Groundwater ecological environment and the mapping of Asia
2015-12-12DONGHuaGELiqiang
DONG Hua, GE Li-qiang
Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, CAGS, Shijiazhuang 050061, China
Abstract: Based on the mapping of groundwater resources and environmental geology in China and its surrounding regions, Groundwater Ecological Environment Map of Asia is drawn to broadly reflect the ecological situation of Asian groundwater, categorize its ecological environment into three basic types and elaborate the research categories. This paper analyzes and summarizes the major characteristics and distribution regularities of the groundwater ecological environment of Asia to reveal the key related problem so as to provide a necessary reference for the construction and planning of One Belt and One Road.
Keywords: Asia; Ecological environment; Groundwater ecological environment; Mapping
Introduction
Despite the fact that ecological environment is one of the most used scientific terms, there are many different understandings and ideas about its meaning. Ecological environment is a general term of both the quantity and quality that would influence water resources, land resources,biological resources and climatic resources for human surviving and development. It is a compound ecological system in relation to the sustainable development of society and economy.Ecological environment problems refer to all kinds of feedback effects hazardous to the survival of mankind occurring along with the damage and pollution which are inflicted on the natural environment as human beings utilize and change the nature for their surviving and development.The book of Geology-Ecological Environment and Sustainable Development-the Development Path for the Karst Area in Southwest China and its Surrounding Region calls “ecological geological environment” as “geological-ecological environment” and explains it as “geological-ecological environment is the environment of living space with mankind as the main part, including the influence from lithosphere, hydrosphere,atmosphere and biological sphere” (LU Yao-ru,2003).
As an important part of geological environment,groundwater environment is a large and dynamic environment system with multiple levels, tasks and factors mutually interweaving and affecting each other (DONG Hua et al. 2008). In the process of its circulation, groundwater would be involved in a lengthy period of evolution, being a quantitative or a qualitative one, subject to the water-rock interaction which forms a related hydrogeochemical system and thus constitutes a basic background for groundwater environment,including such two main categories as groundwater primitive (natural) environment and secondary(artificial) environment (SHEN Zhao-li et al.2012).
Groundwater ecological environment comprises the feedback effects concerning how the ecological environment depends on and interacts with groundwater in the process of human surviving and development. The ecological function of groundwater refers to the influence or feedback on the positive maintenance offered by groundwater system to vegetation above the earth surface, lakes, wetlands and land quality. The four major elements of groundwater ecological environment include: Firstly, precipitation,evaporation capacity and dryness of the climatic elements; secondly, quantity of resources, buried depth of groundwater, and water quality of the groundwater system; thirdly, forest land, grassland and farmland of ecological system; fourthly,activities relating to population, society, economy and major constructions such as population distribution, gross domestic product (GDP),large-scale hydraulic projects (reservoirs as well as water transfer and diversion), oil and gas fields and mines. Therefore, the study on the mapping of groundwater ecological environment represents a broad research of regional scale, a timely response to social demands and a guidance to economic development.
1 Types of ecological environment of groundwater and the principles for classification
1.1 Types of ecological environment of groundwater
The research categories for groundwater ecological environment: Firstly, the relation between regional scale and groundwater based on the difference among ecological systems of regional scales; secondly, the degree of dependency of ecological environment on the storage capacity and support of groundwater;thirdly, the groundwater conservation function of ecological environment; finally, the constraint of the environment on the ecological situation and the effect of social activity on ecological environment.Based on the compilation of Series of Maps of Groundwater in Asia (ZHANG Fa-wang et al.2012), this paper explores the mapping of ecological environment of groundwater under intercontinental scale. Research will focus on the dependence of ecological environment on groundwater, the fragility of ecological environment and the relations among groundwater conditions for maintaining ecological environment.And the types of ecological environment of groundwater will be sorted out to show the characteristics of groundwater ecological environment and its distribution regularities.According to the analysis of the connotation and denotation of groundwater ecological environment,three types can be categorized as groundwater regulation and storage-to support ecological environment, groundwater conservation-to maintain ecological environment and groundwater meagerness-tender ecological environment.
1.2 Principles for classification
The mapping of groundwater ecological environment is unprecedented both domestically and internationally. The basic idea is to establish the relation between ecological environment and groundwater under intercontinental scale, to describe the spatial and temporal distribution of the effects of mutual feedback between ecological environment and groundwater, to propose the division of groundwater ecological environment based on the development strategy of China and its surrounding regions, to provide data for the study on global changes and serve China and its neighboring countries for the planning and decision-making of macro-policies, territorial management and popularization of science. The mapping will observe the following principles:Firstly, to draw the types of groundwater ecological environment mainly based on the patterns of climatic geomorphology; secondly, to reveal the ecological environmental situation of groundwater and its major characteristics under the guidance of groundwater ecological environment problems; thirdly, to divide the ecological environment of groundwater so as to serve the decisionmaking of macro-policies of China and its surrounding countries.
2 Analyses on the situation of ecological environment of groundwater in Asia
2.1 The control of climatic geomorphology on the ecological environment of groundwater in Asia
The Asian Plate is largely surrounded by the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean and the Arctic Ocean and the Eurasian Plate is pushed by the Indian subcontinent. Since the Quaternary Period when the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau rose, the landform pattern caused by the neotectonic movements has shown the typical monsoon climate along with a strong continental climate (LI Ting-dong, 2007;REN Ji-shun et al. 2013). Therefore, climatic geomorphology determines the quality of the ecological environment of groundwater in Asia(CHEN Zhi-ming, 2010). Water circulation is active in the outflow region thanks to the monsoon climate while the circulation is slow in the interior drainage area with a distinct continental climate where water vapor from the oceans is blocked by the plateau and mountains and the water-vapor flux is in short due to the hot and dry climate in the basin area. In particular, the inland area of Central Asia is characteristic of orographic rainfall with poor precipitation in the basin area and the main source of groundwater recharge in the plain and basin region comes from surface water and mountains, leaving the ecological environment of groundwater in arid area seriously fragile (LIN Zhi-guang, 1995). Along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea in the West Asia where there is both coastal lowlands and plateaus and arid desert,the Mediterranean climate makes summer hot and dry, winter mild and rainy. Therefore, the ecological environment in this area is fragile since groundwater ecological environment varies greatly and the groundwater is relatively deficient.Meanwhile, latitudinal zonation of Asian climate and vertical zonation of terrain also play a critical role in controlling groundwater ecological environment. Most part of Northern Asia is in mid and high latitude with a cold climate. In this area where continuous freezing layer and discontinuous island-shape freezing layer widely spread,suprapermafrost water and infrapermafrost water represent an important source of water for maintaining ecological system. As the headstream of the major rivers in Eastern Asia, Southern Asia and Southeastern Asia, mountains in high altitude(the elevation is generally above 4 000 m)centering around the Pamir-Tibetan Plateau,stretching to three directions, belong to alpine-arctic discontinuous freezing layer in terms of ecological environment of groundwater. As to Southeastern Asia and Southern Asia which have tropical rainy climate and tropical monsoon climate respectively and the region surrounding the Equator mainly with tropical rainy climate, water circulation is active and groundwater often emerges as spring water so that the surface water system well develops and the ecological system is diverse.
2.2 Characteristics of ecological environment of groundwater in Asia
(1) Groundwater regulation and storage-to support ecological environment
In Asia, there are broad plains, different sizes of lowlands, valleys and intermontane basins as well as undulating hills and hillocks, all of which are the main places for activities of human society.The geological environment of this area boasts favorable conditions thanks to the fact that the plains, basins and intermontane valleys are covered with loose deposits of different thickness accumulating in the Quaternary Period and the groundwater aquifer system has a strong storage and regulation capacity. Therefore, this region is the main area for agricultural production and has a high urbanization degree, providing a great support for local economic development.
The ecological environment of groundwater in the coastal area comprises coastal zone on the land and delta regions where rivers from the surrounding islands enter the sea. This is the most economically developed area in Asia with over ten large exorheic rivers. The delta regions of these large rivers are located at the intersection of the sea,rivers and the land which is the heart to regional economy and a critical economic hub.Groundwater in this area is greatly affected by the mixture effect of sea water and has a strong storage and regulation capacity. Ecological environment makes a significant contribution to supporting the society and economy. The environment system of mutual feedback between the society and the economy, which is closely related to groundwater,is constituted of urban environment, rural environment, industrial environment, agricultural environment and transportation environment.
The ecological environment of groundwater in plains, basins, hillocks and lowlands involves piedmont alluvial-pluvial inclined plainsfloodplains, intermontane basins, oasis region of inland basins and hillocks and lowlands.Ecological environment in these areas is more complex and affected by diverse factors due to the widespread social and economic activities of human beings. There are the West-Siberian Plain,the Lena River Plain, the Kolyma River Plain, the Songliao-Amur River Plain, the Huanghuaihai Plain, the Middle-Lower Yangtze Plain-Hillock-Low Mountain, the South China Hillock-Low Mountain, the Red River Plain, the Indus River-Ganges River Plain and hillocks along the Mediterranean Coast. These plains, intermon- tane basins, hillocks and lowlands have relatively rich groundwater of good quality that can perform a sound function of supporting the environment.
For the ecological environment of groundwater in the piedmont area of inland arid basins, the storage and regulation capacity of groundwater is clearly influenced by surface water and thus the ecological environment of grassland and oasis in arid area-agricultural and pastoral areas is well maintained. However, the quality of groundwater here is relatively poor and the salinity of groundwater is high in the front of alluvial fan.
In a word, broad plains-basins-hillocks and lowlands and deltas formed out of many rivers boast an exceptional geological environment and groundwater of these areas has good occurrence and strong storage and regulation capacity to support ecological environment. For the ecological environment of groundwater in the piedmont area of inland arid basins, the storage and regulation capacity of groundwater is clearly influenced by surface water and thus the ecological environment of grassland and oasis in arid area-agricultural and pastoral areas is well maintained. Groundwater in this region can serve the social and economic development of the delta area. However, global warming and construction activities of human beings impose many negative effects on the above mentioned ecological environment of groundwater.So it is proposed to rationally tap and utilize groundwater and protect ecological environment in a more efficient way.
(2) Groundwater conservation-maintaining of ecological environment
There is a great irregularity in Asian land which, high in the middle and low on all sides, is mainly composed of plateaus and mountains accounting for three fourths. The major mountains include dozens of mountain ranges such as the Himalayas, Kunlun Mountains, Qilian Mountains,the Tian Shan, the Altai Mountains, the Greater Khingan Range, Lesser Khingan, Taihang Mountains, the Changbai Mountain Range, the Qin Mountains, the Wuyi Mountains, the Hengduan Mountains, East Sayan Mountains, West Sayan Mountains, the Khangai Mountains, the Yablonoi Mountains, Verkhoyanskiy Khrebet, the Chersky Range, the Stanovoy Range (Становой хребет),the Sichote-Alin, the Yablonoi Mountains, the Kuhrud Mountains, the Zagros Mountains, the Hindu Kush, the Ural Mountains, the Caucasus Mountains, the Eastern Ghats, the Western Ghats,the Biandan Mountain, the Cardamom Mountains,the Eland Mountain and the Barisan Mountains.The richness of orographic precipitation in these mountains is affected by the monsoon climatic zone. To mountains vegetation is like skin to human beings. Functions like water conservation and temperature adjustment enable vegetation to on the one hand, prevent the loss of water and other substance and to preserve, as a barrier, the geological environment of the shallow surface on the other hand. Mountains are the source of the surface drainage system in Asia. The surface runoff in the dry season, which equals the output of groundwater, plays as a continuous supplement for the groundwater in plains and basins.
Because influenced by latitude and geographical zoning, the microthermal climate all year round in some parts of Asian Plate results in the broad range of continuous and discontinuous island-shaped frozen layer in high latitude zones north of northern latitude 45° and plateaus and mountains that are over 4 000 m above sea level.Due to the change of temperature, groundwater is either frozen all year round or in seasonal freezing-thawing. The Tibetan Plateau, known as the world “Third Pole” and a rigid region with a high altitude, is there. The vast Siberian cold area is also located in Asia’s high latitude zones(CHENG Yan-pei et al. 2010). The frozen surface in cold area is a special way to store water resources. Freezing-thawing plays an important role in adjusting groundwater conservation and maintaining of ecological environment. The collision between the Arabian Plate and the Eurasian Plate formed folded mountain belts generally 900-1 500 m above sea level in the Iranian Plateau in Southwest Asia. The plateau around the Iranian Plateau is blocked by the surrounding magnificent mountains while a vast inland basin is in the center. Intermontane basins,salt marshes and deserts spread all over it with no river here leading to the ocean. The Greater and Lesser Khingan Ranges and the Paektu Mountain are covered by forest whose total area is up to 805 thousand hectares. With 357 thousand hectares of natural forest, 14.6% of forest coverage and 26.22×106m2of wood storage, this region is called the “Green Bank” in the Great Northern Wilderness and a “Green Barrier” to keep a steady and high agricultural output.
In a word, groundwater in hilly mountains maintains the ecological environment of forest and grassland-farming and grazing so the conservation of water and soil in the superficial surface is very important, especially in intermontane valleys where aquifer is loosely accumulated with a plenty amount of water in groundwater gathering zone to form an ecological barrier to plain area. Plateaus and mountains are covered by vast forest to supply and conserve groundwater. Therefore, it is essential to protect forest resources since the region of high mountains is usually the source of rivers to supply groundwater thanks to the strong control of orographic precipitation. Cold zone of plateaus and mountains has a tundra ecology relying on freezing and thawing to regulate water transfer. In the area at high latitude and high altitude, island-shaped freezing layer and glacier develop as the source region for rivers. The climate is severe here and glacial ablation and freezing layer degradation are obviously influenced by global climate change.
(3) Lack of groundwater-a fragile ecological environment
One third of the land area on the earth is arid area and semi-arid area among which these areas in Asia account for 38% (see Table 1). In China,47.5% of the national territorial area consists of these two areas with arid area whose precipitation is less than 200 mm accounting for 26.6% of this country’s land area. The biggest characteristic of the water system in arid area is that there is a small total amount of water and a sole source of supplementary water with irregular distribution in space and time. Evaporation plays a dominant role in water cycle. Rivers and aquifer are mutually related, dependable and restrictive to form an integrated whole. While shallow groundwater has modern source of water as supplement deep groundwater is left with slow circulation mainly with tritium free water. Since the ecological environment in arid area is extremely fragile, the development and utilization of water resource lead to a series of problems of environmental degradation, such as land desertification, soil salinization and groundwater salinization.

Table 1 Area of arid region in Asian land (106 km2)
The arid area in Central Asia includes:five Central Asian countries (Kazakhstan,Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan),and China’s Xinjiang, Tibet, Qinghai, Hexi Corridor of Gansu Province, northern Ningxia, the whole area of Inner Mongolia and the southwestern area of the Republic of Mongolia.This is terrestrially the largest arid area on the earth. And it is an important and the most special part of the area where the human society develops at a high rate. While the region boasts a relatively great concentration of natural resources, especially energy, the ecological system here is very fragile.
In the geologic epoch, the intense and frequent orogeny and the resulted large frames for geological structures created the prerequisite for the formation of geographical environment of Central Asia. Therefore, a special geomorphologic landscape could be seen with linking mountains and basins and valleys located in the middle of mountains. In arid area, precipitation is rare on one hand while evaporation from water surface is generally between 1 000 and 2 000 mm. However,soil moisture of land surface is often in unsaturation due to small amount of rainfall and therefore evaporation capacity of land surface is restricted with a relatively low absolute quantity of land evaporation. In China, the arid area and semi-arid area are mainly located in such six northwestern provinces as xinjiang Shaanxi, Gansu,Ningxia, Qinghai, autonomous regions and Inner Mongolia. According to the integrated zoning method based on drought index and water balance factors, arid area and semi-arid area with drought index above 3 accounts for 47.5% of the national territorial area and arid area with precipitation below 200 mm makes up 26.6% of the total. In China, there is an area of 1 653×103km2of deserts,gobi and desertified land of which 385.7×103km2belongs to the desertified land caused by human activities. The main landform of these major mountains is characteristic of aridity with deserts such as the Karakum Desert, the Kyzyl Kum, the Salei Yesiggart Desert, the Muyun-Kum Desert,the Taklimakan Desert, the Gurbantünggüt Desert and the Badain Jaran Desert. The desert landform is fully represented by deserts, gobi and scablands that can be seen everywhere and even rocky deserts, salt marshes and salt incrustation. In this area, there exist the Fergana Valley, the Issyk-Kul Lake Basin, the Junggar Basin, the Tarim Basin,the Qaidam Basin, the Chu River Valley, the Alai Valley, the Chatkal Valley, the Talas Valley, the Vakhsh River Valley, the Ili Valley, lowlands around tail end lakes of the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya, the Sarygamysh Depression to the southwest of the Aral Sea (38 m below sea level),the Turan Depression on the delta of the Amu Darya, and the Kara Jiyeh Depression as the lowest place (132 m below sea level). Thousands of small lakes also spread in this arid area in addition to great lakes, including the Caspian Sea, the Aral Sea, Lake Balkhash, Lake Zaysan, Lake Tengiz,Sasse Kerr Lake, and Qinghai Lake. Most lakes are located at the estuary of interior rivers with salt water lakes as the main part.
Besides the inland arid area, the Loess Plateau in the semi-arid region in China’s hinterland was a lake area 8 million years ago and was formed through millions of years of accumulation by sands.The land surface of the plateau is very fragmented as a result of a long period of flowing water erosion with tablelands, hillocks, loess hills and plains interweaving in this area. The ecological environment is very fragile. Additionally, the area of stony desertification is as much as 31 975 km2in the eight provinces in Southwest China. Stony desertification is an extreme performance of land degradation in karst region. In this special karst environment where there is a deep flow of water beneath the earth transferred from rainfall, a large area is exposed with bedrocks or accumulated gravels and groundwater cannot be conserved because vegetation lacks enough water to absorb.And land degradation often happens along with a hard surviving environment for people and livestock to get access to drinking water (YUAN Dao-xian, 2003).
The meagerness of groundwater makes ecological environment fragile. The central part of Asia is high in the southeast and low in the northwest and water vapor acquired from orographic precipitation is the only source of supply. Precipitation is few in plains and basins,widely spreading in oases and deserts in the elevation between 200 m and 400 m. Runoff from mountain rivers flowing out of mountain passes is the main source of supply. The shortness of groundwater leads to a fragile ecological environment where there exists bare surface,infertile land, deserts, rock deserts, gobi,wilderness with rare vegetation for arid area. The main features are: Firstly, on the Loess Plateau,loess accumulates to a deep thickness and develops with vertical joints and loose structure of macrovoid. The land surface is fragmented with ravines. The ecological function of this area is poor due to a arid climate with a serious problem of water and soil erosion caused by concentrated rainfall; secondly, stony desertification occurs in a fragile ecological environment in the karst area with an unfavorable ecological function where rocks are gradually emerging to make the land surface similar to desert landscape and land productive capability is declining or disappearing because water and soil erosion makes it difficult to conserve groundwater; thirdly, deserts and desertification could be seen in the form of rare vegetation, land surface totally covered with sands and undulating sand dunes because sands and wind move wildly as a result of a dry climate and little precipitation; finally, gobi deserts come into shape with exposed land surface and rare vegetation of arid area due to the dry climate and intense vaporization of groundwater.
3 Mapping of groundwater ecological environment in Asia
The Asian groundwater ecological map is among a series of groundwater environment maps in Asia. On the basis of previous maps in this series, this map analyzes the ecological environment of Asian groundwater, the relationship among geological environment, global change and human activities, and uses a systematic theory to build a connection between the groundwater and the ecological environment. It also reveals the types, temporal-spatial characteristics and distribution patterns of the groundwater ecosystem, the material migration and energy conversion in the atmosphere, lithosphere,hydrosphere and biosphere, and especially the control of climate and topography on the groundwater ecological environment. Considering the above information, and taking into account the impact of human beings and other creatures, the groundwater ecology can be divided into several categories.
3.1 Main contents of the mapping
(1) The categories of groundwater environment are: Groundwater development- adjustment and storage ecological environment, groundwater nourishment-supporting ecological environment,groundwater deficient-vulnerable ecological environment.
(2) The main problems of groundwater environment are: land desertification, rocky desertification, soil erosion, soil desertification, soil salinization, shrink of swamps and wetlands,degradation of frozen crust, salt incrustation, salt marsh and the impact of major human activities(such as oil and gas fields and mines) on the ecological environment.
(3) The categorization of Asian groundwater ecological environment is based on development strategies of China and its neighboring regions.Groundwater alternation, water-rock interaction,ecological type and human beings’ impact are all taken into account in the categorization, which aims at striking a balance between human and nature, enabling the water ecological environment to develop in a sound way and raising awareness for major problems of the groundwater ecological environment.
3.2 Legend system of displaying
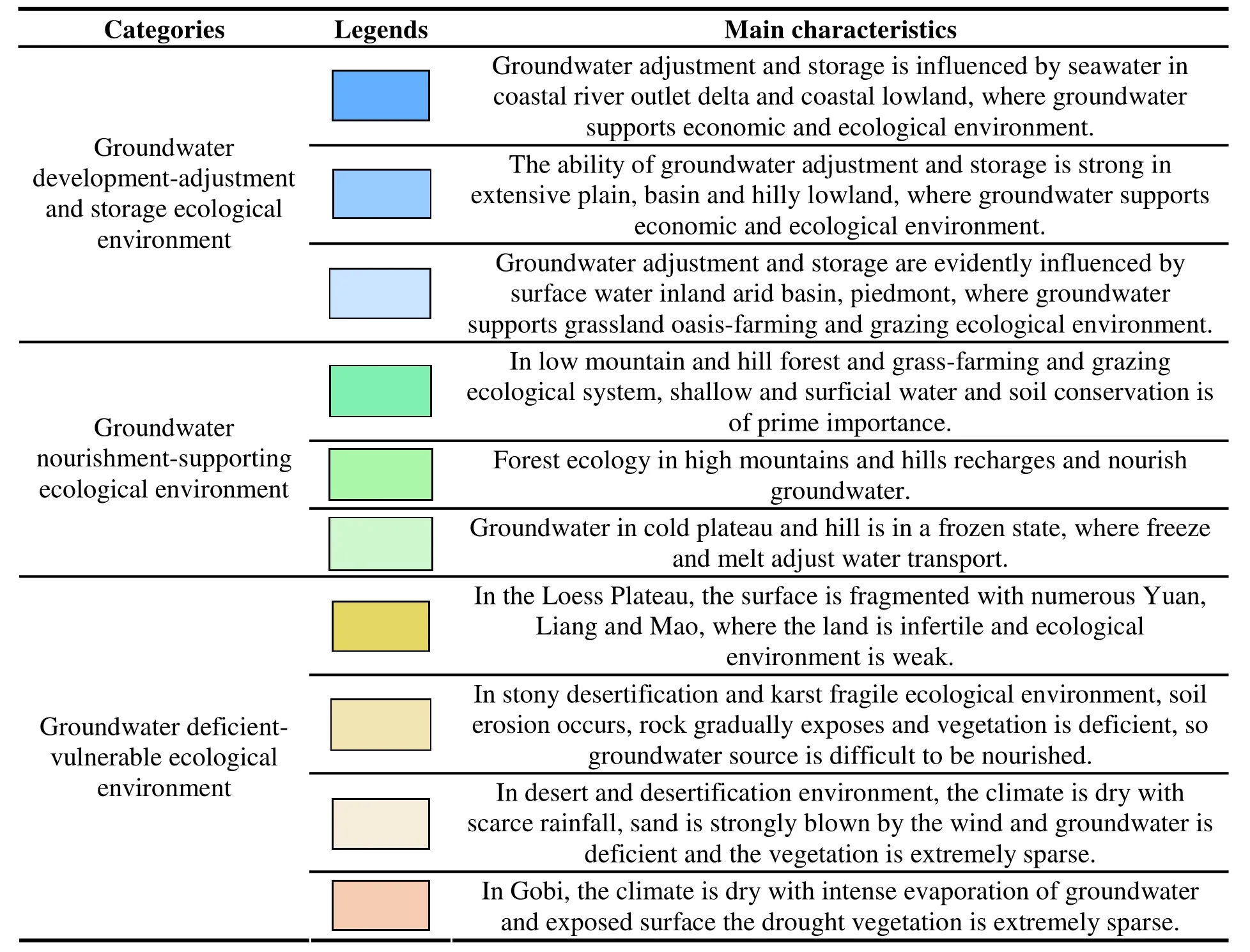
Table 2 Groundwater ecological environment
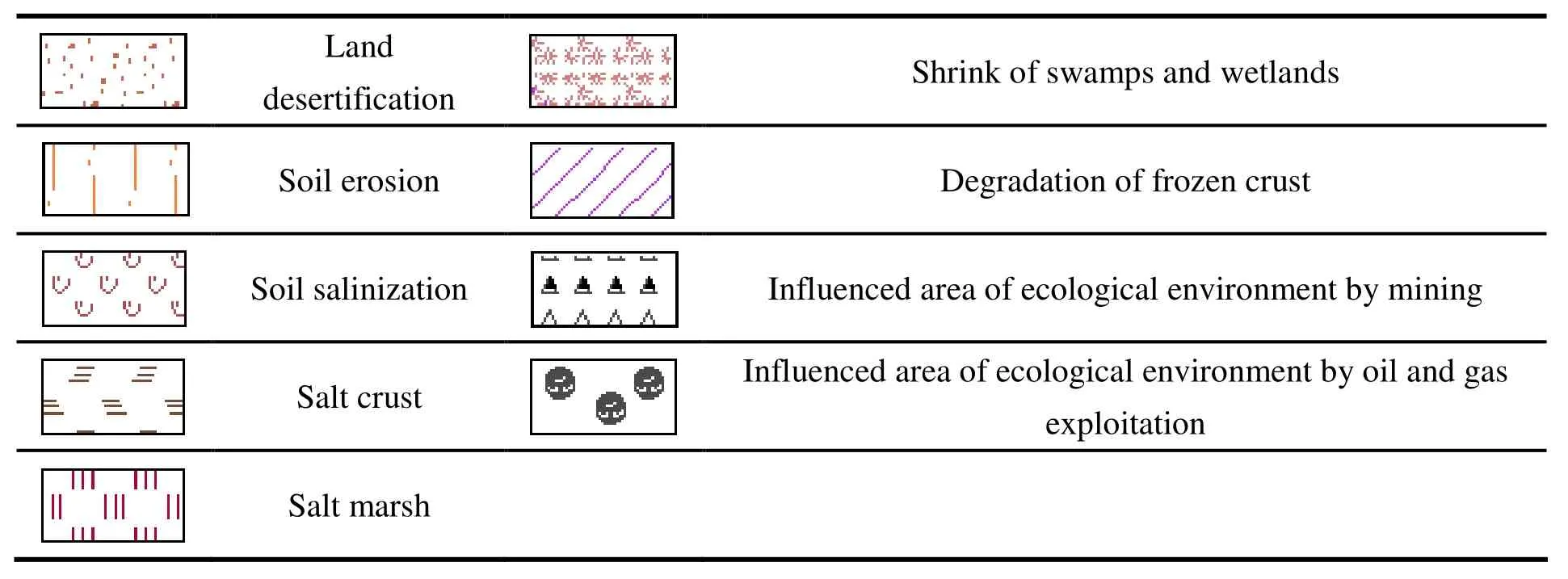
Table 3 Main problems of groundwater ecological environment
Conclusions
At present, the construction of One Road One Belt starts from Asia, by Asia, and for Asia. The ecological environment determines the sound development of the society and economy.Groundwater is an important part of ecological environment. Therefore, making the groundwater ecological map, analyzing the impact of climate and topography on groundwater ecology in Asia,and describing the main types, temporal-spatial characteristics and distribution patterns of the groundwater ecosystem at a macro level are of great significance to the planning of the Silk Road Economic Belt. However, as the research on groundwater ecological environment is still at its very beginning, many research results remain superficial, and many in-depth problems regarding groundwater ecological environment are worth exploring such as research on environmental index system for groundwater, connectivity between groundwater and ecology and economic measures for groundwater ecosystem protection. These researches all require international and inter-disciplinary cooperation.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by Geological Map of Groundwater Resources and Environments of China and Surrounding Areas (12120113014200)and Series Maps of Karst environment geology of China and South East Asia (12120114006401,12120114006301).
杂志排行
地下水科学与工程(英文版)的其它文章
- Analysis of the negative effects of groundwater exploitation on geological environment in Asia
- Specific yield of phreatic variation zone in karst aquifer with the method of water level analysis
- Application of remote sensing technique to mapping of the map series of karst geology in China and Southeast Asia
- Compilation of Groundwater Quality Map and study of hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater in Asia
- Evaluation on water resources carrying capacity of Changchun-Jilin Region
- Comparison of 1,2,3-Trichloropropane reduction and oxidation by nanoscale zero-valent iron, zinc and activated persulfate
