冬凌草甲素对人肺癌A549和PC-9细胞侵袭的抑制作用和机制研究
2015-11-18王健周雯宋秀宇徐文贵黄纯
王健,周雯,宋秀宇,徐文贵,黄纯
冬凌草甲素对人肺癌A549和PC-9细胞侵袭的抑制作用和机制研究
王健1,周雯2△,宋秀宇1,徐文贵1,黄纯3
目的探讨天然产物衍生物冬凌草甲素对人肺癌细胞体外侵袭的抑制作用及其机制。方法冬凌草甲素处理人肺癌细胞系A549和PC-9后,应用细胞增殖实验(MTS)法检测肿瘤细胞生长,Transwell试验检测肿瘤侵袭能力,黏附试验检测肿瘤黏附能力,流式细胞术检测肿瘤细胞周期,Western blotting和Realtime-PCR检测细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶1(CDK1)、雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mTOR)、p53、p21、E-钙黏素(E-cadherin)、CD44、β-catenin、尿激酶型纤溶酶原激活物(uPA)、基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)-2/9、p-AKT和磷酸化酪氨酸激酶(p-Src)表达,报告基因技术考察核因子(NF)-κB转录活性。结果冬凌草甲素显著抑制A549和PC-9细胞的体外增殖、黏附和侵袭,将细胞周期阻滞在G2/M期,冬凌草甲素促进E-cadherin、p53和p21的表达,下调CDK1、mTOR、CD44、β-catenin、uPA、MMP-2/9、p-AKT和p-Src表达和NF-κB转录活性。结论冬凌草甲素可抑制人肺癌细胞系A549和PC-9的体外侵袭能力,可能与其调节酪氨酸激酶活性有关。
冬凌草素;肺肿瘤;肿瘤侵润;A549;PC-9
肺癌是我国一种常见的癌症,复发转移是其治疗的主要困难[1]。目前,对于晚期不能进行手术的患者仍然缺乏有效的治疗药物。研究发现,冬凌草甲素具有广泛且极其显著的抗肿瘤作用,但是其抑制肺癌的作用机制尚不清楚[2-3]。本研究重点考察冬凌草甲素对肺癌A549和PC-9细胞系体外侵袭的抑制作用,并对其分子机制进行初步探讨。
1 材料与方法
1.1 主要试剂与仪器人肺癌A549和PC-9细胞系购自中国科学院典型培养物保藏委员会细胞库(上海);单溶液细胞增殖检测试剂盒(MTS)、Realtime-PCR试剂盒、核因子(NF)-κB荧光素酶质粒和荧光素检测试剂盒购自Promega公司;冬凌草甲素购自Sigma-Aldrich公司;细胞周期和凋亡检测试剂盒购自BD Biosciences;各种单克隆抗体购自Santa Cruz公司;ECL免疫印迹底物试剂盒购自Millipore公司;细胞侵袭检测试剂盒购自R&D Systems公司。
1.2 细胞培养细胞培养于37℃、5%CO2、饱和湿度的培养箱中,培养基为DMEM,添加10%胎牛血清。0.25%胰酶-EDTA消化传代,所有实验均采用对数生长期细胞。
1.3 MTS细胞生长检测取对数生长期的细胞,以8×104个/mL接种于96孔微孔板中,每孔100 μL,培养过夜使细胞贴壁。分别加入0、0.5、1、2、5、10、20、50和100 μmol/L的冬凌草甲素,继续培养48 h,吸去培养基,按照试剂盒说明书的要求加入MTS,继续培养4 h。最后用酶标仪测定490 nm波长下的光密度(OD)值,以OD值表示细胞的数量。计算药物对细胞的抑制率。抑制率(IC)=(1-实验组OD值/对照组OD值)×100%。
1.4 细胞培养细胞分为对照组、8 μmol/L组和16 μmol/L组,后两组分别加入8 μmol/L和16 μmol/L冬凌草甲素,每个实验设置3个复孔,继续培养48 h,备用。
1.5 体外侵袭和黏附试验将肿瘤细胞接种Transwell的上室,同时加入备用细胞,洗去膜上未侵袭细胞,甲醛固定,HE染色,观察肿瘤细胞侵袭情况。侵袭率=(处理组细胞侵袭数/对照组细胞侵袭数)×100%。消化、离心,培养于包裹有Matrigel的96孔板1 h,加入MTS试剂孵育4 h,通过酶标仪在490 nm检测OD值,观察肿瘤细胞黏附情况。黏附率=(处理组OD值/对照组OD值)×100%。
1.6 细胞周期检测备用细胞经70%乙醇透化4℃过夜,洗涤后经含有RnaseA的PI染液孵育30 min,通过流式细胞术在490 nm检测荧光强度,观察细胞周期变化。
1.7 Western blotting实验收集备用细胞裂解提取蛋白。以12%SDS-PAGE法分离蛋白质,然后转移至PVDF膜上,以不同的抗体[细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶1(CDK1)、雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mTOR)、p53、p21、E-钙黏素(E-cadherin)、CD44、β-catenin、尿激酶型纤溶酶原激活物(uPA)、基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)-2和MMP-9为1∶1 500;p-AKT和磷酸化酪氨酸激酶(p-Src)为1∶1 000]4℃孵育过夜,洗去一抗后,以辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)连接的二抗(1∶2 000)温育1 h,洗涤,以增强化学发光法(ECL)试剂盒显示免疫反应条带。β-actin作为内参。
1.8 Realtime-PCR实验备用细胞用Trizol法提取各组总RNA,用Realtime-PCR试剂盒进行逆转录得到cDNA,然后检测mRNA水平,引物序列见表1。
1.9 报告基因实验将NF-κB荧光素酶质粒转染至细胞中,培养6 h,更换培养基,分别加入8 μmol/L和16 μmol/L冬凌草甲素,继续培养48 h,通过荧光素酶检测试剂盒检测细胞荧光强度,考察NF-κB转录活性变化。
1.10 统计学方法使用SPSS 13.0软件进行分析,以均数±标准差表示,采用单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA)进行比较,组间多重比较采用Turkey法,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。

Tab.1 The Real time PCR oligonucleotide sequences表1 Realtime PCR引物序列
2 结果
2.1 冬凌草甲素对A549和PC-9细胞的体外增殖作用冬凌草甲素可抑制A549和PC-9细胞的体外增殖,A549细胞半数抑制率(IC50)为21.3 μmol/L,PC-9细胞IC50为18.4 μmol/L,见图1。
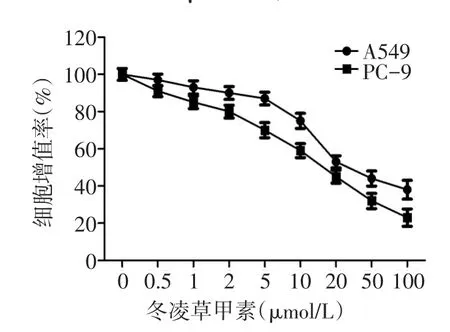
Fig.1 The inhibitory effects of oridonin on the proliferation of human lung cancer A549 and PC-9 cell lines in vitro图1 冬凌草甲素对人肺癌A549和PC-9细胞体外增殖的抑制作用
2.2 冬凌草甲素对A549和PC-9细胞的体外侵袭和黏附的抑制作用A549细胞体外侵袭和黏附能力3组间差异有统计学意义(F分别为97.216和272.727,均P<0.01)。与对照组比较,8 μmol/L和16 μmol/L组体外侵袭率分别为71.2%和53.8%,体外黏附率分别为62.1%和37.1%(均P<0.01)。PC9细胞体外侵袭和黏附能力3组间差异有统计学意义(F分别为145.787和78.830,P<0.01)。与对照组比较,8 μmol/L和16 μmol/L组体外侵袭能力分别下降65.5%和48.6%,体外黏附能力分别下降73.8%和56.5%(均P<0.01),见图2。
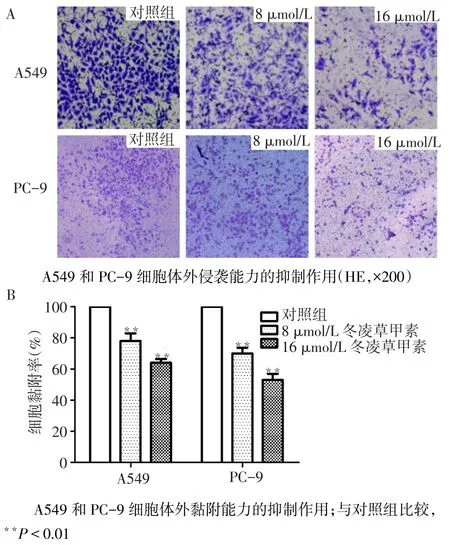
Fig.2 The inhibitory effects oridonin on the invasion and adhesion of human lung cancer A549 and PC-9 cell lines in vitro图2 冬凌草甲素对人肺癌A549和PC-9细胞体外侵袭和黏附的抑制作用
2.3 冬凌草甲素对A549和PC-9细胞阻滞作用流式细胞术结果显示,A549细胞和PC-9细胞冬凌草甲素处理组与对照组相比,G2/M期细胞的比例增加,且呈现剂量相关性,见表2、图3。
2.4 冬凌草甲素对A549和PC-9细胞中肿瘤相关基因、蛋白表达的影响Western blotting结果显示,A549细胞和PC-9细胞冬凌草甲素处理组与对照组相比,E-cadherin、p53和p21的表达上调,CD44、β-catenin、MMP-2、MMP-9、CDK1、mTOR、uPA、p-AKT和p-Src表达下调。Realtime-PCR结果显示,A549细胞和PC-9细胞冬凌草甲素处理组与对照组相比,E-cadherin、p53、p21 mRNA表达上调,CDK1、mTOR、CD44、β-catenin、uPA、MMP-2和MMP-9 mRNA表达下调,见图4。
2.5 冬凌草甲素对A549和PC-9细胞NF-κB转录活性的下调作用经过冬凌草甲素作用后,A549细胞和PC-9细胞NF-κB转录活性均显著下调,见表3。
Tab.2 The effects of different doses of oridonin on cell cycle of human lung cancer A549 and PC-9 cell lines表2 不同剂量冬凌草甲素对A549和PC-9细胞的细胞周期阻滞效果(n=3,%)
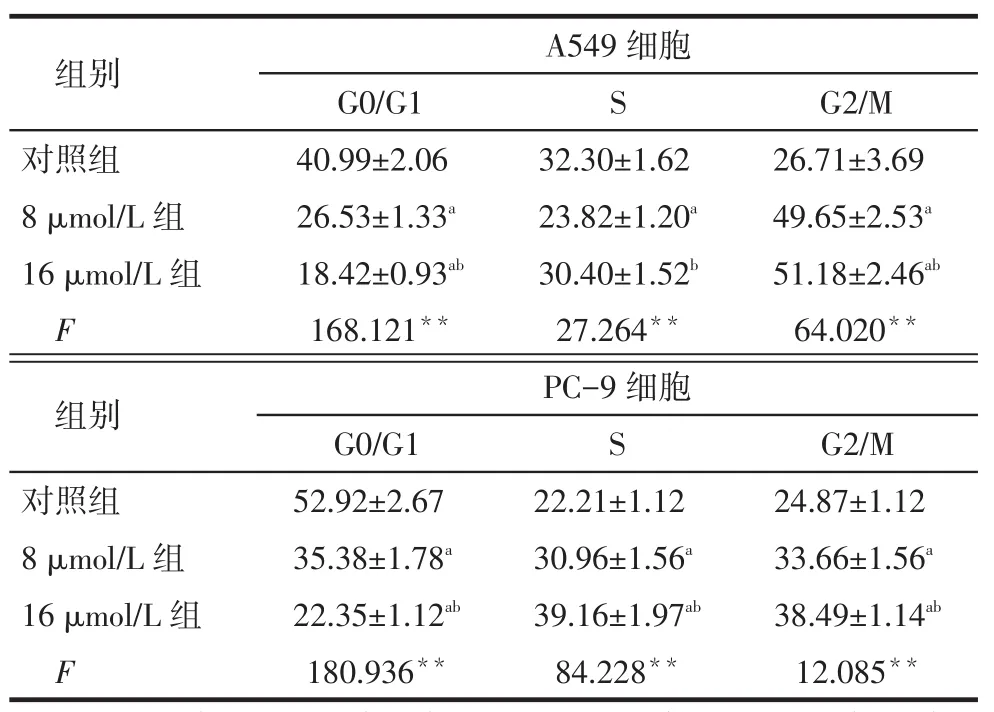
Tab.2 The effects of different doses of oridonin on cell cycle of human lung cancer A549 and PC-9 cell lines表2 不同剂量冬凌草甲素对A549和PC-9细胞的细胞周期阻滞效果(n=3,%)
**P<0.01;a与对照组比较,b与8 μmol/L组比较,P<0.05;表3同
组别对照组8 μmol/L组16 μmol/L组F A549细胞G0/G1 40.99±2.06 26.53±1.33a 18.42±0.93ab 168.121**S 32.30±1.62 23.82±1.20a 30.40±1.52b 27.264**G2/M 26.71±3.69 49.65±2.53a 51.18±2.46ab 64.020**组别对照组8 μmol/L组16 μmol/L组F PC-9细胞G0/G1 52.92±2.67 35.38±1.78a 22.35±1.12ab 180.936**S 22.21±1.12 30.96±1.56a 39.16±1.97ab 84.228**G2/M 24.87±1.12 33.66±1.56a 38.49±1.14ab 12.085**
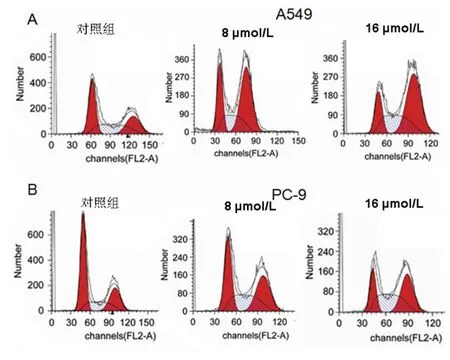
Fig.3 The effects of oridonin on cell cycle of human lung cancer A549 and PC-9 cell lines图3 冬凌草甲素对人肺癌A549和PC-9细胞周期的影响
3 讨论
冬凌草甲素是冬凌草中的主要活性成分,对前列腺癌、乳腺癌等多种细胞均有显著的抑制作用。最近研究发现,冬凌草甲素对肺癌细胞也有较强的抑制作用,但是其对肺癌细胞体外侵袭的抑制作用和机制尚不清晰。本研究发现,冬凌草甲素可显著抑制肺癌A549和PC9细胞体外增殖和侵袭。笔者采用较低浓度(8 μmol/L)和接近IC50浓度(16 μmol/ L)进行后续研究,用以考察不同浓度的药物对肿瘤侵袭的影响,并探讨其机制。
为探讨冬凌草甲素阻滞细胞周期的机制,笔者利用Western blotting和Realtime-PCR检测发现冬凌草甲素可上调肿瘤细胞中p53和p21的表达。p53和p21均是细胞周期的负调控蛋白,其中p21是细胞G1期所必需的细胞周期性激酶,可抑制CDK1、CDK2和CDK4/6的活性,具有更加广泛的作用,可将细胞阻滞在G1和S期[4-7],说明冬凌草甲素可能通过上调p53和p21的表达以实现对肿瘤细胞周期的抑制。
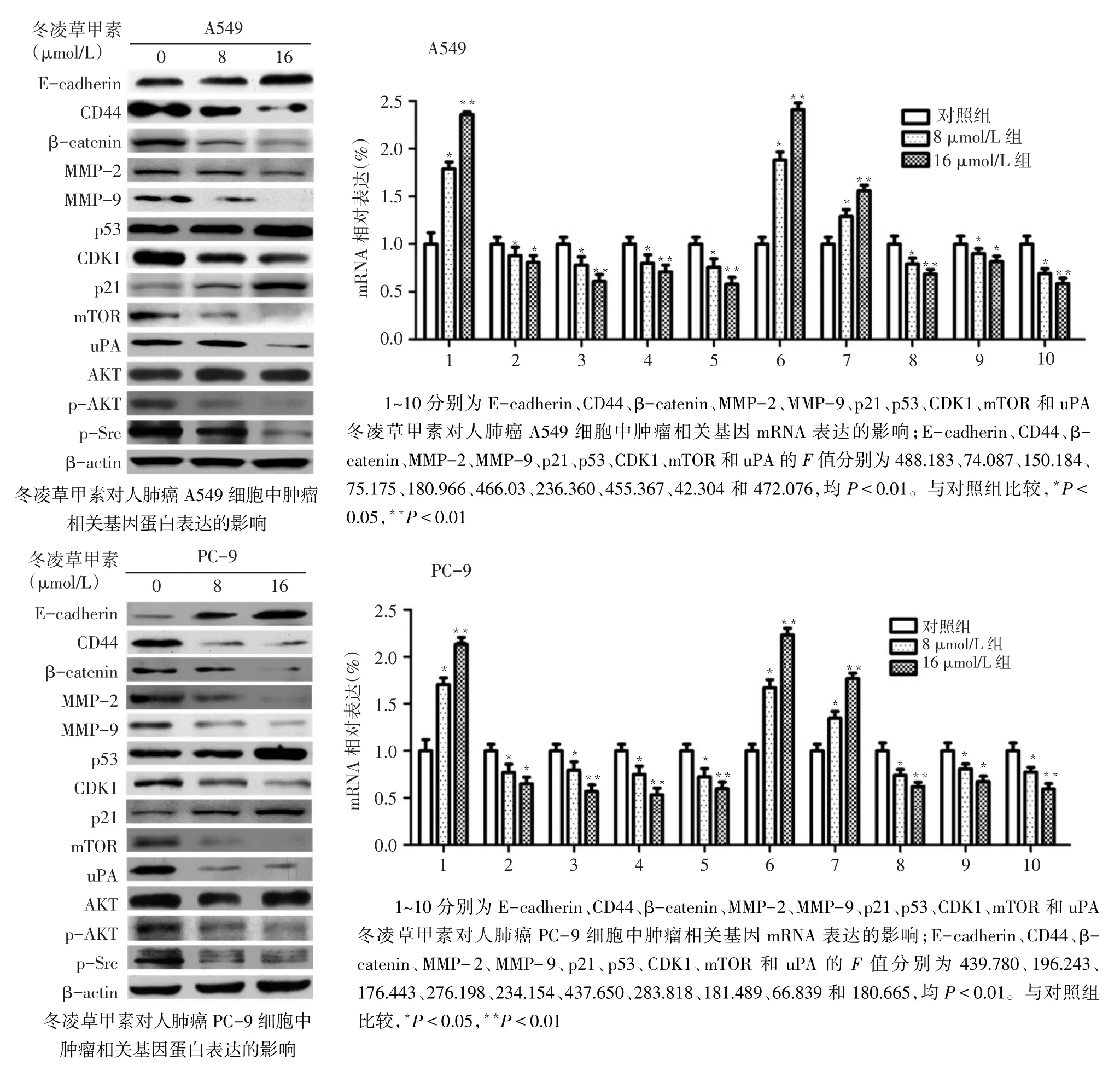
Fig.4 The effects of oridonin on the expression of tumor-related gene of human lung cancer A549 and PC-9 cell lines图4 冬凌草甲素对人肺癌A549和PC-9细胞中肿瘤相关基因表达的影响
Tab.3The effects of different doses of oridonin on promoter activity of NF-κB of human lung cancer A549 and PC-9 cell lines表3 不同剂量冬凌草甲素对A549和PC-9细胞NF-κB转录活性的影响(n=3,%,)
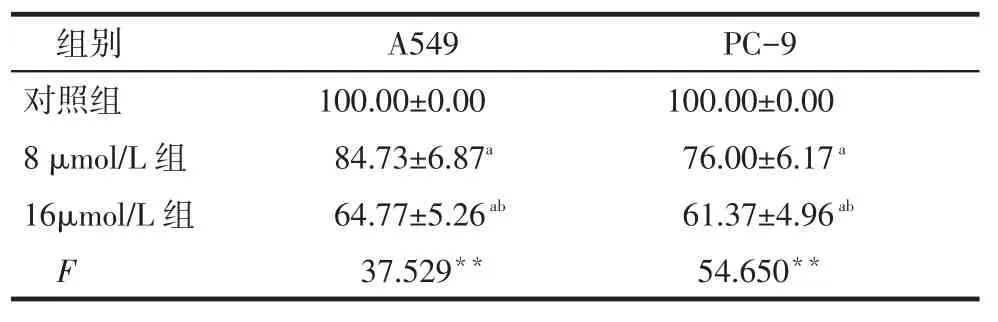
Tab.3The effects of different doses of oridonin on promoter activity of NF-κB of human lung cancer A549 and PC-9 cell lines表3 不同剂量冬凌草甲素对A549和PC-9细胞NF-κB转录活性的影响(n=3,%,)
组别对照组8 μmol/L组16μmol/L组F A549 100.00±0.00 84.73±6.87a64.77±5.26ab37.529**PC-9 100.00±0.00 76.00±6.17a61.37±4.96ab54.650**
本研究发现,冬凌草甲素还可下调肿瘤细胞中CD44和MMP-2/9表达,从而抑制肿瘤细胞异质黏附和基质穿透能力。uPA被证明与肿瘤发生发展和转移密切相关,酪氨酸激酶能催化多种蛋白酪氨酸残基磷酸化,在肿瘤细胞的发生发展过程中具有重要作用[8-10]。本研究发现冬凌草甲素还可以下调uPA表达和酪氨酸激酶活性,被认为是其抑制肿瘤侵袭的另一潜在机制。
β-catenin是Wnt/β-catenin信号通路中的关键调控因子,其过度活化可造成肿瘤等疾病[11]。AKT/ NF-κB信号通路对肺癌的进展发挥重要作用,是常见的肿瘤治疗靶点。mTOR是一种丝/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,受到AKT/NF-κB调控,抑制其活化可调控癌基因的转化[12-14]。本研究结果显示,冬凌草甲素可以调节AKT/NF-κB信号通路的活性,下调β-catenin和mTOR表达。
总之,本研究显示冬凌草甲素可抑制人肺癌A549和PC-9细胞增殖和侵袭,其机制可能与抑制酪氨酸激酶活性有关,今后将进一步深入探讨其对肿瘤抑制作用的机制,为临床应用提供实验基础。
[1]Leong D,Rai R,Nguyen B,et al.Advances in adjuvant systemic therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer[J].World J Clin Oncol,2014,5(4):633-645.doi:10.5306/wjco.v5.i4.633.
[2]Zhu M,Hong D,Bao Y,et al.Oridonin induces the apoptosis of met⁃astatic hepatocellular carcinoma cells via a mitochondrial pathway[J].Oncol Lett,2013,6(5):1502-1506.
[3]Li FF,Yi S,Wen L,et al.Oridonin induces NPM mutant protein translocation and apoptosis in NPM1c+acute myeloid leukemia cells in vitro[J].Acta Pharmacol Sin,2014,35(6):806-813.doi:10.1038/aps.2014.25.
[4]Chen HH,Almontashiri NA,Antoine D,et al.Functional genomics of the 9p21.3 locus for atherosclerosis:clarity or confusion[J]?Curr Cardiol Rep,2014,16(7):502.doi:10.1007/s11886-014-0502-7.
[5]Mungamuri SK,Yang X,Thor AD,et al.Survival signal-ing by Notch1:Mammalian target of rapamycin(mTOR)-dependent inhibition of p53[J].Cancer Res,2006,66(9):4715-4724.
[6]Nagathihalli NS,Merchant NB.Src-mediated regulation of E-cad⁃ herin and EMT in pancreatic cancer[J].Front Biosci,2012,17:2059-2069.
[7]Bernhart E,Damm S,Heffeter P,et al.Silencing of protein kinase D2 induces lung cancer cell senescence via p53-dependent andindependent pathways[J].Neuro Oncol,2014,16(7):933-945.doi:10.1215/15228517-2008-096.
[8]Chang JW,Kang SU,Shin YS,et al.Non-thermal atmospheric pres⁃sure plasma inhibits thyroid papillary cancer cell invasion via cyto⁃skeletal modulation,altered MMP-2/-9/uPA activity[J].PLoS One,2014,9(3):e92198.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0092198.
[9]Lee KR,Lee JS,Song JE,et al.Inonotus obliquus-derived polysac⁃charide inhibits the migration and invasion of human non-small cell lung carcinoma cells via suppression of MMP-2 and MMP-9[J].Int J Oncol,2014,45(6):2533-2540.doi:10.3892/ijo.2014. 2685.
[10]Hsieh SC,Tsai JP,Yang SF,et al.Metformin inhibits the invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells and enhances the chemo⁃sensitivity to sorafenib through a downregulation of the ERK/JNK-mediated NF-κB-dependent pathway that reduces uPA and MMP-9 expression[J].Amino Acids,2014,46(12):2809-2822.doi:10.1007/s00726-014-1838-4.
[11]Liu Y,Liu YZ,Zhang RX,et al.Oridonin inhibits the proliferation of human osteosarcoma cells by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signal⁃ing[J].Int J Oncol,2014,45(2):795-803.doi:10.3892/ijo.2014. 2456.
[12]Chang L,Graham PH,Hao J,et al.PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway inhibi⁃tors enhance radiosensitivity in radioresistant prostate cancer cells through inducing apoptosis,reducing autophagy,suppressing NHEJ and HR repair pathways[J].Cell Death Dis,2014,2(5):e1437.doi:10.1038/cddis.2014.415.
[13]Chan G,Kalaitzidis D,Neel BG.The tyrosine phosphatase Shp2(PTPN11)in cancer[J].Cancer Metastasis Rev,2008,27(2):179-192.doi:10.1007/s10555-008-9126-y.
[14]Eskander RN,Tewari KS.Exploiting the therapeutic potential of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway in enriched populations of gynecologic malignancies[J].Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol,2014,7(6):847-858. doi:10.1586/17512433.2014.968554.
(2015-05-29收稿2015-06-24修回)
(本文编辑魏杰)
The inhibitory effects and mechanisms of oridonin on invasion of human lung cancer A549 and PC9 cells
WANG Jian1,ZHOU Wen2△,SONG Xiuyu1,XU Wengui1,HUANG Chun3
1 Department of Molecular Imaging and Nuclear Medicine,Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital,National Clinical Research Center for Cancer,Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy,Tianjin 300060,China;2 Tianjin Key Laboratory on Technologies Enabling Development of Clinical Therapeutics and Diagnostics(Theranostics),School of Pharmacy,Tianjin Medical University;3 Department of Thoracic Medical Oncology,Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital△
ObjectiveTo investigate the inhibitory effects and mechanisms of a nature product derivate oridonin on in⁃vasion of human lung cancer.MethodsHuman lung cancer A549 and PC-9 cell lines were treated with oridonin.MTS as⁃say was used to determine cell proliferation.Transwell assay was used to determine the cell invasion,and adhesion assay to determine the cell adhesion.Flow cytometry was used to determine cell cycle.Western blotting and realtime-PCR were used to detect expression levels of CDK1,mTOR,p53,p21,E-cadherin,CD44,β-catenin,uPA,MMP-2/9,p-AKT and p-Src. The luciferase reporter assay was used to detect the NF-κB promoter activity.ResultsIn vitro proliferation,invasion and adhesion of A549 and PC-9 cells were significantly inhibited by oridonin.The cell cycle was halted by G2/M phase,and ex⁃pressions of E-cadherin,p53 and p21 were promoted,while expressions of CDK1,mTOR,CD44,β-catenin,uPA,MMP-2/ 9,p-AKT and p-Src and promoter activity of NF-κB were down-regulated.ConclusionOridonin is able to inhibit the in vitro invasion of human lung cancer A549 and PC-9 cell lines,which might be correlated with its abilities to regulate the ty⁃rosine kinase activity.
Rubescensine;lung neoplasms;neoplasm invasiveness;A549;PC-9
R734.2
A
10.11958/j.issn.0253-9896.2015.09.002
国家自然科学基金资助项目(81372467,81101776)
1天津医科大学肿瘤医院分子影像与核医学诊疗科、国家肿瘤临床医学研究中心、天津市"肿瘤防治"重点实验室(邮编300060);2天津市临床药物关键技术重点实验室、天津医科大学药学院;3天津医科大学肿瘤医院肺部肿瘤内科
王健(1981),男,主管药师,主要从事药物化学方面研究
△通讯作者E-mail:wwbzzl@sina.com
