鳞翅目昆虫触角感器研究进展
2017-07-10张健程彬周毓麟
张健 程彬 周毓麟
摘要 介绍了鳞翅目昆虫触角感器的常见类型:鳞形感器、毛形感器、锥形感器、刺形感器、耳形感器、栓锥形感器、腔锥形感器、板形感器和Bhm氏鬃毛,综述了各类型感器形态特征、分布和功能的研究进展,并展望了今后鳞翅目昆虫触角感器的研究方向。
关键词 鳞翅目;触角;感器
中图分类号 S433.4 文献标识码 A 文章编号 0517-6611(2017)18-0129-04
Abstract Sensilla squamiformia,sensilla trichodea,sensilla basiconica,sensilla chaetica,sensilla auricillica,sensilla styloconica,sensilla coeloconica,sensilla placodea and Bhm bristles were common sensillum types of lepidopteran insect species.The structure and function of each antennal sensillum type were also summarized.Research directions on antennal sensilla of lepidopteran insect species in the future were also discussed.
Key words Lepidoptera;Antennal;Sensilla
鳞翅目是昆虫纲中仅次于鞘翅目的第二大类群,全世界已知约20万种,除极少数种类外,它们的幼虫均取食显花植物,其中有许多是农林生产上的重要害虫,具有极大的经济重要性。鳞翅目昆虫的触角上有很多感受器官,能感受分子级化学物质和微小机械作用的刺激。如菜粉蝶(Pieris rapae)对十字花科植物散发的芥子油气味敏感,许多昆虫可为损伤果实所散发的酸甜酒香味所引诱,许多蛾类的雌虫分泌的性激素能吸引千米外的雄虫飞来交尾[1]。因此,可利用昆虫触角对某些化学物质的特殊嗅觉作用对害虫的发生動态进行测报,并对害虫进行诱集、诱杀或趋避防治。
触角是昆虫觅食、聚集、求偶、寻找产卵场所、避敌等生命活动中的重要感觉器官,具有触觉和嗅觉功能。20世纪70年代以来,昆虫触角感器的研究得到国内外学者的广泛关注,对触角感器超微构造的研究越来越清晰,并且已经取得显著进展[2-5]。近年来,国内外学者采用扫描电镜(SEM)和透射电镜(TEM)技术对鳞翅目昆虫触角感器进行了广泛而深入的研究,研究类群主要包括夜蛾科、卷蛾科、螟蛾科、菜蛾科、舟蛾科、毒蛾科、枯叶蛾科、凤蝶科、蛱蝶科、弄蝶科、蚬蝶科、眼蝶科、粉蝶科、灰蝶科等。筆者介绍了鳞翅目昆虫触角感器的常见类型,综述了各类型感器形态特征、分布和功能的研究进展,并展望了今后鳞翅目昆虫触角感器的研究方向。
1 鳞翅目昆虫常见触角感器的形态及分布特征
根据感器表皮的结构特征及其着生于触角表面的方式,Schneider[2]将昆虫触角感器划分为毛形感器、刺形感器、锥形感器、鳞形感器、腔锥形感器、栓锥形感器、耳形感器、板形感器、钟形感器、瓶形感器等10余个种类。
鳞翅目昆虫常见的感器类型主要包括鳞形感器、毛形感器、刺形感器、锥形感器、耳形感器、栓锥形感器、腔锥形感器、板形感器、Bhm氏鬃毛等[2,4]。不同类群昆虫的触角感器类型、数量、分布等存在差异,各类型感器的形态特征在鳞翅目昆虫中通常无差别。
1.1 鳞形感器
形状类似剑鞘,表面结构与普通鳞片相似,表面具有纵脊,较狭长且端部尖锐,基部位于臼状窝里。一般每节3~5根,分布于触角梗节和鞭节临近鳞片的位置。
1.2 毛形感器
形态较纤细,由基部向端部逐渐变细,顶端较钝。直立或略向触角表面弯曲,表面有斜环状或螺状纹,基部无臼状窝。在触角鞭节表面大量分布。在一些蛾类昆虫中,毛形感器的数量雄虫通常多于雌虫,且长毛形感器也多分布在雄虫触角表面。例如,毛形感器在大蚕蛾雄性触角上数量约为6万个,而云杉卷叶蛾仅有约2 300个。
1.3 刺形感器
呈镰刀状,顶端较尖,基部具有较宽关节窝,向触角顶端弯曲或与触角表面平行,表面具有纵沟、无孔。刺型感器不同亚型间长度变异较大。分布于触角鞭节的背面、腹面和侧面,一般每节着生5~6根。
1.4 锥形感器
较短小,顶端较钝,直立于触角表面或稍弯曲,通常零散或成簇分布,基部无臼状窝。表面有较多的孔,壁很薄,内有大量的神经细胞。分布于鞭节腹面近端或中部及背面鳞片之间,一般每节着生2~6根。
1.5 耳形感器
外形类似禾本科植物卷心叶片状,具有耳状凹槽,与触角表面平行。多数分布于鞭节腹面两侧,少数分布于鞭节腹面,一般每节着生1~10个。
1.6 栓锥形感器
由触角表皮凹陷而形成的圆形腔,圆形腔顶部中央有感觉锥突出表面。一般每个鞭节末端中央具有1个。
1.7 腔锥形感器
为触角表皮下陷形成的浅圆形腔,中央着生感觉锥。分布于触角柄节和鞭节表面。一般每节着生3~10个。
1.8 板形感器
基部较光滑,端部钝圆。着生在鞭节中部。
1.9 Bhm氏鬃毛
顶端较尖,垂直于触角表面,基部关节窝较宽。通常成簇分布于柄节和梗节相连接的地方。
2 鳞翅目昆虫常见触角感器的功能
2.1 各类型感器的功能
2.1.1 机械感器。
鳞形感器在夜蛾科的Copitarsia consueta[6]和粘虫(Mythimna separata)[7]、螟蛾科的印度谷螟蛾(Plodia interpunctella)[8]和透翅蛾科的Synanthedon scitula[9]等鳞翅目昆虫触角上均有分布。这类感器通常被认为是一类具有感受机械刺激功能的感受器[2,10]。
Bhm氏鬃毛在小翅蛾科的Micropterix calthella[11]、鞘蛾科的兴安落叶松鞘蛾(C.obducta)[12]、螟蛾科的稻纵卷叶螟(Cnaphalocrocis medinalis)[13]和舟蛾科的分月扇舟蛾(Clostera anastomosis)[14]等种类触角中均有记述。Schneider[2]认为Bhm氏鬃毛具有感受重力的功能,是一种机械感器,当触角遇到外界机械刺激时具有缓冲重力的作用,从而控制触角下落的角度和速度。
2.1.2 化学感器。
毛形感器通常根据其长度划分为不同的亚型。螟蛾科的印度谷螟蛾[8]和菜蛾科的Plutella xylostella[15]触角上的毛形感器均是依据长度不同分为长型毛形感器、中型毛形感器和短型毛形感器共3个亚型。Ebbinghaus等[16]发现卷蛾科的苹果蠹蛾(Cydia pomonella)的较长的毛形感器内部具有感受信息素的嗅觉受体神经元(ORN)。通常雄蛾触角表面较长的毛形感器表面具有大量的孔的结构,且这类感器在雌蛾触角表面没有分布,根据电生理实验判断这类感器具有感受雌蛾性信息素的功能[17-20]。此外,在鳞翅目昆虫表面大量分布的毛形感器据推断可能承担识别其自身性信息素和寄主植物挥发物的功能[21]。雌蛾触角表面较短的毛形感器承担着识别其寄主挥发物的功能[22-23]。
刺形感器在鳞翅目昆虫触角表面比较常见,如在小翅蛾科的Micropterix calthella[24]、枯叶蛾科的油松毛虫(Dendrolimus tabulaeformis)[25]、夜蛾科的Catocala remissa[26]和刺蛾科的黄刺蛾(Monema flavescens)[27]的触角上均有分布。刺形感器一般分为2类:一类表面无孔,基部的关节窝不能自由活动,所以通常认为它们具有感受机械刺激的功能[20];另一类刺形感器末端表面通常有1个孔且表面有纵沟[28],Zacharuk[3]根据这类感器的内部结构推断它们为接触性的化学感器,这类感器可能与味觉有关,在寄主识别中发挥作用。
多数锥形感器表面具有大量的孔的结构,说明它们是一类嗅觉受体或是承担感受植物氣味分子的功能[23]。按照其表面孔的排列特點,锥形感器也可分为2个亚型:一类是孔呈线性排列,如卷蛾科的Adoxophyes orana[29]、苹果蠹蛾和C.succedana[21]和螟蛾科的Homoeosoma nebulella[30];另一类是孔无规则排列,如斑蛾科的Zygaena hippocrepidis[31]。在某些昆虫类群中发现雄性锥形感器数量显著大于雌性,如在稻纵卷叶螟(Cnaphalocrocis medinalis)中雄性的大量锥形感器起到感受雌性性信息素的功能[13]。
耳形感器在对夜蛾科的刺翘夜蛾(Scoliopteryx libatrix)[22]、卷蛾科的Adoxophyes orana[32]和C.succedana[21]的研究中被发现,据推断这类感器与探测植物气味有关,Ebbinghaus等[16]报道在卷蛾科的C.pomonella上发现其起到感受微量信息素的功能。
腔锥形感器的表面具有大量的孔,一般分为2个类型:一类是具有环形围栏状的微毛,另一类是不具有环形围栏状的微毛。具有环形围栏状微毛的腔锥形感器在螟蛾科的C.cactorum[23]和稻纵卷叶螟[13]、卷蛾科的T.batesi[29]和苹果蠹蛾[21]等的触角上发现;不具有环形围栏状微毛的腔锥形感器在颚蛾科的Agathiphaga vitiensis 和A.queenslandensis[33]、微蛾科的Ectoedemia atricollis[34]和卷蛾科的Cydia nigricana[35]等的触角上发现。Shanbhag等[36]认为环形围栏状微毛具有保护内部中央着生的感觉锥不受到外界环境所产生的物理损伤的作用。在鳞翅目昆虫中由于这类感器具有感觉神经元,通常被认为是嗅觉刺激的受体,主要感受短链脂肪酸和单萜醇类等物质,以及在雌性寄主产卵地选择上起作用[17,37-38]。
板形感器首次被发现是在小翅蛾科Micropterix calthella[11]的触角上。在鞘蛾科的兴安落叶松鞘蛾(Coleophora obducta)[12]的触角上也被发现,据推断其可能承担味觉的功能。
2.1.3 温湿度感器。
栓锥形感器广泛地分布在夜蛾科的C.consueta[6]、卷蛾科的C.nigricana[35]、刺蛾科的黄刺蛾[27]和菜蛾科的P.xylostella[15]等鳞翅目昆虫的触角上。该类感器通常为无孔型感器,一般具有感受温湿度的功能[39]。也有研究认为这类感器承担味觉的功能[15]。
2.2 鳞翅目昆虫感受外界刺激的机制
昆虫感受器一般由表皮、极孔、嗅觉神经元(OSN)、鞘原细胞、毛原细胞和膜原细胞构成[40],其中的嗅觉神经元是一种双极细胞,一端浸没在感受器淋巴液中,另一端连接着触角叶[41]。外观上看,嗅觉感器是触角表面上突起的多孔状结构单元,这种结构有利于大量的气味分子通过感器体壁顺利进入感器腔,但在突起的结构下面含有很多元件。
鳞翅目昆虫感受外界的化学物质主要是通过触角上的嗅觉感受器来完成的。嗅觉信号传导过程可概括为以下几个步骤:首先,气味分子通过感器表面的极孔进入到感器组织的淋巴液中,存在于感器淋巴液中的气味结合蛋白(OBP)或化学感受蛋白(CSP)负责将这些疏水性的分子运输至嗅觉神经元(OSN)[42];其次,气味分子激活在嗅觉神经元上表达的嗅觉受体(OR)或离子型受体(IR),嗅觉受体或离子型受体将化学信号转化为电信号传递至触角叶进而激活脑部的中枢神经系统[43];最后,气味分子被分解。目前,激活嗅觉受体的模式存在2种观点:一种是气味结合蛋白和气味分子的复合体共同激活气味受体;另一种是气味结合蛋白将气味分子释放后由气味分子单独刺激。为了避免持续性的神经刺激,多余的气味分子会被处理掉。目前猜测的气味分子被处理方式有2种:一种是由气味降解酶(ODE)降解气味分子[44-45],另一种是气味分子被一种目前还不清楚的分子圈套抑制住[44,46]。
3 鱗翅目昆虫触角感器研究展望
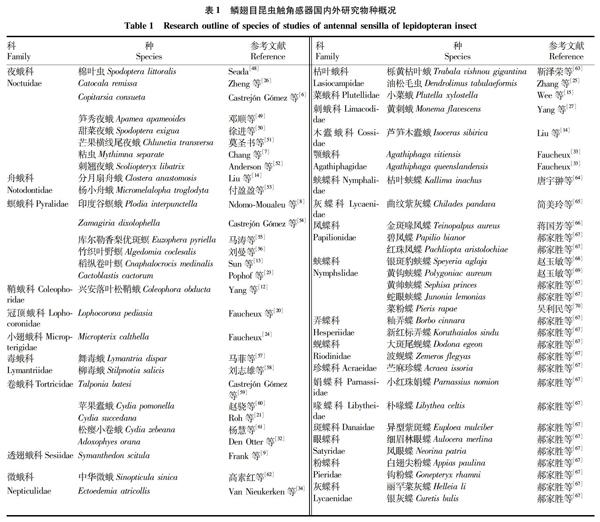
根据目前已报道的鳞翅目昆虫触角感器的情况(表1),各种类型感器十分丰富,其具体功能还有待于以后采用电生理手段进一步研究证实。昆虫触角感器超微结构的研究为进一步进行的触角电位、单细胞记录、细胞内记录等电生理技术提供了基础信息,为未来揭示鳞翅目昆虫的寄主选择、交配、产卵等行为反应和种内、种间识别机制、寄主选择机制奠定基础,从而为鳞翅目昆虫信息素合成、农林害虫化学生态手段防控提供更有价值的信息。
许多鳞翅目昆虫类群是农林类的重要害虫,要采取有针对性的手段对这些害虫进行防治,必须明确其寄主选择等行为学机理,最终实现对农林害虫的基因调控和生态调控,从而达到控制其种群数量的目的。随着实验技术的不断改进和发展,今后应进一步加强对鳞翅目昆虫与植物信息联系、与外界化学通讯的理论研究,深入探索昆虫行为反应的本质并最终应用于生产实践,开辟昆虫行为控制剂新领域。利用昆虫的感受特性,设计性信息素类似物或嗅觉抑制剂等行为控制剂,在外围嗅觉系统中选择性干扰化学信息的识别、运输、降解等编码过程,从而达到监测和防治害虫的目的。此外,日本学者模仿鳞翅目昆虫嗅觉系统制成了仿生机器蛾,当收到受害虫危害的植物和腐烂的果实释放出特定的气味化合物时,机械蛾可以检测出植物受危害程度、果实腐烂的程度等[47],昆虫仿生也将有着广阔的应用前景,能为人类解决更多生产实践中遇到的实际问题。
参考文献
[1] GULLAN P J,CRANSTON P S.The Insects:An Outline of Entomology[M].Oxford:Blackwell Science,2014.
[2] SCHNEIDER D.Insect antennae[J].Annual review of entomology,1964,9:103-122.
[3] ZACHARUK R Y.Antennae and sensilla[C]//KERKUT G A,GILBERT L Y.Comprehensive insect physiology,biochemistry and pharmacology.Oxford:United Kingdom,1985.
[4] 馬瑞燕,杜家纬.昆虫的触角感器[J].昆虫知识,2000,37(3):179-183.
[5] 余海忠.昆虫触角感受器研究进展[J].安徽农业科学,2007,35(14):4238-4240,4243.
[6] CASTREJN GMEZ V R,VALDEZCARRASCO J,CIBRIANTOVAR J,et al.Morphology and distribution of the sense organs on the antennae of Copitarsia consueta (Lepidoptera:Noctuidae)[J].Florida entomologist,1999,82(4):546-555.
[7] CHANG X Q,ZHANG S,LV L,et al.Insight into the ultrastructure of antennal sensilla of Mythimna separata(Lepidoptera:Noctuidae)[J].Journal of insect science,2015,15(1):124.
[8] NDOMOMOUALEU A F,ULRICHS C,RADEK R,et al.Structure and distribution of antennal sensilla in the Indianmeal moth,Plodia interpunctella(Hübner,1813)(Lepidoptera:Pyralidae)[J].Journal of stored products research,2014,59:66-75.
[9] FRANK D L,LESKEY T C,BERGH J C.Morphological characterization of antennal sensilla of the Dogwood Borer(Lepidoptera:Sesiidae)[J].Annals of the entomological society of america,2010,103(6):993-1002.
[10] MCIVER S B.Structure of cuticular mechanoreceptors of arthropods[J].Annual review of entomology,1975,20(1):381-397.
[11] FAUCHEUX M J.Structures sensorielles et glandulaires particulières de lantenne de Micropterix calthella L.(Lepidoptera:Micropterigidae)[J].Bulletin de la Société des sciences naturelles de louest de la france(Nouvelle Série),1992,14:114-118.
[12] YANG H,YAN S C,LIU D.Ultrastructural observations on antennal sensilla of Coleophora obducta (Meyrick)(Lepidoptera:Coleophoridae)[J].Micron,2009,40(2):231-238.
[13] SUN X,WANG M Q,ZHANG G A.Ultrastructural observations on antennal sensilla of Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Lepidoptera:Pyralidae)[J].Microscopy research and technique,2011,74(2):113-121.
[14] LIU Q,CHEN J,HAO D J.Antennal morphology and sensilla of the blackback Prominent Moth,Clostera anastomosis Linnaeus(Lepidoptera:Notodontidae)[J].Entomological news,2013,123(2):110-130.
[15] WEE S L,OH H W,PARK K C.Antennal sensillum morphology and electrophysiological responses of olfactory receptor neurons in trichoid sensilla of the diamondback moth(Lepidoptera:Plutellidae)[J].Florida entomologist,2016,99(S1):146-158.
[16] ZEBITZ C P,SCHERKENBECK J,LINDEMANN M,et al.Detection of major and minor sex pheromone components by the male codling moth Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera:Tortricidae)[J].Journal of insect physiology,1998,44(1):49-58.
[17] HANSSON B S.Olfaction in lepidoptera[J].Experientia,1995,51(11):1003-1027.
[18] COSS A A,TODD J L,BAKER T C.Neurons discovered in male Helicoverpa zea antennae that correlate with pheromonemediated attraction and interspecific antagonism[J].Journal of comparative physiology A,1998,182(5):585-594.
[19] BAKER T C,OCHIENG S A,COSS A A,et al.A comparison of responses from olfactory receptor neurons of Heliothis subflexa and Heliothis virescens to components of their sex pheromone[J].Journal of comparative physiology A,2004,190:155-165.
[20] FAUCHEUX M J,KRISTENSEN N P,SHENHORN Y.The antennae of neopseustid moths:Morphology and phylogenetic implications,with special reference to the sensilla(Insecta,Lepidoptera,Neopseustidae)[J].Zoologischer anzeiger,2006,245(2):131-142.
[21] ROH H S,PARK K C,OH H,et al.Morphology and distribution of antennal sensilla of two tortricid moths,Cydia pomonella and C.succedana (Lepidoptera)[J].Microscopy research and technique,2016,79(11):1069-1081.
[22] ANDERSON P,HANSSON B S,LFQVIST J.Plantodourspecific receptor neurones on the antennae of female and male Spodoptera littoralis[J].Physiological entomology,1995,20(3):189-198.
[23] POPHOF B,STANGE G,ABRELL L.Volatile organic compounds as signals in a plantherbivore system:Electrophysiological responses in olfactory sensilla of the moth Cactoblastis cactorum[J].Chemical senses,2005,30(1):51-68.
[24] FAUCHEUX M J.Sensory organs on the antennae of Micropterix calthella L.(Lepidoptera,Micropterigidae)[J].Acra zoologica,1997,78(1):1-8.
[25] ZHANG S F,ZHANG Z,KONG X B,et al.Sexual dimorphism in antennal morphology and sensilla ultrastructure of Dendrolimus tabulaeformis Tsai et Liu(Lepidoptera:Lasiocampidae)[J].Microscopy research and technique,2013,76(1):50-57.
[26] ZHENG H X,LIU H X,GUO S Y,et al.Scanning electron microscopy study of the antennal sensilla of Catocala remissa[J].Bulletin of insectology,2014,67(1):63-71.
[27] YANG S,LIU H,ZHANG J T,et al.Scanning electron microscopy study of the antennal sensilla of Monema flavescens Walker(Lepidoptera:Limacodidae)[J].Neotropical entomology,2017,46(2):175-181.
[28] LIU H X,LIU Z X,JING X Y,et al.Scanning electron microscopy studies of antennal sensilla of Isoceras sibirica Alpheraky(Lepidoptera,Cossidae)[J].Annales de la société entomologique de france(N.S.):International journal of entomology,2014,50(3/4):350-357.
[29] CUPERUS P L.Inventory of pores in antennal sensilla of Yponomeuta spp(Lepidoptera:Yponomeutidae)and Adoxophyes orana F.v.R.(Lepidoptera:Tortricidae)[J].International journal of insect morphology and embryology,1985,14(6):347-357.
[30] FAUCHEUX M J.Morphology and distribution of sensilla on the cephalic appendages,tarsi and ovipositor of the european sunflower moth,Homoeosoma nebulella Den.& Schiff.(Lepidoptera:Pyralidae)[J].International journal of insect morphology and embryology,1991,20:291-307.
[31] FAUCHEUX M J.Morphology and distribution of antennal neuroreceptors in male and female Zygaena hippocrepidis Hübner(Lepidoptera:Zygaenidae)[J].Bulletin de la société des sciences naturelles de louest de la france(ns),1987,9:164-177.
[32] DEN OTTER C J,SCHUIL H A,VAN OOSTEN A S.Reception of hostplant odors and female sex pheromone in Adoxophyes orana (Lepidoptera:Tortricidae):Electrophysiology and morphology[J].Entomologia experimentalis et applicata,1978,24(3):370-378.
[33] FAUCHEUX M J.Antennal sensilla in adult Agathiphaga vitiensis Dumbl.and A.queenslandensis Dumbl.(Lepidoptera:Agathiphagidae)[J].International journal of insect morphology and embryology,1990,19(5):257-268.
[34] VAN NIEUKERKEN E J,DOP H.Antennal sensory structures in Nepticulidae(Lepidoptera)and their phylogenetic implications[J].Journal of zoological systematics and evolutionary research,1987,25(2):104-126.
[35] WALL C.Morphology and histology of the antenna of Cydia nigricana (F.)(Lepidoptera:Tortricidae)[J].International journal of insect morphology and embryology,1978,7(3):237-250.
[36] SHANBHAG S R,SINGH K,SINGH R N.Fine structure and primary sensor projections of sensilla located in the sacculus of the antenna of Drosophila melanogaster[J].Cell and tissue research,1995,282(2):237-249.
[37] HUNGER T,STEINBRECHT R A.Functional morphology of a double-walled multiporous olfactory sensillum:The sensillum coeloconicum of Bombyx mori (Insecta,Lepidoptera)[J].Tissue & cell,1998,30(1):14-29.
[38] FAUCHEUX M J.Antennal sensilla in adult males of five species of Coleophora(Coleophoridae):Considerations on their structure and function[J].Nota lepidopterologica,2011,34(2):93-101.
[39] ALTNER H,LOFTUS R.Ultrastructure and function of insect thermoand hygroreceptors[J].Annual review of entomology,1985,30:273-295.
[40] STEINBRECHT R A.Pore structures in insect olfactory sensilla:A review of data and concepts[J].International journal of insect morphology and embryology,1997,26(3/4):229-245.
[41] FORET S.Function and evolution of putative odorant carriers in the honey bee(Apis mellifera)[D].Australian:The australian national university,2006.
[42] LEAL W S.Pheromone reception[M].SCHULZ S.The chemistry of pheromones and other semiochemicals II.Berlin:Springer,2005:341-360.
[43] LEAL W S.Odorant reception in insects:Roles of receptors,binding proteins,and degrading enzymes[J].Annual review of entomology,2013,58(1):373-391.
[44] ISHIDA Y,CHEN A M,TSURUDA J M,et al.Intriguing olfactory proteins from the yellow fever mosquito,Aedes aegypti[J].Naturwissenschaften,2004,91(9):426-431.
[45] ISHIDA Y,LEAL W S.Rapid inactivation of a moth pheromone[J].Proceedings of the national academy of sciences,2005,102:14075-14079.
[46] KAISSLING K E.Olfactory perireceptor and receptor events in moths:A kinetic model[J].Chemical senses,2001,26(2):125-150.
[47] 王琛柱,趙新成.昆蟲的嗅觉与仿生[J].大自然,2005,5(3):7.
[48] SEADA M A.Antennal morphology and sensillum distribution of female cotton leaf worm Spodoptera littoralis (Lepidoptera:Noctuidae)[J].Journal of basic & applied zoology,2015,68:10-18.
[49] 邓顺,舒金平,董双林,等.笋秀夜蛾触角感器的扫描电镜观察[J].林业科学,2010,46(12):101-105.
[50] 徐进,李怡萍,成卫宁,等.甜菜夜蛾触角感器种类与分布的形态学研究[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2008,36(1):189-193.
[51] 莫圣书,赵冬香.芒果横线尾夜蛾触角感觉器扫描电镜观察[J].华东昆虫学报,2006,15(2):96-98.
[52] ANDERSON P,HALLBERG E,SUBCHEV M.Morphology of antennal sensilla auricillica and their detection of plant volatiles in the herald moth,Scoliopteryx libatrix L.(Lepidoptera:Noctuidae)[J].Arthropod structure & development,2000,29(1):33-41.
[53] 付盈盈,汤方,赵文亮.杨小舟蛾触角感觉器的电镜扫描观察[J].南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2012,36(5):97-101.
[54] CASTREJN GMEZ V R,NIETO G,VALDES J,et al.The antennal sensilla of Zamagiria dixolophella Dyar(Lepidoptera:Pyralidae)[J].Annals of the entomological society of america,2003,96(5):672-678.
[55] 马涛,朱雪姣,张蒙,等.库尔勒香梨优斑螟触角感受器超微结构观察[J].林业科学研究,2013,26(3):274-280.
[56] 刘曼,任春光,杨茂发,等.竹织叶野螟触角感器的超微形态特征[J].林业科学,2013,49(9):107-111.
[57] 马菲,于艳雪,陈乃中,等.舞毒蛾触角感器的超微结构观察[J].植物保护,2013,39(3):120-123.
[58] 刘志雄,刘红霞,张金桐,等.柳毒蛾的触角结构与感受器扫描电镜观察[J].电子显微学报,2015,34(3):257-260.
[59] CASTREJN GMEZ V R,CARRASCO J V.Morphological characteristics of antennal sensilla in Talponia batesi (Lepidoptera:Tortricidae)[J].Annals of the entomological society of america,2008,101(1):181-188.
[60] 趙驍,张雅林,冯纪年.苹果蠹蛾成虫触角感器的超微结构观察[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2012,40(11):119-124.
[61] 杨慧,严善春,李杰,等.落叶松重要枝梢害虫松瘿小卷蛾触角感器的超微结构[J].林业科学,2008,44(2):93-98.
[62] 高素红,吉志新,王长青,等.中华微蛾(Sinopticula sinica Yang)触角感器的扫描电镜观察[J].安徽农业科学,2010,38(7):3499-3502.
[63] 靳泽荣,刘志雄,陈旭鹏,等.栎黄枯叶蛾触角感器的扫描电镜观察[J].电子显微学报,2016,35(3):282-285.
[64] 唐宇翀,周成理,陈晓鸣.枯叶蛱蝶触角感器的扫描电镜观察[J].林业科学研究,2013,26(1):88-93.
[65] 简美玲,张来丽,毛润乾.曲纹紫灰蝶触角感受器的扫描电镜研究[J].华南农业大学学报,2011,32(2):52-54,56.
[66] 蒋国芳,何达崇,颜增光.金斑喙凤蝶雄虫触角感觉器的扫描电镜观察[J].广西科学,2000,7(2):144-146,149.
[67] 郝家胜,殷先兵,苏成勇,等.12科国产蝶类代表种类触角的扫描电镜观察及其系统学意义[J].安徽师范大学学报(自然科学版),2007,30(3):354-360.
[68] 赵玉敏,姜秀,王艳萍.银斑豹蛱蝶触角感器的扫描电镜分析[J].通化师范学院学报,2007,28(10):38-39.
[69] 赵玉敏,王艳平.黄钩蛱蝶触角感器的扫描电镜观察[J].通化师范学院学报,2008,29(12):45-46,49.
[70] 吴利民,吕文彦,原国辉,等.菜粉蝶触角感器的扫描电镜观察[J].河南农业大学学报,2009,43(4):422-425.
