颈部彩色多普勒超声、CT血管成像与数字减影血管造影诊断颈内动脉狭窄、斑块形态及溃疡的准确性比较
2015-09-19张圆圆孟秀君田沈车玉琴林巧颜丙旺
张圆圆,孟秀君,田沈,车玉琴,林巧,颜丙旺
颈部彩色多普勒超声、CT血管成像与数字减影血管造影诊断颈内动脉狭窄、斑块形态及溃疡的准确性比较
张圆圆,孟秀君,田沈,车玉琴,林巧,颜丙旺
目的以数字减影血管造影(DSA)为金标准,分析彩色多普勒超声(CDUS),CT血管成像(CTA)对颈内动脉狭窄、斑块形态及溃疡诊断的准确性。方法采用回顾性分析方法,收集中国医科大学附属第四医院2009—2014年收治的经DSA检查确诊的颈内动脉狭窄患者168例,并先后行CDUS、CTA检查。用Pearson相关性分析CDUS、CTA检查颈内动脉狭窄率与DSA检查颈内动脉狭窄率的相关性;以DSA为金标准,计算CDUS、CTA诊断颈内动脉狭窄率≥70%、斑块形态、是否有溃疡的正确率、灵敏度、特异度、阳性预测值和阴性预测值;ROC曲线和ROC曲线下面积(AUC)分析CDUS、CTA检查对斑块形态和溃疡检测的准确性;Kappa检验分析CDUS、CTA检查与DSA检查的一致性。结果CDUS(64.73±22.91)%、CTA(62.38±22.31)%检查颈内动脉狭窄率与DSA(62.52 ±22.31)%检查颈内动脉狭窄率均呈正相关(r值分别为0.922和0.992,P<0.05)。DSA确诊患者颈内动脉狭窄率≥70%的血管条数为146条,<70%的血管条数为190条。CDUS、CTA检查颈内动脉狭窄率≥70%的正确率分别为85.7%(288/336)、95.8%(322/336),灵敏度分别为83.6%(122/146)、94.5%(138/146),特异度分别为87.4%(166/190)、96.8%(184/190),阳性预测值分别为83.6%(122/146)、95.8(138/144)%,阴性预测值分别为87.4%(166/190)、95.8%(184/192)。CDUS、CTA检查诊断颈内动脉狭窄率≥70%的Kappa值分别为0.709、0.915。DSA确诊患者颈内动脉规则型斑块的血管条数为168条,不规则型斑块的血管条数为168条;DSA确诊患者颈内动脉有溃疡的血管条数为68条,无溃疡的血管条数为268条。CDUS、CTA检查颈内动脉斑块形态的正确率分别为82.7%(278/336)、99.1%(333/336),灵敏度分别为84.8%(144/168)、98.8%(166/168),特异度分别为79.8%(134/168)、99.4%(167/168),阳性预测值分别为80.9%(144/178)、99.4%(166/167),阴性预测值分别为84.8%(134/158)、99.4%(167/169);CDUS、CTA检查颈内动脉斑块形态的Kappa值分别为0.655、0.982。CDUS、CTA检查颈内动脉溃疡的正确率分别为88.7%(298/336)、98.5%(331/336),灵敏度分别为85.3%(58 /68)、94.0%(64/68),特异度分别为89.6%(240/268)、99.6%(267/268),阳性预测值分别为67.4%(58/86)、98.5%(64/65),阴性预测值分别为96.0%(240/250)、98.5%(267/271)。CDUS检查诊断颈内动脉不规则斑块AUC为0.818〔95%CI(0.711,0.866)〕,CTA检查诊断颈内动脉不规则斑块AUC为0.997〔95%CI(0.923,1.000)〕;CDUS检查诊断颈内动脉溃疡AUC为0.708〔95%CI(0.633,0.788)〕,CTA检查诊断颈内动脉溃疡AUC为0.969〔95%CI(0.934,1.000)〕。CDUS、CTA检查诊断颈内动脉溃疡的Kappa值分别为0.681、0.953。结论CTA检查对于颈内动脉狭窄率≥70%,不规则斑块和有溃疡的诊断具有简单可行且正确率高的优点,较CDUS占有明显优势,与金标准DSA诊断的准确性具有高度一致性,在一定情况下可代替DSA检查,避免其有创性和潜在的危险性。
颈动脉狭窄;超声检查,多普勒,彩色;体层摄影术,螺旋计算机;血管造影术,数字减影;灵敏度;特异度
张圆圆,孟秀君,田沈,等.颈部彩色多普勒超声、CT血管成像与数字减影血管造影诊断颈内动脉狭窄、斑块形态及溃疡的准确性比较[J].中国全科医学,2015,18(30):3763-3768.[www.chinagp.net]
Zhang YY,Meng XJ,Tian S,et al.Accuracy of carotid CDUS,CTA and DSA in the diagnosis of internal carotid artery stenosis,plaque morphology and ulcer:a comparative study.[J].Chinese General Practice,2015,18(30):3763-3768.
脑卒中是当今世界上导致死亡的第3大疾病,是致肢体瘫痪的主要原因,在西方国家每年大约有2亿的患者因为脑血管缺血导致永久性肢体瘫痪,其中25%的患者由颈动脉狭窄或闭塞引起[1]。颈动脉硬化是颈内动脉狭窄的主要原因,斑块逐渐增大或脱落均可导致脑缺血的发生。早期发现颈内动脉狭窄,对狭窄程度和斑块特征做出准确诊断,并采取积极有效的治疗,对预防脑卒中的发生有重要意义。按照北美症状性颈动脉内膜切除术试验(north American symptomatic carotid endarterectomy trial,NASCET),颈内动脉剥脱术治疗Ⅳ度颈内动脉狭窄(70%~99%)[2]或选择性治疗Ⅲ度颈内动脉狭窄(50%~69%)患者[3],对降低脑血管缺血事件的发生有重要意义。有研究强调,脑血管缺血事件的发生不仅要强调血管狭窄的程度,同时要注意造成血管狭窄斑块的形态学特征(斑块是否有溃疡或裂隙),是否导致自身斑块脱落,引起脑血管事件的发生[4-6]。以上因素均需考虑在内才能更好地预防和治疗脑血管事件。数字减影血管造影(digital subtractionangiography,DSA)是血管影像诊断的“金标准”,包含头颈动脉狭窄的诊断。但是DSA作为一种侵入性的、有创的诊断方法,会导致多种并发症的发生,如造影剂可造成肾功能及神经损伤。有报道发现,DSA有0.3%~5.7%的致残率和<0.1%的病死率[7]。因此,对于颈内动脉狭窄的诊断,由DSA为主逐渐被无创伤性的彩色多普勒超声(colour Doppler ultrasonography,CDUS)、CT血管成像(computed tomography angiography,CTA)、磁共振血管造影(MR angiography,MRA)代替,并通过这些无创的检查手段检测斑块是否规则、是否有溃疡及斑块的成分,来判断斑块的稳定性,进一步明确诊疗方案,为患者提供有效的治疗[8-9]。本研究以DSA为金标准,分析比较CDUS、CTA诊断颈内动脉狭窄、斑块形态和溃疡的准确性。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料回顾性分析中国医科大学附属第四医院于2009—2014年收治的经DSA检查确诊的颈内动脉狭窄患者168例,并先后行CDUS、CTA检查,其中男104例,女64例;年龄36~82岁,平均年龄(68.0±6.0)岁。体质指数(27.0 ±1.6)kg/m2,血糖水平(98±49) mg/d l,总胆固醇水平(214±92) mg/d l,高密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平(55 ±10)mg/dl,低密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平(158±43)mg/dl。医生对患者进行详细的术前交代,并签署手术或有创操作同意书。
1.2 检测方法
1.2.1 CDUS检查采用PHILLIPSHD11为主的多种彩色多普勒诊断仪,探头频率设为8~14 MHz。嘱患者平卧,充分暴露颈部,自下而上分别观察、测量并记录两侧颈内动脉颅外段的血管走行、血流充盈情况,着重观察颈内动脉内径和内-中膜厚度、管腔内有无斑块(若出现斑块,记录斑块形态、大小及回声特征)。
1.2.2 CTA检查采用64排GECT,扫描范围为从主动脉弓平面向上扫描至头顶,扫描条件为120 kV/240 mA,矩阵512×512,层厚1.0 mm,螺距1.375∶1,重建层厚0.5 mm,常规平扫后经右侧肘静脉注射非离子型对比剂碘海醇注射液
2 结果
(欧乃派克,350 mgI/m l、注射速率4 m l/s)作增强扫描。
1.2.3 DSA检查应用SIEMENSAXIOM dTA血管造影机进行血管造影检查,嘱患者平卧,充分暴露双侧腹股沟区,常规消毒铺巾,2%利多卡因局部麻醉,采用sledinger技术穿刺股动脉,置入5 F导管鞘,经导管鞘在导丝导引下送入5 F猪尾巴管造影主动脉弓,采集颈内动脉造影图像,更换5F椎动脉管造影左、右侧锁骨下动脉、椎动脉,观察是否有管腔狭窄及斑块、闭塞等,若发现有动脉狭窄,计算狭窄率,记录斑块形态及有无溃疡。
1.3 诊断标准根据NASCET标准[10]评估颈内动脉狭窄程度,狭窄率(%) =(1-最狭窄处直径/狭窄远端动脉直径)×100%。斑块形态:不规则型为不可准确测得的管壁不均匀性斑块,表面结节状高低不平或伴有管壁多发不规则尖角状突起,规则型无上述表现;溃疡为斑块形成明显的局限性腔内充盈缺损或充盈缺损内可见龛影[11]。
1.4 观察指标分别记录CDUS检查、CTA检查和DSA检查时间;记录颈内动脉狭窄率、斑块形态、是否有溃疡及不良反应。
1.5 统计学方法采用SPSS 17.0软件对数据进行统计分析,采用Pearson相关性分析CDUS、CTA检查颈内动脉狭窄率与DSA检查颈内动脉狭窄率的相关性;以DSA为金标准,计算CDUS、CTA检查诊断颈内动脉狭窄率≥70%、斑块形态、是否有溃疡的正确率、灵敏度、特异度、阳性预测值和阴性预测值;应用ROC曲线和ROC曲线下面积(AUC)分析CDUS、CTA检查对斑块形态和是否有溃疡诊断的准确性(注:AUC>0.900表示诊断正确率较高,0.700<AUC≤0.900表示诊断正确率中等,AUC≤0.700表示诊断正确率较低);采用Kappa检验分析CDUS、CTA检查与DSA检查的一致性(Kappa值≥0.700表示一致性程度极高,0.400<Kappa值<0.700表示一致性程度较高,Kappa值≤0.400表示一致性程度差)。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2.1 CDUS检查、CTA检查和DSA检查
CDUS平均检查时间为(14±2)min,CTA平均检查时间为(16±3)min,DSA平均检查时间为(50±4)min;DSA、CDUS、CTA检查平均间隔时间为(6 ±3)d。行DSA检查注射造影剂后14例出现不良反应,其中7例出现穿刺点血肿,5例出现造影剂轻-中度不良反应(皮疹、一过性胸闷、血压低),2例大脑局部缺血;行CTA检查注射造影剂后9例患者出现轻度不良反应(皮疹、恶心、脸红),1例出现中度不良反应(哮喘)。造影剂引起的不良反应通过注射地塞米松或泼尼松后治愈。大脑局部缺血通过住院治疗,7 d后出院。穿刺点血肿压迫后自行吸收。
2.2 CDUS检查、CTA检查颈内动脉狭窄CDUS(64.73±22.91)%、CTA (62.38±22.31)%检查颈内动脉狭窄率与DSA(62.52±22.31)%检查颈内动脉狭窄率均呈正相关(r值分别为0.922和0.992,P<0.05,见图1)。DSA确诊患者颈内动脉狭窄率≥70%的血管条数为146条,<70%的血管条数为190条。CDUS、CTA检查颈内动脉狭窄率≥70%的正确率分别为85.7%(288/336)、95.8%(322/336),灵敏度分别为83.6%(122/146)、94.5%(138/146),特异度分别为87.4%(166/190)、96.8%(184/190),阳性预测值分别为83.6%(122/146)、95.8(138/144)%,阴性预测值分别为87.4%(166/190)、95.8%(184/192)(见表1、2)。CDUS、CTA检查诊断颈内动脉狭窄率≥70%的Kappa值分别为0.709、0.915。

表1 CDUS检查诊断颈内动脉狭窄率≥70%的四格表Table 1 Four fold table of the diagnosis of internal carotid artery stenosis degree≥70%by CDUS
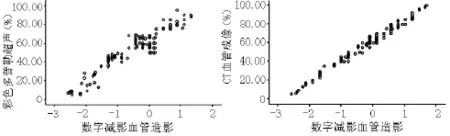
图1 CDUS、CTA检查颈内动脉狭窄率与DSA检查颈内动狭窄率相关性散点图Figure1 Linear regression of the correlation between the rates of artery stenosis diagnosed by CDUSand CTA and the rate of artery stenosis diagnosed by DSA
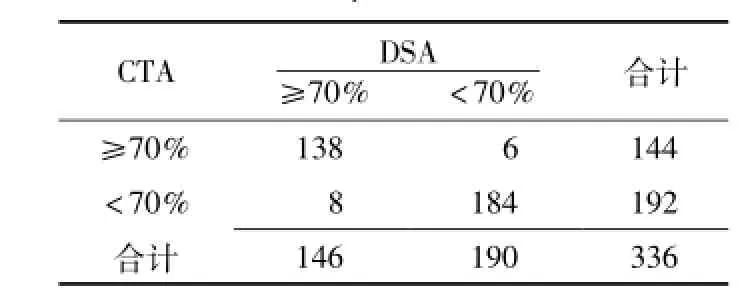
表2 CTA检查诊断颈内动脉狭窄率≥70%的四格表Table 2 Four fold table of the diagnosis of internal carotid artery stenosis degree≥70%by CTA
2.3 CDUS、CTA检查颈内动脉斑块形态和溃疡DSA确诊患者颈内动脉规则型斑块的血管条数为168条,不规则型斑块的血管条数为168条;DSA确诊患者颈内动脉有溃疡的血管条数为68条,无溃疡的血管条数为268条。CDUS、CTA检查颈内动脉斑块形态的正确率分别为82.7%(278/336)、99.1%(333/336),灵敏度分别为84.8%(144/168)、98.8%(166/168),特异度分别为79.8%(134/168)、99.4%(167/168),阳性预测值分别为80.9%(144/178)、99.4%(166/167),阴性预测值分别为84.8%(134/158)、99.4%(167/169) (见表3、4);CDUS、CTA检查颈内动脉斑块形态的Kappa值分别为0.655、0.982。CDUS、CTA检查颈内动脉溃疡的正确率分别为88.7%(298/336)、98.5%(331/336),灵敏度分别为85.3%(58/68)、94.0%(64/68),特异度分别为89.6%(240/268)、99.6% (267/268),阳性预测值分别为67.4% (58/86)、98.5%(64/65),阴性预测值分别为96.0%(240/250)、98.5% (267/271)(见表5、6)。CDUS检查诊断颈内动脉不规则斑块AUC为0.818〔95%CI(0.711,0.866)〕,CTA检查诊断颈内动脉不规则斑块AUC为0.997〔95%CI(0.923,1.000)〕(见图2A); CDUS检查诊断颈内动脉溃疡AUC为0.708〔95%CI(0.633,0.788)〕,CTA检查诊断颈内动脉溃疡AUC为0.969〔95%CI(0.934,1.000)〕(见图2B)。CDUS、CTA检查诊断颈内动脉溃疡的Kappa值分别为0.681、0.953。
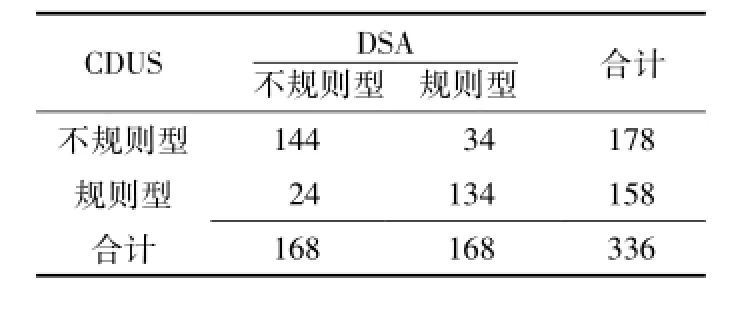
表3 CDUS检查诊断颈内动脉斑块形态四格表Table 3 Evaluation of irregular internal carotid plaque morphology CDUS versus DSA.Values are expressed as number of cases
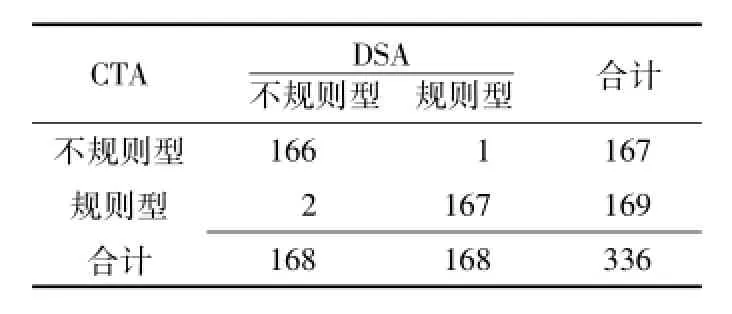
表4 CTA检查诊断颈内动脉斑块形态四格表Table 4 Evaluation of irregular internal carotid plaque morphology CTA versus DSA.Values are expressed as number of cases
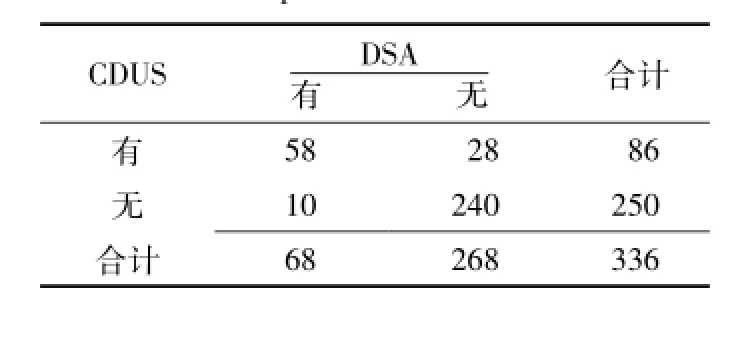
表5 CDUS检查诊断颈内动脉溃疡四格表Table 5 Evaluation of internal carotid plaque ulcers with CDUS versus DSA.Values are expressed as number of cases
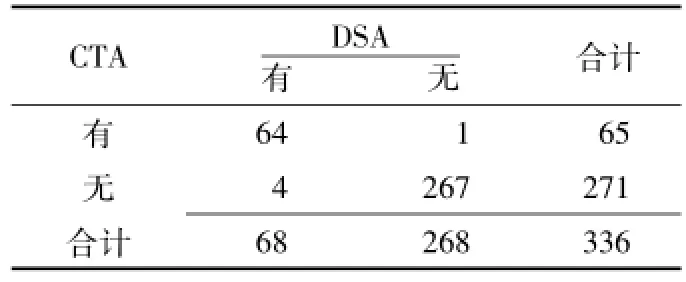
表6 CTA检查诊断颈内动脉溃疡四格表Table 6 Evaluation of internal carotid p laque ulcers with CTA versus DSA.Values are expressed as number of cases
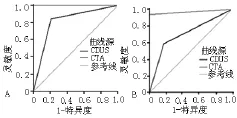
图2 CDUS、CTA检查诊断颈内动脉斑块形态和溃疡的ROC曲线Figure 2 ROC curves and AUC values of irregular plaque morphology evaluation and ulcer identification
3 讨论
准确诊断颈内动脉狭窄程度和斑块特征,是做出正确诊疗计划的基础,根据国际指南[10],颈内动脉剥脱术治疗可用于无临床症状的颈内动脉狭窄或选择性治疗引起临床症状颈内动脉狭窄的患者。颈内动脉狭窄的诊断长期以来有赖于DSA检查,其在判定狭窄程度和范围方面优于其他检查。但DSA检查为创伤性操作,且偶可出现动脉粥样硬化斑块和/或血栓脱落、动脉痉挛等并发症[11-12],故无创影像诊断颈内动脉狭窄的技术逐渐被应用,有Meta分析指出,对于颈内动脉狭窄率≥70%的血管,非侵入性的检查可代替DSA检查[13-14];同时有新的报道称,其他因素(斑块形态和斑块成分)同血管狭窄程度一样重要,均应作为脑血管事件发生的危险因素进行评估[15]。因此,对患者的检查不仅要评价血管是否狭窄,同时要评价造成血管狭窄斑块的特征。
CDUS作为颈内动脉狭窄检查的一级检查方法,能够有效显示颈内动脉管腔和管壁,根据血流充盈情况判断出有无斑块和斑块大小,对确定斑块表面有无溃疡和颈内动脉狭窄率做出正确判断,并通过彩色血流显像可以测得狭窄所致的血流动力学改变。Herzig等[15]研究发现,诊断颈内动脉狭窄率≥70%的灵敏度为100%、特异度为75%、阳性预测值为75%、阴性预测值为100%。有研究表明,CDUS检查诊断颈内动脉狭窄率≥70%的灵敏度为65%~98%[16-17],特异度为83%~98%[18-19]。本研究结果显示,CDUS诊断颈内动脉狭窄率≥70%的正确率为85.7%、灵敏度为83.6%、特异度为87.4%、阳性预测值为83.6%、阴性预测值为87.4%,与其他研究结果比较[20-21],本研究结果较为理想,诊断价值更高。Anzidei等[22]研究发现,CDUS诊断不规则型斑块的灵敏度为86.9%、特异度为80.9%、阳性预测值为82.0%、阴性预测值为82.0%;诊断溃疡的灵敏度为87.5%、特异度为88.9%、阳性预测值为65%、阴性预测值为65%。本研究结果显示,CDUS诊断不规则型斑块的正确率为82.7%、敏感度为85.7%、特异度为79.8%、阳性预测值为80.9%、阴性预测值为84.8%,Kappa值为0.655;诊断颈内动脉溃疡的正确率为88.7%、敏感度为85.3%、特异度为89.6%、阳性预测值为67.4%、阴性预测值为96.0%,Kappa值为0.681,提示CDUS诊断不规则型斑块和溃疡与DSA检查具有高度一致性。
CTA扫描速度快,完成图像时间短,受到辐射小,其从肘部静脉注射造影剂,不良反应少,较DSA安全。CTA不但可以有效、准确而无创地检查颅内和颅外动脉狭窄或闭塞,而且可以清晰显示动脉管壁情况,反映粥样斑块的质地、大小、斑块表面状况,区分斑块的成分[23]。CTA诊断颈内动脉狭窄率≥70%的灵敏度为65%~95%[24-25],也有报道发现,其灵敏度为100%[26],特异度为98%和100%[24]。本研究结果显示,CTA诊断颈内动脉狭窄率≥70%的灵敏度为94.5%、特异度为96.8%、阳性预测值为95.8%、阴性预测值为95.8%;诊断不规则型斑块的正确率为99.1%、灵敏度为98.8%、特异度为99.4%、阳性预测值为99.4%、阴性预测值为98.8%,Kappa值为0.982,;诊断颈内动脉溃疡的正确率为98.5%、灵敏度为94.0%、特异度为99.6%、阳性预测值为98.5%、阴性预测值为98.5%,Kappa值为0.953。提示CTA检查诊断不规则型斑块和溃疡与DSA检查具有极高的一致性。
本研究发现,CTA对颈内动脉狭窄、不规则型斑块及溃疡的诊断具有很高的可靠性,CTA诊断颈内动脉狭窄率≥70%、不规则型斑块、溃疡的正确率均高于CDUS;CTA检查颈内动脉狭窄率与DSA检查颈内动脉狭窄率呈高度正相关;CTA检查与DSA检查诊断不规则型斑块的Kappa值为0.982,诊断溃疡的Kappa值为0.953;CDUS检查诊断颈内动脉不规则斑块AUC为0.818〔95%CI(0.711,0.866)〕,CTA检查诊断颈内动脉不规则斑块AUC为0.997〔95%CI(0.923,1.000)〕;CDUS检查诊断颈内动脉溃疡AUC为0.708〔95%CI(0.633,0.788)〕,CTA检查诊断颈内动脉溃疡AUC为0.969〔95%CI(0.934,1.000)〕。提示CTA对颈内动脉狭窄、不规则型斑块及溃疡的诊断均优于CDUS,一定情况下可代替DSA检查。
综上所述,虽然CDUS检查在诊断颈内动脉狭窄时可作为首选的检查方法,但CDUS检查在诊断的准确性方面,对操作者的技术水平和主观判断有较强的依赖性。而CTA检查可以显示血管狭窄的斑块形态、是否有溃疡等形态学改变,进一步评价斑块的稳定性,为患者选择治疗方案时,特别是需要行手术治疗的患者,提供更有效、全面的信息,尽可能地避免了DSA检查带来的有创性操作方法,也可能为其他血管病变的诊断治疗提供帮助。
[1]Rothwell PM,Coull AJ,Silver LE,et al. Population-based study of event-rate,incidence,case fatality,and mortality for all acute vascular events in all arterial territories(Oxford Vascular Study)[J].Lancet,2005,366(9499):1773-1783.
[2]Rothwell PM,Eliasziw M,Gutnikov SA,et al.Analysis of pooled data from the randomised controlled trials of endarterectomy for symptomatic carotid stenosis[J].Lancet,2003,361 (9352):107-116.
[3]Rothwell PM,Mehta Z,Howard SC,et al. From subgroups to individuals:general principles and the example of carotid endarterectomy[J].Lancet,2005,365 (9455):256-265.
[4]Wintermark M,Arora S,Tong E,et al. Carotid plaque computed tomography imaging in stroke and nonstroke patients[J].Ann Neurol,2008,64(2):149-157.
[5]Dahl T,Cederin B,Myhre HO,et al.The prevalence of carotid artery stenosis in an unselected hospitalized stroke population[J].Int Angiol,2008,27(2):142-145.
[6]de Weert TT,Cretier S,Groen HC,et al. Atherosclerotic plaque surface morphology in the carotid bifurcation assessed with multidetector computed tomography angiography[J].Stroke,2009,40(4): 1334-1340.
[7]Connors JJ 3rd,Sacks D,Furlan AJ,et al. Training,competency,and credentialing standards for diagnostic cervicocerebral angiography,carotid stenting,and cerebrovascular intervention:a joint statement from the American Academy of Neurology,the American Association of Neurological Surgeons,the American Society of Interventional and Therapeutic Neuroradiology,the American Society of Neuroradiology,the Congress of Neurological Surgeons,the AANS/CNS Cerebrovascular Section,and the Society of Interventional Radiology[J].Neurology,2005,64 (2):190-198.
[8]Anzidei M,Napoli A,Geiger D,et al. Passariello Preliminary experience with MRA in evaluating the degree of carotid stenosis and plaque morphology using highresolution sequences after gadofosveset trisodium(Vasovist)administration: comparison with CTA and DSA[J].Radiol Med,2010,115(4):634-647.
[9]Zavanone C,Ragone E,Samson Y.Concordance rates of Doppler ultrasound and CT angiography in the grading of carotid artery stenosis:a systematic literature review[J].J Neurol,2012,259(6):1015-1018.
[10]North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators.Beneficial effect of carotidendarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high grade carotid stenosis[J].N Engl J Med,1991,325(7):445-453.
[11]Wintermark M,Jawadi SS,Rapp JH,et al.High-resolution CT imaging of carotid artery atherosclerotic plaques[J].AJNR Am JNeuroradiol,2008,29(5): 875-882.
[12]Nonent M,Serfaty JM,Nighoghossian N,et al.Concordance rate differences of 3 noninvasive imaging techniques to measure carotid stenosis in clinical routine practice[J].Stroke,2004,35(3):682-686.
[13]Wardlaw JM,Chappell FM,Best JJ,et al.Non-invasive imaging compared with intra-arterial angiography in the diagnosis of symptomatic carotid stenosis: a meta-analysis[J].Lancet,2006,367(9521):1503-1512.
[14]Wang LW,Fahim MA,Hayen A,et al. Carotidartery stenosis:accuracy of noninvasive tests-individual patient data meta-analysis[J].Cochrane Database Syst Rev,2011,7(12):CD008691.
[15]Herzig R,Burval S,Krupka B,et al. Comparison of ultrasonography,CT angiography,and digital subtraction angiography in severe carotid stenoses[J].Eur J Neurol,2004,11(11): 774-781.
[16]Johnston DC,Goldstein LB.Clinical carotid endarterectomy decision making: noninvasive vascular imaging versus angiography[J].Neurology,2001,56 (8):1009-1015.
[17]Patel SG,Collie DA,Wardlaw JM,et al. Outcome,observer reliability,and patient preferences if CTA,MRA,or Doppler ultrasound were used,individually or together,instead of digital subtraction angiography before carotidendarterectomy[J].J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry,2002,73(1):21-28.
[18]Rotstein AH,Gibson RN,King PM.Direct B-mode NASCET-style stenosis measurement and Doppler ultra-sound as parameters for assessment of internal carotidartery stenosis[J].Austral Radiol,2002,46(1):52-56.
[19]Keberle M,Jenett M,Wittenberg G,et al.Comparison of 3D power doppler ultrasound,color doppler ultrasound and digital subtraction angiography in carotid stenosis[J].Rofo,2001,173(2): 133-138.
[20]Huston J 3rd,James EM,Brown RD Jr,et al.Redefined duplex ultrasonographic criteria for diagnosism of carotid artery stenosis[J].Mayo Clin Proc,2000,75 (11):1133-1140.
[21]Johnston DC,Goldstein LB.Clinical carotid endarterectomy decision making: noninvasive vascular imaging versus angiography[J].Neurology,2001,56 (8):1009-1015.
[22]Anzidei M,Napoli A,Zaccagna F,et al. Diagnostic accuracy of colour Doppler ultrasonography,CT angiography and blood-pool-enhanced MR angiography in assessing carotid stenosis:a comparative study with DSA in 170 patients[J].Radiol Med,2012,117(1):54-71.
[23]Nguyen-Huynh MN,Wintermark M,English J,et al.How accurate is CT angiography in evaluating intracranial atherosclerotic disease?[J].Stroke,2008,39(4):1184-1188.
[24]Alvarez-Linera J,Benito-León J,Escribano J,et al.Prospective evaluation of carotid artery stenosis:elliptic centric contrast-enhanced MR angiography and spiral CT angiography compared with digital subtrac-tion angiography[J].AJNR Am J Neuroradiol,2003,24(5):1012-1019.
[25]Anderson GB,Ashforth R,Steinke DE,et al.CT angiography for the detection and characterization of carotid artery bifurcation disease[J].Stroke,2000,31(9): 2168-2174.
[26]Randoux B,Marro B,Koskas F,et al. Carotid artery stenosis:prospective comparison of CT,three-dimensional gadolinium-enhanced MR,and conventional angiography[J].Radiology,2001,220(1):179-185.
Accuracy of Carotid CDUS,CTA and DSA in the Diagnosis of Internal Carotid Artery Stenosis,Plaque Morphology and Ulcer:A Comparative Study
ZHANG Yuan-yuan,MENG Xiu-jun,TIAN Shen,et al.Department of Neurology,the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University,Shenyang 110032,China
Objective To analyze the accuracy of colour Doppler ultrasonography(CDUS)and computed tomography angiography(CTA)in the diagnosis of internal carotid artery stenosis,plaque morphology and ulcer with DSA as the gold standard.Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on the collected data of 168 patients with internal carotid artery stenosis diagnosed by DSA who were admitted into the Fourth Hospital Affiliated to China Medical University from 2009 to 2014,and CDUS and CTA were undertaken successively.Pearson correlation analysis was conducted on the correlation between the rates of internal carotid artery stenosis screened by CDUS and CTA and the rate of internal carotid artery stenosis screened by DSA;with DSA as golden criteria,we worked out the number of subjects diagnosed as internal carotid artery stenosis degree≥70%,plaque morphology,the accuracy of ulcer diagnosis,sensitivity,specificity,positive predictive value and negative predictive value;the accuracy of CDUS and CTA in the diagnosis of plaque morphology and ulcer were was analyzed by ROC curve and AUC;the consistency of the results of CDUS,CTA and DSA was analyzed by Kappa test.Results There was positive correlation among CDUS(64.73±22.91)%,CTA(62.38±22.31)%and DSA(62.52±22.31)%in the rate of internal carotid artery stenosis(r=0.922 and 0.992,P<0.05).The number of blood vessels with internal carotid artery stenosis degree≥70% diagnosed by DSA was 146,and the number of that<70%was 190.The accuracy rates of CDUS and CTA diagnosing blood vessels with internal carotid artery stenosis degree≥70%were 85.7%(288/336)and 95.8%(322/336)respectively;the sensitivity degrees were 83.6%(122/146)and 94.5%(138/146);the specificity degrees were 87.4%(166/190)and 96.8%(184/190);the positive predictive values were 83.6%(122/146)and 95.8(138/144)%;the negative predictive values were 87.4%(166/190)and 95.8%(184/192)respectively.The Kappa values of CDUS and CTA diagnosing internal carotid artery stenosis degree≥70%were 0.709 and 0.915 respectively.The number of blood vessels of internal carotid artery with regular plaque diagnosed by DSA was 168,and the number of blood vessels with irregular plaque was 168;the number of blood vessels of internal carotid artery with ulcer diagnosed by DSA was 68,and the number of blood vessels without ulcer was 268.The accuracy rates of CDUS and CTA diagnosing ulcer of internal carotid artery were 82.7%(278/336)and 99.1%(333 /336)respectively;the sensitivity degrees were 84.8%(144/168)and 98.8%(166/168);the specificity degrees were 79.8%(134/168)and 99.4%(167/168);the positive predictive values were 80.9%(144/178)and 99.4%(166/167); the negative predictive values were 84.8%(134/158)and 99.4%(167/169)respectively.The accuracy rates of CDUS and CTA diagnosing ulcer of internal carotid artery were 88.7%(298/336)and 98.5%(331/336)respectively;the sensitivity degrees were 85.3%(58/68)and 94.0%(64/68);the specificity degrees were 89.6%(240/268)and 99.6%(267 /268);the positive predictive values were 67.4%(58/86)and 98.5%(64/65);the negative predictive values were 96.0% (240/250)and 98.5%(267/271)respectively.The AUC of CDUS diagnosing the irregular plaque of internal carotid artery was 0.818〔95%CI(0.711,0.866)〕,and the AUC of CTA diagnosing the irregular plaque of internal carotid artery was 0.997〔95%CI(0.923,1.000)〕;the AUC of CDUS diagnosing the ulcer of internal carotid artery was 0.708〔95%CI(0.633,0.788)〕,and the AUC of CTA diagnosing the ulcer of internal carotid artery was 0.969〔95%CI(0.934,1.000)〕.The Kappa values of CDUS and CTA diagnosing ulcer of internal carotid artery were 0.681 and 0.953 respectively.Conclusion CTA is simple and feasible and has high accuracy degree in the diagnosis of internal carotid artery stenosis degree≥70%,irregular plaque and ulcer,which is superior to CDUS and highly consistent with the diagnosis by DSA.Therefore,CTA can be used as a substitute of DSA in some cases,so as to avoid invasiveness and potential risk.
Carotid stenosis;Ultrasonography,Doppler,color;Tomography,spiral computed;Angiography,digital subtraction;Sensitivity;Specificity
R 543.4
A
10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2015.30.028
2015-03-21;
2015-07-13)
(本文编辑:李婷婷)
110032辽宁省沈阳市,中国医科大学附属第四医院神经内科
孟秀君,110032辽宁省沈阳市,中国医科大学附属第四医院神经内科;E-mail:1356120017@qq.com
