甲状腺功能减退致间歇性高度房室传导阻滞13例诊治分析
2015-09-14葛振嵘李秀芬姜述斌李岚马骏徐风燕
葛振嵘,李秀芬,姜述斌,李岚,马骏,徐风燕
甲状腺功能减退致间歇性高度房室传导阻滞13例诊治分析
葛振嵘,李秀芬,姜述斌,李岚,马骏,徐风燕
甲状腺功能减退非缓慢性心律失常的常见病因,其引起的缓慢性心律失常常表现为窦性心动过缓或Ⅰ度房室传导阻滞,引起高度房室传导阻滞较为罕见。本文回顾性分析了13例甲状腺功能减退致间歇性高度房室传导阻滞患者的临床资料,就其机制、临床表现和治疗进行了探讨,认为甲状腺功能减退致间歇性高度房室传导阻滞的治疗应以积极改善甲状腺功能为主,并动态观察心律,可取得良好预后。
房室传导阻滞;甲状腺功能减退症;诊断;治疗
葛振嵘,李秀芬,姜述斌,等.甲状腺功能减退致间歇性高度房室传导阻滞13例诊治分析[J].中国全科医学,2015,18(32):3991-3993.[www.chinagp.net]
Ge ZR,Li XF,Jiang SB,et al.Analysis of the diagnosis and treatment of 13 patients with intermittent high degree atrioventricular block induced by hypothyroidism[J].Chinese General Practice,2015,18(32):3991-3993.
引起高度房室传导阻滞的原因有心肌缺血[1-3]、传导系统退化、心脏手术[4-5]及药物中毒[6-9]等,甲状腺功能减退引起缓慢性心律失常临床较为少见,且多表现为窦性心动过缓或Ⅰ度房室传导阻滞[10],高度房室传导阻滞报道较少[11-13]。本文报道了13例甲状腺功能减退引起高度房室传导阻滞患者,探讨其可能的机制及治疗策略。
1 病例简介
2009年1月—2014年1月新疆医科大学附属中医医院诊断为甲状腺功能减退致间歇性高度房室传导阻滞患者13例,其中女9例,男4例;年龄33~76岁,平均年龄(59.3 ±12.8)岁。临床表现为畏寒、少汗、倦怠、少语、动作迟缓、记忆力减退、心悸、气促、胸闷、头晕、乏力等不同症状。
结合患者症状,经甲状腺功能检查〔血清总甲状腺素(TT4,参考值66~181 nmol/L)、三碘甲状腺原氨酸(TT3,参考值1.3~3.1 nmol/L)、游离三碘甲状腺原氨酸(FT3,参考值3.1~6.8 pmol/L)、游离甲状腺素(FT4,参考值12.0~22.0 pmol/L)、促甲状腺素(TSH,参考值0.3~4.2 mU/L)、抗甲状腺过氧化物酶抗体(TPOAb,参考值<34 U/ml)〕及促甲状腺激素释放激素(TRH)兴奋试验,诊断为原发性甲状腺功能减退,其中血清TSH水平增高、TT4、FT4水平降低为诊断必备指标,TPOAb阳性可考虑甲状腺功能减退的病因为自身免疫性甲状腺炎。心电图或动态心电图检查示间歇性高度房室传导阻滞(高度房室传导阻滞指房室传导比超过2∶1,表现为3∶1、4∶1或5∶1等)。排除心肌梗死、电解质异常、洋地黄中毒、血管迷走神经性晕厥及应用β受体阻滞剂者。13例患者临床资料见表1。
患者因高度房室传导阻滞均建议行永久心脏起搏器植入术,但因无明显症状或经济原因等均拒绝接受该治疗。患者长期口服左旋甲状腺素钠片,起始剂量25~50μg/d,每1~2周增加25μg,直至甲状腺功能指标达参考值。患者2~4周后畏寒、倦怠等症状减轻,10~12周不适症状消失,甲状腺功能恢复正常。6个月后随访动态心电图未出现间歇性高度房室传导阻滞。
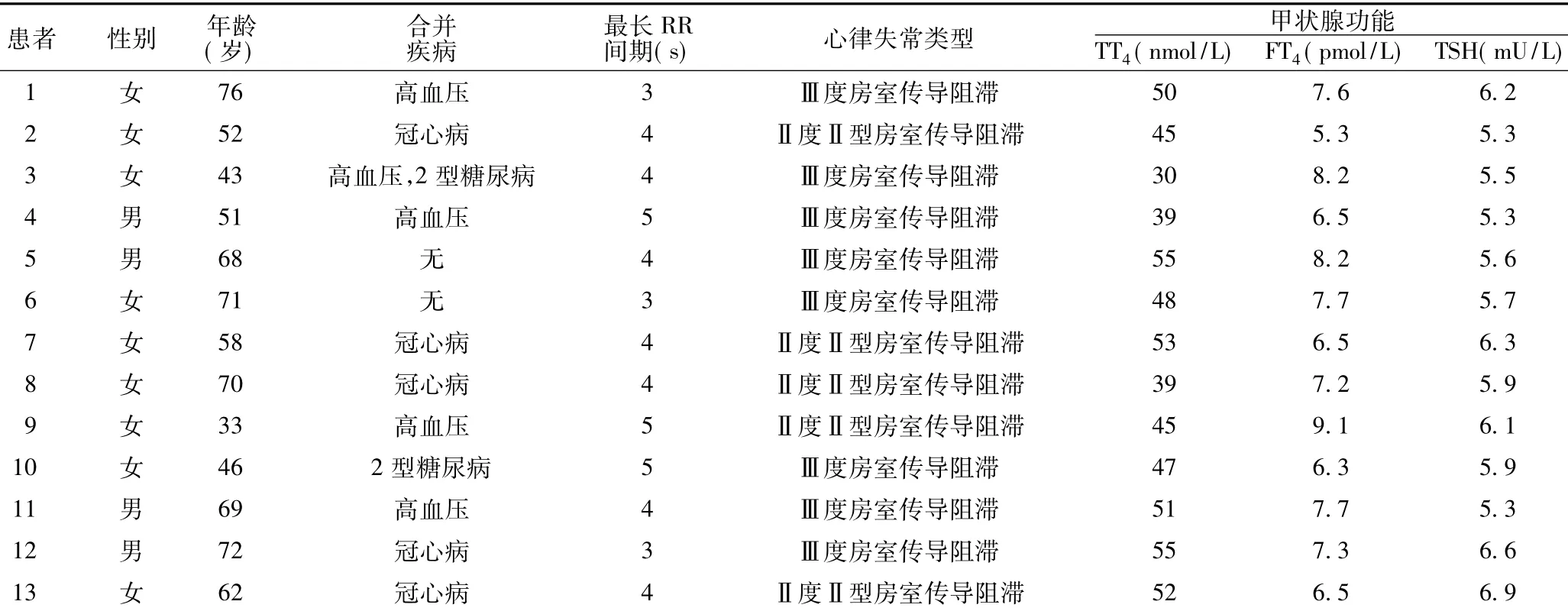
表1 13例甲状腺功能减退致间歇性高度房室传导阻滞患者临床资料Table 1 Clinical data of the 13 patients with intermittent high degree atrioventricular block induced by hypothyroidism
2 讨论
2.1机制原发性甲状腺功能减退占成人甲状腺功能减退的90%~95%,是由甲状腺本身疾病、甲状腺手术和甲状腺功能亢进131I治疗等原因引起甲状腺素合成、分泌不足或生物效应低下所致的内分泌疾病。目前认为,70%~80%甲状腺功能减退患者合并心血管病变。甲状腺功能减退患者细胞间质黏蛋白和黏多糖沉积,而Na+-K+-ATP酶活性降低,清除黏多糖障碍,致使心肌细胞肿胀、缺血、变形、坏死,肌浆纤维断裂且有空泡和退行灶,细胞间质及细胞内水肿,出现心脏电传导异常,甲状腺功能减退时心输出量和心脏指数降低,增加了心脏传导系统缺血性损伤,从而出现传导阻滞。甲状腺功能减退使心肌细胞对肾上腺素和去甲肾上腺素的敏感性下降,加之耗氧量减少及代谢率降低,出现房室传导阻滞。
2.2临床表现甲状腺功能减退起病隐匿,临床表现多样,特别是早期临床表现缺乏特异性,易造成误诊和漏诊。部分患者甲状腺功能减退导致心脏形态、结构、功能及传导出现异常而引起心肌收缩力减弱、心排血量和外周血流量减少等一系列症状和体征的甲状腺功能减退性心脏病的临床表现,一般心血管系统症状有心悸、胸闷、呼吸困难、心包积液及心功能不全,实验室检查出现高脂血症、心肌酶谱升高。
2.3治疗高度房室传导阻滞包括Ⅱ度Ⅱ型房室传导阻滞及Ⅲ度房室传导阻滞,是行永久心脏起搏器植入术的绝对适应证。甲状腺功能减退造成高度房室传导阻滞并不常见[14],有报道指出,该原因造成的高度房室传导阻滞是可逆的,给予左旋甲状腺素钠片后可恢复[15];严重甲状腺功能减退引起的房室传导阻滞,至正常窦性心律的逆转通常需数天到数周[16];部分患者在甲状腺功能恢复正常后仍需行永久起搏器植入术[15]。
本研究分析了甲状腺功能减退引起的间歇性高度房室传导阻滞的诊治过程,体现了临床工作中对病因进行治疗的重要性。由于窦性停搏和间歇性高度房室传导阻滞是永久性心脏起搏器植入术的适应证,临床医生通常会积极给予患者安装永久起搏器治疗。但本研究随访发现,患者甲状腺功能恢复正常后缓慢性心律失常也逐渐消失。因此,对于甲状腺功能减退引起的缓慢性心律失常,若症状不明显,应积极使甲状腺功能恢复正常,后密切随访观察动态心电图。
本研究患者根据TRH兴奋试验排除中枢性甲状腺功能减退,经甲状腺功能检查诊断为原发性甲状腺功能减退,给予长期口服左旋甲状腺素钠片治疗后,患者多种症状逐渐消失。依据2008年美国心脏病学会(ACC)/美国心脏联合会(AHA)/美国心律学会(HRS)指南[17],患者均应接受永久起搏器植入术。但2013年欧洲心脏病学会(ESC)相关指南新增部分也指出,无症状性停搏(窦性停搏或房室传导阻滞)永久起搏器植入术应考虑用于有晕厥史、无症状性停搏>6 s的患者[18]。本研究患者病因去除后心律恢复正常,只需继续目前治疗,长期随访监测甲状腺功能和动态心电图,无需行永久起搏器植入术治疗。
[1]Knudtzen FC,Christophersen TB.Third degree atrioventricular block associated with treatment with rivastigmine transdermal patch[J].J Geriatr Cardiol,2013,10(1):113-115.
[2]Agarwal N,Burkart TA.Transient,high-grade atrioventricular block from high-dose cyclophosphamide[J].Tex Heart Inst,2013,40(5):626-627.
[3]Brvar M,Bunc M.High-degree atrioventricular block in acute ethanol poisoning:a case report[J].Cases J,2009,2:8559.
[4]Chen Q,Cao H,Zhang GC,et al.Atrioventricular block of intraoperative device closure perimembranous ventricular septal defects;a serious complication[J].BMC Cardiovasc Disord,2012,12:21.
[5]Chen Q,Cao H,Zhang GC,etal.Atrioventricular block subsequent to intraoperative device closure atrial septal defect with transthoracic minimal invasion;a rare and serious complication[J].PLoSOne,2012,7(12):e52726.
[6]Cagli KE,Tufekcioglu Q,Sen N,et al.Atrioventricular block induced by mad-honey intoxication:confirmation of diagnosis by pollen analysis[J].Tex Heart Inst J,2009,36(4):342-344.
[7]Lee WS,Kim DH,Shin SH,et al.Complete atrioventricular block secondary to bortezomib use in multiple myeloma[J].2011,52 (1):196-198.
[8]van Cleef AN,Schuurman MJ,Busari JQ.Third-degree
atrioventricular block in an adolescent following acute alcohol
intoxication[J].BMJCase Rep,2011,2011:bcr0720114547.
[9]Sawers JS,Toft AD,Irvine WJ,et al.Transient hypothyroidism after iodine-131 treatment of thyrotoxicosis[J].Clin Endocrinol Metab,1980,50(2):226-229.
[10]Da Costa D,Brady WJ,Edhouse J.Bradycardias and atrioventricular conduction block[J].BMJ,2002,324 (7336):535-538.
[11]Patton KK,Levy M,Viswanathan M.Atrial lead dysfunction:an unusual feature of hypothyroidism[J].Pacing Clin Electrophysiol,2008,31(12):1650-1652.
[12]Levy EG.Thyroid disease in elderly[J].Med Clin North Am,1991,75(1):151-167.
[13]Schoenmakers N,de GraaffWE,Peters RH.Hypothyroidism as the cause of atrioventricular block in an elderly patient[J].Neth Heart J,2008,16(2):57-59.
[14]Olguntürk R,Tunaoglu FS,Oguz D,et al.Complete atrioventricular heart block in congenital hypothyroidism[J].Turk JPediatr,1998,40(3):431-435.
[15]Ozcan KS,Osmonov D,Erdinler I,et al.Atrioventricular block in patients with thyroid dysfunction:prognosis after treatment with hormone supplementation or antithyroid medication[J].JCardiol,2012,60(4):327-332.
[16]Nakayama Y,Ohno M,Yonemura S,etal.A case of transient2∶1 atrioventricular block,resolved by thyroxin supplementation for subclinical hypothyroidism[J].Pacing Clin Electrophysiol,2006,29(1):106-108.
[17]Epstein AE,DiMarco JP,Ellenbogen KA,et al.ACC/AHA/HRS 2008 Guidelines for Device-Based Therapy of Cardiac Rhythm Abnormalities:a report of the American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (W riting Committee to Revise the ACC/AHA/NASPE 2002 Guideline Update for Implantation of Cardiac Pacemakers and Antiarrhythmia Devices)developed in collaboration with the American Association for Thoracic Surgery and Society of Thoracic Surgeons[J].JAm Coll Cardiol,2008,51(21):e1-62.
[18]The Task Force on cardiac pacing and resynchronization therapy of the European Society of Cardiology(ESC),Developed in collaboration with the European Heart Rhythm Association(EHRA),Brignole M,et al.2013 ESC Guidelines on cardiac pacing and cardiac resynchronization therapy[J].Rev Esp Cardiol(Engl Ed),2014,67(1):58.
(本文编辑:吴立波)
Analysis of the Diagnosis and Treatm ent of 13 PatientsW ith Interm ittent High Degree Atrioventricular Block Induced by Hypothyroidism
GE Zhen-rong,LI Xiu-fen,JIANG Shu-bin,et al.CCU,Chinese Medical Hospital Affiliated to Xinjiang Medical University,Urumqi830000,China
Hypothyroidism is an uncommon cause for chronic arrhythmia,and it oftenmanifests as tachycardia or first-degree atrioventricular block,and it is rare in causing high degree atrioventricular block.The paper made a retrospective analysis of 13 cases of intermittent high degree atrioventricular block induced by hypothyroidism and investigated themechanism,clinicalmanifestations and treatment of the disease.We suggested that the patients with intermittent high degree atrioventricular block caused by hypothyroidism should be primarily given active treatment to improve thyroid function and the rhythm of heart should be dynamically observed,so that favorable prognosis could be generated.
Atrioventricular block;Hypothyroidism;Diagnosis;Therapy
R 541.76 R 581.2
D
10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2015.32.023
830000新疆乌鲁木齐市,新疆医科大学附属中医医院CCU
姜述斌,830000新疆乌鲁木齐市,新疆医科大学附属中医医院CCU;E-mail:13565852840@139.com
2015-03-18;
2015-07-27)
