免疫磁分离技术在食源性单增李斯特菌检测中应用的研究进展
2015-10-24黄小林许恒毅熊勇华
毛 燕,黄小林,许恒毅,熊勇华
(南昌大学食品科学与技术国家重点实验室,江西南昌330047)
免疫磁分离技术在食源性单增李斯特菌检测中应用的研究进展
毛 燕,黄小林,许恒毅,熊勇华*
(南昌大学食品科学与技术国家重点实验室,江西南昌330047)
食源性单增李斯特菌是李斯特菌属中的唯一能引起人类疾病的病原菌,致死率30%~70%,并严重威胁着人类健康。早期快速准确地检测出食品中可能污染的单增李斯特菌对于减少死亡率非常重要,因此亟需建立一些快速、灵敏和高特异性的检测方法。现有单增李斯特菌的检测方法对未经前增菌的食品样本检测灵敏度较低,限制了这些方法直接用于食品样本中单增李斯特菌的快速检测。免疫磁分离是一种可以短时间内高效富集样本中目的菌的技术,与常用的检测方法结合,可以缩短检测周期,提高检测灵敏度。本文综述了免疫磁分离技术在食源性单核细胞增生性李斯特检测中应用的研究进展。
单增李斯特菌,免疫磁分离技术,检测
单增李斯特菌(Listeria monocytogenes)是兼性厌氧的革兰氏阳性短杆菌,是李斯特菌属中唯一一种能引起人类和动物疾病的病原菌,感染后临床表现为脑膜炎、败血症、胃肠炎和流产等,死亡率较高[1-2]。1981年,加拿大首次报道了L.monocytogenes引起的食物中毒事件,随后在欧美其他国家也相继出现对此类事件的报道[3]。2011年美国有147人因食用了被L.monocytogenes污染的甜瓜而染病,其中33人死亡,1人流产[4]。因此,早期快速检测出食品中可能污染的L.monocytogenes对于预防由L.monocytogenes引起的食物中毒尤为重要。目前用于L.monocytogenes的检测方法主要包括基于前增菌、选择性平板分离以及生理生化鉴定的传统检测方法及基于免疫学和分子生物学的检测方法。然而,上述检测方法都需要对目的菌进行预增菌,以达到检测方法所需的最低检测浓度。但预增菌过程耗时较长,难以实现早期快速检测。近几年免疫磁分离技术(Immunomagnetic separation,IMS)被广泛应用于食源性致病菌的富集和分离。该技术可以对目的菌进行特异性捕获并在磁场下进行分离,从而达到较高的富集效率,缩短预增菌时间。此外,可以将目的菌从复杂的食品基质中分离出来,有效地消除了食品基质对后续检测的干扰。本文综述了免疫磁分离技术在食源性单增李斯特菌检测中应用的研究进展。
1 免疫磁分离技术(IMS)
免疫磁分离技术是70年代中期发展起来的一项免疫学技术,已被广泛应用于蛋白纯化、微生物富集和细胞纯化等方面。其原理是通过抗体(或抗原)包被磁珠,与目标抗原(或抗体)发生特异性免疫学反应,在外加磁场作用下将目标物从复杂的样本基质中分离出来。因此,免疫磁分离技术既具备了固相化试剂特有的优点(如较好的稳定性),又具备了免疫学反应的高度专一性。相对于传统细菌分离方法,免疫磁分离技术是一种利用抗体偶联于磁性粒子表面快速高效且特异性浓缩目的菌的新方法。使用该技术可以浓缩目的菌以达到检测方法的最低浓度,从而使目的菌不经预增菌被快速检出,最大程度降低致病菌污染引起的危害。目前,该技术与相关后续检测方法结合被广泛用于L.monocytogenes的检测,见图1。表1详细比较了结合IMS的检测方法在食源性致病菌检测中应用的优缺点。
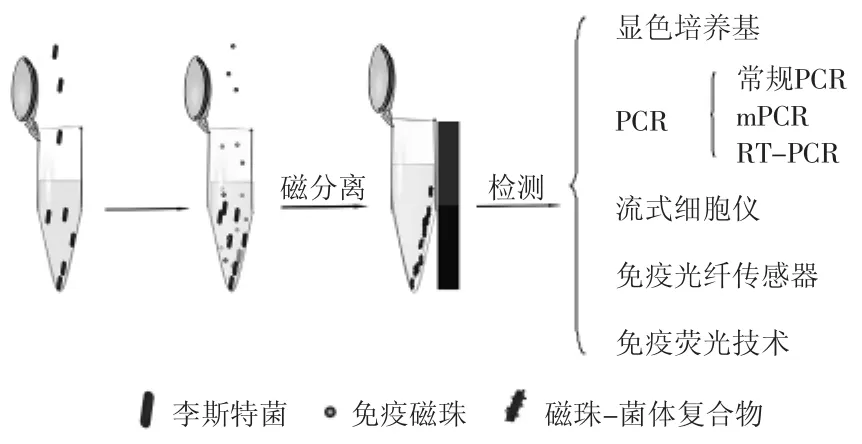
图1 IMS与其它技术结合用于检测单增李斯特菌Fig.1 IMS combined with other techniques for detecting Listeria monocytogenes
2 结合IMS的检测技术用于检测单增李斯特菌
2.1 IMS-显色培养基
显色培养基是利用微生物自身代谢产生的酶与相应显色底物反应显色的原理来检测微生物的新型培养基,利用显色培养基进行微生物的筛选分离,其反应的灵敏度和特异性远优于传统培养基。Wadud等[23]通过IMS结合ALOA显色培养基检测方便食品中污染的L.monocytogenes。检测时间为4d,最低检测限为1CFU/25g。同时Wen等[24]将IMS与显色培养基进行结合,对牛奶样本中的L.monocytogenes进行检测,检测时间30h,最低检测限达到0.7CFU/m L。两种方法结合检测时间较长,但检测灵敏度高。
2.2 IMS与PCR技术的结合
聚合酶链式反应(polymerase chain reaction,PCR)是一种可在体外快速扩增特定基因或DNA序列的技术,可短时间内获得数百万个特异DNA序列拷贝。该方法简单快速、灵敏度高、实用性强并能实现自动化,在基因工程研究、分子生物学研究以及对遗传病、恶性肿瘤和传染病的研究中得到广泛应用。近年来,随着IMS技术的逐渐成熟,其结合PCR技术也受到了广泛的关注。IMS结合PCR技术巧妙地将二者的优点结合在一起。即PCR方法良好的特异性与免疫磁珠良好的敏感性互相弥补,可提高PCR方法的灵敏度和特异性;此外,IMS通过抗体(或抗原)包被的免疫磁珠特异性地结合目标抗原或抗体,在外加磁场的作用下,将目标物从复杂的食品基质中分离出来,可有效地去除反应体系中对PCR具有抑制作用的抑制因子。IMS还可以起到浓缩目标物,缩短检测周期的作用。
2.2.1 IMS-PCR 一般PCR仅应用一对引物,通过PCR扩增产生一个核酸片段,可用于单一致病因子的鉴定。Hudson等[25]使用IMS分离火腿样本中污染的L.monocytogenes,结合常规PCR检测,结果发现,每1g样本中可检测出1.1个细菌,检测时间仅需24h。Wang等[26]通过IMS富集苹果汁中的A licyclobacillus acidoterrestris,结合常规PCR检测,得到最低检测限为2×101CFU/m L,且检测时间为3~4h。Moreira等[27]使用IMS-PCR技术分离检测猪肉和鸡肉样本中污染的S.typhimurium,结果发现,最低检测限为1~10CFU/25g,检测时间为27h。
2.2.2 IMS-RT-PCR 实时荧光定量PCR技术是在PCR反应体系中加入荧光染料或荧光探针,利用荧光信号积累实时监测整个PCR反应进程,通过标准曲线对未知模板进行定量分析,具有操作简便、快速高效、高通量及高敏感性等特点。此外,RT-PCR检测的是荧光信号的改变,省去凝胶电泳程序,避免实验过程中接触致癌物质,且缩短检测周期。IMS结合RT-PCR可用于L.monocytogenes定性及定量检测,其检测灵敏度较高。Yang等[28]将IMS与实时PCR技术结合用于检测牛奶样本中的L.monocytogenes,结果发现,检测灵敏度达102CFU/0.5m L。该研究还发现在103~107CFU/0.5m L范围内,由IMS结合实时PCR检测所得的菌落数比平板计数所得的菌落数高出1.5~7倍,表明通过IMS与实时PCR结合可提高样品中L.monocytogenes的检测灵敏度。同时这两种方法的结合在其他细菌的检测中也有应用。Ha等[29]通过IMS结合实时PCR检测植物和土壤样本中的Ralstonia solanacearum R3Bv2,结果发现,其最低检测限低于500个细菌/m L,且检测时间缩短到几小时。Li等[30]使用IMS结合实时PCR检测六种食品样本中Salmonella spp.,结果发现,有3h前增菌过程的检测限为0.6CFU/m L,而无前增菌过程的最低检测限也达到了60CFU/m L。
2.2.3 IMS-mPCR 多重PCR(multiplex PCR,mPCR),又称多重引物PCR或复合PCR,是在同一PCR反应体系里加上两对或两对以上引物,同时扩增出多个核酸片段的PCR反应,其反应原理、操作过程和反应试剂与常规PCR相同。多重PCR可用于多种致病菌的同时检测或鉴定,即在同一PCR反应管中同时加上多对特异性引物,进行扩增,可特异性的检测并鉴定出致病菌种类。Yang等[31]将IMS与mPCR技术结合检测加标的生菜、西红柿和碎牛肉中三种不同的细菌,结果发现,S.typhimurium、E.coli O157∶H7和L.monocytogenes的最低检测限分别为5.1×103、7.5×103CFU/g和8.4× 103CFU/g。Wang等[32]将IMS与mPCR结合同时定量检测牛肉样本中的E.coli O157∶H7、Salmonella和Shigella,结果发现,最低检测限分别为105、103CFU/g和104CFU/g。
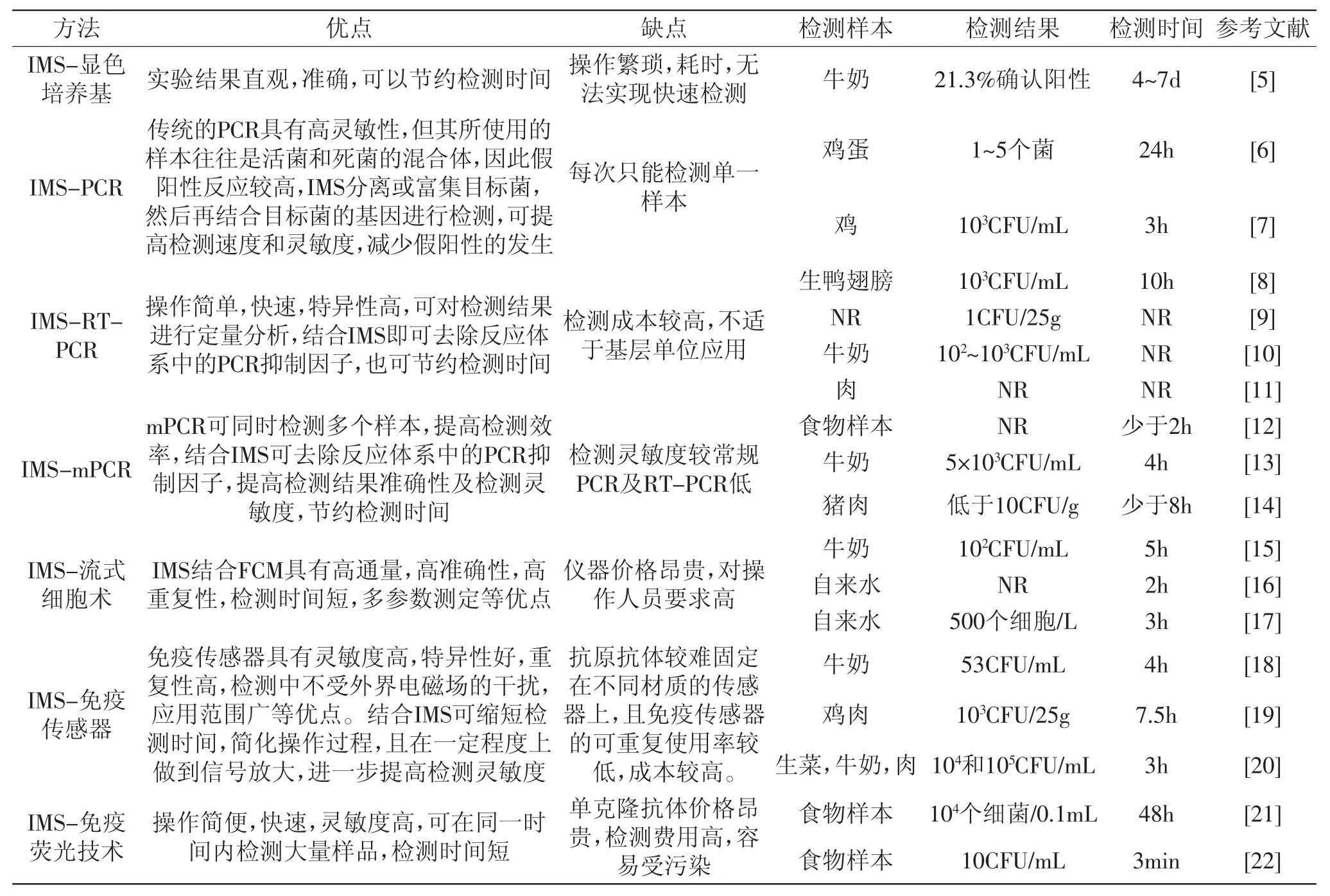
表1 结合IMS的检测方法在食源性致病菌检测中应用的比较Table 1 Comparision for IMS combining with other technologies for the detection of foodborne pathogen
2.3 IMS-流式细胞术
流式细胞术(flow cytometry,FCM)是一种在功能水平上对单细胞或其他生物粒子进行定量分析和分选的检测手段,通过检测标记的荧光信号,实现逐一和高速的细胞定量分析或分选的技术。FCM具有进行多参数分析、速度快等优点,是一种综合性方法。Kyoko等[33]将IMS与FCM技术结合分离检测食品样本中L.monocytogenes,结果发现,该方法的检测范围达102~108CFU/m L,且检测时间仅需1m in。
2.4 IMS-免疫传感器
免疫传感器的出现和发展正在促使免疫检测手段朝电器化、自动化、简便化和快速化方向发展。抗原与抗体的结合具有很高的特异性,从而减少了非特异性干扰,实时检测抗原抗体的反应,进行定量检测,即在抗原抗体反应的同时将反应连续记录下来,以便进行动态分析。IMS与免疫传感器相结合,可以提高灵敏度,降低检测限;减少分析时间;简化分析过程。Marcelo等[34]结合IMS与光纤免疫传感器在热狗中快速检测L.monocytogenes和L.innocua,结果发现,检测灵敏度为3×102CFU/m L。这两种方法的结合,对检测L.monocytogenes具有高效特异性,且可以在较低浓度下进行检测。
2.5 IMS-免疫荧光技术
免疫荧光技术(immunofluorescence technique)是在免疫学、生物化学以及显微镜技术的基础上发展起来的一项检测技术,用荧光标记的抗体或抗原与待测样品中相应的抗原或抗体进行结合,在显微镜下检测荧光强度,并对样品进行分析的方法。它把显微镜技术的精确性和免疫学检测的特异性、敏感性有机地结合。该方法特异性强、灵敏度高。作为一种快速检测方法,目前广泛应用于致病菌的检测。将IMS与免疫荧光检测技术进行结合检测致病菌,能极大的缩短检测时间,提高检测灵敏度。Cho等[35]将IMS与免疫荧光检测技术相结合,分别检测菠菜中的E.coli O157∶H 7、鸡肉中的S.typhimurium和牛奶中的L.monocytogenes,结果发现,这两种方法的结合极大的缩短了检测时间仅需2h,及低于5CFU/m L的高检测灵敏度。Wang等[36]将IMS与免疫荧光技术结合同时检测三种食源性致病菌(S.typhimurium,E.coli O157∶H 7,L.monocytogenes),检测时间低于2h,检测灵敏度低于20~50CFU/m L。
3 总结与展望
目前常用的L.monocytogenes的检测方法已有很多,大部分方法都需要对目标菌进行预增菌,使其达到检测方法所需的最低检测浓度。如何在食品基质中快速高效特异地分离出数量极少的食源性L.monocytogenes,实现对目标菌高特异性和高灵敏度的检测,是食品安全领域一个亟待突破的环节。
IMS技术在食源性致病菌检测中,作为一种可以短时高效富集基质中目的菌的技术,在一定程度上可以代替前增菌的过程。将IMS与各种常用的检测方法进行结合,可以达到缩短检测周期,提高灵敏度,增强特异性等作用,其优势不断体现,已被广泛应用于食源性致病菌的分离检测。但是,仍然还有许多值得改进的地方,例如IMS结合PCR技术的优化条件复杂,且优化获得的程序不具有通用性,其适用性被大大地限制;IMS与免疫学方法以及流式细胞术结合存在着仪器价格昂贵,操作要求高,实验材料制备复杂等问题。此外,在较复杂的食品基质中,IMS因磁场强度影响磁分离速度,分离效率以及IMS过程中磁性粒子对细菌体存在的潜在毒性等缺点也需要进一步研究[37]。另一方面,IMS结合其他的方法,如:拉曼增强[38-39]、免疫层析法[40]和免疫比浊法[41]等用于检测常见致病菌已有研究,然而针对L.monocytogenes的检测仍未报道,需要研究者们进一步探讨。
[1]ShoukatS,Malik SV S,RawoolDB,etal.A study on detection of pathogenic Listeria monocytogenes in ovine's of kashmir region faving abortion or history of abortion[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,India Section B:Biological Sciences,2014,84(2):311-316.
[2]Guha S,Klees M,Wang X,et al.Influence of planktonic and sessile Listeria monocytogenes on Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Archives of Microbiology,2013,195(1):19-26.
[3]李翠云.单核细胞李斯特菌研究近况[J].中国热带医学,2010,10(1):120-122.
[4]Lomonaco S,Verghese B,Gerner-Smidt P,et al.Novel epidemic clones of Listeria monocytogenes,United States,2011[J].Emerging Infectious Diseases,2013,19(1):147-150.
[5]Frece J,Markov K.Comparison of conventional and molecular methods for the routine confirmation of Listeria monocytogenes in milk products produced domestically in Croatia[J].Journal of Dairy Research,2010,77(1):112-116.
[6]JeníkováG,PazlarováJ,DemnerováK.Detection of Salmonella in food samples by the combination of immunomagnetic separation and PCR assay[J].International Microbiology,2010,3(4):225-229.
[7]Tram L L T,Cao C,HØgberg J,et al.Isolation and detection of Campylobacter jejuni from chicken fecal samples by immunomagnetic separation-PCR[J].Food Control,2012,24(1):23-28.
[8]Zheng Q,Mikš-Krajnik M,Yang Y,et al.Real-time PCR method combined with immunomagnetic separation for detecting healthy and heat-injured Salmonella Typhimurium on raw duck wings[J].International Journal of Food Microbiology,2014,186:6-13.
[9]Cheng J,Zeng J,Liu L,et al.The establishment of a noval method of nano-immunomagnetic separation and real-time PCR for detecting Vibrio choleraes from seafood[J].Chinese Journal of Preventive Medicine,2014,48(2):133-137.
[10]Walcher G,Stessl B,Wagner M,et al.Evaluation of paramagnetic beads coated with recombinant Listeria phage endolysin-derived cell-wall-binding domain proteins for separation of Listeria monocytogenes from raw milk in combination with culture-based and real-time polymerase chain reaction based quantification[J].Foodborne Pathogens and Disease,2010,7(9):1019-1024.
[11]Koo O K,Aroonnual A,Bhunia A K.Human heat-shock protein 60 receptor-coated paramagnetic beads show improved capture of Listeria monocytogenes in the presence of other Listeria in food[J].Journal of Applied Microbiology,2011,111(1):93-104.
[12]Ozalp V C,Bayramoglu G,Arica M Y,et al.Design of a core-shell type immuno-magnetic separation system andmultiplex PCR for rapid detection of pathogens from food samples[J]. AppliedMicrobiologyand Biotechnology,2013,97(21):9541-9551.
[13]Wang L,Li P,Yang Y,et al.Development of an immunomagnetic separation-propidium monoazide-polymerase chain reaction assay with internal amplification control for rapid and sensitive detection of viable Escherichia coli O157∶H7 in milk[J].International Dairy Journal,2014,34(2):280-286.
[14]Ma K,Deng Y,BaiY,etal.Rapid and simultaneous detection of Salmonella,Shigella,and Staphylococcus aureus in fresh pork using amultiplex real-time PCR assay based on immunomagnetic separation[J].Food Control,2014,42:87-93.
[15]Ikeda M,Yamaguchi N,Nasu M.Rapid on-chip flow cytometric detection of Listeria monocytogenes inmilk[J].Journal of Health Science,2009,55(5):851-856.
[16]Keserue H A,Baumgartner A,Felleisen R,et al.Rapid detection of total and viable Legionella pneumophila in tap water by immunomagnetic separation,double fluorescent staining and flow cytometry[J].Microbial Biotechnology,2012,5(6):753-763.
[17]Füchslin H P,Kötzsch S,Keserue H A,et al.Rapid and quantitative detection of Legionella pneumophila applying immunomagnetic separation and flow cytometry[J].Cytometry Part A,2010,77(3):264-274.
[18]Shen Z Q,Wang J F,Qiu Z G,et al.QCM immunosensor detection of Escherichia coli O157∶H7 based on beacon immunomagnetic nanoparticles and catalytic growth of colloidal gold[J].Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2011,26(7):3376-3381.
[19]Park M K,Oh JH.Immunomagnetic bead separation coupled with a dithiobis-succinimidyl propionate(DSP)-modified immunosensor to detect Listeria monocytogenes in chicken skin[J].Journal of the Electrochemical Society,2014,161(12):B237-B242.
[20]Kanayeva D A,Wang R,Rhoads D,etal.Efficient separation and sensitive detection of Listeria monocytogenes using an impedance immunosensor based on magnetic nanoparticles,a microfluidic chip,and an interdigitated microelectrode[J].Journal of Food Protection®,2012,75(11):1951-1959.
[21]Lee W,Kwon D,Chung B,et al.Ultra-rapid detection of pathogenic bacteria using a 3D Iimmunomagnetic flow assay[J]. Analytical Chemistry,2014,86(13):6683-6688.
[22]Cavaiuolo M,Paramithiotis S,Drosinos E H,et al. Development and optimization of an ELISA based method to detect Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli O157 in fresh vegetables[J].Analytical Methods,2013,5(18):4622-4627.
[23]Wadud Shaila,Carlos G Leon-Velarde,Nathan Larson,etal. Evaluation of immunomagnetic separation in combination with ALOA Listeria chromogenic agar for the isolation and identification of Listeria monocytogenes in ready-to-eat foods[J].Journal of Microbiological Methods,2010,81(2):153-159.
[24]闻一鸣,李志清,童吉宇,等.免疫磁珠富集技术联合选择性培养基快速检测单增李斯特菌[J].Chinese Journal of Biotechnology,2013,29(5):672-680.
[25]Hudson JA,Lake R J,Savill M G,et al.Rapid detection of Listeria monocytogenes in ham samples using immunomagnetic separation followed by polymerase chain reaction[J].Journal of Applied Microbiology,2001,90(4):614-621.
[26]Wang Z,Wang J,Yue T,et al.Immunomagnetic separation combined with polymerase chain reaction for the detection of Alicyclo bacillus acidoterrestris in apple juice[J].PloS One,2013,8(12):e82376.
[27]MoreiraÂN,Conceição FR,Conceição RdCS,etal.Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium in rawmeatsusing in-house prepared monoclonal antibody coated magnetic beads and PCR assay of the fimA gene[J].Journalof Immunoassay and Immunochemistry,2007,29(1):58-69.
[28]Yang H,Qu L,Wimbrow AN,et al.Rapid detection of Listeria monocytogenes by nanoparticle-based immunomagnetic separation and real-time PCR[J].International Journal of Food Microbiology,2007,118(2):132-138.
[29]Ha Y,Kim JS,Denny TP,etal.A rapid,sensitive assay for Ralstonia solanacearum race 3 biovar 2 in plant and soil samples using magnetic beads and real-time PCR[J].Plant Disease,2012,96(2):258-264
[30]Li A,Zhang H,Zhang X,et al.Rapid separation and immunoassay for low levels of Salmonella in foods using magnetosome-antibody complex and real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR[J].Journal of Separation Science,2010,33(21):3437-3443.
[31]Yang Y,Xu F,Xu H.et al.Magnetic nano-beads based separation combined with propidium monoazide treatment and multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of viable Salmonella Typhimurium,Escherichia coli O157∶H7 and Listeria monocytogenes in food products[J].Food Microbiol,2013,34(2):418-424.
[32]Wang L,Li Y,Mustapha A.Rapid and simultaneous quantitation of Escherichia coli O157∶H7,Salmonella,and Shigella in ground beef by multiplex real-time PCR and immunomagnetic separation[J].Journal of Food Protection,2007,70(6):1366-1372.
[33]Hibi K,Abe A,Ohashi E,et al.Combination of immunomagnetic separation with flow cytometry for detection of Listeria monocytogenes[J].Analytica Chimica Acta,2006,573:158-163.
[34]Mendonça M,Conrad N L,Conceição F R,et al.Highly specific fiber optic immunosensor coupled with immunomagnetic separation for detection of low levels of Listeria monocytogenes and L.ivanovii[J].BMCMicrobiology,2012,12(1):275.
[35]Cho I H,Mauer L,Irudayaraj J.In-situ fluorescent immunomagnetic multiplex detection of foodborne pathogens in very low numbers[J].Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2014,57:143-148.
[36]Wang H,Li Y,Wang A,et al.Rapid,sensitive,and simultaneous detection of three foodborne pathogens using magnetic nanobead-based immunoseparation and quantum dotbased multiplex immunoassay[J].Journal of Food Protection,2011,74(12):2039-2047.
[37]黄小林,许恒毅,熊勇华,等.磁性纳米材料在食源性致病菌分离中应用的研究进展[J].食品科学,2014,35(11):280-285.
[38]Sundaram J,Park B,Kwon Y,etal.Surface enhanced raman scattering(SERS) with biopolymer encapsulated silver nanosubstrates for rapid detection of foodborne pathogens[J]. International Journalof Food Microbiology,2013,167(1):67-73.
[39]Banerjee P.Development of a single assay comprising nanoimmunomagnetic separation of Escherichia coli O157∶H7 from apple juice followed by surface enhanced raman scattering based detection[C].2014 Annual Meeting Iafp,2014.
[40]钟珍.免疫层析法结合免疫磁分离技术在大肠杆菌检测中的应用[D].广州:暨南大学,2010.
[41]肖敏,易勇,毛旭虎,等.免疫磁分离及免疫比浊分析对福氏志贺菌的自动快速定量检测[J].免疫学杂志,2009(3):341-345.
Research advance on immunomagnetic separation for detection of foodborne Listeria monocytogenes
MAO Yan,HUANG Xiao-lin,XU Heng-yi,XIONG Yong-hua*
(State Key Laboratory of Food Science and Technology,Nanchang University,Nanchang 330047,China)
Listeria monocytogenes was the only human foodborne pathogen of Listeria,which was responsiblefor listeriosis with high mortality rate of 30% to 70%. Early prevention for L. monocytogenes was of the utmostimportance to reduce the disease mortality. Therefore,it was required to achieve the detection methods withrapidity,sensitivity and high specificity. Detection sensitivity of existing detection methods for L. monocytogeneswas low in food samples without pre-enrichment,limiting these methods directly used for rapid detection ofL. monocytogenes. Immunomagnetic separation was a technology which could efficiently enrich target bacteriain the sample within short time. This technology combined with commonly used detection methods could shortenthe detection period and improve the detection sensitivity. Recent advance of the application of immunomagneticseparation technology for the detection of foodborne L. monocytogenes was reviewed in this paper.
Listeria monocytogenes;immunomagnetic separation;detection
TS207.4
A
1002-0306(2015)08-0351-05
10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2015.08.065
2014-06-19
毛燕(1990-),女,硕士研究生,研究方向:免疫磁分离。
*通讯作者:熊勇华(1970-),男,博士,研究员,研究方向:食品生物技术。
国家自然科学基金资助项目(81201691,31271863);“十二五”国家科技支撑计划项目(2011BAK10B06);高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金(20123601120005);江西省教育厅基金资助项目(GJJ13093)。
