不同氮效率小麦品种苗期根系氮代谢及其吸收能力差异分析
2016-05-27熊淑萍吴克远王小纯吴懿鑫马新明
熊淑萍,吴克远,王小纯,2,吴懿鑫,杜 盼,马新明
(1.河南农业大学农学院/河南粮食作物协调创新中心/小麦玉米作物学国家重点实验室,河南郑州 450002;2.河南农业大学生命科学学院,河南郑州450002)
不同氮效率小麦品种苗期根系氮代谢及其吸收能力差异分析
熊淑萍1,吴克远1,王小纯1,2,吴懿鑫1,杜 盼1,马新明1
(1.河南农业大学农学院/河南粮食作物协调创新中心/小麦玉米作物学国家重点实验室,河南郑州 450002;2.河南农业大学生命科学学院,河南郑州450002)
摘要:为了解不同氮效率小麦品种根系氮代谢特征及其吸收能力的差异,明确小麦氮高效利用的生理机制,在水培条件下,研究了氮高效小麦品种漯麦18和氮低效小麦品种西农509的根系氮代谢特征和对吸收的动力学特征。结果表明,漯麦18的根系GS活性、硝酸还原酶活性、游离氨基酸含量、可溶性蛋白质含量均高于西农509;而西农509的根系硝态氮和铵态氮含量高于漯麦18;漯麦18根系对吸收的最大吸收速率(Vmax)显著高于西农509;漯麦18根系对的亲和力(以Km的倒数衡量)低于西农509。结果说明,氮高效型小麦品种根系对的吸收能力和同化能力均显著高于氮低效型小麦品种;小麦根系对的吸收和同化是相互促进的关系。
关键词:小麦;根系;氮代谢;吸收动力学特征

1材料与方法
1.1试验材料与设计
利用前期筛选的氮高效小麦品种漯麦18和氮低效小麦品种西农509为试验材料[9]。采用溶液培养的方法于2014年在河南农业大学小麦玉米作物学国家重点实验室人工气候室进行。供试种子用75%酒精消毒5 min,1 g·L-1HgCl2消毒10 min;无离子水洗净后浸种24 h,于25 ℃ 培养箱中催芽。幼苗一叶一心时, 用蒸馏水冲洗后取大小均匀一致的幼苗,移到完全营养液中培养。营养液配方为:K2SO40.75×10-3mol·L-1、MgSO40.65×10-3mol·L-1、KCl 0.1×10-3mol·L-1、Ca(NO3)22.0×10-3mol·L-1、KH2PO40.25×10-3mol·L-1、H3BO31×10-6mol·L-1、MnSO41×10-6mol·L-1、CuSO41×10-7mol·L-1、ZnSO41×10-6mol·L-1、 (NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O 1×10-9mol·L-1、Fe-EDTA 1×10-4mol·L-1。每3 d更换1次营养液,用稀HCl和稀NaOH调节营养液pH在6.5左右,培养温度模拟大田。
1.2.1氮素吸收动力学特征的测定(常规耗竭法[13])

1.2.2氮代谢相关指标测定

1.3数据处理
采用Excle 2010和SPSS 20软件进行数据处理和方差分析,用Origin Lab 9.0作图。
2结果与分析
2.1两个小麦品种苗期氮吸收动力学特征的差异
虽说我国已经实施了很多的发展策略,包括:丝路基金、亚投行等,但就实际情况而言,并未完全覆盖多样化的融资需求。在保障风险控制的前提下,我国金融机构应当积极探索全新的融资模式,不断吸引各项资本的参加,为“一带一路”项目建设奠定基础。与此同时,强化PPP模式的应用,联合民间资本与社会资本,为“一带一路”建设提供资金支持,政府部门应当强化各类形式合作模式的鼓励。


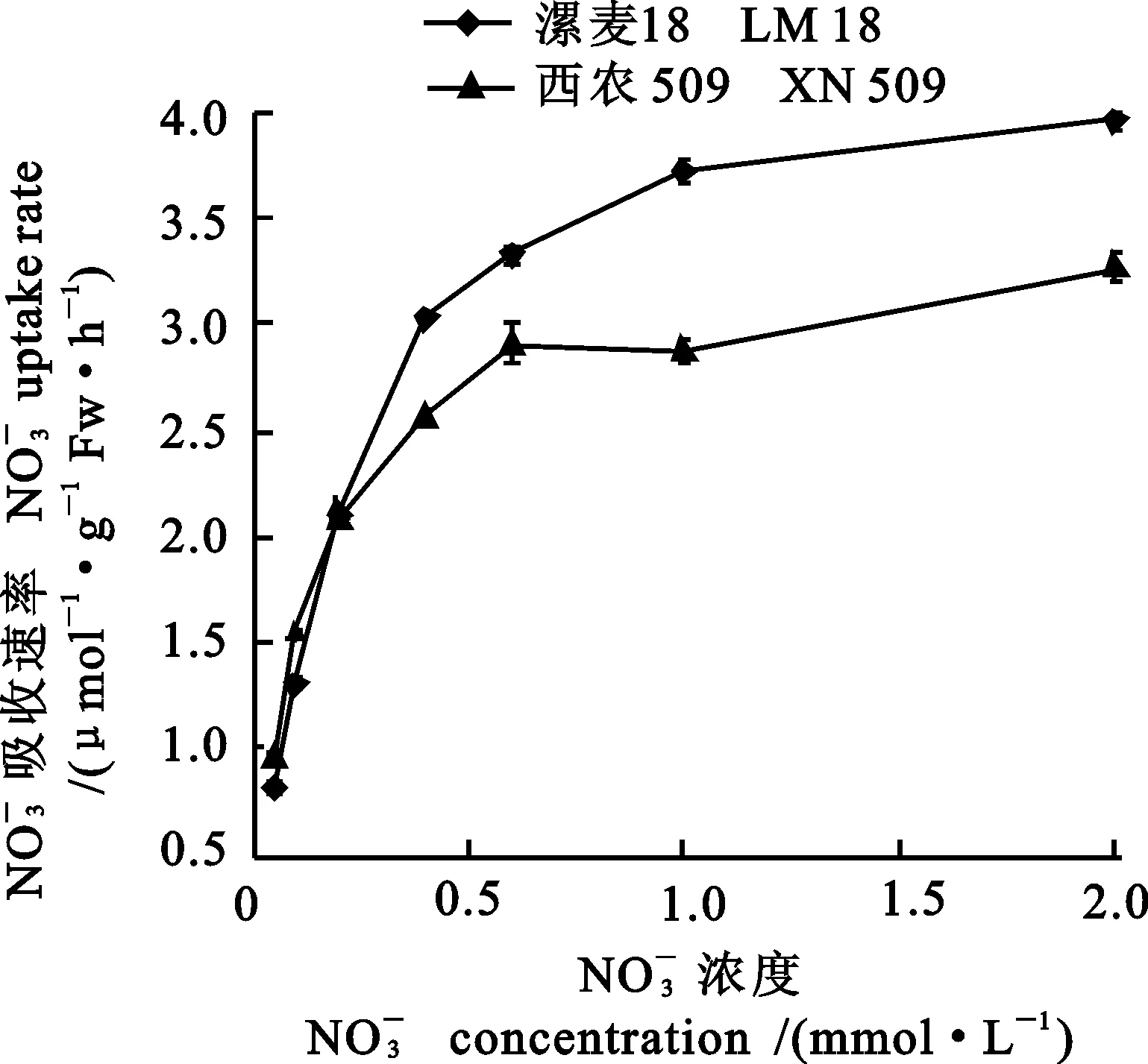
图1 两个小麦品种苗期吸收速率

1 NO-3

Fig. uptake rate of two wheat varieties
同一列数值后的不同小写字母表示5%水平差异显著。下同
Values followed by different lower case letters are significant difference at 5% level.The same as table 2
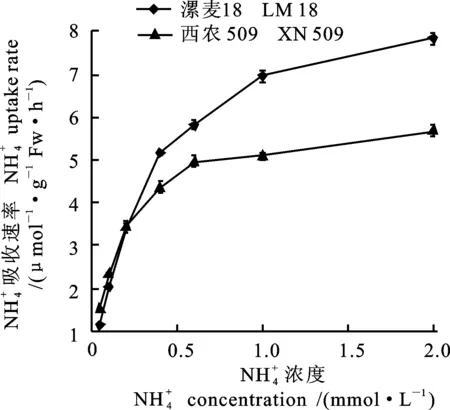
图2 两个小麦品种苗期吸收速率

2 NH+4

Fig. uptake rate of two wheat varieties
2.2两个小麦品种根系氮代谢的差异
2.2.1谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)活性的差异
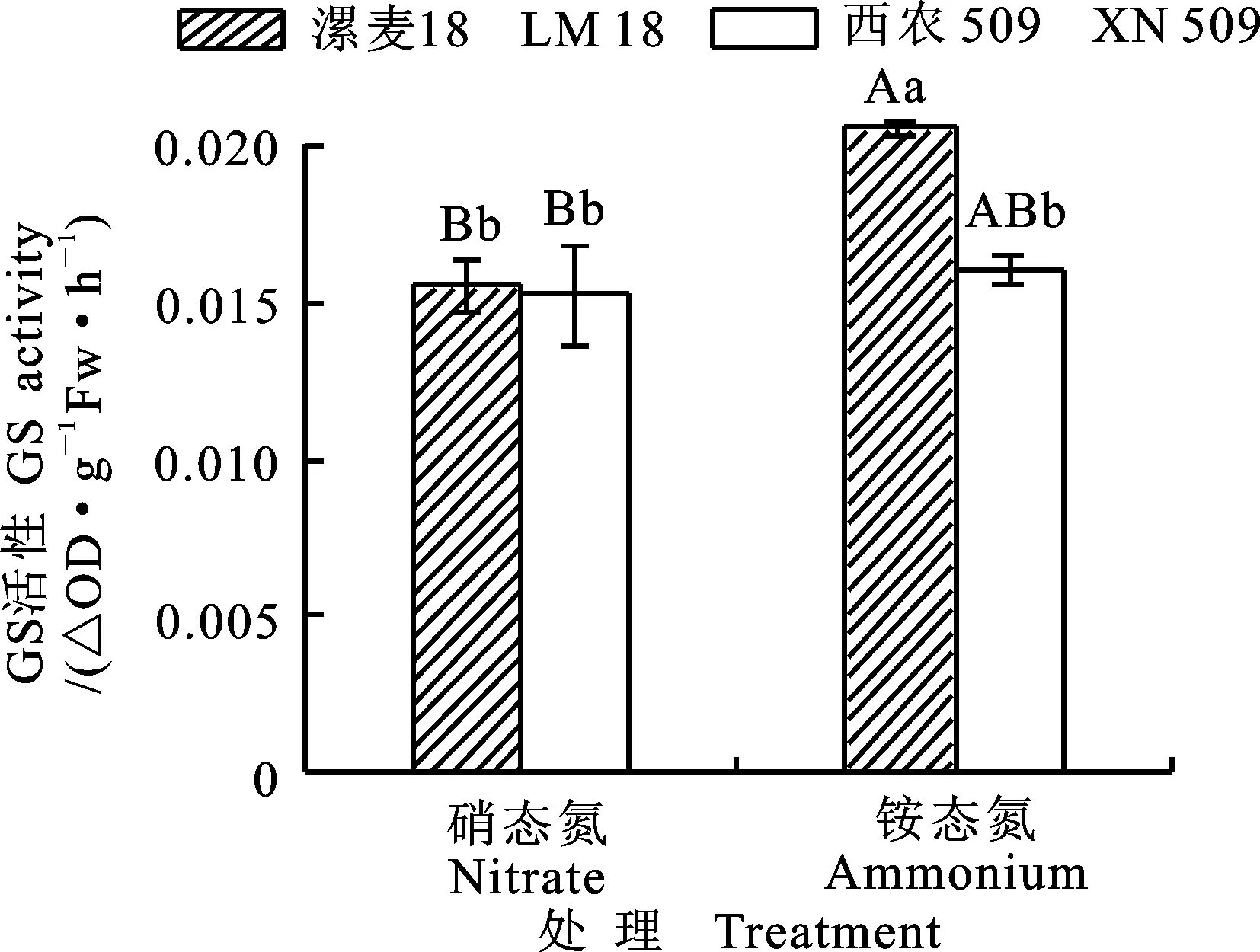
图中不同大、小写字母分别表示在1%、5%水平下差异显著。下同
Different capital and lower case letters mean significant difference at 1% and 5% level.The same as following figures
图3 两个小麦品种苗期在不同氮
处理下根系GS活性的差异
Fig.3Differences of GS activity in root of two
wheat varieties with different N
forms at seedling stage
2.2.2硝酸还原酶活性(NR)的差异
2.2.3游离氨基酸含量的差异
2.2.4可溶性蛋白质含量的差异
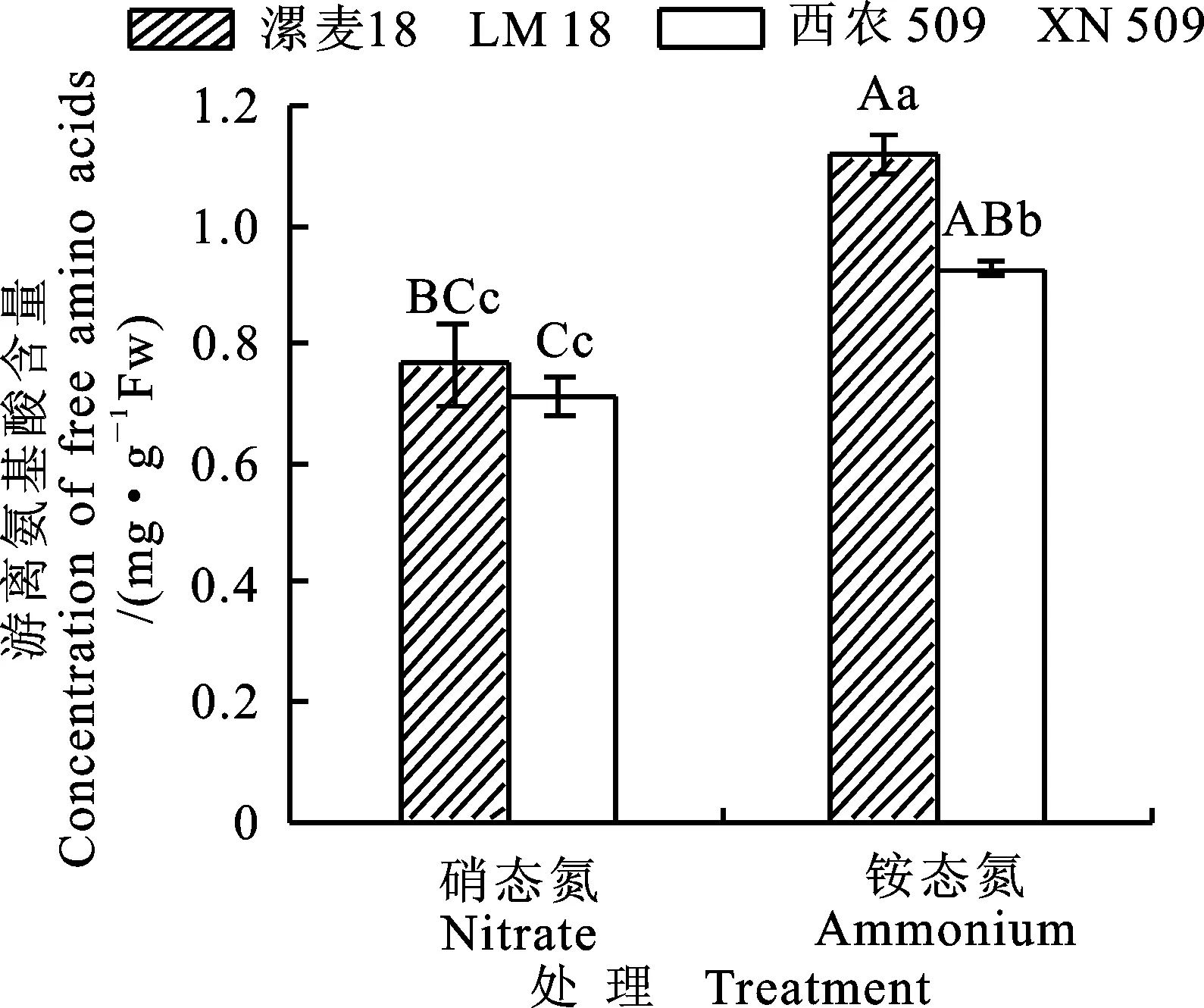
图5 两个小麦品种苗期在不同氮处理
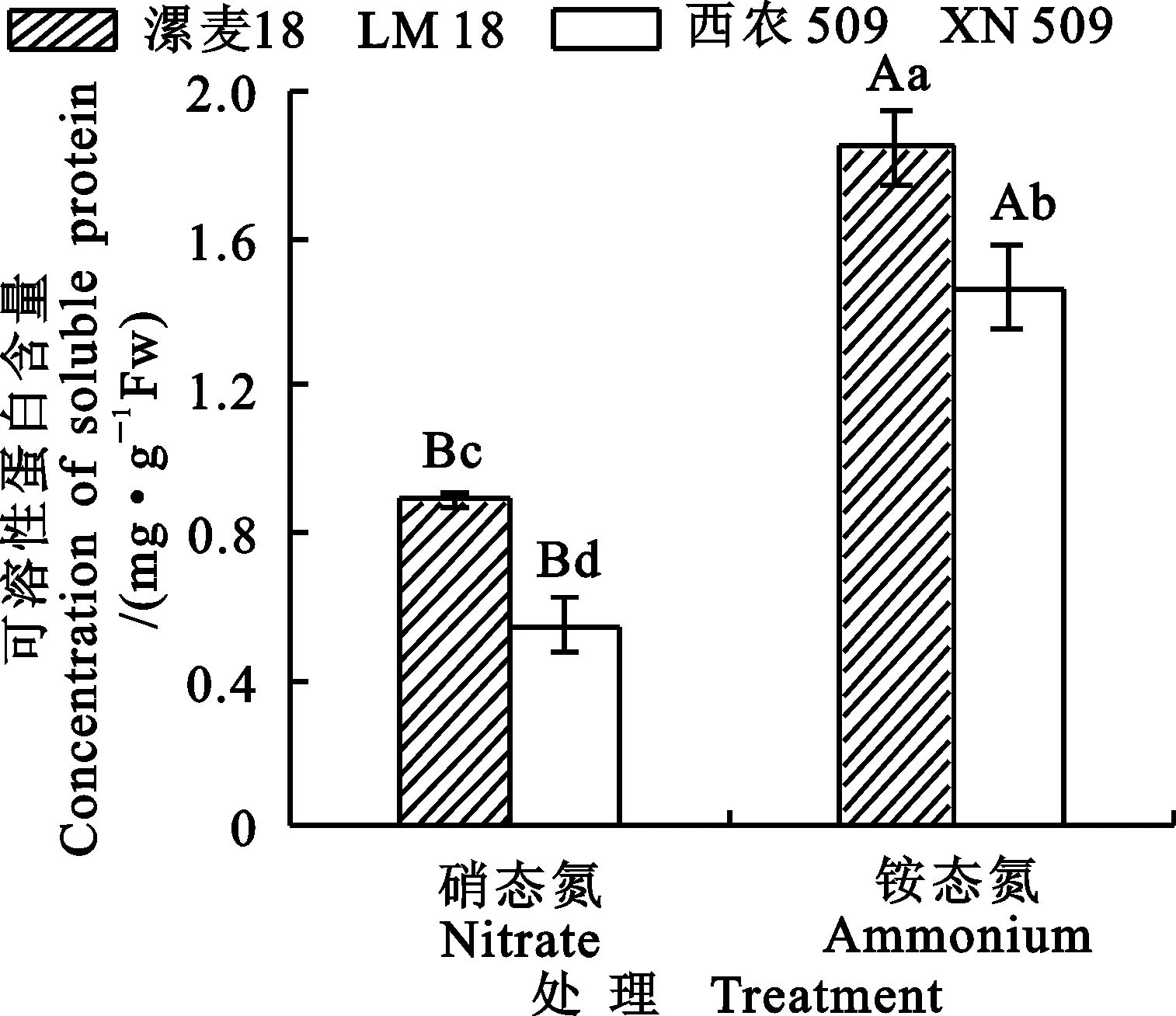
图6 两个小麦品种苗期在不同氮处理
2.2.5硝态氮含量的差异
2.2.6铵态氮含量的差异
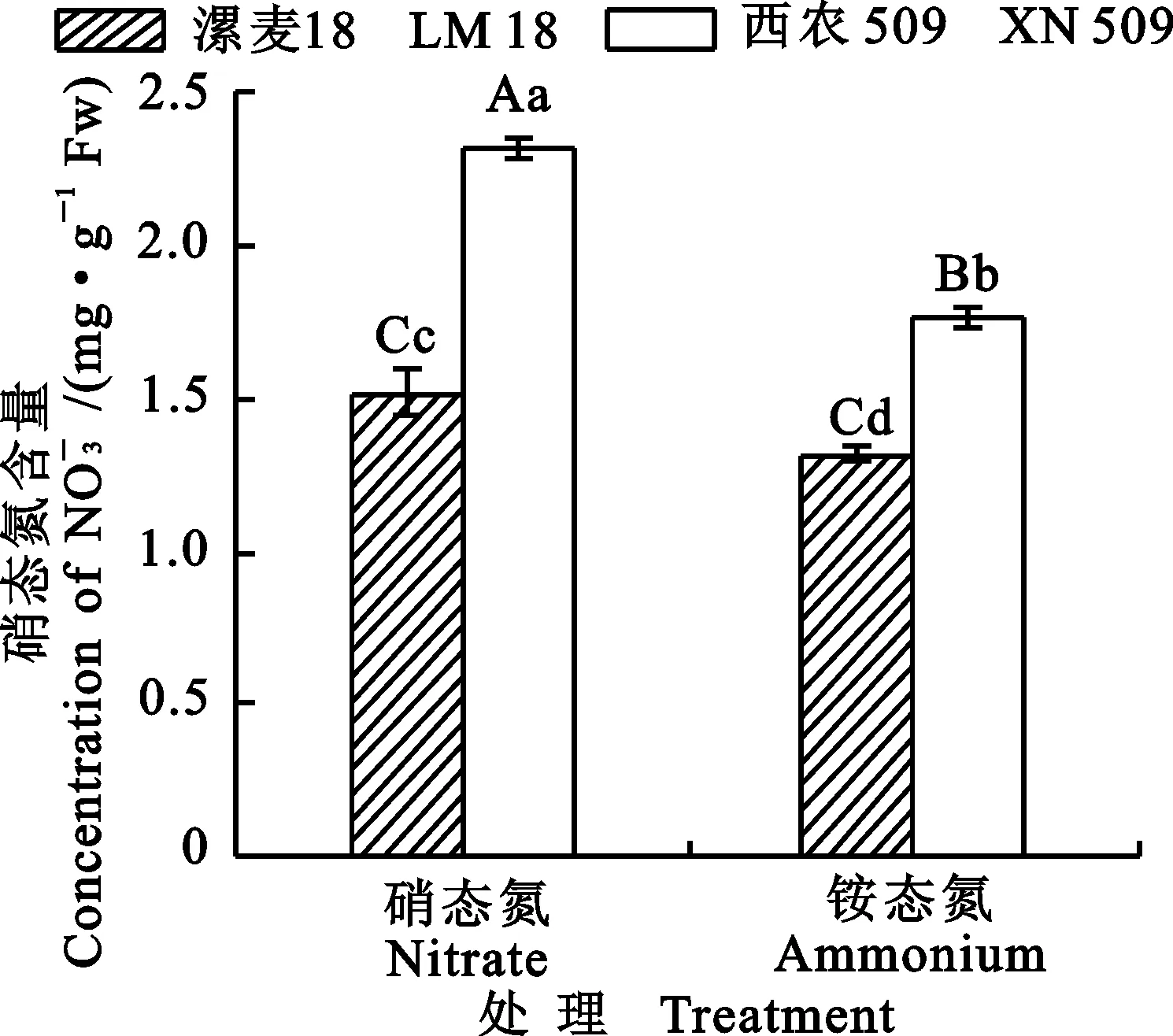
图7 两个小麦品种苗期在不同氮处理
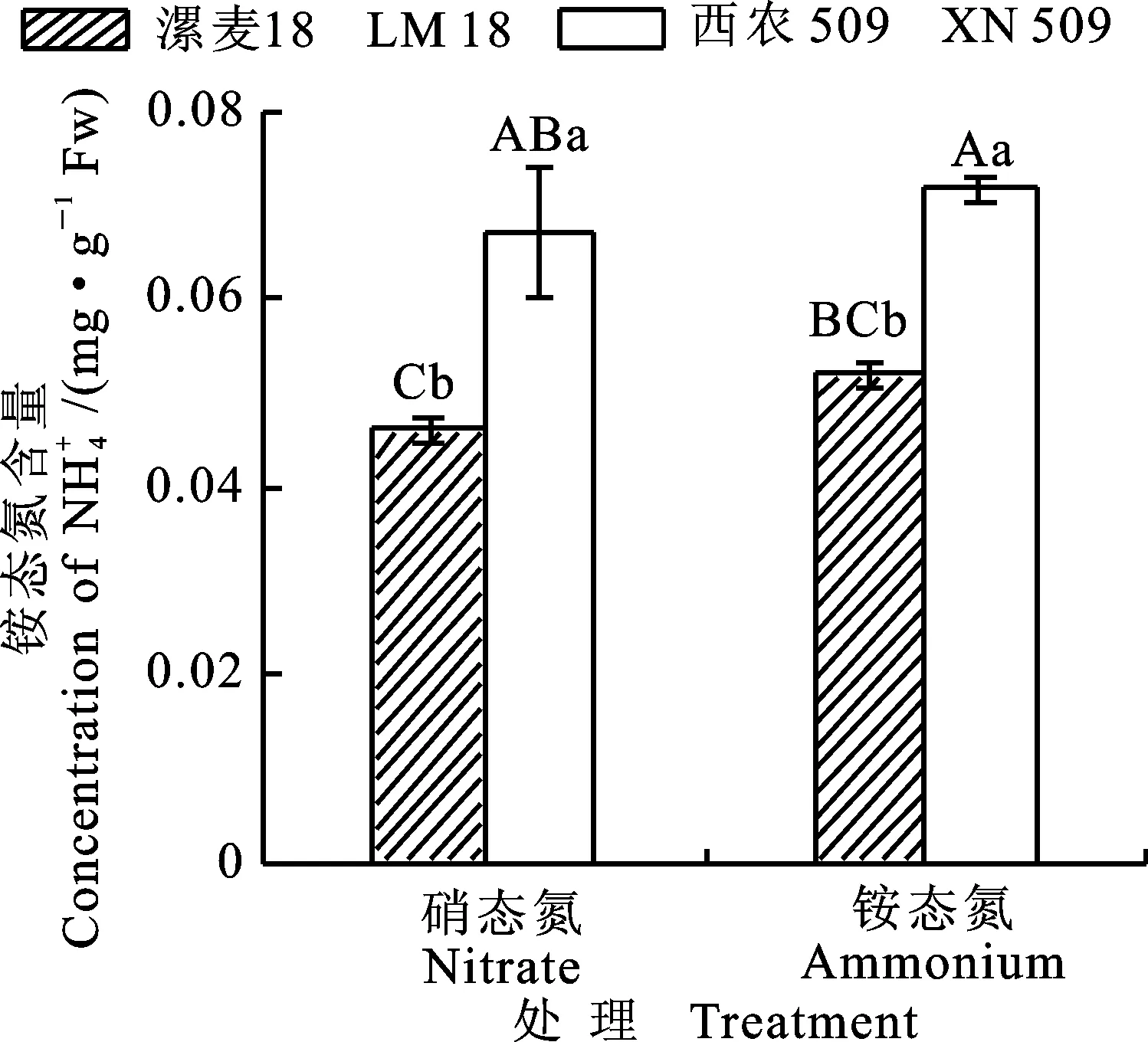
图8 两个小麦品种苗期在不同氮处理
3讨 论
硝酸还原酶是氮代谢过程中的第一种酶,是硝酸盐同化的限速酶,其活性受底物的诱导[18],本研究中硝态氮培养条件下漯麦18、西农509根系的硝酸还原酶活性显著高于铵态氮处理,与前人研究结论一致。GS参与多种氮素代谢途径的调节,是氮代谢的关键酶[19]。可溶性蛋白在氮素代谢中起着代谢库的作用,可以反映植株氮素代谢的强弱[20]。游离氨基酸是植物体内氮化物的主要存在方式和运输形式[21]。本研究中硝态氮培养条件下漯麦18、西农509根系的GS活性、游离氨基酸含量、可溶性蛋白质含量显著低于铵态氮处理;这是由于硝态氮被根系吸收后先被硝酸还原酶和亚硝酸还原酶还原成铵态氮后才能被同化、合成氨基酸和蛋白质,而铵态氮被吸收后可直接参与氨基酸和蛋白质的合成。
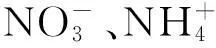
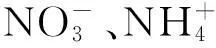
参考文献:
[1]欧阳威,蔡冠清,黄浩波,等.小流域农业面源氮污染时空特征及与土壤呼吸硝化关系分析[J].环境科学,2014,(35)6:2411-2418.
Ou Y W,Cai G Q,Huang H B,etal.Temporal-spatial distribution of agricultural diffuse nitrogen pollution and relationship with soil respiration and nitrification [J].EnvironmentalScience,2014,(35)6:2411-2418.
[2]Baligar V C,Fageria N K,He Z L.Nutrient use efficiency in plants [J].CommunicationsinSoilScienceandPlantAnalysis,2001,32(7-8):921-950.
[3]Kant S,Bi Y M,Rothstein S J.Understanding plant response to nitrogen limitation for the improvement of crop nitrogen use efficiency [J].JournalofExperimentalBotany,2011,62(4):1499-1509.
[4]赵俊晔,于振文,李延奇,等.施氮量对土壤无机氮分布和微生物量氮含量及小麦产量的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2006,12(4):466-472.
Zhao J H,Yu Z W,Li Y Q,etal.Effects of nitrogen application rate on soil inorganic nitrogen distribution,microbial biomass nitrogen content and yield of wheat [J].PlantNutritionandFertilizerScience,2006,12(4):466-472.
[5]霍常富,孙海龙,范志强,等.根系氮吸收过程及其主要调节因子[J].应用生态学报,2007,18(6):1356-1364.
Huo C F,Sun H L,Fan Z Q,etal.Physiological processes and major regulating factors of nitrogen uptake by plant roots [J].ChineseJournalofAppliedEcology,2007,18(6):1356-1364.
[6]Haynes R.Mineral Nitrogen in the Plant-soil System [M].Amsterdam:Elsevier,2012:304.
[7]李志军,张富仓,康绍忠.小麦和大麦吸收 N、P、K的动力学参数及相互作用机制研究[J].应用基础与工程科学学报,2002,10(1):36-41.
Li Z J,Zhang F C,Kang S Z.Absorption kinetics of N,P,and K and mechanism of ion mutual effect in wheat and barley [J].JournalofBasicScienceandEngineering,2002,10(1):36-41.
[8]董召娣,易 媛,张明伟,等.春性和半冬性小麦花后旗叶和籽粒氮代谢关键酶活性的差异[J].麦类作物学报,2015,35(8):1098-1106.
Dong Z D,Yi Y,Zhang M W,etal.Difference of activities of nitrogen metabolism enzymes in flag leaves and grain after anthesis of semi-winter and spring wheat varieties [J].JournalofTriticeacCrops,2015,35(8):1098-1106.
[9]王小纯,王晓航,熊淑萍,等.不同供氮水平下小麦品种的氮效率差异及其氮代谢特征[J].中国农业科学,2015,48(13):2569-2579.
Wang X C,Wang X H,Xiong S P,etal.Differences in nitrogen efficiency and nitrogen metabolism of wheat varieties under different nitrogen levers [J].ScientiaAgriculturaSinica,2015,48(13):2569-2579.
[10]童依平,李振声.不同小麦品种 (系) 吸收利用氮素效率的差异及有关机理研究Ⅱ.影响吸收效率的因素分析[J].西北植物学报,1999,19(3):393-401.
Tong Y P,Li Z S.Genotypic variations of nitrogen use efficiency in winter wheat (TriticumaestivumL.) Ⅱ.Factors affecting nitrogen uptake efficiency [J].ActaBotanicaBoreali-OccidentaliaSinica,1999,19(3):393-401.
[11]汪晓丽,陶玥玥,盛海君,等.硝态氮供应对小麦根系形态发育和氮吸收动力学的影响[J].麦类作物学报,2010,30(1):129-134.
Wang X L,Tao Y Y,Sheng H J,etal.Effects of nitrate supply on morphology development and nitrate uptake kinetics of wheat roots [J].JournalofTriticeacCrops,2010,30(1):129-134.
[12]韩胜芳,李淑文,吴立强,等.不同小麦品种氮效率与氮吸收对氮素供应的响应及生理机制[J].应用生态学报,2007,18(4):807-812.
Han S F,Li S W,Wu L Q,etal.Responses and corresponding physiological mechanisms of different wheat varieties in their nitrogen efficiency and nitrogen uptake to nitrogen supply [J].ChineseJournalofAppliedEcology,2007,18(4):807-812.
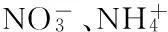
Sun M,Guo W S,Zhu X K,etal.Kinntics of nitrate and ammonium uptake by different wheat genotypes at seeding stage [J].JournalofTriticeacCrops,2006,26(5):84- 87.
[14]马新明,李 琳,赵 鹏,等.土壤水分对强筋小麦“豫麦34”氮素同化酶活性和籽粒品质的影响[J].植物生态学报,2005,29(1):48-53.
Ma X M,Li L,Zhao P,etal.Effect of water control on activities of nitrogen assimilation enzymes and grain quality in winter wheat [J].ActaPhytoecologicaSinica,2005,29(1):48-53.
[15]王学奎.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2006:124.
Wang X K.Principle and Techniques of Plant Physiological Biochemical Experiment [M].Beijing:Higher Education Press,2006:124.
[16]赵俊晔,于振文.高产条件下施氮量对冬小麦氮素吸收分配利用的影响[J].作物学报,2006,32(4):484-490.
Zhao J Y,Yu Z W.Effects of nitrogen fertilizer rate on uptake,distribution and utilization of nitrogen in winter wheat under high yielding cultivated condition [J].ActaAgronomicaSinica,2006,32(4):484-490.
[17]曹翠玲,李生秀.氮素水平对冬小麦分蘖期某些含氮化合物及生物量的影响[J].西北农林科技大学学报 (自然科学版),2002,30(6):11-15.
Cao C L,Li S X.Influence of nitrogen level on some nitrogenous substance in winter wheat [J].JournalofNorthwestSci-TechUniversityofAgricultureandForestry(NaturalScienceEdition),2002,30(6):11-15.
[18]肖焱波,李文学,段宗颜,等.植物对硝态氮的吸收及其调控[J].中国农业科技导报,2002,4(2):56-59.
Xiao Y B,Li W X,Duan Z Y,etal.Uptake and regulation of nitrate in plants [J].ReviewofChinaAgriculturalScienceandTechnology,2002,4(2):56-59.
[19]王 静,王小纯,熊淑萍,等.耕作方式对砂姜黑土小麦氮代谢及氮素利用效率的影响[J].麦类作物学报,2014,34(8):1111-1117.
Wang J,Wang X C,Xiong S P,etal.Effects of different tillage methods on nitrogen metabolism and nitrogen utilization efficiency of wheat grown in lime concretion black soil region [J].JournalofTriticeacCrops,2014,34(8):1111-1117.
[20]郭 丽,贾秀领,张凤路,等.定位水氮组合对冀 5265 小麦叶片硝酸还原酶、可溶性蛋白及产量的影响[J].华北农学报,2010,25(1):180-184.
Guo L,Jia X L,Zhang F L,etal.Effects of water and nitrogen location study on leave NRA,soluble protein content and yield of winter wheat [J].ActaAgriculturaeBoreali-Sinica,2010,25(1):180-184.
[21]Sivasankar S,Oaks A.Nitrate assimilation in higher plants:the effect of metabolites and light [J].PlantPhysiologyandBiochemistry,1996,34(5):609-620.
[22]李新鹏,童依平.植物吸收转运无机氮的生理及分子机制[J].植物学通报,2007,24(6):714-725.
Li X P,Tong Y P.Physiological and molecular basis of inorganic nitrogen transport in plants [J].ChineseBulletinofBotany,2007,24(6):714-725.
[23]门中华,李生秀.水培硝态氮浓度对冬小麦幼苗氮代谢的影响[J].广西植物,2010,30(4):544-550.

Analysis of Nitrogen Metabolism in Roots and Uptake Characteristic of Wheat Cultivars with Different Nitrogen Efficiency at Seedling Stage
XIONG Shuping1,WU Keyuan1,WANG Xiaochun1,2,WU Yixin1,DU Pan1,MA Xinming1
(1.College of Agronomy,Henan Agricultural University/Collaborative Innovation Center of Henan Grain Crops/National Key Laboratory of Wheat and Maize Crop Science,Zhengzhou,Henan 450002,China;2.College of Life Sciences,Henan Agriculture University,Zhengzhou,Henan 450002,China)
Abstract:In order to clarify the physiological mechanisms of higher nitrogen use efficiency of wheat,the difference of nitrogen metabolism in roots and uptake characteristics of wheat cultivars with different nitrogen efficiency were investigated.Under hydroponic conditions,the nitrogen metabolism in roots and uptake kinetics to and of N high efficiency wheat variety Luomai 18 and N low efficiency wheat variety Xinong 509 were studied.The results showed that the GS activity,NR activity,free amino acids concentration and soluble protein concentration in root of Luomai 18 were higher than those of Xinong 509.But the nitrate concentration and ammonium concentration in root of Xinong 509 were higher than those of Luomai 18.The maximum absorption rate(Vmax) to and of Luomai 18 were higher than those of Xinong 509.But the affinity(1/Km) of Xinong 509 was higher than that of Luomai 18.In conclusion,the root absorptive capacity to and and assimilative capacity of Luomai 18 was significantly higher than that of Xinong 509.There is a mutually reinforcing relationship between wheat roots absorption and assimilation to and .
Key words:Wheat; Root; Nitrogen metabolism; Uptake kinetics
中图分类号:S512.1;S311
文献标识码:A
文章编号:1009-1041(2016)03-0325-07
通讯作者:马新明(E-mail:xinmingma@126.com)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(31301281);河南省现代农业(小麦)产业技术体系技术创新团队项目(S2010-01-G04)
收稿日期:2015-10-16修回日期:2015-10-29
网络出版时间:2016-03-01
网络出版地址:http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/61.1359.S.20160301.1338.018.html
第一作者E-mail:shupxiong@163.com
