噪声扰动下时滞复杂网络动力学参数及拓扑结构辨识
2016-01-11卫亭,杨晓丽,孙中奎
噪声扰动下时滞复杂网络动力学参数及拓扑结构辨识
卫亭1,杨晓丽1,孙中奎2
(1.陕西师范大学数学与信息科学学院,西安710062;2.西北工业大学应用数学系,西安710072)
摘要:针对随机噪声及时间滞后普遍存在于耦合网络,且其结构往往未知或部分未知问题,基于网络间随机广义投影滞后同步原理,通过合理设计控制器与自适应更新规则,构建辨识网络模型未知动力学参数及拓扑结构的识别方案;结合随机时滞微分方程LaSalle型不变性原理,从数学上严格证明识别方案的准确性。通过具体网络模型,借助计算仿真验证识别方案的有效性。数值模拟结果表明,网络未知动力学参数及拓扑结构不但能准确辨识,且识别方案不依赖耦合时滞、更新增益及网络拓扑结构等选取。
关键词:网络结构识别;网络同步;耦合时滞;随机噪声
中图分类号:O322文献标志码:A
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(11372081)
收稿日期:2014-09-22修改稿收到日期:2014-11-06
基金项目:国家自然科学基金重大研究计划重点支持项目“古建木构的状态评估、安全极限与性能保持”(51338001);北京交通大学人才基金项目(2014RC011)
收稿日期:2014-07-29修改稿收到日期:2014-10-17
Identification of system parameters and network topology of delay-coupled complex networks under circumstance noise
WEITing1,YANGXiao-Li1,SUNZhong-kui2(1. Shanxi Normal University, Xi’an 710062, China; 2. Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China)
Abstract:Noting that the random noise and time delay are prevalent in complex networks and the topology of a network is often unknown or partially unknown, based on the principle of random generalized projective lag synchronization, an approach was proposed to estimate the system parameters and topological structure of delay-coupled complex networks under circumstance noise. By constructing an appropriate controller and adaptive updating rules, the unknown network parameters and topological structure of the concerned networks were identified simultaneously. The accuracy of the method was rigorously proved by the LaSalle-type theorem for stochastic differential delay equations.An example of network with chaotic oscillator was provided to illustrate the method. The numerical results indicate that the unknown network parameters and topological structure can be accurately identified, and yet the proposed method is robust against the time delay, the update gain and the network topology.
Key words:topology identification; network synchronization; coupled delay; random noise
在网络结构已知条件下,有关其统计特征(如平均路径长度、度分布、聚类系数)的动力学行为及控制、网络结构对动力学影响等获得广泛研究[1-7]。然而,由于各种因素的不确定性,诸多(如蛋白质相互作用、生物神经、电力等)网络动力学参数或拓扑结构往往未知或部分未知,因此,辨识网络模型的动力学参数及拓扑结构在复杂动力网络研究中具有重要的理论意义与应用价值。
Yu等[8]首次提出利用网络动力学演化信息,通过构造含控制器的新网络,并基于两网络间完全同步追踪原网络的拓扑结构。该思想在具有相同[9-11]、不同节点动力学[12-13]网络拓扑结构及动力学参数识别中广泛研究。文献[14]采用摄动法反演网络模型的连接矩阵,由于信息传递速度的有限性、交通堵塞及脑神经系统与其它网络系统信息传播路径长短不同,网络节点之间进行信息传输时存在时间滞后。因此,对网络结构识别研究需拓展到含耦合时滞的复杂网络情形。基于网络间完全同步,文献[15-21]通过设计自适应反馈控制器,分别研究含常数时滞或时变时滞、节点动力学相同或不同、加权网络或等权复杂网络的动力学参数或拓扑结构识别。网络间其它同步类型如投影同步[22]、超前同步[23]及滞后同步[24]在时滞耦合网络结构识别中也发挥重要作用。而基于最优化法[25]、稳态控制法[26]也用于时滞复杂网络的拓扑结构识别研究。因现实网络系统会受随机噪声影响,如何识别复杂网络的拓扑结构及动力学参数仍为具有挑战性的前沿课题。对含噪声的网络模型, Ren等[27]通过定义网络节点动力学信息间相关性,推导信息相关矩阵与决定网络拓扑结构的Laplacian矩阵关系。吴晓群等[28]通过设计自适应反馈控制器,基于网络间随机同步研究节点动力学含随机噪声的复杂动力网络模型拓扑结构识别。文献[29-33]采用基于最优化法、格林因果检验法、ROC曲线分析法及反复性理论法研究噪声扰动下复杂网络的拓扑结构识别。
考虑随机噪声及耦合时滞普遍存在于复杂网络,尤其利用网络间同步原理反演网络结构时,耦合网络亦会受时间滞后、随机噪声影响。针对噪声扰动下含耦合时滞的复杂网络模型,采用反复性理论法[34]、时滞反馈控制法[35]及信息论法[36]研究网络模型的拓扑结构识别。而基于同步法辨识噪声扰动下时滞复杂网络模型的动力学参数及网络拓扑结构研究较少。本文构建含耦合时滞及噪声扰动的驱动-响应网络模型,通过合理设计控制器与自适应更新规则,基于网络间随机广义投影滞后同步辨识网络模型的动力学参数与拓扑结构,并数值仿真验证理论推理的有效性。
1网络模型及预备知识
1.1网络模型
考虑含N个节点的一般复杂动力网络,其动力学方程为
(1)
式中:xi(t)=(xi1(t),xi2(t),…,xin(t))T∈Rn为第i个节点状态变量;f∈Rn×1,F∈Rn×m1为光滑向量函数及矩阵函数;ξ∈Rm1为未知或不确定的动力学参数; B=(bij)N×N为耦合矩阵,表示未知或不确定的网络拓扑结构,bij定义为:若从节点i到节点j有一个连接,则bij≠0,否则,bij=0;Γ∈Rn×n为决定变量间相互关系的内部耦合矩阵;τ(t)为网络内部节点间时变耦合时滞。
将方程(1)作为驱动网络,构建响应网络为
dyi(t)=[g(yi(t))+G(yi(t))θ+
σi(yi(t)-γxi(t-δ),yi(t-τ(t))-
γxi(t-τ(t)-δ),t)dW(t),(i=1,2,…,N)
(2)
式中:yi(t)=(yi1(t),yi2(t),…,yin(t))T∈Rn为响应网络第i个节点状态变量;g∈Rn×1,G∈Rn×m2为光滑向量函数及矩阵函数,其中驱动网络与响应网络可具有不同节点动力学;θ∈Rm2为未知或不确定的动力学参数; D=(dij)N×N为耦合矩阵,表示对耦合矩阵B的估计;Ui(t)∈Rn为控制器;δ为网络间耦合时滞;σi:Rn×Rn×R+→Rn×m为噪声强度函数;W(t)=(w1(t),w2(t),…,wm(t))T∈Rm为定义在完备概率空间(Ω,H,P)的m维布朗运动,σidW(t)用于刻画响应网络与驱动网络的耦合过程中,会受外界环境浮动、耦合强度设计不精确性等不确定因素影响。本文设m=1。
1.2预备知识

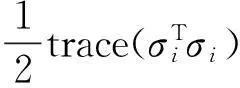
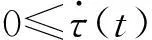
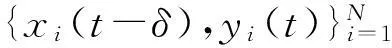
引理对任意向量x,y∈Rn及正定矩阵Q∈Rn×n,有2xTy≤xTQx+yTQ-1y成立。
2网络动力学参数及拓扑结构识别方案
通过设计适当的控制器与自适应更新规则,基于网络间随机广义投影滞后同步,研究网络模型的动力学参数与拓扑结构识别。
定理对驱动-响应网络模型式(1)、(2),在假设1-3下,所用控制器及自适应更新规则为
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
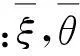

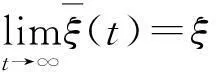
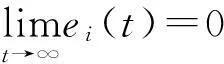
dei(t)=dyi(t)-γdxi(t-δ)=
ki(t)ei(t)]dt+σi(ei(t),ei(t-τ(t)),t)dW(t)
(8)
建立V函数为
式中:V∈C1,2(R+;G),G=Rm1+m2+N2+N+nN ;k*为可确定的足够大正常数。
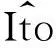

(9)
由假设1知
peTi(t)ei(t)
式(9)进一步变为
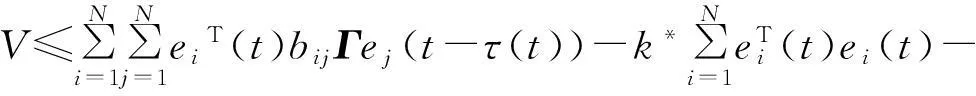
令e(t)=(eT1(t),eT2(t),…,eTN(t))T∈RnN,A=B⊗Γ,将lV写成紧积形式为

peT(t)e(t)+qeT(t-τ(t))e(t-τ(t))
(10)
由引理知
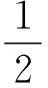
将式(10)改写为

qeT(t-τ(t))e(t-τ(t))≜-ω1(x)+ω2(y)
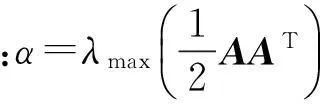
据随机时滞微分方程LaSalle型不变性原理[37-38],可得

由假设3、更新规则(7)、状态误差系统(8),得
0,ki(t)=const,ei(t)=0}
至此,在控制器、更新规则作用及几乎必然渐近稳定性意义下,网络模型未知动力学参数与拓扑结构能得到正确识别、反馈强度能自适应调整到常数、驱动网络与响应网络间亦能实现随机广义投影滞后同步。
3数值仿真
对具体网络系统进行数值仿真,验证推论推理的有效性。设驱动网络局部动力学为四维超混沌系统[39],节点数N=6,构造含未知动力学参数及未知拓扑结构的驱动网络为
dxi(t)=[f(xi(t))+F(xi(t))ξ+
式中:
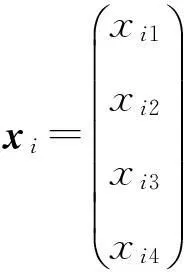
构造含未知动力学参数的响应网络[40]为
dyi(t)=[g(yi(t))+G(yi(t))θ+
σi(yi(t)-γxi(t-δ),yi(t-τ(t))-
γxi(t-τ(t)-δ),t)dW(t),(i=1,2,…,6)
式中:

选噪声强度函数为
σi(ei(t),ei(t-τ(t)),t)=(ei1(t)+ei1(t-τ(t)),
ei2(t)+ei2(t-τ(t)),ei3(t)+ei3(t-τ(t)),
ei4(t)+ei4(t-τ(t)))T
易验证该函数满足假设1,即
eTi(t-τ(t))ei(t-τ(t))
数值仿真时,为使网络节点动力学呈混沌行为,验证所提识别方案的有效性,选动力学参数为
ξ=(a1,b1,c1,k1,g1)T=(35,3,35,-8,-10)T
θ=(a2,b2,c2,k2)T=(-1.0,0.25,0.5,0.05)T
选决定驱动网络拓扑结构的耦合矩阵为
为进一步刻画驱动网络与响应网络间的同步动力学,引入两网络间同步总误差为
式中:wk∈Ω;h为样本轨道。
取内部耦合矩阵Γ=diag(1,0,0,0)、网络内部与网络之间的耦合时滞分别为τ(t)=0.02与δ=0.03、比例因子γ=2.0、更新增益λi=30.0,样本轨道h=10。易验证构造的驱动-响应网络模型满足假设3。


图1 响应网络耦合矩阵d ij(t)的演化曲线 Fig.1 The evolution of the topological structure d ij(t) of response network

图2 网络未知动力学参数的估计值 ξ(t)与θ(t)的演化曲线 Fig.2 The evolution of the unknown parameter’s estimation ξ(t) and θ(t)

图3 反馈强度k i(1≤i≤6)的演化曲线 Fig.3 The evolution of the feedback strength k i(1≤i≤6)
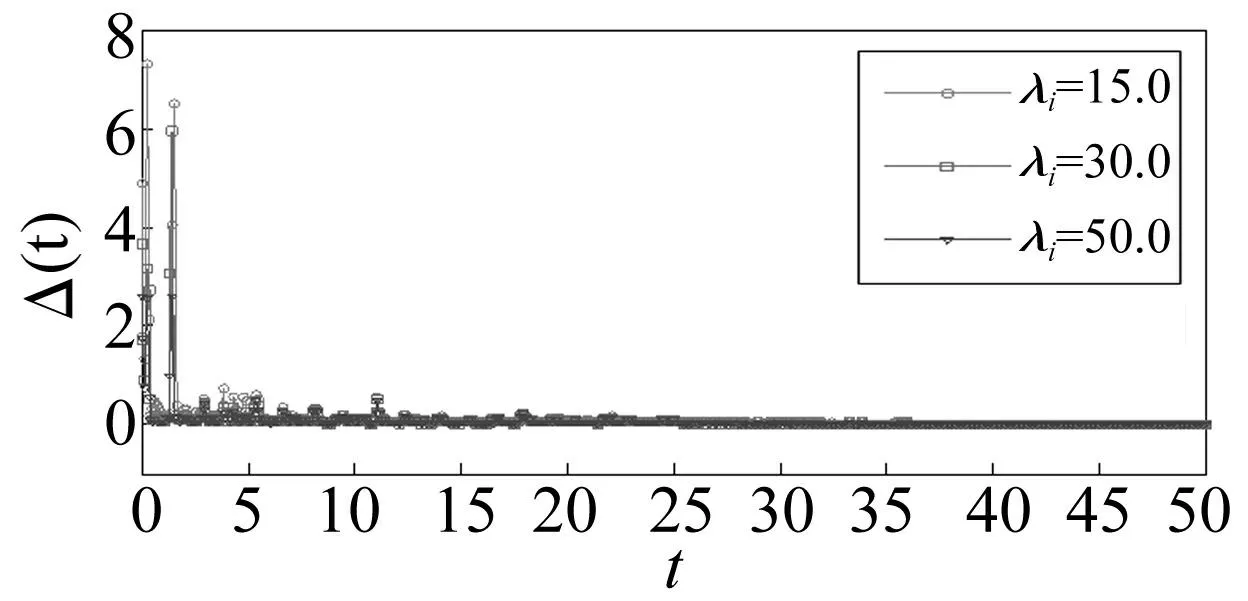
图4 不同更新增益λ i下网络同步总误差Δ(t)演化曲线 Fig.4 The evolution of the total synchronization error Δ(t) for different λ i
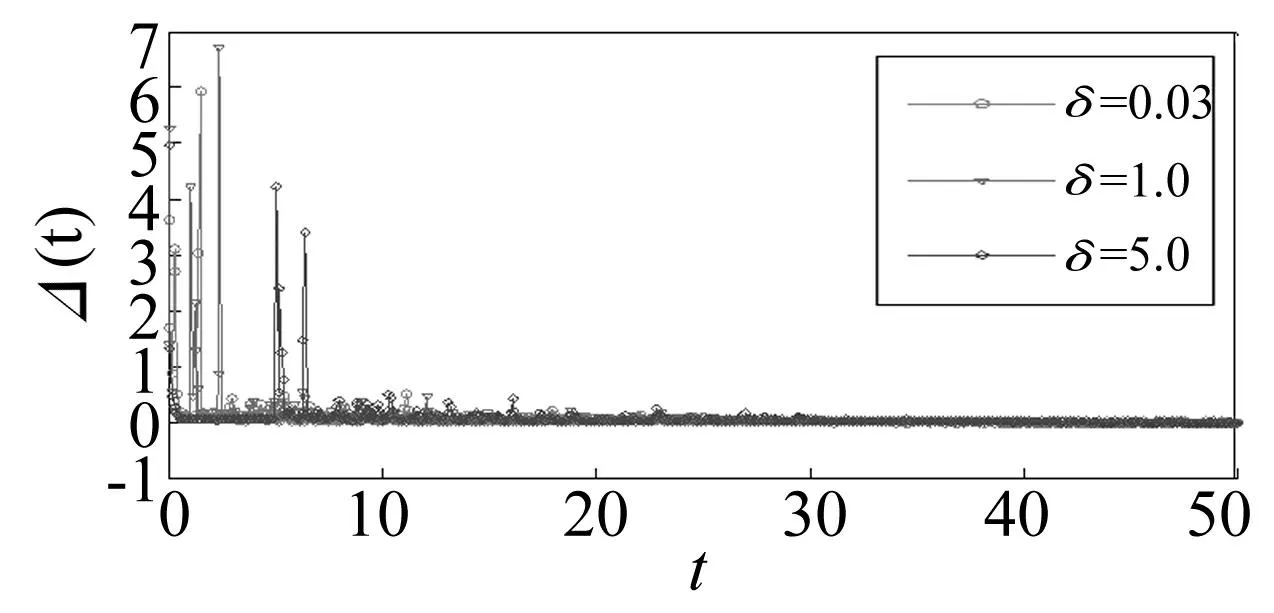
图5 不同耦合时滞δ下网络同步总误差Δ(t)演化曲线 Fig.5 The evolution of the total synchronization errorΔ(t) for different δ
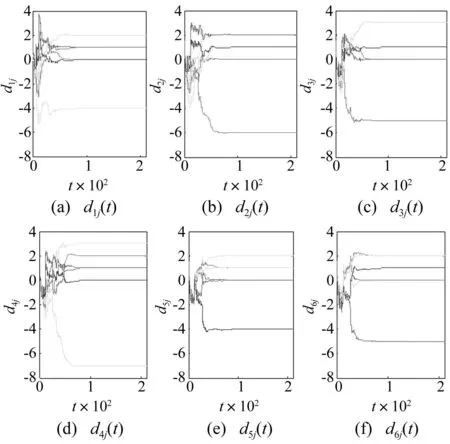
图6 响应网络耦合矩阵d ij(t)的演化曲线 Fig.6 The evolution of the topological structure d ij(t) of response network
由6图计算结果看出,随时间演化,dij(t)仍能分别收敛到预设的bij,即驱动网络耦合矩阵B通过响应网络耦合矩阵D得到正确识别。
4结论
(1)针对噪声扰动下含耦合时滞的驱动-响应网络模型,基于网络间随机广义投影滞后同步原理,提出辨识网络未知动力学参数及拓扑结构的研究方案。
(2)通过设计合理的控制器及自适应更新规则,利用随机时滞微分方程的LaSalle型不变性原理,严格证明识别方案不仅能使网络未知动力学参数及拓扑结构得到正确识别,亦能使驱动网络、响应网络在几乎必然渐近稳定性意义下实现随机广义投影滞后同步。
(3)通过具体网络模型,利用计算机仿真验证理论推理的有效性,且数值模拟结果也表明识别方案对耦合时滞、更新增益、拓扑结构等的选取具有鲁棒性。
参考文献
[1]Arenas A, Díaz-Guilera A, Kurths J, et al. Synchronization in complex networks[J]. Physics Reports, 2008, 469:93-153.
[2]Kocarev L, Amato P. Synchronization in power-law networks [J].Chaos, 2005, 15:24101.
[3]Newman M E J. The structure and function of complex networks[J]. SIAM Review, 2003, 45(2):167-256.
[4]Watts D J, Strogatz S H. Collective dynamics of small-world networks[J].Nature, 1998, 6684 (393):440-442.
[5]Guimera R, Diaz-Guilera A, Vega-Redondo F, et al. Optimal network topologies for local search with congestion[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2002, 89(24):248701.
[6]Wang Xiao-nan, Lu Ying, Jiang Min-xi, et al. Attraction of spiral waves by localized inhomogeneities with small-world connections in excitable media[J].Physical Review E, 2004, 69:056223.
[7]Roxin X, Riecke H, Solla S A. Self-sustained activity in a small-world network of excitable neurons[J].Physical Review Letters, 2004, 92(19):198101.
[8]Yu D C, Righero M, Kocarev L. Estimating topology of networks[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2006, 97:188701.
[9]Zhou Jin, Lu Jun-an. Topology identification of weighted complex dynamical networks[J]. Physica A,2007,386:481-491.
[10]Xu Yu-hua, Zhou Wu-neng, Fang Jian-an, et al. Structure identification and adaptive synchronization of uncertain general complex dynamical networks[J].Physics Letters A, 2009, 374:272-278.
[11]Fan Chun-xia, Wan You-hong, Jiang Guo-ping. Topology identification for a class of complex dynamical networks using output variables[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2012, 21:020510.
[12]Xu Yu-hua, Zhou Wu-neng, Fang Jian-an, et al. Topology identification and adaptive synchronization of uncertain complex networks with adaptive double scaling functions[J]. Commum. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat., 2011, 16:3337-3343.
[13]Sun Zhi-yong, Si Gang-quan. Comment on“topology identification and adaptive synchronization of uncertain complex networks with adaptive double scaling functions”[J]. Commum. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat.,2012, 17: 3461-3463.
[14]Timme M. Revealing network connectivity from response dynamics[J].Physical Review Letters, 2007, 98:224101.
[15]Zhao Jun-chan, Li Qin, Lu Jun-an, et al. Topology identification of complex dynamical networks[J].Chaos, 2010, 20:23119.
[16]Wu Xiao-qun. Synchronization-based topology identification of weighted general complex dynamical networks with time-varying coupling delay[J]. Physica A, 2008, 387: 997-1008.
[17]Guo Wan-li, Chen Shi-hua, Sun Wen. Topology identification of the complex networks with non-delayed and delayed coupling [J].Physics Letters A, 2009, 373:3724-3729.
[18]Xu Jiang, Zheng Song, Cai Guo-liang. Topology identification of weighted complex dynamical networks with non-delayed and time-varying delayed coupling[J].Chinese Journal of Physics, 2010, 48(4):482-492.
[19]Liu Hui, Lu Jun-an, Lü Jin-hu, et al. Structure identification of uncertain general complex dynamical networks with time delay[J].Automatica, 2009, 45:1799-1807.
[20]Xu Yu-hua, Zhou Wu-neng, Fang Jian-an. Topology identification of the modified complex dynamical networks with non-delayed and delayed coupling[J]. Nonlinear Dyn., 2012, 68:195-205.
[21]Wu Xiang-jun, Lu Hong-tao. Outer synchronization of uncertain general complex delayed networks with adaptive coupling[J]. Neurocomputing, 2012, 82:157-166.
[22]Zheng Song, Bi Qin-sheng, Cai Guo-liang. Adaptive projective synchronization in complex networks with time-varying coupling delay[J].Physics Letters A, 2009, 373:1553-1559.
[23]Che Yan-qiu, Li Rui-xue, Han Chun-xiao, et al. Topology identification of uncertain nonlinearly coupled complex networks with delays based on anticipatory synchronization [J].Chaos, 2013, 23:13127.
[24]Che Yan-qiu, Li Rui-xue, Han Chun-xiao, et al. Adaptive lag synchronization based topology identification scheme of uncertain general complex dynamical networks[J].Eur. Phys. J. B, 2012, 85:265.
[25]Tang Sheng-xue, Chen Li, He Yi-gang. Optimization-based topology identification of complex networks[J].Chinese Physics B, 2011, 20:110502.
[26]Yu Dong-chuan. Estimating the topology of complex dynamical networks by steady state control:Generality and Limitation[J]. Automatica, 2010, 46:2035-2040.
[27]Ren Jie, Wang Wen-xu, Li Bao-wen, et al. Noise bridges dynamical correlation and topology in complex oscillator networks[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2010, 104:58701.
[28]吴晓群,赵雪漪,吕金虎.节点动力学含随机噪声的复杂动力网络拓扑结构识别[C].第30届中国控制会议, 2011.
[29]He Tao, Lu Xi-liang, Wu Xiao-qun, et al. Optimization-based structure identification of dynamical networks[J]. Physica A, 2013, 392:1038-1049.
[30]Wu Xiao-qun, Zhou Chang-song, Chen Guan-rong, et al. Detecting the topologies of complex networks with stochastic perturbations[J]. Chaos, 2011, 21:43129.
[31]Wu Xiao-qun, Wang Wei-han, Zheng Wei-xing. Inferring topologies of complex networks with hidden variables[J]. Physical Review E, 2012, 86:46106.
[32]Chen Juan, Lu Jun-an, Zhou Jin. Topology identification of complex networks from noisy time series using ROC curve analysis[J]. Nonlinear Dyn., 2014, 75:761-768.
[33]Nawrath J, Romano M C, Thiel M, et al. Distinguishing direct from indirect interactions in oscillatory networks with multiple time scales[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2010, 104:38701.
[34]Marwan N, Romano M C, Thiel M, et al. Recurrence plots for the analysis of complex systems[J]. Physics Reports, 2007, 438:237-329.
[35]Yu D C, Parlitz U. Inferring network connectivity by delayed feedback control[J]. Plos One, 2011,6(9):e24333.
[36]Pomped B, Runge J. Momentary information transfer as a coupling measure of time series[J].Physical Review E, 2011, 83:51122.
[37]Mao Xue-rong. Stochastic versions of the LaSalle theorem[J]. Journal of Differential Equations, 1999, 153:175-195.
[38]Mao Xue-rong. A note on the LaSalle-type theorems for stochastic differential delay equations[J]. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 2002, 268:125-142.
[39]刘明华.一类新超混沌系统的产生、同步及其应用[D].广州:华南理工大学,2011.
[40]刘秉正,彭建华.非线性动力学[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2007:504.
[41]陆君安,吕金虎,刘慧,等.复杂动力网络结构识别的某些新进展[J].复杂系统与复杂性科学,2010,7(2/3):63-69.
LU Jun-an, LÜ Jin-hu, LIU Hui, et al. New progress on structure identification of complex dynamical networks[J]. Complex Systems and Complexity Science, 2010,7(2/3): 63-69.

第一作者邹广平男,博士,教授,博士生导师,1963年生

第一作者高延安男,博士生,1986年生
通信作者杨庆山男,博士,教授,1968年生
