左旋金黄紫堇碱抗精神分裂症作用研究
2016-03-21高赟赟米桂芸
高赟赟,米桂芸,2,刘 帅,杨 征
( 1.军事医学科学院基础医学研究所,北京 100850;2.62301部队门诊部,北京 100071)
左旋金黄紫堇碱抗精神分裂症作用研究
高赟赟1,米桂芸1,2,刘帅1,杨征1
( 1.军事医学科学院基础医学研究所,北京100850;2.62301部队门诊部,北京100071)
中国图书分类号: R-332; R284.1; R749.302.2; R749. 305. 31
摘要:目的研究左旋金黄紫堇碱( l-SLR)的抗精神分裂症作用。方法采用NMDA受体拮抗剂MK-801在动物模型上诱发精神分裂症的阳性症状、阴性症状及认知损伤;评价了化合物l-SLR对MK-801诱发的精神分裂症的作用;并评价了l-SLR对小鼠锥体外系功能的影响。结果MK-801 ( 0. 3 mg·kg-1,ip)引起大鼠前脉冲抑制损伤,l-SLR( 10、15 mg·kg-1,ip)能抑制MK-801引起的大鼠前脉冲抑制损伤; l-SLR( 30 mg·kg-1,ip)能抑制多巴胺受体激动剂阿扑吗啡( 2 mg·kg-1,sc)引起小鼠的攀爬行为,说明l-LSR对MK-801及阿扑吗啡诱发的精神分裂症阳性症状有抑制作用。l-SLR( 30 mg·kg-1,ip)能抑制MK-801( 0. 2 mg·kg-1,ip)引起的小鼠群居接触抑制及MK-801诱发的小鼠认知损伤,说明l-SLR能改善MK-801诱发的精神分裂症阴性症状和认知障碍。经典抗精神分裂药氟哌啶醇在治疗剂量下( 0. 8 mg ·kg-1,ip)诱发小鼠木僵行为,l-SLR在抗精神分裂的剂量下( 30 mg·kg-1,ip)不会诱发木僵行为。结论化合物l-SLR对精神分裂症的阳性症状、阴性症状以及认知障碍均有效,而且其在有效剂量时对锥体外系的影响明显小于氟哌啶醇和l-SPD。
关键词:精神分裂症; l-SLR; MK-801;阳性症状;阴性症状;认知障碍;锥体外系
杨征( 1953-),女,博士,博士生导师,E-mail: yangzhengchina@ aliyun.com
精神分裂症( schizophrenia)是一种常见的重大精神疾病,具有反复发作、不易治愈的特点,临床上根据症状表现一般可分为阳性症状(妄想、幻觉和幻听)和阴性症状(社会功能退缩等),以及以注意力、执行能力、解决问题能力和短期记忆能力缺失或减弱等为主的认知障碍。目前临床上的抗精神病药物均能拮抗多巴胺D2受体,经典抗精神病药物氟哌啶醇对阳性症状有效,但对阴性症状和认知障碍无效甚至加重;精神分裂症的阴性症状和认知障碍难于治疗,有些病人即使长期服药认知障碍也有可能持续存在,因此改善病人阴性症状与认知障碍是治疗精神分裂症的核心问题。由于该病的病理机制不清楚,严重妨碍了新型抗精神分裂药物的开发。
近年来精神分裂症患者脑内皮层与皮层下多巴胺失衡假说日益受到关注[1]。该假说认为皮质下结构的多巴胺释放过多,皮层下边缘系统多巴胺D2受体功能亢进与精神分裂症的阳性症状有关,而前额叶皮质的多巴胺D1受体功能的低下可能与精神分裂症的阴性症状有关,应用多巴胺D1激动剂可以改善精神分裂症模型动物的工作记忆[2-4]。基于该假说,具有多巴胺受体D2拮抗与D1激动的化合物有望更有效地改善精神分裂症病人的阳性、阴性及认知障碍[5]。
化合物左旋千金藤啶碱( l-Stepholidine,l-SPD)和左旋金黄紫堇碱( l-Scoulerine,l-SLR)均属于异喹啉类生物碱,主要存在于中药罂粟科植物延胡索( Corydalis yanhusuo W.T.Wang)和防己科植物华千金藤( Stephaniasinica Diels)中。l-SPD在动物模型及临床上均显示出较好的抗精神病作用[6-7],但是其生物利用度及昂贵的工业生产成本限制了其进一步的研究发展[8]。体外受体结合实验表明化合物l-SLR 对D1和D2的亲和力与l-SPD相似,均是D1激动和D2拮抗[6-7,9],但是l-SLR对D2受体的拮抗作用较l-SPD要弱。国外的研究文献表明,中等程度的D2拮抗会产生抗精神分裂症作用,而D2受体的结合率达0. 75~0. 80将会产生锥体外系副反应[10]。因此我们推测化合物l-SLR应具有抗精神分裂症的作用而其锥体外系副作用应弱于l-SPD。
NMDA受体拮抗剂如苯环己哌啶( phencyclidine,PCP)和地卓西平马来酸盐( MK-801)单次给药后便可引起认知功能损伤、信息加工缺陷、高活动性及刻板行为等与精神分裂症相关的行为变化[11-12],该结果也在临床上得到证实,因此NMDA受体拮抗剂已成为建立精神分裂症模型的常用方法[13]。本实验拟利用NMDA受体拮抗剂MK-801诱发的小鼠精神分裂症动物模型,系统评价l-SLR对MK-801诱发的精神分裂症的作用,旨在为开发新型抗精神病药物提供理论及实验依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1动物昆明♂小鼠,体质量( 18±2) g,订购于军事医学科学院实验动物中心,合格证号为SCXK-(军) 2012-0004;♂SD大鼠( 320±20) g,购自于北京维通利华实验动物技术有限公司,许可证号为SCXK(京) 2012-0001,动物在实验室适应环境3天进行实验,自由进水觅食,12 h光照,12 h黑暗( 8: 00~20: 00),温度为( 24±2)℃,湿度为( 45±5) %。
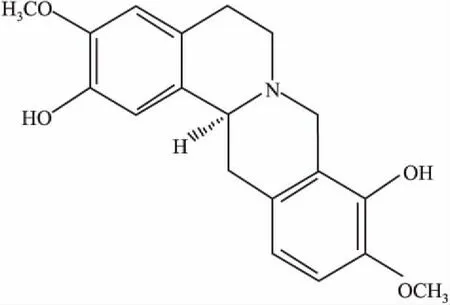
1.2药物MK-801购自美国Tocris公司(生产批号: 8B/109741) ; l-SLR由军事医学科学院基础研究所自行合成;氟哌啶醇注射液( haloperidol,HAL,湖南洞庭药业股份有限公司,批准文号: H43020555) ;阿扑吗啡( apomorphine,APO)购自美国Sigma公司。除阿扑吗啡为皮下注射给药外,其他药物均为腹腔注射给药。化合物左旋金黄紫堇碱结构如下:
1.3方法
1.3.1听觉前脉冲抑制实验( PPI)[14-15]人类震惊反射实验系统Xeye Human Startle Reflex System ( V1. 20版)北京天鸣宏远科技发展有限公司;将大鼠随机分为共10组,每组8只。组别为:溶剂对照组( VEH)、溶剂对照+ MK-801组( VEH + MK-801)、氟哌啶醇组( HAL)、氟哌啶醇+ MK-801组( HAL + MK-801)、l-SLR组( l-SLR)、l-SLR与MK-801组( l-SLR + MK-801)。氟哌啶醇剂量为0. 2 mg ·kg-1; l-SLR剂量为5、10、15 mg·kg-1; MK-801剂量为0. 3 mg·kg-1。给予溶剂对照、氟哌啶醇或l-SLR 15 min后给予盐水或MK-801,给予MK-801 30 min后进行前脉冲抑制测定。前脉冲实验开始前先让大鼠适应环境2次,每次5 min,背景噪音为60 dB,前脉冲分别设为63 dB、66 dB、72 dB,持续时间为20 ms,脉冲设为100 dB,持续时间为40 ms,前脉冲与脉冲之间的时间间隔为100 ms,将3个前脉冲、脉冲和背景噪音组成5个不同的实验区组,每个实验区组之间都是以8~22 s的时间间隔随机出现,将5个不同的实验区组组成8个实验模块,在大鼠适应环境5 min结束后给予5个脉冲刺激以提示大鼠实验即将开始,然后进行8个实验模块部分。
PPI% =[(脉冲时的惊跳反射振幅-有前脉冲时的惊跳反射振幅)÷脉冲时的惊跳反射振幅]×100%
1.3.2攀爬实验多巴胺激动剂阿扑吗啡( APO)诱发多巴胺释放增加,导致动物出现跳跃和攀爬行为。拮抗阿扑吗啡诱发的攀爬行为是筛选抗精神分裂药物的经典模型[16]。攀爬使用为网格边长1. 2 cm方格的铁丝筐。将小鼠随机分为溶剂组( VEH)、溶剂+阿扑吗啡组( VEH + APO)、HAL( 0. 2 mg·kg-1) + APO( 2 mg·kg-1)、l-SLR( 10、30 mg·kg-1) +APO( 2 mg·kg-1) 5组,每组10只。给予对照、抗精神分裂药物30 min后给予阿扑吗啡,15 min后测定小鼠在10 min内的累计攀爬时间。小鼠的攀爬以至少小鼠2只前爪均搭在铁丝网上为准。
1.3.3群居接触实验[17]群居接触仪器为长和宽均为36 cm的方形木箱。将小鼠随机分为溶剂对照( VEH)、VEH + MK-801、HAL( 0. 2 mg·kg-1)、HAL + MK-801、l-SLR( 10、30 mg·kg-1)、l-SLR( 10、30 mg·kg-1) + MK-801 8组,每组10对,每对老鼠取自不同的饲养笼。给予溶剂对照、HAL、l-SLR 15 min后给予MK-801 0. 2 mg·kg-1,30 min后将小鼠放入木箱中,测定每对小鼠在10 min内的接触时间。评价标准:互相嗅闻、互相理毛、骑跨、互相攀爬、小鼠除尾巴以外身体的任意部位接触计为群居接触时间。
1.3.4Y迷宫实验[18-20]Y迷宫每个臂长为40 cm,宽为8 cm,高为20 cm,每两个臂之间的夹角为120°。将小鼠随机分为VEH、VEH + MK-801( 0. 2 mg·kg-1)、HAL( 0. 2 mg·kg-1)、HAL + MK-801、l-SLR( 10、30 mg·kg-1)、l-SLR( 10、30 mg·kg-1) + MK-801 8组,每组10只,给与溶剂对照、HAL、l-SLR 15 min后给予MK-801 0. 2 mg·kg-1,30 min后将小鼠放入木箱中进行Y迷宫实验。将Y迷宫的3个臂随机标记为A、B、C,将小鼠放入迷宫中自由探索2 min,2 min后记录小鼠8 min内进入各个臂的名称。结果记录为交替百分率( alternation rate),交替( alternation)定义为小鼠连续进入3个不同的臂的次数。交替百分率/% =[交替总次数+ (入臂总次数-2)]×100%。
1.3.5木僵实验[21-22]高20 cm,宽9. 5 cm的纸盒,在离纸盒底部5 cm处两侧开口,固定一半径为0. 25 cm的玻璃棒。将小鼠随机分为VEH、HAL ( 0. 8 mg·kg-1)、l-SPD( 30、60、80 mg·kg-1)、l-SLR( 10、30、60、80 mg·kg-1) 9组,每组8只。每组小鼠腹腔注射相应的药物45 min和90 min后分别测定小鼠的木僵时间。将小鼠置于水平玻璃棒上,小鼠维持站立不动,保持原姿态的时间计为木僵时间。
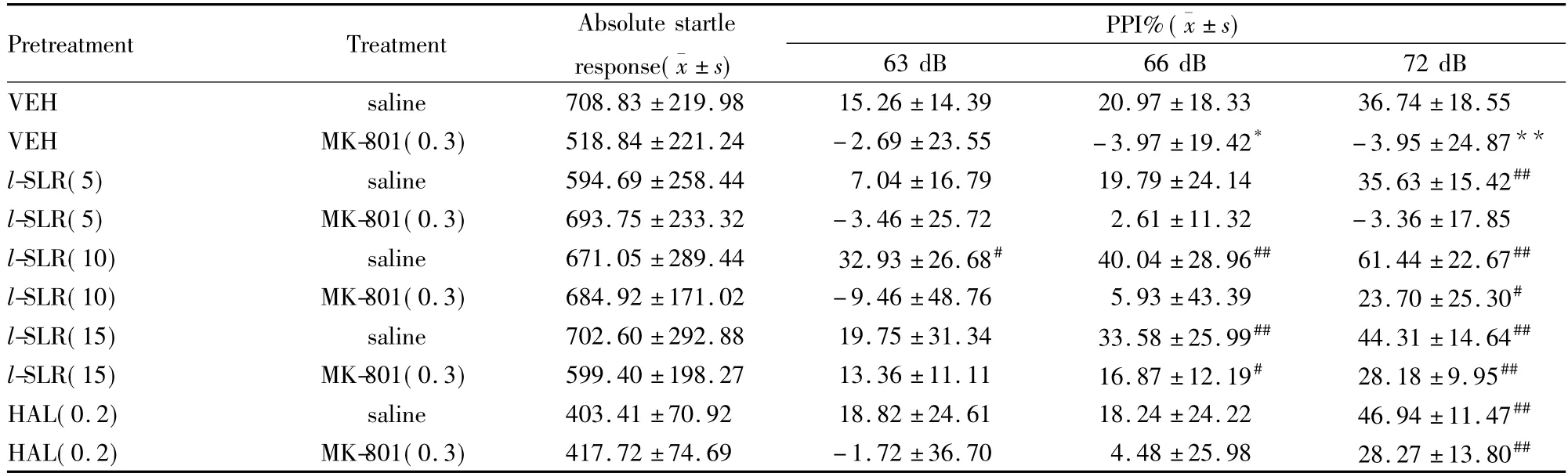
Tab 1 Effects of drug treatment on absolute startle amplitude( 100 dB) and PPI( %)
2 结果
2.1听觉前脉冲抑制实验( PPI)如Tab 1所示,与VEH组相比,MK-801( 0. 3 mg·kg-1)能够明显降低大鼠的前脉冲抑制中的震惊反射( F5,44= 6. 696,P<0. 01),而注射l-SLR( 10、15 mg·kg-1)和氟哌啶醇( 0. 2 mg·kg-1)能够明显改善由MK-801引起的前脉冲抑制损伤( P<0. 01),这说明化合物l-SLR和氟哌啶醇对MK-801引起的精神分裂症的阳性症状均有效。
2.2攀爬实验如Fig 1所示,与VEH组相比,阿扑吗啡( 2 mg·kg-1)皮下注射能够明显增加小鼠的攀爬时间( F4,45= 19. 13,P<0. 01),氟哌啶醇( 0. 2 mg·kg-1)和l-SLR( 30 mg·kg-1)能够明显抑制阿扑吗啡所引起的攀爬行为,这说明化合物l-SLR和氟哌啶醇对MK-801引起的精神分裂症的阳性症状有效。
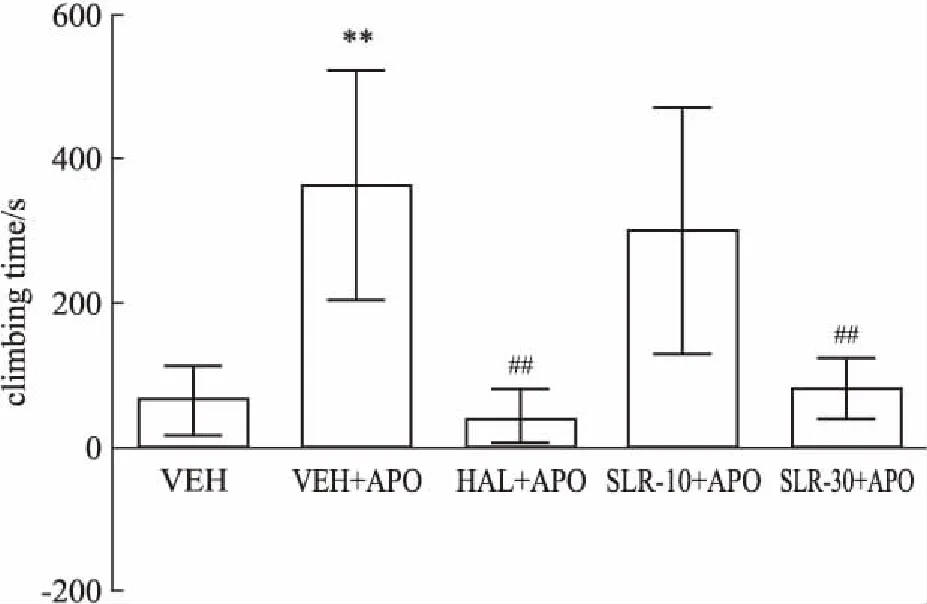
Fig 1 Effects of haloperidol and l-SLR on climbing test(±s,n =10)
2.3群居接触实验如Fig 2A所示,与VEH组相比,MK-801能够明显抑制小鼠的群居接触行为,使小鼠的群居接触时间明显降低( F3,36= 7. 566,P = 0. 0084),而典型的抗精神病药氟哌啶醇却不能使小鼠的群居接触时间延长;如Fig 2B所示,l-SLR在30 mg·kg-1时能够明显增加小鼠的群居接触时间( F5,54=6. 285,P =0. 0001),说明l-SLR在30 mg· kg-1时对精神分裂症的阴性症状有效。
2.4Y迷宫实验如Fig 3A所示,与VEH组相比,MK-801能够明显地抑制小鼠的空间认知能力( F3,36=10. 60,P<0. 01),而给予氟哌啶醇并不能改善小鼠的这种空间认知损伤;如Fig 3B所示,l-SLR在30 mg·kg-1时能够明显改善小鼠的空间认知障碍( F5,54= 11. 58,P<0. 01),说明l-SLR在30 mg·kg-1时能够改善精神分裂症的认知损伤。
2.5木僵实验如Fig 4所示,与VEH组相比,在给药45 min后,氟哌啶醇( 0. 8 mg·kg-1)和l-SPD ( 60、80 mg·kg-1)能够使小鼠的木僵时间明显增加( F8,64=13. 63,P<0. 01) ;给药90 min以后,氟哌啶醇和l-SPD( 30、60、80 mg·kg-1)引起的木僵行为仍然存在( F8,64=14. 54,P<0. 01),而l-SLR在30、60 mg·kg-1并不产生木僵,说明l-SLR在抗精神分裂症的有效剂量下不产生锥体外系的副作用。
3 讨论
前脉冲抑制是指在强感觉刺激出现之前的很短时间内出现的弱感觉刺激对震惊反射的抑制作用,是感觉门控对人体的一种保护措施。临床研究证实,精神分裂症患者存在前脉冲抑制损伤[23]。药理学研究证实,给予多巴胺受体激动剂可以破坏PPI[24];内侧前额叶皮质( medial prefrontal cortex)对PPI的调节作用被认为是多巴胺依赖的,突触前易化作用增加中脑腹侧被盖区( VTA)在伏隔核的多巴胺释放使PPI减弱[25],而给予多巴胺D2受体拮抗剂却能逆转[26]。说明精神分裂症患者的PPI降低是由于前额叶皮质多巴胺释放增加所引起的,化合物l-SLR抑制MK-801引起的PPI降低可能是其拮抗多巴胺D2受体的结果。
阿扑吗啡引发小鼠的攀爬实验是研究突触后多巴胺活性及筛选抗精神病药物的经典模型[27-29]。阿扑吗啡引起动物攀爬时间增加可能与其激动纹状体多巴胺D2受体,使多巴胺释放增加有关[17,30-31]。氟哌啶醇与化合物l-SLR均对阿扑吗啡诱导的小鼠攀爬行为产生明显的抑制作用,可能是通过拮抗D2受体发挥作用。
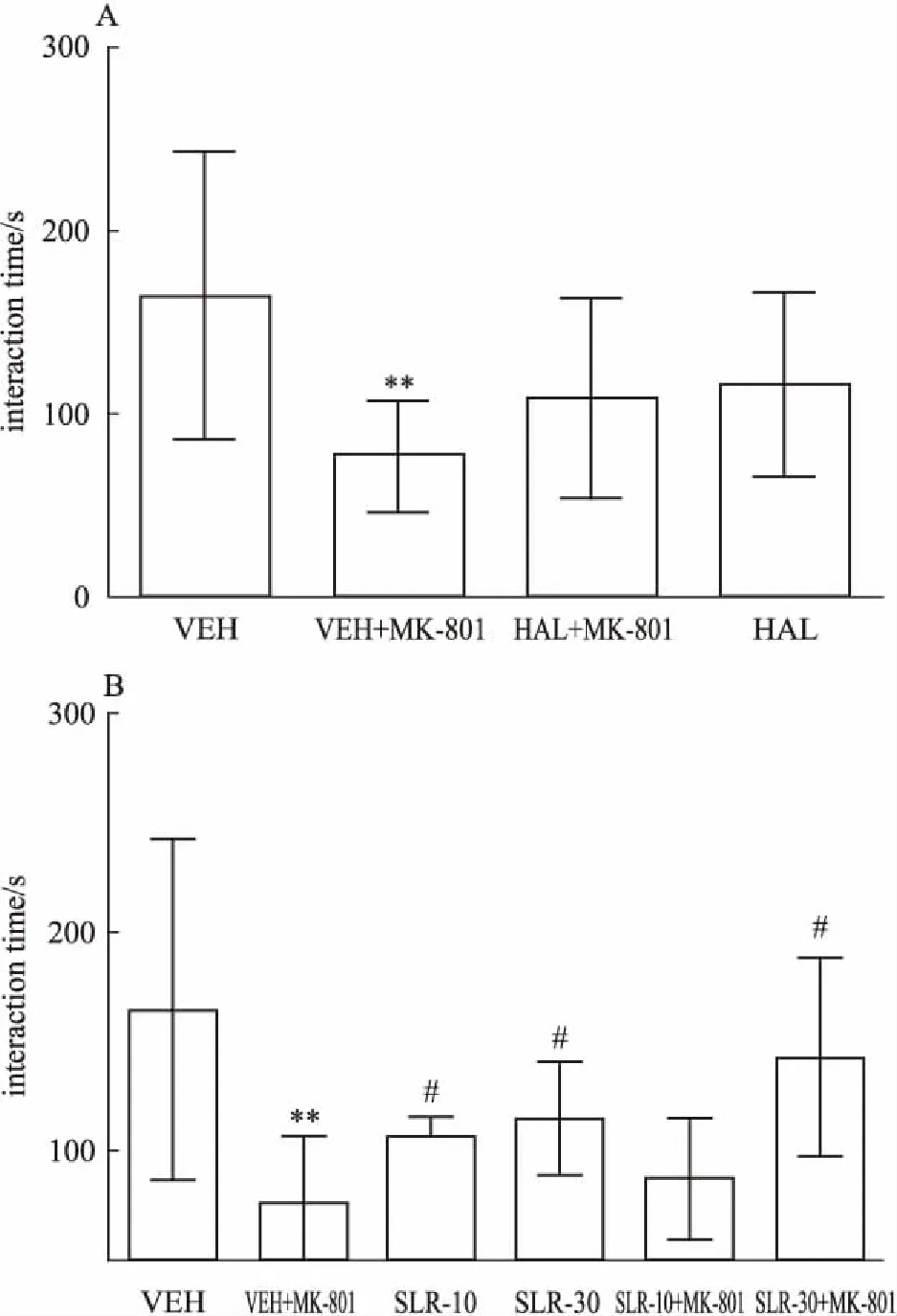
Fig 2 Effects of haloperidol( A) and I-SLR( B) on social interaction test induced by MK-801(±s,n =10)
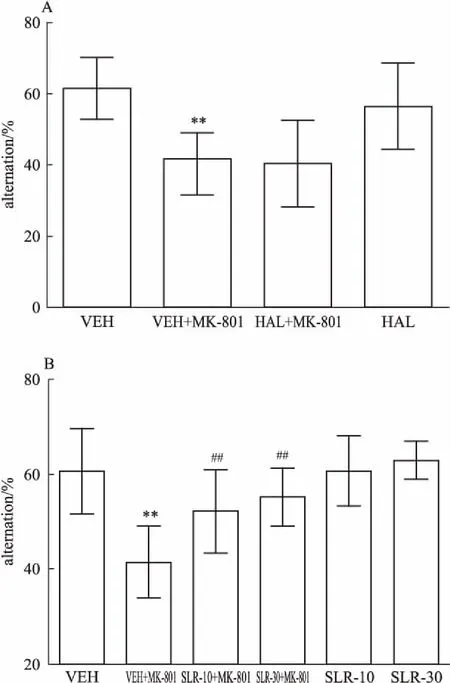
Fig 3 Effects of haloperidol( A) and l-SLR( B) on Y-maze(±s,n =10)
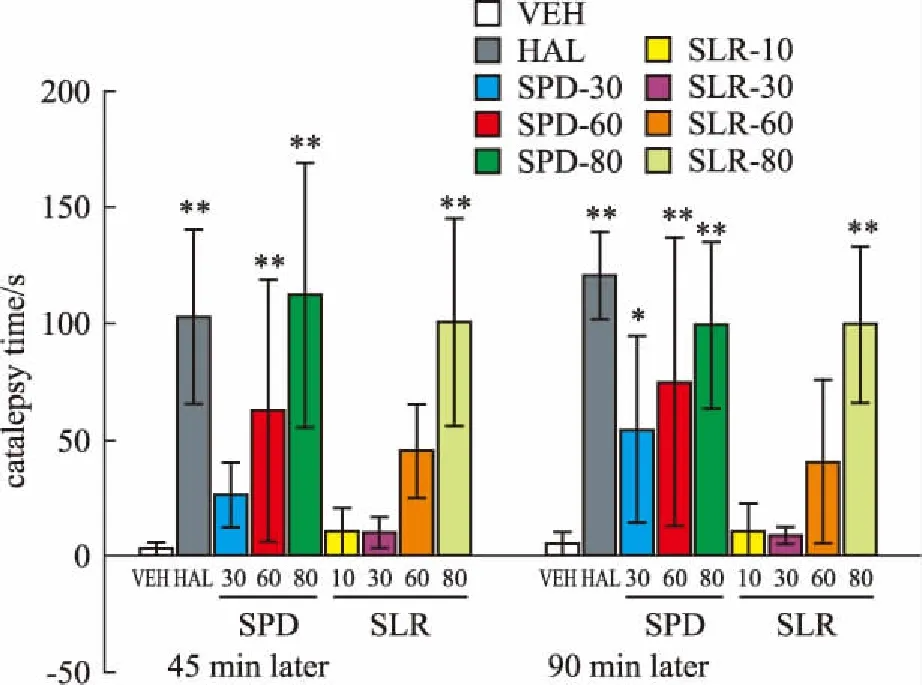
Fig 4 Effects of haloperidol,I-SPD and l-SLR on extrapyramidal system(±s,n =8)
精神分裂症病患者存在着社会退缩,极大影响了患者的日常生活和工作效率[32],改善社交障碍是帮助精神病患者进入社会生活的重要因素[33]。群居接触是测定陌生的两只动物之间的接触时间,反映了动物的群体接触意愿[34-35]。已有研究证实对5-HT1A部分激动和5-HT2A拮抗作用的化合物Brex piprazole对PCP诱发的群居接触障碍有改善作用[35-36],而化合物l-SLR的受体结合实验也表明其对5-HT1A和5-HT2A受体均有亲和力[6],这可能是l-SLR能明显增加小鼠间的接触时间而经典的抗精神病药物氟哌啶醇无效的原因。
认知障碍被认为是精神分裂症的一个重要特征[38-40],而且是在精神分裂症的所有症状中治疗效果最差的[41-42]。研究表明前皮质D1受体功能低下可能与精神分裂症患者工作记忆障碍有关,而激动D1受体可改善精神分裂症的认知障碍[2-3]。本次实验结果表明氟哌啶醇不能改善MK-801小鼠的认知损伤,化合物l-SLR能够改善MK-801诱发小鼠记忆障碍可能与l-SLR激动D1受体有关。
锥体外系是人体运动系统的组成部分,其主要功能是调节肌张力、肌肉的协调运动与平衡。这种调节功能有赖于其调节中枢的神经递质多巴胺和乙酰胆碱的动态平衡,当多巴胺减少或乙酰胆碱相对增多时,则可出现胆碱能神经亢进的症状,即锥体外系副作用。氟哌啶醇与D2受体的结合率高达0. 60 ~0. 80[10],可能是氟哌啶醇过于拮抗D2受体,导致胆碱能系统功能相对亢进而产生木僵行为。研究表明,许多经典抗精神病药均能引起锥体外系副作用[43],而非经典抗精神分裂药物氯氮平等对D2受体的拮抗作用较弱,但氯氮平作用于多靶点,对5-HT受体也有作用,在临床上对精神分裂症的各种症状均有效而没有锥体外系的副作用[10]。我们发现化合物l-SLR在有效剂量下不诱发小鼠木僵行为可能与其对D2受体的亲和力明显低于氟哌啶醇和化合物l-SPD有关[6,10]。
我们的实验的结果表明,化合物l-SLR对MK-801诱发的精神分裂症的阳性症状、阴性症状以及认知障碍均有改善作用,而且在抗精神分裂症的有效剂量下并不引起木僵等锥体外系副作用,提示l-SLR具有成为新型抗精神病药的潜力,值得进一步深入研究。
(致谢:本项工作是在军事医学科学院基础医学研究所药理学实验室完成,感谢实验室所有成员的帮助。)
参考文献:
[1]Hess E J,Bracha H S,Kleinman J E,Creese I.Dopamine receptor subtype imbalance in schizophrenia[J].Life Sci,1987,40( 15) : 1487-97.
[2]Okubo Y,Suhara T,Suzuki K,et al.Decreased prefrontal dopamine D1 receptors in schizophrenia revealed by PET[J].Nature,1997,385( 6617) : 634-6.
[3]Granon S,Passetti F,Thomas K L,et al.Enhanced and impaired attentional performance after infusion of D1dopaminergic receptor agents into rat prefrontal cortex[J].J Neurosci,2000,20( 3) : 1208-15.
[4]Castner S A,Williams G V,Goldman-Rakic P S.Reversal of antipsychotic-induced working memory deficits by short-term dopamine D1 receptor stimulation[J].Science,2000,287 ( 5460) : 2020-2.
[5]Bruin S,Slot L A,Kleven M S,Newman-Tancredi A.Effects of novel antipsychotics with mixed D2antagonist/5-HT1Aagonist properties on PCP-induced social interaction deficits in the rat[J].Neuropharmacology,2005,49( 7) : 996-1006.
[6]Sun H,Zhu L,Yang H,et al.Asymmetric total synthesis and identification of tetrahydroprotoberberine derivatives as new antipsychotic agents possessing a dopamine D1,D2and serotonin5-HT1Amulti-action profile[J].Bioorg Med Chem,2013,21( 4) : 856-68.
[7]Mo J,GuoY,Yang Y S,et al.Recent developments in studies of l-stepholidine and its analogs: chemistry,pharmacology and clinical implications[J].Curr Med Chem,2007,14( 28) : 2996-3002.
[8]Sun Y,Dai J,Hu Z,et al.Oral bioavailability and brain penetration of (-) -stepholidine,a tetrahydroprotoberberine agonist at dopamine D( 1) and antagonist at D( 2) receptors,in rats[J].Br J Pharmacol,2009,158( 5) : 1302-12.
[9]Fu Y,Zhu Z T,Zhu X Z,et al.Biphasic firing response of nucleus accumbens neurons elicited by THPB-18 and its correlation with DA receptor subtypes[J].Acta pharmacol Sin,2004,25: 1597-605.
[10]Divac N,Prostran M,Jakovcevski I,Cerovac N.Second-generation antipsychotics and extrapyramidal adverse effects[J].Biomed Res Int,2014,2014: 656370.
[11]Du Bois T M,Huang X F.Early brain development disruption from NMDA receptor hypofunction: relevance to schizophrenia [J].Brain Res Rev,2007,53( 2) : 260-70.
[12]Lim A L,Taylor D A,Malone D T.Consequences of early life MK-801 administration: long-term behavioural effects and relevance to schizophrenia research[J].Behav Brain Res,2012,227 ( 1) : 276-86.
[13]颜慧,宫泽辉.斑马鱼谷氨酸功能低下精神分裂行为模型的建立[J].中国药理学通报,2011,27( 1) : 134-7.
[13]Yan H,Gong Z H.A behavioral model of hypoglutamatergic schizophrenia in the zebrafish[J].Chin Pharmacol Bull,2011,27( 1) : 134-7.
[14]Mattei D,Djodari-Irani A,Hadar R,et al.Minocycline rescues decrease in neurogenesis,increase in microglia cytokines and deficits in sensorimotor gating in an animal model of schizophrenia [J].Brain Behav Immun,2014,38: 175-84.
[15]Valsamis B,Schmid S.Habituation and prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle in rodents[J].J Vis Exp,2011,sep1: ( 55) : e3446.
[16]Yun J,Jung Y S.A Scutellaria baicalensis radix water extract inhibits morphine-induced conditioned place preference[J].Pharma Biol,2014,52( 11) : 1382-7.
[17]Xu H,Yang H J,Zhang Y,et al.Behavioral and neurobiological changes in C57BL/6 mice exposed to cuprizone[J].Behav Neurosci,2009,123( 2) : 418-29.
[18]Lipina T V,Palomo V,Gil C,et al.Dual inhibitor of PDE7 and GSK-3-VP1. 15 acts as antipsychotic and cognitive enhancer in C57BL/6J mice[J].Neuropharmacology,2013,64: 205-14.
[19]Suryavanshi P S,Ugale R R,Yilmazer-Hanke D,et al.GluN2C/ GluN2D subunit-selective NMDA receptor potentiator CIQ reversesMK-801-induced impairment in prepulse inhibition and working memory in Y-maze test in mice[J].Br J Pharmacol,2014,171 ( 3) : 799-809.
[20]Dall'Igna O P,Da Silva A L,Dietrich M O,et al.Chronic treatment with caffeine blunts the hyperlocomotor but not cognitive effects of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist MK-801 in mice[J].Psychopharmacology ( Berl),2003,166( 3) : 258-63.
[21]Mahmoudi J,Mohajjel Nayebi A,Samini M,et al.5-HT( 1A)receptor activation improves anti-cataleptic effects of levodopa in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats[J].Daru,2011,19( 5) : 338.
[22]Jeon J,Dencker D,Wörtwein G,et al.A subpopulation of neuronal M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors plays a critical role in modulating dopamine-dependent behaviors[J].J Neurosci,2010,30( 6) : 2396-405.
[23]Swerdlow N R,Geyer M A,Braff D L.Neural circuit regulation of prepulse inhibition of startle in the rat: current knowledge and future challenges[J].Psychopharmacology ( Berl),2001,156( 2-3) : 194-215.
[24]Wan F J,Geyer M A,Swerdlow N R.Presynaptic dopamine-glutamate interactions in the nucleus accumbens regulate sensorimotor gating[J].Psychopharmacology ( Berl),1995,120( 4) : 433-41.
[25]李量,邵枫.精神分裂症的听感觉运动门控障碍的动物模型[J].科学通报,2003,48( 15) : 1603-12.
[25]Li L,Shao F.Animal model of auditory sensorimotor gating disorder in schizophrenia[J].Sci Bull,2003,48( 15) : 1603-12.
[26]Geyer M A,Krebs-Thomson K,Braff D L,et al.Pharmacological studies of prepulse inhibition models of sensorimotor gating deficits in schizophrenia: a decade in review[J].Psychopharmacology ( Berl),2001,156( 2-3) : 117-54.
[27]Corbett R,Hartman H,Kerman L L,et al.Effects of atypical antipsychotic agents on social behavior in rodents[J].Pharmacol Biochem Behav,1993,45( 1) : 9-17.
[28]Ryu J H,Yanai K,Sakurai E,et al.Ontogenetic development of histamine receptor subtypes in rat brain demonstrated by quantitative autoradiography[J].Brain Res Dev Brain Res,1995,87( 2) : 101-10.
[29]Protais P,Costentin J,Schwartz J C.Climbing behavior induced by apomorphine in mice: a simple test for the study of dopamine receptors in striatum[J].Psychopharmacology ( Berl),1976,50 ( 1) : 1-6.
[30]Depoortere R,Boulay D,Perrault G,et al.SSR181507,a dopamine D2receptor antagonist and 5-HT1A receptor agonist.Ⅱ: Behavioral profile predictive of an atypical antipsychotic activity[J].Neuropsychopharmacology,2003,28( 11) : 1889-902.
[31]Zalcman S S.Interleukin-2-induced increases in climbing behavior: inhibition by dopamine D-1 and D-2 receptor antagonists[J].Brain Res,2002,944( 1-2) : 157-64.
[32]Tse S,Chan S,Ng K L,et al.Meta-analysis of predictors of favorable employment outcomes among individuals with bipolar disorder[J].Bipolar Disord,2014,16( 3) : 217-29.
[33]Horan W P,Green M F,DeGroot M,et al.Social cognition in schizophrenia,part 2: 12-month stability and prediction of functional outcome in first-episode patients[J].Schizophr Bull,2012,38( 4) : 865-872.
[34]Moy S S,Nadler J J,Perez A,et al.Sociability and preference for social novelty in five inbred strains: an approach to assess autistic ‐like behavior in mice[J].Genes Brain Behav,2004,3( 5) : 287-302.
[35]van der Kooij M A,Sandi C.Social memories in rodents: methods,mechanisms and modulation by stress[J].Neurosci Biobehav Rev,2012,36( 7) : 1763-72.
[36]Yoshimi N,Fujita Y,Ohgi Y,et al.Effects of brexpiprazole,a novel serotonin-dopamine activity modulator,on phencyclidine-induced cognitive deficits in mice: a role for serotonin 5-HT 1A receptors[J].Pharmacol Biochem Behav,2014,124: 245-9.
[37]Yoshimi N,Futamura T,Hashimoto K.Improvement of dizocilpine-induced social recognition deficits in mice by brexpiprazole,a novel serotonin-dopamine activity modulator[J].Eur Neuropsychopharmacol,2015,25( 3) : 356-64.
[38]Bora E,Lin A,Wood S J,et al.Cognitive deficits in youth with familial and clinical high risk to psychosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Acta Psychiatr Scand,2014,130( 1) : 1-15.
[39]Fatouros-Bergman H,Cervenka S,Flyckt L,et al.Meta-analysis of cognitive performance in drug-naïve patients with schizophrenia [J].Schizophr Res,2014,158( 1) : 156-62.
[40]Schaefer J,Giangrande E,Weinberger D R,et al.The global cognitive impairment in schizophrenia: consistent over decades and around the world[J].Schizophr Res,2013,150( 1) : 42-50.
[41]Fagerlund B,Mackeprang T,Gade A,et al.Effects of low-dose risperidone and low-dose zuclopenthixol on cognitive functions in first-episode drug-naive schizophrenic patients[J].CNS Spectr,2004,9( 5) : 364-74.
[42]Harvey P D,Keefe R S.Studies of cognitive change in patients with schizophrenia following novel antipsychotic treatment[J].Am J Psychiatry,2001,158( 2) : 176-84.
[43]Holloman L C,Marder S R.Management of acute extrapyramidal effects induced by antipsychotic drugs[J].Am J Health Syst Pharm,1997,54( 21) : 2461-77.
On antipsychotic effects of l-Scoulerine
GAO Yun-yun1,MI Gui-yun1,2,LIU Shuai1,YANG Zheng1
( 1.Institute of Basic Medical Science,Academy of Military Medical Sciences,Beijing 100850,China; 2.Out-patient Dept,the 62301 unit of the People’s Liberation Army,Beijing 100071,China)
Abstract:AimTo study the antipsychotic effects of l-Scoulerine( l-SLR).Methods NMDAreceptorantag-book=109,ebook=118onist MK-801 was used to induce the positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia and cognitive impairment in animal models.The effects of l-SLR were evaluated on schizophrenia induced by MK-801 and on extrapyramidal system.Resultsl-SLR ( 10,15 mg· kg-1,ip) could suppress pre-pulse inhibition damage in rats induced by MK-801( 0. 3 mg·kg-1,ip) ; l-SLR( 30 mg·kg-1,ip) could inhibit climbing behaviors in mice induced by apomorphine,which suggested that l-SLR had significant inhibiting effects on the positive symptoms of schizophrenia by MK-801 and apomorphine.l-SLR could also induce social contact inhibition and cognitive impairment induced by MK-801 ( 0. 2 mg·kg-1,ip),which proposed that l-SLR could improve the negative symptoms and cognitive impairment by MK-801.Catalepsy in mice could be caused by the treatment dose of haloperidol ( 0. 8 mg· kg-1,ip),not by that of l-SLR( 30 mg·kg-1,ip).ConclusionI-SLR has significant effects on the positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia and cognitive impairment and,the effect of l-SLR under effective dose on extrapyramidal system is obviously much less than that of haloperidol and l-SPD.
Key words:schizophrenia; l-SLR; MK-801; positive symptoms; negative symptoms; cognitive impairment; extrapyramidal system
作者简介:高赟赟( 1989-),女,硕士生,研究方向:神经精神药理学,E-mail: gaoyunyun12@126.com;
基金项目:国家自然科学基金面上项目( No 81473193) ;军队“十二五”重大专项课题( No 2012ZX09031)
收稿日期:2015-10-18,修回日期: 2015-11-15
文献标志码:A
文章编号:1001-1978( 2016) 01-0103-07
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2016.01.022