腹腔镜子宫肌瘤切除术的临床价值分析
2015-12-08江向洁
江向洁

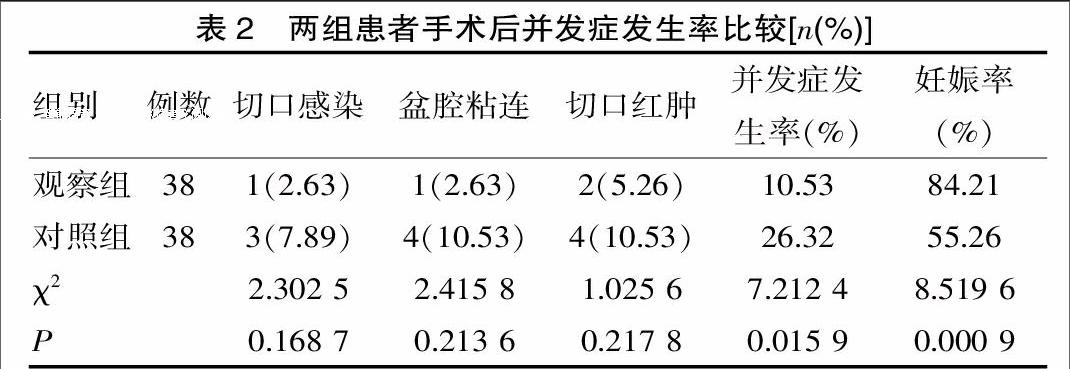
[摘要] 目的 探讨腹腔镜子宫肌瘤切除术的治疗效果及临床应用价值。 方法 整群选择该院2013年2月—2014年2月间收治的76例子宫肌瘤患者为研究对象,随机分为对照组38例,实施传统开腹子宫肌瘤切除术治疗,观察组38例,实施腹腔镜子宫肌瘤切除术治疗,对两组患者手术情况及术后恢复情况进行分析。 结果 观察组术手术时间较对照组长,但是术中出血量较低,术后排气时间及住院时间明显较对照组短,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组术后出现切口感染、盆腔粘连、切口红肿等并发症发生率为10.53%,较对照组26.32%低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),观察组术后妊娠率为84.21%,明显较对照组55.26%高(P<0.05)。 结论 子宫肌瘤采取腹腔镜子宫肌瘤切除术的创伤较小,并发症较少,可利于术后快速恢复,减少患者痛苦,提高术后妊娠率,值得推广。
[关键词] 子宫肌瘤;腹腔镜;开腹手术
[中图分类号] R5 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-0742(2015)09(c)-0059-03
[Abstract] Objective To study the therapeutic effect and clinical value of laparoscopic myomectomy. Methods 76 patients with uterine fibroids admitted to this hospital between February 2013 and February 2014 were randomized to undergo traditional open surgery (the control group, n=38) and laparoscopic myomectomy (the observation group,n=38). We analyzed the operation and postoperative recovery of the two groups. Results The operation duration was longer, but the intraoperative blood loss and postoperative exhaust time and hospital stay were shorter in the observation group than in the control group, and the differences were statistically significant, P<0.05; the rate of complications including incision infection, pelvic adhesion, incision inflammation(10.53% vs 26.32%) was lower in the observation group than in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant, P<0.05; the postoperative pregnancy rate (84.21% vs 55.26%) was significant higher in the observation group than in the control group with statistical difference, P<0.05. Conclusions With less trauma and complications, laparoscopic myomectomy in the treatment of uterine fibroids is conducive to rapid postoperative recovery and can reduce the patients' pain and improve pregnancy rate, therefore it is worthy of promotion.
[Key words] Uterine fibroids; Laparoscope; Open operation
子宫肌瘤是常见女性生殖器官良性肿瘤,患者主要表现为下腹坠胀、腹部包块、压迫及子宫出血。子宫肌瘤发病率极高,特别是中年女性,发病率达75%左右,严重影响女性的生活质量及生殖健康[1]。子宫肌瘤主要采取积极手术方案切除治疗,以往主要实施开腹切除术,创伤大,术后并发症较多,导致术后恢复较慢,不利于术后恢复。随着外科微创技术的不断发展,腹腔镜手术开始逐渐应用于临床,其创伤小,安全性高,作为首选子宫肌瘤手术方案[2]。该组研究对子宫肌瘤患者分别实施开腹手术及腹腔镜手术治疗,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
整群选择该院2013年2月—2014年2月收治的76例子宫肌瘤患者为研究对象,所有患者均符合《实用妇科学》[3]中子宫肌瘤诊断标准。随机分为对照组38例,观察组38例,观察组:年龄23~47岁,平均年龄(31.5±4.7)岁;孕次0~6次,平均孕次(2.3±0.5)次;单发肌瘤23例,多发肌瘤15例;对照组:年龄24~48岁,平均年龄(31.1±4.2)岁;孕次0~5次,平均孕次(2.6±0.7)次;单发肌瘤21例,多发肌瘤17例;纳入标准:符合子宫肌瘤诊断标准;与该组研究配合;18~60岁;排除标准:严重免疫性疾病及血液疾病者;心、肾、肝功能不全者;妊娠期、哺乳期女性。两组患者一般资料差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),存在可比性。
1.2 方法
两组患者均实施气管插管全麻,对照组:根据病灶位置选择切口,分离肌瘤系膜,直接切除,随后彻底止血、清洗腹腔,最后逐层缝合创口;观察组:取膀胱截石位,脐窝部纵形切口,置入套管及腹腔镜设备,分别取两侧操作孔,置入腹腔镜设备,使用6U垂体后叶素注入肌瘤切口部位,经纵轴切开肌瘤表面基层,直至瘤体,肌瘤作完整剥离后,使用双极电凝止血。瘤腔缝合时,使用可吸收线作切缘内翻卷折填充瘤窝缝合法,可起到压迫止血作用,保持创面平滑。
