Larval descriptions of two species Teliphasa Moore feeding on Castanea mollissima Blume (Lepidoptera:Pyralidae:Epipaschiinae)
2015-12-09XIAOYunLiFANGChengXUYanXiaXUXiangYangZHONGYuLinHubeiKeyLaboratoryofEconomicForestGermplasmImprovementandResourcesComprehensiveUtilizationCollegeofLifeScienceHubeiCollaborativeInnovationCenterfortheExploitationofDabie
XIAO Yun-Li,FANG Cheng,XU Yan-Xia,XU Xiang-Yang,ZHONG Yu-Lin (.Hubei Key Laboratory of Economic Forest Germplasm Improvement and Resources Comprehensive Utilization College of Life Science,Hubei Collaborative Innovation Center for the Exploitation of Dabie Mountains Featuring Resources,Huanggang Normal University,Huanggang 438000,Hubei Province,China;.Luotian County Forestry Administration,Luotian 436600,Hubei Province,China)
The genus Teliphasa Moore was erected in 1888 based on the type species Teliphasa orbiculifer Moore,1888.Nine species were described from the Oriental,Palaearctic,Ethiopian and Australian regions.To data,four species including T.amica (Butler,1879)and T.elegans (Butler,1881)were recorded in China(Li et al.,2009).
In subfamily Epipaschiinae,the larval external morphologies and the primary biological characters of three species,that is,Orthaga achatina Butler,Macalla sp.and Locastra muscosalis (Walker)were reported from China (Cai et al.,2005;Piao and Ni,2008).This study adds the larval descriptions of Teliphasa amica (Butler,1879) and T.elegans(Butler,1881)infesting on the leaves of Castanea mollissima Blume.
1 Materials and Methods
The larvae were collected from the leaves of Castanea mollissima Blume in Luotian County,Hubei Province,China,then were raised to get adults in the laboratory.The ecological and morphological bodies of the mature larvae are photographed by Canon PC1817 camera.After putting to death in 30% alcohol,the head was removed from the body and soaked in 10%KOH for 24 h,in sequence,dyed in the saturated water solution of tetrabromofluorescein for 12 h.In the distilled water,the head capsule and the mouthparts including the labrum,mandible,maxillae and labium complex are photographed under stereoscopic microscope by Nikon P7100 camera.The nomenclature of larvae setae follows Hinton (1946).
2 Descriptions
Teliphasa elegans (Butler,1881)(Figs.1-2)
Larvae length 22-35 mm (n=6).Head yellowish brown,covered with blank or dark brown spots and streaks.Body yellowish white,dorsal side medially with a yellowish ocherouos bead shaped line,laterally having three blank spots in each segment forming two interrupted broad longitudinal strips,between anterior and medial spots of prethorax,a large blank transversal spot extending to lateral margin of shield,anterior spots of metathorax expanded to form a somewhat oval.Lateral sides carrying three blank longitudinal strips,interrupted or irregular in thorax and caudal abdomen,the lowest one slender,extended obliquely from caudal margin of each segment through spiracle to anterior margin.The crochets of each third to sixth abdominal segments biordinal,arranged in a circle.

Fig.1 Larva of Teliphasa elegans (Butler)
Head.The adfrontal apex midway between vertical triangle and front apex;the fron extends 1/3 of the distance to vertical triangle.A1,A2 and A3 forming a somewhat 150° angle at A2,distance between A2 and A3 about 2.5 times of that between A1 and A2;O1,O2 and O3 forming a somewhat 120°angle at O2,distance between O1 and O2 slightly shorter than between O2 and O3.Labrum with anterior margin emarginated to 1/5 of depth in an arc,M1,M2 and M3 arranged in an acute-angled triangle,E1,E2 and E3 along lateral margin forming an arc.Mandible melanised on outer surface,strongly sclerotized and melanised in distal portion,with five shallow teeth in broad cutting edge,a large transversal internal tooth in inner surface.Labium having two LB1 bristles in center of membranous postmentum,with spinneret medially and labial palpi laterally in prementum,spinneret length about 7.7 times of width of middle,labial palpi about 1/3 length of spinneret,apically bristle reaching 2/3 of spinneret.Maxillae with MX1 anterolateral to MX2 in stips,one MX3 bristle in palpifer.
Thorax.Prethorax:XD1,D1 and D2 forming a somewhat right triangle at D1,XD2,SD1 and SD2 arranged in an isosceles triangle at SD2;L group front of spiracle,bisetose;SV group bisetose.Mesothorax and metathorax:D1 dorsal to D2,approximated;SD1 dorsal to D2,approximated;L group trisetose,L1 approximated to L2;SV group unisetose.
Abdomen.First to eighth segment:D1 front of D2;SD group above spiracle,unisetose;L group under spiracle,bisetose;SV group unisetose.Ninth segment:D1 anteroventral to D2;SD group unisetose;L group trisetose;SV group unisetose.

Fig.2 Larva head structures of Teliphasa elegans (Butler)
Host-plant.Rosaceae:Chaenomeles speciosa(Sweet)Nakai,Rosa rugosa Thunb.;Fabaceae:Glycine max (Linn.)Merrill,et al.(Li,et al.,2009);Fagaceae:Castanea mollissima Blume.
Living habits.From early July to late August,the larvae usually inhabited the lower crown of the chestnut in Luotian County,Hubei Province.It usually spins threads to knot a sparse net around with main vein of the chestnut leaf,eating the leaf around the net,resting and excreting the faeces under the nets.
Distribution.China (Tianjin,Hebei,Fujian,Henan,Hubei,Hunan,Guangxi,Guizhou,Shaanxi);Japan.
The species is characterized by the yellowish brown head with blank maculation;the body dorsally with a yellowish ocherous medial line and two interrupted broad longitudinal bands consist of blank spots,carrying three blank longitudinal bands in lateral sides.
Teliphasa amica (Butler,1879)(Figs.3-4)
Larvae length 28-40 mm (n=8).Head yellowish brown,covered with brown spots and strips.Body yellow,segments each carrying blank transversal strips.Prethorax with three blank strips on anterior margin,medial 1/2 and caudal margin;mesothorax and metathorax each along anterior margin having a blank arc shaped strip,joined with caudal strip of anterior segment,along caudal margin with a blank narrow strip in mesothorax and an elongated oval loop shaped strip in mesathorax.Abdomen from first to eighth segment each caudally having a blank similar strip with metathorax,anteriorly having a blank strip forked near spiracle line;ninth abdominal segment both carrying a blank strip on anterior and caudal margins;anal plate anteriorly bearing a blank strip joined with caudal strip of ninth segment,caudally with a blank arc shaped strip.The crochets of third to sixth abdominal segments each biordinal,arranged in a circle.
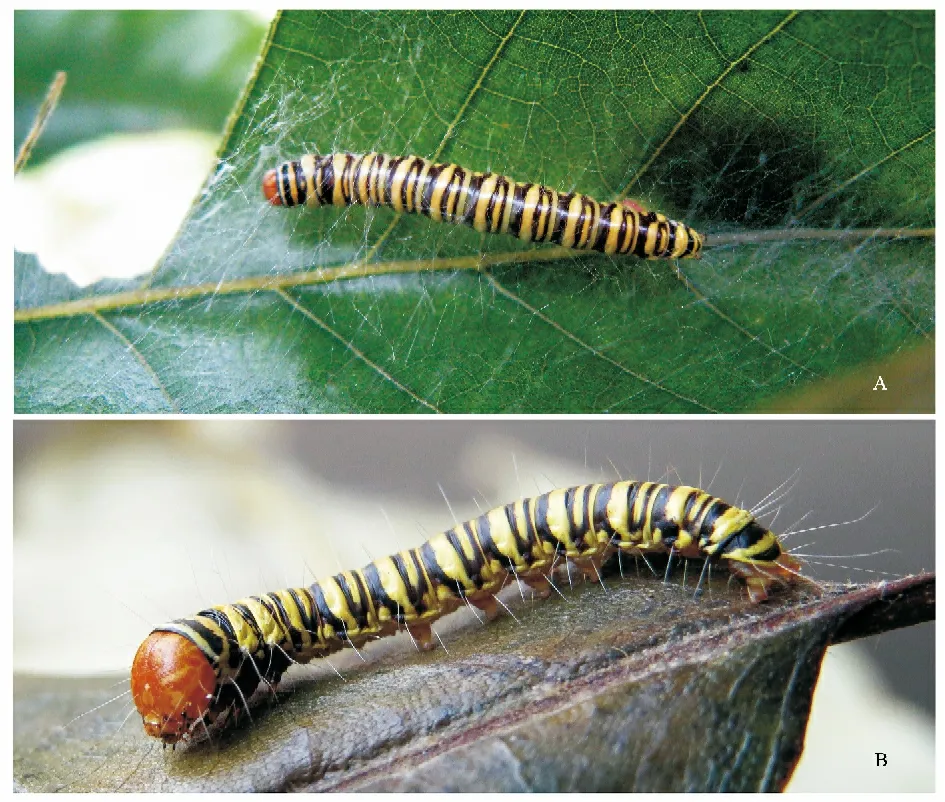

Fig.3 Larva of Teliphasa amica (Butler)
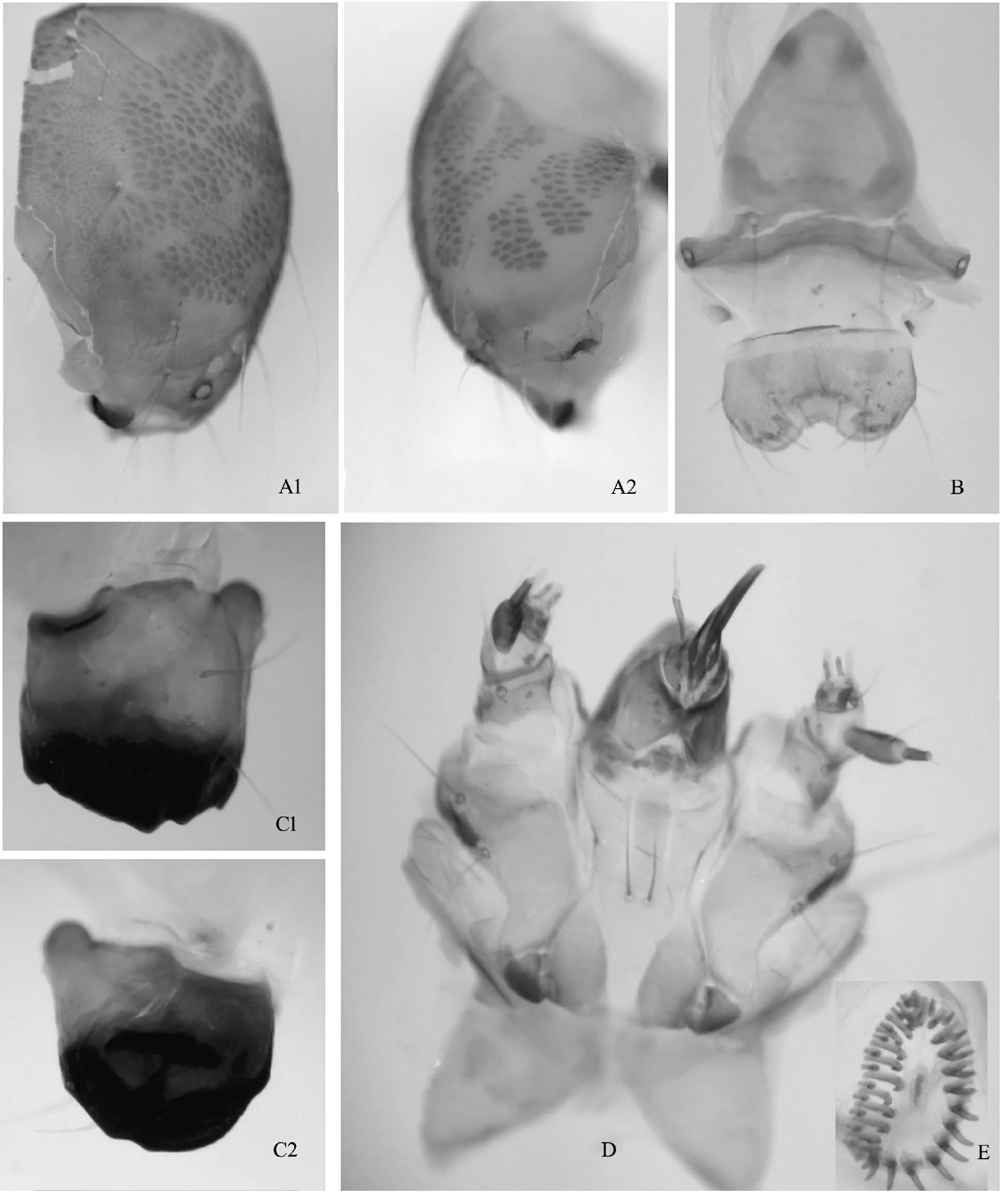
Fig.4 larva head structures of Teliphasa amica (Butler)
Head.The adfrontal apex midway between vertical triangle and front apex;the front extends 2/7 of the distance to vertical triangle.A1,A2 and A3 arranged in a somewhat 150° angle at A2,O1,O2 and O3 forming a somewhat 120° angle at O2.Labrum with anterior margin medially emarginated to 1/4 of depth in an arc,M1,M2 and M3 arranged in an equilateral triangle,E1,E2 and E3 along lateral margin forming an arc.Mandible strongly sclerotized and melanised in cutting portion,with four shallow teeth in broad cutting edge,a large subrectangular internal tooth in inner surface.Labium having two LB1 bristles in center of membranous postmentum,with median spinneret distally and labial palpi laterally in prementum,spinneret length about 10.0 times of width of middle,labial palpi about 1/3 length of spinneret,apically bristle reaching 3/5 of spinneret.Maxillae with MX1 anterolateral to MX2 in stips,one MX3 bristle in palpifer.
Thorax.Prethorax:XD1,D1 and D2 forming a somewhat right angle at D1,XD2,SD1 and SD2 forming an acute angle at XD2;L1 and L2 front of spiracle;SV group bisetose.Mesothorax and Metathorax:D1 dorsal to D2,approximated;SD1 dorsal to SD2,approximated;L group trisetose,L1 approximated with L2;SV group single setose.
Abdomen.First to eighth segments:D1 front of D2;SD group dorsal to spiracle,unisetose;L group ventral to spiracle,bisetose;SV group unisetose.Ninth segment:D1 anteroventral to D2,SD group unisetose,L group trisetose,SV group unisetose.
Host-plant.Fagaceae:Castanea mollissima Blume.
Living habit.In the early and middle August,the larvae are founded inhabiting the lower crown of the chestnut in Luotian County,Hubei Province.It usually spins threads to knot a sparse net around with main vein of the chestnut leaf,eating the leaf around the net and resting under the nets.
Distribution.China (Tianjin,Zhejiang,Fujian,Jiangxi,Henan,Hubei,Guangxi,Sichuan,Yunnan);Japan.
The species is characterized by the yellow head with yellowish brown maculation;the body yellow with blank or brownish blank transversal strips on anterior and caudal margin of each segment.
References)
Cai XG,Zheng DX,Huang WQ,et al.Bionomics and integrated management of Macalla sp.[J].Forest Pest and Disease,2005,24 (3):9-11.[蔡选光,郑道序,黄武强,等.橄榄锄须丛螟生物学特性与综合防治[J].中国森林病虫,2005,24 (3):9-11]
Hinton HE.On the homology and nomenclature of the setae of Lepidoptera larvae,with some notes on the phylogeny of the Lepidoptera [J].Transactions of the Entomological Society of London,1946,97:1-37.
Li HH,Ren YD,et al.Insect Fauna of Henan,Lepidoptera:Pyraloidea[M].Beijing:Scinece Press,2009.[李后魂,任应党,等.河南昆虫志,鳞翅目:螟蛾总科[M].北京:科学出版社,2009]
Piao MH,Ni CX.Larval Descriptions of three species of Epipaschiinae(Lepidoptera:Pyralidae)from China [J].Entomotaxonomia,2008,30 (4):273-279.[朴美花,倪翠侠.中国丛螟亚科三种幼虫记述(鳞翅目:螟蛾科)[J].昆虫分类学报,2008,30 (4):273-279]
