In vitro Maturation of Tan Sheep Oocytes
2015-12-14ShulingYANGYongshunLIYanbinZHANG
Shuling YANG, Yongshun LI, Yanbin ZHANG
College of Agronomy, Ningxia University, Yinchuan 750021, China
Ningxia Tan sheep, well known at home and abroad as the‘white treasure’ in Ningxia, is a unique fur-type sheep breed in China, which is mainly bred in various neighboring counties of Yinchuan City,Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region[1].Tan sheep has uniform fat distribution,tender mutton, and slight smell, which has been famous throughout China as an outstanding representative of‘Ningxia mutton’. In 2000, Tan sheep was included into the lists of class Ⅱnational protected species by the Ministry of Agriculture of China; Yanchi County was included into the core protection areas and core producing regions of Tan sheep germplasm resources[2]. The reproductive rate of Tan sheep is very low, and the lambing percentage is about 103%.In general, Tan sheep gives birth to a lamb once a year[3]. Therefore, improving the reproductive performance of Tan sheep to increase the population quantity has become a bottleneck that restricts the development of Tan sheep industry.
Although the reproductive rate of females can be improved by superovulation and embryo transfer techniques, the number of embryos obtained is extremely limited. So far, a large number of studies have been carried out on in vitro maturation of oocytes to fully tap the breeding potential of females. Establishing an effective system of in vitro maturation has become an essential part of in vitro culture of oocytes. There are multiple factors involved in oocyte maturation. Hormones are necessary for oocyte maturation, which play a key role in the maturation, but different hormones or hormone combinations exert various effects on oocytes from the same animal species[4-5].Currently,pregnant mare serum gonadotropin(PMSG)[6], human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)[5],follicle stimulating hor-mone (FSH)[7], luteotropic hormone(LH)and estrodiol (E2)[8]have become the most important hormones for in vitro maturation of oocytes. However,very few studies have been reported on in vitro culture of Tan sheep oocytes. In this study, the effects of different concentrations of FSH, LH and E2on in vitro maturation of Tan sheep oocytes, aiming at improving the culture system for in vitro maturation of Tan sheep oocytes,tapping the breeding potential of Tan sheep, and accelerating the breeding process.
Materials and Methods
Collection and preservation of ovaries
Ovaries were collected immediately from the slaughtered Tan sheep in a slaughterhouse of Yanchi County,rinsed with normal saline containing double antibodies, transferred into a thermos bottle that contained 28 ℃normal saline with double antibodies,and brought back to the laboratory within 4 h.
Collection of oocytes
Excess tissues and fats on the surface of ovaries were removed using sterile scissors,and rinsed three times with normal saline containing double antibodies before use.
Oocyte collection The ovaries were placed on a petri dish (Φ125 mm) with grids on the bottom,added with 2 ml of pre-equilibrated extraction fluid (PBS containing 3 mg/ml BSA, incubated in a 38 ℃incubator overnight), and fixed gently using sterile ophthalmic tweezers. Subsequently, large ovarian follicles on the surface of ovaries were scratched with a scalpel blade; the follicular fluid was collected and transferred onto a petri dish for microscopic examination, and the oocytes were collected.
Microscopic examination In this study, oocytes with intact cumulus cells and uniform cytoplasm were selected for in vitro maturation culture.
In vitro maturation of oocytes
The collected COCs were rinsed 3 -4 times with extraction fluid, and pre-equilibrated for 2 -3 h before in vitro maturation culture. COCs were cultured at 38.5 ℃ in an incubator containing 5% CO2under saturated humidity for 22-24 h.
Preparation of basal culture medium Preparation of M199 media: 9.5 g M199 powder + 2.2 g NaHCO3+ 25 mg sodium pyruvate+4.8 g HEPES+50 μg ampicillin sodium+ 50 μg streptomycin sulfate, added with ultrapure water to a final volume of 1 000 ml, filtered through 0.22 μm filter paper for sterilization,and preserved at 4 ℃.
Preparation of mature media:M199 + 5% FCS + 5% FBS, added with different concentrations of folliclestimulating hormone (10, 50, 100, 200 and 300 μg/ml FSH, respectively), luteotropic hormone (5, 10, 20, 50 and 100 μg/ml LH, respectively), estrodiol(5, 10, 25, 50 and 100 μg/ml E2, respectively),and FSH+LH (100 μg/ml FSH + 20 μg/ml LH), respectively. All the hormones were purchased from Ningbo Second Hormone Factory;other reagents were purchased from Sigma Corporation.
Droplet culture Under sterile conditions,50 μl of culture medium was collected using a pipette, covered with a layer of sterile paraffin oil and prepared into droplets, which were preequilibrated in a carbon dioxide incubator at 38.0 ℃for 3 h. The obtained COCs were rinsed twice with mature media and transferred into the equilibrated culture droplets. Each droplet contained 15-20 COCs. The droplets were cultured at 38.5 ℃in an incubator containing 5%CO2under saturated humidity for 22 h.
Evaluation of mature oocytes
After in vitro culture, the oocytes were rinsed three times with PBS solution, and digested using 0.3%hyaluronidase to obtain denuded oocytes. The collected denuded oocytes were observed under an inverted phase contrast microscope,and those releasing first polar bodies were identified as mature oocytes.
Data analysis
The experimental data were analyzed using Excel and represented by mean ± standard deviation. Significance test was preformed with Duncan’s new multiple range method using DPS7.05 software. The significance of difference was assessed at two levels: P<0.05 (significant difference) and P<0.01 (extremely significant difference).
Results and Analysis
Effects of different concentrations of FSH and LH on in vitro maturation of Tan sheep oocytes
The effects of different concentrations of FSH and LH on in vitro maturation of Tan sheep oocytes were shown in Fig.1 and Fig.2. As shown in Fig.1, different concentrations of FSH exerted various effects on in vitro maturation of Tan sheep oocytes. To be specific, when FSH concentration ranged from 0 to 100 μg/ml, the maturation rate of Tan sheep oocytes was improved gradually as FSH concentration increased, which reached the peak (55.15%) when FSH concentration was 100 μg/ml;subsequently,with the continuous increase of FSH concentration, the maturation rate of Tan sheep oocytes was reduced.Similarly,as shown in Fig.2,different concentrations of LH exhibited various effects on in vitro maturation of Tan sheep oocytes.To be specific, when LH concentration ranged from 0 to 20 μg/ml,the maturation rate of Tan sheep oocytes was improved gradually as LH concentration increased, which reached the peak (50% ) when LHconcentration was 20 μg/ml; subsequently, as LH concentration increased continuously, the maturation rate of Tan sheep oocytes was reduced. The results indicated that excessively high concentrations of FSH and LH could inhibit in vitro maturation of Tan sheep oocytes.
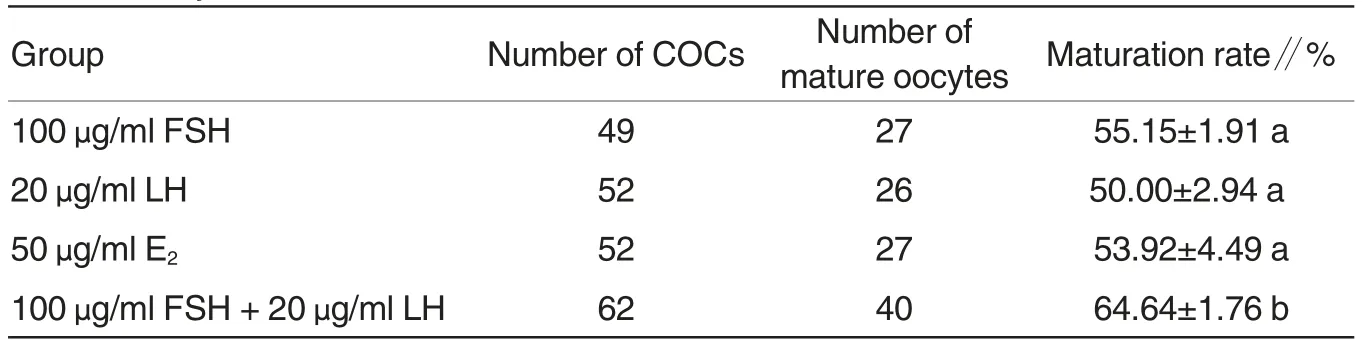
Table 1 Effects of the combination of FSH and LH on in vitro maturation of Tan sheep oocytes
Effects of different concentrations of E2 on in vitro maturation of Tan sheep oocytes
The effects of different concentrations of E2on in vitro maturation of Tan sheep oocytes were shown in Fig.3.As shown in Fig.3,when E2concentration ranged from 0 to 50 μg/ml,the maturation rate of Tan sheep oocytes was improved gradually as E2concentration increased, which reached the peak (53.92%) when E2concentration was 50 μg/ml; subsequently, with the continuous increase of E2concentration, the maturation rate of Tan sheep oocytes was reduced,indicating that excessively high concentrations of E2could inhibit in vitro maturation of Tan sheep oocytes.
Effects of the combination of FSH and LH on in vitro maturation of Tan sheep oocytes
Based on data in Fig.1 and Fig.2,100 μg/ml FSH and 20 μg/ml LH was used in combination, to observe the effects on in vitro maturation of Tan sheep oocytes. As shown in Table 1,the maturation rate of Tan sheep oocytes in 100 μg/ml FSH + 20 μg/ml LH group was 64.64%,which was significantly higher than that in 100 μg/ml FSH group (55.15%), 20 μg/ml LH group (50%) and 50 μg/ml E2group(53.92%), exhibiting significant differences (P <0.05), but the maturation rate of Tan sheep oocytes in other three groups exhibited no significant differences(P>0.05).
Discussions
During in vitro maturation of oocytes, in addition to basal culture media M199 and serum, several hormones are commonly added into the media to promote oocyte maturation,such as follicle-stimulating hormone(FSH),luteotropic hormone (LH), mixture of FSH and LH, and other reproductive hormones. Studies have confirmed that these hormones can promote in vitro maturation of oocytes[9].Qu et al.[10]reported that adding FSH into culture media was conducive to the release of first polar bodies by Tan sheep oocytes, because FSH induces cumulus expansion, inhibits apoptosis of granulosa cells, maintains contact between granulosa cells and oocytes,temporarily inhibits germinal vesicle breakdown, changes time of first maturation division, and promotes cytoplasmic maturation in the process of in vitro maturation of oocytes[11-12].Therefore, FSH is quite necessary for nuclear maturation and cytoplasmic maturation of oocytes. According to the experimental results, adding FSH into culture media could significantly improve the maturation rate of oocytes.Especially, the maturation rate of Tan sheep oocytes reached the peak(55.15% ) when FSH concentration was 100 μg/ml,which was significantly higher than that in other groups (P<0.05). Grupen et al.[13]found that, similar to FSH, LH can temporarily inhibit germinal vesicle breakdown and delay nuclear maturation of oocytes, which provides a longer time for oocytes to complete cytoplasmic maturation. The same results were drawn in this study.Specifically, 20 μg/ml LH significantly improved the release of first polar bodies by Tan sheep oocytes. In addition, the maturation rate of Tan sheep oocytes in FSH+LH group was 9.49%-14.64%higher than in groups with single hormone.
Mikkelsen[14]found that E2and other steroid hormones can maintain oocyte meiotic arrest, induce oocyte meiosis recovery and promote nuclear and cytoplasmic maturation synchronization, which is conducive to in vitro maturation of oocytes, and subsequent fertilization and cleavage. Xiong et al.[15]reported that 10 μg/ml FSH,10 μg/ml LH and 1 μg/ml E2could promote maturation of sheep oocyte cytoplasm.Zheng et al.[8]indicated that E2could improve the formation rate of embryotic sphere and blastula during in vitro maturation of bovine oocytes,suggesting that E2can promote the maturation of oocyte cytoplasm. Li et al.[16]also confirmed that E2could promote the maturation of oocyte cytoplasm and improve the fertilization rate of mature oocytes. Therefore, E2is conducive to the maturation of oocytes. In this study, the results also indicate that 5-100 μg/ml E2can promote in vitro maturation of Tan sheep oocytes. Specifically,the maturation rate of Tan sheep oocytes reached the peak (53.92%)when E2concentration was 50 μg/ml,and the high application dose might be related with the low fertility of Tan sheep and ovary collection time,which requires further investigation.
In summary, under the experimental conditions,100 μg/ml FSH+20 μg/ml LH was most appropriate hormone combination, which was conducive to in vitro maturation of Tan sheep oocytes.
[1]MAO N(毛宁),WEN ZL(文志林),WANG JH(王菊花).Problems and countermeasures in the development of Tan sheep industry in Yanchi County, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region(宁夏盐池县滩羊产业发展面临的问题及对策)[J]. AnimalHusbandry and Feed Science(畜牧与饲料科学),2011,32(5):55-56.
[2]CUI MQ(崔明巧).Protection and development of Tan sheep germplasm resources in Yanchi County (盐池滩羊品种资源的保护与发展的探讨)[J]. The Chinese Livestock Breeding (中国畜禽种业),2012,3:45-48.
[3]TIAN GF(田贵丰),KONG XW(孔宪炜).Investigation on genetic resources of Tan sheep in Gansu Province(甘肃滩羊品种遗传资源调查报告)[J]. Journal of Animal Sciaence and Veterinary Medicine (畜牧兽医杂志),2011, 30(4):60-63.
[4]MA H(马红),FU B(付博),REN L(仁亮),et al. Effects of hormones on in vitro maturation of porcine oocytes and development of porcine solitary female embryos(激素对猪卵母细胞体外成熟及孤雌胚胎发育的影响)[J]. Animal Husbandry&Veterinary Medicine(畜牧与兽医),2013,45(4):41-44.
[5]ZOU J(邹军),HUO SD(霍生东).Effects of HCG on maturation in vitro of sheep oocytes(HCG 对绵羊卵母细胞体外成熟的影响)[J].China Herbivores (中国草食动物科学),2012,3(6):71-72.
[6]CAI LB (蔡令波),WANG F (王峰),GU SQ(顾熟琴),et al.Effects of PMSG and hCG on IVM of oocytes in porcine(PMSG 和hCG 对猪卵母细胞体外成熟的影响)[J]. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine(畜牧与兽医),2002,34(12):1-2.
[7]XU M, FAZLEABAS AT, SHIKANOV A,et al.in vitro oocyte maturation and preantral follicle culture from the lutcalphase baboon ovary produce mature oocytes [J]. Biol Reprod, 2011, 84(4):689-697.
[8]ZHENG P, SI W, BAVISTER BD, et al.17β-estrxdiol and progesterone improve in vitro cytoplxsmic maturation of oocytes from unstimulated prepuhertal and adult rhesus monkeys[J].Hum Reprod,2003,18(10):2137-2144.
[9]LU HN (陆会宁), QI YJ (齐燕蛟). Research progresses on the factors influencing maturation in vitro of sheep oocyte(影响绵羊卵母细胞体外成熟因素研究进展)[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences (黑龙江农业科学), 2013, 9:147-150.
[10]QU YY(曲杨燕),ZHAO YW(赵雁伟),LI K(李凯),et al.Effect of FSH on nuclear maturation of sheep oocyte matured in vitro(FSH 对绵羊卵母细胞体外核成熟的影响)[J].China Animal Husbandry&Veterinary Medicine (中国畜牧兽医),2008,35(12):81-83.
[11]LEIBFRIED-RUTLEDGE ML, CRITSER ES, PARRISH JJ, et al. In vitro maturation and fertilization of bovine oocytes [J]. Theriogenology, 1989, 31(1):61-74.
[12]ARMSTRONG DT, LRVINE BJ, EARL CR, et al. Gonadotropin stimulation regimens for follicular aspiration and in vitro embryo production from calf oocytes [J]. Theriogenology, 1994, 42(7):1227-1236.
[13]GRUPEN CG, GILCHRIST RB, NAYUDU PL,et al.Effects of ovarian stimulation,with and without human chorionic gonadotrophin, on oocyte meiotic and developmental competence in the marmoset monkey (Callithrix jacchus)[J].Theriogenology,2007,68(6):861-872.
[14]MIKKELSEN AL. Strategics in human in vitro maturation and their clinical outcome[J]. Reprod Biomed Online,2005,10(5):593-599.
[15]XIONG ZC(熊炤成), SU L(苏雷). Research progresses on the external maturation culture of mammalian oocyte (哺乳动物卵母细胞体外成熟培养的研究进展)[J].China Animal Husbandry&Veterinary Medicine (中国畜牧兽医),2007(1):71-74.
[16]LI Y(李莹),TAN L(谭丽).Effect of follicle stimulation hormone and pentanoic acid estradioi on mouse oocyte in vitro maturation (卵泡刺激素及戊酸雌二醇对小鼠卵母细胞体外成熟的影响)[J].Journal of International Reproductive Health/Family Planning(国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志),2012,31(6):445-448.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Effect of Tree Species and Dosage of Rhizomorph Wood on Asexual Propagation of Wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Ganzi
- Effects of Different Application Times of Tillering Fertilizer on Grain Yield and Population Development of Double-cropping Rice Transplanted by Machine
- Biological Characteristics and Pathogenicities of Shewanella algae and Shewanella abalone from Babylonia
- Research on Physiological Characteristics of Tall Fescue under Nitrogen Stress
- Cloning and Characterization of Phytochrome A Gene FaPHYA from Tall Fescue
- Changes in Physiological Indexes of SPDS Transgenic Potato Plants under Low Temperature Stress
