,4′-isomers,is generally synthesized from phenoland formaldehyde under the presence ofacidic catalysts,and among them,a linear structure of4,4′-bisphenol F has the best performance[1–2].The selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F was 55%using phosphoric acid as catalyst[3],and 45%of the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F in 15 min was obtained with Al-MCM-41 mesoporous molecular sieve catalysts[4–5].Due to the adjustable solid acid structure[6]and shape-selective effect,the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenolF can be improved.But the microporous solid acid reaction system is susceptible to watermolecules with microporous blocked,which affects the catalytic activity and reusability[7–8].Ionic liquids,with the regulation ofstructure and functioning as catalystand solvent,have been used to F–C alkylation catalytic reactions[9–12],and both the anion/cation and the chain length of alkyl substituted group in ionic liquids have in fluence on the catalytic activity and the selectivity[13–17].In our previous research,the synthesis bisphenol F was investigated using ionic liquids as catalysts and the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F is only 42.7%under the high phenol/formaldehyde ratio 30:1 and reaction temperature 90 °C[12–14].Highly selective synthesis of4,4′-bisphenol F is few reported and need to further research.
The hydrogen bonding between ionic liquid and reactants can signi ficantly improve the product selectivity,and has attracted much attention.The[Bmim][PF6]ionic liquid gave a high endo-selectivity from cyclopentadiene and methylacrylate,which is mainly due to the hydrogen bonding formed between the cation ofionic liquid and the methyl acrylate[18].Furthermore,there was an additionalacid from the C2-position hydrogen ofimidazolium moiety in the hydrophilic imidazolebased ionic liquid,which was used as catalyst for selectively synthesis the high molecular weightand oligomeric phenolpolymers from phenol and paraformaldehyde[19–20].
Based on both the additionalacid from the C2-position hydrogen of imidazolium moiety in the hydrophilic imidazole-based ionic liquid and its formed hydrogen bonding with the phenolic hydroxylgroup,some typicalionic liquids with different anions and cations ofdifferent alkyl chain lengths were investigated for the catalytic activity and the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F,and a high selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F was obtained under the condition of the low molar ratio of phenol/formaldehyde and low reaction temperature,which greatly reduce energy consumption and environmental safety in distillation of phenol from reaction products,and has important signi ficance for industrial application.
2.Experimental
2.1.Reaction reagents
1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazole hydrogen sulfate([C2mim][HSO4]),1-butyl-3-methylimidazole hydrogen sulfate([C4mim][HSO4]),1,2-dimethyl-3-butyl-imidazolium hydrogen sulfate([C4dmim][HSO4]),1-hexyl-3-methylimidazole hydrogen sulfate ([C6mim][HSO4]),1-octyl-3-methylimidazole hydrogen sulfate([C8mim][HSO4]),1-decyl-3-methylimidazole hydrogen sulfate([C10mim][HSO4])and 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium dihydrogen phosphate([C6mim][H2PO4])were purchased from Chinese Linzhou Energetic Materials Scienti fic Technology Co.N-ethyl pyridine hydrogen sulfate([EPy][HSO4]),N-butyl pyridine hydrogen sulfate([BPy][HSO4]),1-sulfobutyl-3-methylimidazolium hydrogen sulfate([MBSim][HSO4]),1-sulfonic acid propyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride([MPSim]Cl)and 1-sulfonic acid propyl-3-methylimidazolium hydrogen sulfate([MPSim][HSO4])were purchased from Shanghai Cheng Jie Chemical Co.Phenol and 37%formalin were purchased from West Long ChemicalCo.and Changsha AntaiChemical IndustrialCo,respectively.Ethylacetate and diethyl ether were purchased from Tianjin Fuyu Chemical Co.
2.2.The synthesis ofbisphenol F
Phenol,37%formaldehyde solution,deionized water and ionic liquid catalystwith some feeding proportion were added into the reactor.The reaction proceeded under low temperature heating and stirring re flux.After the reaction ended,the reaction system was cooled to room temperature and some samples were taken for analyses.The externalstandard method with agilent-1260 HPLC was used for analyzing three isomers of bisphenol F with operation conditions:4.6×250 mm of Agilent SB-C18 chromatographic column,methanol/water 3:2(v/v)of mobile phase,1 ml·min-1of flow rate,the UV detector 270 nm,column temperature 30°C.After the completion ofreaction,some amount of ethylacetate was added to reaction liquid to form two phases after sufficient oscillation strati fication.The upper solution contained phenol,ethyl acetate and bisphenol F products,while the lower solution contained ionic liquid catalyst.The bisphenol F product was obtained through the distillation ofphenoland ethylacetate from the organic phase under reduced pressure.The ionic liquid catalyst was reused after washing respectively with ethylacetate and diethylether,dried in vacuo at 60°C.
3.Results and Discussion
3.1.The comparison ofionic liquid catalytic activity
The catalytic activity of different ionic liquids for the synthesis of bisphenol F was shown in Table 1.For the alkylsubstituted imidazole hydrogen sulfate[Cnmim][HSO4](n=2,4,6,8,10),when the carbon atom number ofalkylsubstituted group chain length increased from 2 to 6,the yield ofbisphenol F increased from 41.9%to 49.5%,but when n continued to increase to 8,the yield ofbisphenol F dropped to 47.5%,instead.The reason for this is that when the alkyl substituted group chain length increases,the electrostatic interaction between anion and cation makes the increasing of associated degree among ionic liquid molecules in reaction system,even forming the complex vesicle structure owing to the mutualpenetration between water and ionic liquid[21],which reduces the acidic sites'freedom of ionic liquid in reaction system,resulting in the decreasing ofcatalytic activity ofionic liquid.The selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F increased from 62.6%to 69.1%with increasing the carbon atom number ofalkylchain length from 2 to 4,but decreased from 69.1%to 62.1%with increasing the carbon atom number ofalkylchain length from 4 to 10.

Table 1 Catalytic activity ofdifferent ionic liquids for the synthesis ofbisphenolF
Both the anion and the cation ofionic liquid have certain in fluence on the yield of bisphenol F yield and the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F.Compared with anion,the cation ofionic liquid has more in fluence on the yield of bisphenol F yield and the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F.[EPy][HSO4]has the highest catalytic activity(52.3%of bisphenol F yield)but the lowest selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenolF(50.1%),while for[BPy][HSO4],both the catalytic activity and the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenolF are worse than[Cnmim][HSO4].This isbecause the hydrogen bonding was formed between the C2-position hydrogen of imidazole moiety in[Cnmim][HSO4](n=2,4,6,8,10)and the hydroxylof phenol,which increased the ortho-and meta-positions steric hindrance ofphenol[19],resulting in favor of the forming of 4,4′-bisphenol F.Despite the introduction ofsulfuric acid group in ionic liquids[MBSim][HSO4],[MPSim][HSO4]and[MPSim]Cl,resulting in the increasing ofboth acid strength and acid site density[22],both the yield ofbisphenolF and the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F didn't increase any more.It is because under the high concentration ofionic liquid,the intramolecular association effect inhibited the ionization ofhydrogen proton in sulfonic acid group.Compared with[C4mim][HSO4]ionic liquid,[C4dmim][HSO4]ionic liquid withoutHin the C2-position ofimidazole moiety has the lowest catalytic activity(29.4%ofbisphenol F yield).It is attributed to the a methyl in the C2-position of imidazole moiety,the proton on C2-position of the imidazole ring blocked,which reduces the acidic sites'freedom and catalytic activity[23–24].Thus,underthe condition ofhigh concentration ionic liquid[C4mim][HSO4]catalyst,a moderate amount of water content and low reaction temperature,the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenolF reached to 69.1%which is higherthan 55%reported in the literature[3].Therefore,the ionic liquid[C4mim][HSO4]was selected as both catalyst and solvent to further investigate the effect of reaction time,reaction temperature,water content and the ratio of phenol to formaldehyde on the yield of bisphenol F and the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenolF.
3.2.The effectof[C4mim][HSO4]concentration
The effect of[C4mim][HSO4]concentration on the yield and the selectivity for bisphenol F was shown in Table 2.With the increasing of[C4mim][HSO4]concentration,the yield of bisphenol F first increased and then decreased,when the mole ratio of phenol/[C4mim][HSO4]was 1:1,the yield ofbisphenolF reached a maximum 42.0%.When the mole ratio of phenol/[C4mim][HSO4]from 4:1 to 1:1,the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F increased from 52.2%to 69.1%.With[C4mim][HSO4]concentration further increased,the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F decreased slightly,while the selectivity for 2,4′-bisphenol F increased a bit.The hydrogen bonding could be formed between the hydroxylof phenol and the C2-position hydrogen of imidazole moiety in imidazole-based ionic liquids[19].When[C4mim][HSO4]concentration increased,more and more hydrogen bondings were formed betweenhydroxylofphenoland the C2-position hydrogen of imidazole moiety of[C4mim][HSO4],thus increasing the ortho-and meta-positions steric hindrance of phenoland favoring in forming of 4,4′-bisphenol F.But owing to the viscosity of ionic liquids,excessive amount of[C4mim][HSO4]would increase the mass transfer resistance in reaction system,which led to reduce the yield ofbisphenol F,with a slightly decreasing in selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F.Therefore,the suitable mole ratio ofphenol/[C4mim][HSO4]is 1:1.
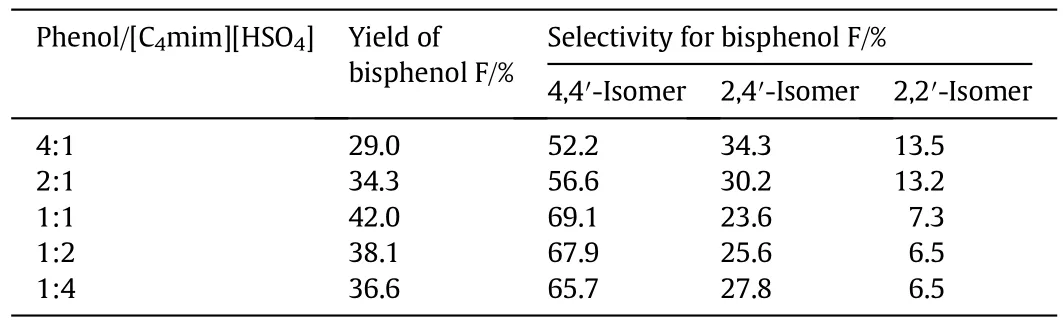
Table 2 Effect ofphenol/[C4mim][HSO4]molar ratio on the yield and selectivity for bisphenolF
3.3.The effectofreaction time
The effect of reaction time on the yield and the selectivity for bisphenol F was shown in Fig.1.At the beginning of reaction,more than 97%of 4,4′-bisphenol F was formed,but with the reaction proceeded,the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F decreased,both the yield ofbisphenolF and the selectivities for2,4′-and 2,2′-bisphenolF increased.After reacting 6 h,the yield and the distributions of4,4′-,2,4′-and 2,2′-bisphenolF isomers keptat42%,69%,24%and 7%,respectively.This is because that although there are more electron cloud density existed in ortho-and para-positions ofphenol,atthe same time,the hydrogen bonding is formed between the hydroxylofphenoland the C2-position hydrogen ofimidazole moiety in[C4mim][HSO4],which makes the ortho-position steric hindrance of phenol is greater than that at para-position where the reaction occurs firstly.And then,with more and more 4,4′-bisphenol F formed,its steric hindrance becomes increased accordingly,which lead to the decreasing of the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F with the stable result appeared after reaction time 6 h.

Fig.1.Effect of reaction time on the yield and selectivity for bisphenol F Reaction conditions:phenol:[C4mim][HSO4]:formaldehyde:water=2:2:1:6(mole ratio)and reaction temperature 65°C.
3.4.The effectofreaction temperature
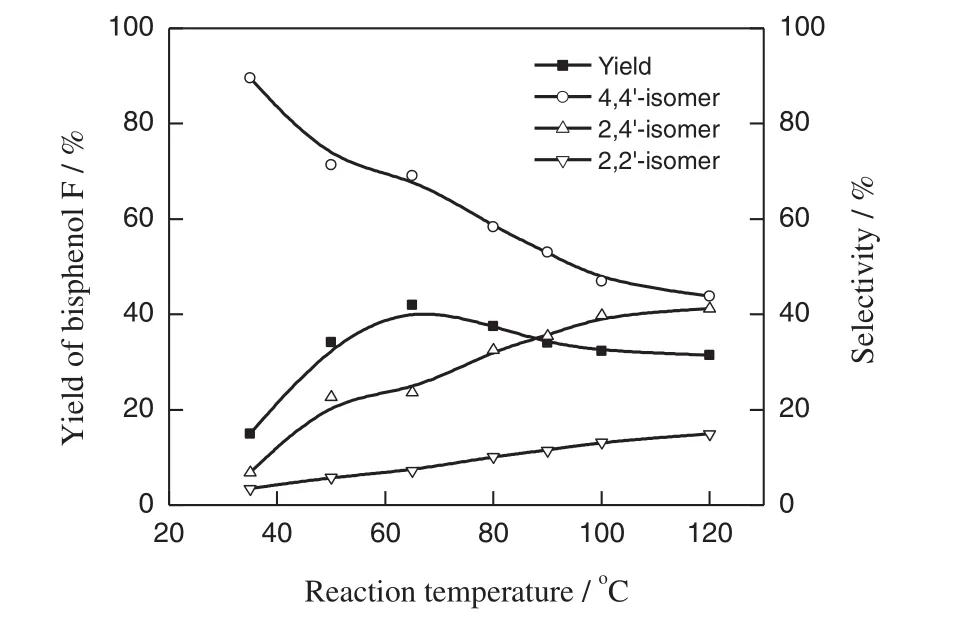
Fig.2.Effect ofreaction temperature on the yield and selectivity for bisphenolF Reaction conditions:phenol:[C4mim][HSO4]:formaldehyde:water=2:2:1:6(mole ratio),reaction time 6 h.
The effectofreaction temperature on the yield ofand the selectivity for bisphenol F was shown in Fig.2.At low temperature 35°C,main product formed was 4,4′-bisphenol F accounted for more than 89%.With the increase oftemperature,the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenolF decreased,while both the selectivities for 2,4′-and 2,2′-bisphenol F and the yield of bisphenol F increased.When the reaction temperature reached 65°C,a maximum yield ofbisphenol F appeared at42%,while the selectivities for 4,4′-,2,4′-,2,2′-bisphenol F were 69%,24%and 7%,respectively.Afterwards,with the increasing of reaction temperature,both the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenolF and the yield ofbisphenolF continued to decrease,while the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F increased continually untilreaction temperature 120°C.It can be explained that under low reaction temperature,the catalytic activity of[C4mim][HSO4]wasn'thigh,and atthe same time,there was the hydrogen bonding interaction between the anion and the cation of[C4mim][HSO4]existed in mesh structure under high[C4mim][HSO4]concentration in reaction system[25],which made the mass transfer resistance increase and reduce the freedom of acidic protons,resulting in very low yield of bisphenol F.With the increasing of temperature,the catalytic activity of[C4mim][HSO4]increased,the viscosity ofreaction system reduced,which speed up the mass transfer and reaction rate with the result of the yield ofbisphenol F increased.For the three isomers ofbisphenol F,the formation of4,4′-bisphenolF was controlled by the kinetics ofreaction time and reaction activation energy,while the formation ofboth 2,4′-and 2,2′-bisphenol F was controlled by thermodynamics[5,26].It made the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F decrease with the rise ofreaction temperature.In addition,when the reaction temperature increased,the hydrogen bonding formed between the C2-position hydrogen ofimidazole moiety in[C4mim][HSO4]and the hydroxylofphenolbecame weak,which reduced the ortho-position steric hindrance of phenol with the results ofboth the selectivities for 2,4′-and 2,2′-bisphenolF increased and the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenolF decreased.
3.5.The effect ofwater content
The effect of water content in reaction system on the yield of bisphenolF and the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenolF was shown in Fig.3.With the increasing ofwater content,the yield ofbisphenolF and the selectivities for 2,4′-,2,2′-bisphenol F decreased,while the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F increased.It is because that when the water content was low,both the anion and the cation ofionic liquid played synergistic catalytic role in reaction,butwhen the water contentincreased,the interaction between water and the anion of ionic liquid became strong gradually,which reduced the synergistic catalytic role with a result of the decreasing of the yield ofbisphenolF[27].In addition,owing to the miscibility ofphenolwith water above 65°C,when the water content increased,the water molecules would form the hydrogen bonding with the hydroxylofphenol,which increased the ortho-position steric hindrance resulting in favor of the forming of 4,4′-bisphenol F.Hence,a moderate amount of water content added in reaction system was adopted to obtain the high selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenolF,and the optimized molar ratio offormaldehyde/water was 1:6.

Fig.3.Effect of water content on the yield and selectivity for bisphenol F Reaction conditions:phenol:[C4mim][HSO4]:formaldehyde=2:2:1,reaction temperature 65°C and reaction time 6 h.
3.6.The effect ofphenol/formaldehyde ratio
The effect of phenol/formaldehyde molar ratio on the yield of bisphenol F and the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F was shown in Fig.4.With the increasing of phenol/formaldehyde molar ratio,the yield of bisphenol F increased.When the phenol/formaldehyde molar ratio increased from 2 to 4,the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenolF increased slightly from69.1%to 72.7%,butwhen the phenol/formaldehyde molarratio furtherincreased to 10,the selectivity for4,4′-bisphenolF decreased sharply untilstable about 45%.It is because when the phenol/formaldehyde molar ratio was low,[C4mim][HSO4]concentration was comparatively high,thus the reaction system with high viscosity hindered the mass transfer in reaction system with the result of the synthesis ofbisphenol F being blocked.But when the phenol/formaldehyde molar ratio increased,excess phenol diluted[C4mim][HSO4]concentration and reduced the mass transfer resistance in reaction system,which favored the forming ofbisphenol F.When the phenol/formaldehyde molar ratio was more than 4,excess phenol made both the ortho-and metapositions with lower steric hindrance ofphenolexposed more in reaction system,thus in favor of the forming of2,4′-and 2,2′-bisphenol F.

Fig.4.Effectofphenol/formaldehyde molar ratio on the yield and selectivity for bisphenol F Reaction conditions:[C4mim][HSO4]:formaldehyde:water=2:1:6(mole ratio),reaction time 6 h and reaction temperature 65°C.
3.7.The reaction mechanism
The reaction mechanism for the formation of bisphenol F was proposed as shown in Fig.5.The hydrogen bonding formed between the C2-position hydrogen ofimidazole moiety in[C4mim][HSO4]and the hydroxylof phenol[19].The H+of hydrogen sulfate combined with the carbonyl of formaldehyde,forming the methylolcarbenium with strong activity.And this methylol-carbenium would attack mainly the para-position of phenol with low steric hindrance[12],forming the hydroxylbenzene methanolintermediates which reacted with the H+of hydrogen sulfate to form p-hydroxy benzylcation and water.And then the p-hydroxy benzyl cation continued to attack the para-position of phenol with the result of 4,4′-bisphenol F formed[13].

Fig.5.The reaction mechanism for the formation ofbisphenolF.
3.8.The recycling of[C4mim][HSO4]ionic liquid
The recycling of[C4mim][HSO4]ionic liquid was shown in Table 3.The ionic liquid[C4mim][HSO4]before and after regenerated has been characterized by1HNMR(Fig.S4 and Fig.S5 of the supporting information).The yield of bisphenol F decreased with the recycling time of[C4mim][HSO4],while the distribution ofthree isomers of bisphenol F had only a little change.This is because there was some loss of[C4mim][HSO4]in recycling,resulting in a decrease of its acidity and the catalytic activity.In addition,the water content absorbed in[C4mim][HSO4]increased with the recycling,which also made the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F increase a bit.

Table 3 Recycling of[C4mim][HSO4]ionic liquid
4.Conclusions
The differentalkylchain length and sulfonic functionalgroups in imidazole ring ofionic liquids,and differenttypes ofanions and cations of ionic liquids were investigated for the catalytic activity and the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F.Compared with anions,the cations of ionic liquids have larger impact on the catalytic activity and the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F.Due to the hydrogen bonding formed between the C2-position hydrogen of imidazolium cation in the hydrophilic imidazole-based ionic liquid and the phenolic hydroxyl group,the imidazole-based ionic liquids were in favor of the formation of 4,4′-bisphenol F.Using the suitable ionic liquid[C4mim][HSO4]as catalyst and solvent,under optimized reaction conditions of phenol/[C4mim][HSO4]/formaldehyde/water molar ratio of 2:2:1:6,reaction temperature 65 °C and reaction time 6 h,the selectivity for 4,4′-bisphenol F reached 69.1%.Compared with the high phenol/formaldehyde ratio reported in the literatures,the low molar ratio of phenol/formaldehyde and the low reaction temperature can greatly reduce energy consumption and environmentalsafety in distillation of phenol from reaction products,and has important signi ficance for industrial application.
Appendix A.Supplementary data
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2016.02.005.
[1]L.Pilato,Phenolic resins:A century of progress,Springer Berlin Heidelberg,New York,2014.
[2]G.R.Roussilon,M.F.Lyons,Solid bisphenol F particulatesUS 43364706[P]1982.
[3]R.O.Morris,M.Wilbraham,Process for making bis(hydroxyphenyl)methanesUS 4400554[P]1983.
[4]K.J.Suman,K.Tsuyoshi,N.Seitaro,Aluminum-grafted MCM-41 molecular sieve:An active catalyst for bisphenol F synthesis process,Appl.Catal.A Gen.266(2)(2004)245–250.
[5]K.J.Suman,O.Takeshi,K.Tsuyoshi,N.Seitaro,Selective synthesis ofbisphenolF catalyzed by microporous H-beta zeolite,Appl.Catal.A Gen.288(1–2)(2005)80–85.
[6]J.Q.Yan,Y.Tan,Y.F.Li,Z.M.Wu,M.Chen,L.S.Pan,Y.J.Liu,Synthesis of bisphenol F catalyzed by phosphotungstic acid encapsulated in metal–organic frameworks MIL-100(Cr)and MIL-101(Cr),CIESC J.66(2)(2015)576–583.
[7]A.C.Cole,J.L.Jensen,N.Ioanna,K.L.T.Tran,K.J.Weaver,D.Forbes,Novel brønsted acidic ionic liquids and their use as dual solvent-catalysts,J.Am.Chem.Soc.124(21)(2002)5962–5963.
[8]Z.Y.Hou,Toshio Okuhara,Condensation of benzene and aqueous formaldehyde to diphenylmethane in a biphasic system consisting ofan aqueous phase ofheteropoly acid,J.Mol.Catal.A Chem.206(1–2)(2003)121–130.
[9]A.X.Pan,T.He,L.L.Xu,Ef ficient synthesis of 1-acetylpyrene using[Bmim]Cl-FeCl3ionic liquid as dualcatalyst and solvent,Int.J.Chem.React.Eng.11(1)(2013)1–7.
[10]A.L.Wang,X.L.Zheng,Z.Z.Zhao,Brønsted acid ionic liquids catalyzed friedel–crafts alkylations of electron-rich arenes with aldehydes,Appl.Catal.A Gen.48(2014)198–204.
[11]G.H.Gao,L.F.Zhang,B.S.Wang,Hydroxyalkylation ofindole with cyclic carbonates catalyzed by ionic liquids,Chin.J.Catal.34(6)(2013)1187–1191.
[12]Q.Wang,Z.M.Wu,Y.F.Li,Y.Tan,N.Liu,Y.J.Liu,The ef ficient hydroxyalkylation of phenol with formaldehyde to bisphenol F over a thermoregulated phaseseparable reaction system containing water-soluble Brønsted acidic ionic liquid,RSC Adv.63(4)(2014)33466–33473.
[13]Z.C.He,Z.M.Wu,Y.F.Li,L.S.Pan,Q.Wang,Y.J.Liu,Synthesis ofbisphenolF catalyzed by sulfonic acid-functionalized dicationic imidazolium ionic liquids,J.Mol.Catal.28(6)(2014)535–543.
[14]Q.Wang,J.Liu,Y.F.Li,D.Xiao,Y.Tian,Y.J.Liu,Synthesis of bisphenol F through hydroxyalkylation of phenolcatalyzed by brønsted acidic ionic liquid,J.Chem.Eng.Chin.Univ.28(4)(2014)758–763.
[15]M.Lei,Y.W.Zhao,L.Wu,The prins reaction of alkenes with triformolcatalyzed by acidic functional ionic liquds,J.Mol.Catal.27(2)(2013)108–114.
[16]L.F.Zhang,S.J.Yang,G.H.Gao,The reaction ofaromatic amines with propylene carbonate catalyzed by anion–cation cooperativity in ionic liquids,Chin.J.Catal.32(12)(2011)1875–1879.
[17]B.Yi,Y.Zhang,L.M.Dang,Z.P.Liu,X.M.Shu,Y.Liu,Synthesis ofnovelguanidiniumbased ionic liquids and their application in henry reaction,Nat.Sci.J.Xiangtan Univ.33(2)(2011)73–77.
[18]A.Aggarwal,N.L.Lancaster,A.R.Sethi,T.Welton,The role of hydrogen bonding in controlling the selectivity of Diels–Alder Reactions in room-temperature ionic liquids,Green Chem.4(4)(2002)517–520.
[19]T.Ogoshi,T.Onodera,T.Yamagishi,Y.Nakamoto,Green polymerization ofphenolin ionic liquids,Macromolecules 41(22)(2008)8533–8536.
[20]L.Crowhurst,P.R.Mawdsley,J.M.Perez-Arlandis,P.A.Perez-Arlandis,Salter,T.Welton,Solvent–solute interactions in ionic liquids,Phys.Chem.Chem.Phys.5(13)(2003)2790–2794.
[21]Y.Wang,H.R.Li,S.J.Han,A theoretical investigation of the interactions between water molecules and ionic liquids,J.Phys.Chem.B 110(48)(2008)24646–24651.
[22]G.R.Xu,J.H.Liu,D.Y.Song,J.Chen,C.G.Xia,Ester exchange polymerization of 3-hydroxylpopionic acid methylester catalyzed by SO3H-functionalized ionic liquids,J.Mol.Catal.26(2012)293–296.
[23]A.G.Avent,P.A.Chaloner,M.P.Day,K.R.Seddon,T.Welton,Evidence for hydrogenbonding in solutions of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium halides,and its implications for room-temperature halogenoaluminate(iii)ionic liquids,J.Chem.Soc.Dalton Trans.23(23)(1994)3405–3413.
[24]A.K.Abdul-Sada,S.Al-Juaid,A.M.Greenway,P.B.Hitchcock,M.J.Howells,K.R.Seddon,Upon the hydrogen-bonding ability of the H4 and H5 protons of the imidazolium cation,Struct.Chem.1(4)(1990)391–394.
[25]L.M.Zhang,The aqueous IL solution exhibits a liquid–liquid phase separation phenomenon with all upper critical solution temperature(master degree thesis)He Nan Normal Univ,He Nan,2011.
[26]A.C.Garade,V.S.Kshirsagar,C.V.Rode,Selective hydroxyalkylation of phenol to bisphenolF over dodecatungstophosphoric acid(DTP)impregnated on fumed silica,Appl.Catal.A Gen.354(1–2)(2009)176–182.
[27]C.P.Zhai,J.J.Wang,X.P.Xuan,H.Q.Wang,NMR study on the interactions of ionic liquid with acetone,Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.22(4)(2006)456–459.
杂志排行
Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering的其它文章
- Heat transfer ofnano fluidics in hydrophilic pores:Insights from molecular dynamics simulations☆
- Numericalsimulation ofstirred tanks using a hybrid immersed-boundary method☆
- Numericalsimulation ofmicromixing effect on the reactive flow in a co-rotating twin screw extruder☆
- Coalescence behaviour ofwater droplets in water-oilinterface under pulsatile electric fields
- Effects of Sn residue on the high temperature stability of the H2-permeable palladium membranes prepared by electroless plating on Al2O3 substrate after SnCl2–PdCl2 process:A case study☆
- Application ofdiffusive transport modelfor better insight into retardation mechanisms involved in ion-imprinted membrane transport
