葡聚糖硫酸钠致大鼠急性溃疡性结肠炎模型建立与评价
2015-08-23孔鹏飞赵兵覃勤李敏唐学贵
孔鹏飞 赵兵 覃勤 李敏 唐学贵
·论著 ·
葡聚糖硫酸钠致大鼠急性溃疡性结肠炎模型建立与评价
孔鹏飞 赵兵 覃勤 李敏 唐学贵
目的 探讨葡聚糖硫酸钠(dextran sulfate sodium,DSS)诱导大鼠溃疡性结肠炎(ulcerative colitis,UC)急性期模型的建立。方法 60只SD大鼠,雌雄各半,随机分成空白组(n=12)、模型组(n=48),空白组给予自由饮食,模型组给予3%DSS溶液自由饮用7天。应用疾病活动指数(DAI)及组织学评分(HI)对各组进行对比。结果 模型组DAI及HI评分与空白组比较均有统计学意义(P<0.01)。模型组均不同程度的出现腹泻、隐血试验阳性、脓血便,病理可见炎症主要累及黏膜和黏膜下层,上皮内杯状细胞减少,隐窝破坏。结论 DSS诱导的UC急性期模型的临床和病理表现与人类UC相似,是理想的UC模型之一。
结肠炎,溃疡性; 疾病模型,动物; 急性期
溃疡性结肠炎(UC)是一种主要累及直肠、结肠黏膜的慢性非特异性炎症,以腹痛、腹泻、粘液血便和里急后重为主要临床表现。近十几年的统计表明,溃疡性结肠炎在我国也是一种较常见的消化道疾病,并且正逐渐成为消化病学研究的一个新热点[1]。随着对UC的不断重视,对UC的研究也在不断的深入。建立一种类似于人类UC的动物模型,对研究UC的发病机制、病变发展规律和临床治疗有着重要的应用价值。
资料与方法
一、一般资料
60只SD大鼠(川北医学院实验动物中心),体重200 g±20 g,雌雄各半。葡聚糖硫酸钠(Dextran Sulfate Sodium,DSS),AR分析纯,分子量5000,(上海西宝生物科技有限公司),OLYMPUS DP71显微镜照相系统。
二、实验方法
(一)模型建立
将60只SD大鼠随机分为空白组(n=12)、模型组(n=48),雌雄各半。空白组给予正常饮食,模型组给予3%DSS自由饮用7天。
(二)疾病活动指数与组织学损伤指数
疾病活动指数(disease activity index,DAI)的评估:每日观察大鼠的体重、大便性状和隐血、便血情况,按表1进行评分[2],以评估疾病活动情况。

表1 DAI评分标准表
DAI=(体重降低+大便性状+出血)/3
组织学损伤指数(histological index,HI)的评估:处死大鼠后,解剖,取直肠距肛门0.5 cm及回盲部远端0.5 cm处各一块肠粘膜组织,约0.5 cm×0.5 cm大小,固定、修整,石蜡包埋、切片(4 μm)、HE染色(过程由川北医学院附属医院病理科完成)。观察组织学改变并按表2进行HI评分[2]。
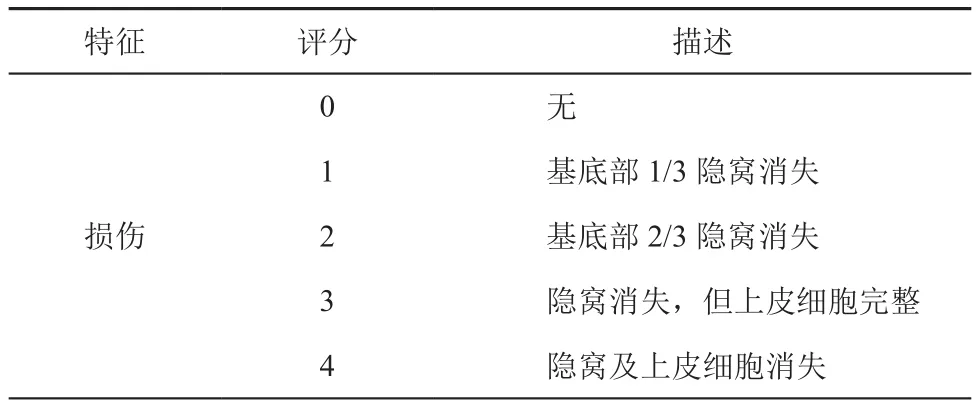
表2 HI评分标准
三、统计学分析
数据均采用SPSS13.0软件分析处理,应用Shapiro-Wilk法进行正态分布检验,非正态分布计量资料则采用M(QR)表示,采用秩和检验Wilcoxon Mann-Whitney test法进行两两比较。
结 果
一、DAI及HI评分比较
空白组:大鼠体重平均增长约3~5 g/天,雌鼠体重增长略少于雄鼠,12只大鼠中有1只出现大便松散情况,但无便稀、血便发生。模型组:各大鼠体重降低不明显,仅有6例出现体重减少,但均小于5%,这可能与造模时间有关;第3天大鼠开始逐渐出现不同程度的活动减少,精神萎靡,大便隐血或肉眼血便等症状;7天后模型组中有35只出现了不同程度的肉眼血便;余13只未见明显血便,但大部分出现大便松散、便稀同时伴大便隐血的情况。根据DAI评分及HI组织学损伤评分各组大鼠评分见表3。

表3 DAI 评分及HI 评分表
二、组织学观察
空白组:肉眼观察直肠、结肠黏膜光滑,血管纹理清晰,黏膜无水肿充血,无出血点、糜烂、溃疡或新生物形成;镜下观,黏膜上皮完整、连续,腺体排列规则、结构清楚,极少炎症细胞浸润(图1)。
模型组:见直肠、结肠有散在粘膜水肿、充血,甚至溃疡形成。镜下观,炎症细胞广泛浸润,主要累及粘膜和粘膜下层,上皮内杯状细胞减少,隐窝破坏,浸润的炎症细胞以中性粒细胞为主(图2~4)。
讨 论
UC模型制备方法的选择
目前,国内外常用的UC制作方法有7种:(1)乙酸模型;(2)二硝基氯苯(DNCB)模型;(3)过氧化亚硝酸钠模型;(4)葡聚糖硫酸钠模型;(5)三硝基苯磺酸(TNBS)-乙醇模型;(6)二硝基苯磺酸(DNBS)-乙酸模型;(7)其他方法:人体结肠组织致敏诱导法、兔结肠组织致敏诱导法、胎鼠结肠种植诱导法、大鼠结肠细菌致敏诱导法等多种方法也能实现诱导大鼠UC模型的建立。
DSS是由蔗糖合成的一种硫酸多糖体。其机制可能与巨噬细胞功能失调、肠道菌群失调及DSS对结肠上皮的毒性作用有关[3],也可能与DSS上调TNF-α,IFN-γ,IL-10的表达及与嗜酸性粒细胞脱颗粒有关[4-5]。根据Granger et al[6]研究给出了DSS 摄取量的计算公式DSS(mg/g)=总饮水量(ml)×[DSS(mg)/100 ml ]/鼠的初始体重(g),我们应用SD大鼠给予3 %的DSS溶液成功复制了UC急性期模型,根据观察大鼠的体重、大便性状和隐血、便血情况及组织学观察,模型符合急性炎症的组织病理改变,这些改变与人类的UC相似[7-8]。

图1 空白组(×20);图2 模型组(×20);图3 模型组(×20);图4 模型组(×20)
结合此实验结果及依据Vowinkel等[9]的报道,我们认为采用SD大鼠饮用3%的DSS(分子量为5000左右)溶液7天的方法可建立理想的UC急性期模型。较其它UC动物模型更接近人类UC。通过本实验我们可以看出,其经济性与重复性好,具有制作过程简单、方便等特点。
[ 1 ] Jiang XL, Wang ZK, Qin CY. Current research starus and strategy on ulcerateve colitis in China. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi, 2000, 8:610-613.
[ 2 ] Murano M, Maemura K, Hirata I, et al. Therapeutic effect of intro colonically administered nuclear factor kappaB(p65) antisense oligonucleotide on mouse dextran sulphate sodium(DSS)-induced colitis. Clin Exp Immunol, 2000, 120: 51-58.
[ 3 ] Jurius AR, Khoury NN, Reimund JM, et a1. Animal models of infammatory bowel disease. J Pharmacol Toxicolog M ethods, 2004, 50: 81.
[ 4 ] Ohkawara T, Nishihira J, Takeda H, et al. Amelioration of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by anti-macrophage migration inhibitory factor antibody in mice. Gastroenterology, 2002, 123 (1):256-270.
[ 5 ] Forbes E, Murase T, Yang M, et al. Immunopathogenesis of experimental ulcerative colitis is mediated by eosinophil peroxidase. J Immunol, 2004, 172 (9) : 5664-5675.
[ 6 ] VowinkeT, Kalogeris TJ, Mori M, et al. Impact of dextran sulfate sodium load on the severity of infammation in experimental colitis. Dig Dis Sci, 2004, 49 (4): 556-564.
[ 7 ] Osman N, Adawi D, Ahrne S, et al. Modulation of the effect of dextran sulfate sodium induced acute colitis by the administration of different probiotic strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Dig Dis Sci, 2004, 49 (2) : 320-327.
[ 8 ] Luk HH, Ko JK, Fung HS, et al. Delineation of the protective action of zinc sulfate on ulcerative colitis in rats. Eur J Pharm acol, 2002,443 (123) : 197-204.
[ 9 ] Melgar S, Karlsson A, Michaelsson E. Acute colitis induced by dextran sulphate sodium progresses into chronicity in C57BL/6 but not in BALB/c mice-correlation between symptoms and infammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2005, 288 (6) :G1328-1338.
(本文编辑:杨明)
孔鹏飞, 赵兵, 覃勤, 等. 葡聚糖硫酸钠致大鼠急性溃疡性结肠炎模型建立与评价[J/CD].中华结直肠疾病电子杂志,2015, 4(6): 617-619.
The establishment and evaluation of acute ulcerative colitis in rat model induced with DSS
Kong Pengfei, Zhao Bing, Qin Qin, Li Min, Tang Xuegui. Anorectal section, The Affliated Hospital of North of Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan, China
Corresponding author: Tang Xuegui, Emali: txg668nc@sohu.com
Objective To explore the dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) to induce mice acute ulcerative coutis model. Methods Sixty Spragur-Dawley rats, 30 female and 30 male, the sixty SD rats were randomized to blank group and model group. Animals in blank group were diet random, the model groups were given 3% DSS solution as drinking water for 7 days. After that, Observe the DAI、HI. Results DAI and HI in model group were higher than the blank group, the difference was significant (P<0.01). Model group were different degrees of diarrhea、fecal occult blood and bloody purulent stool. Infammation mainly involving the mucosa and submucosa, intraepithelial goblet cells decreased, crypt destruction. Conclusions This colitis model in DSS to induce mice acute ulcerative coutis appears to share nearly all the morphological characteristics with human UC. The colitis model is one of the ideal model of UC.
Colitis, ulcerative; Disease models, animal; Acute stage
10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3224.2015.06.09
637000 四川南充,川北医学院附属医院肛肠科
唐学贵,Emali:txg668nc@sohu.com
(2015-11-07)
