巴氏腺脓肿造瘘术式的临床观察
2015-08-22王宇翀孙梦妍薛春雨
朱 吉, 吕 川, 赵 辉, 王宇翀, 孙梦妍, 武 铠, 邢 新, 薛春雨
作者单位:200433 上海,上海长海医院 整形外科
巴氏腺脓肿造瘘术式的临床观察
朱 吉, 吕 川, 赵 辉, 王宇翀, 孙梦妍, 武 铠, 邢 新, 薛春雨
作者单位:200433 上海,上海长海医院 整形外科
目的 寻找一种治疗巴氏腺脓肿的简单有效方法。方法 自2011年1月至2012年6月,我们对12例会阴部巴氏腺脓肿患者采用造瘘术进行治疗。局部麻醉下,于巴氏腺开口及其上方分别设计2个切口,排除腔内脓液,橡胶半管贯穿两切口留置腔内,端端缝合成环状。术后每天换药至无脓性分泌物。结果 12例患者置管期间均无不适主诉。4周后无困难取出环状导管,巴氏腺脓肿愈合,产生2个上皮化的窦道。随访2年以上,脓肿无复发。结论 造瘘术是治疗巴氏腺脓肿的一种简单、安全、有效的方法,可作为巴氏腺脓肿的治疗方法之一。
巴氏腺脓肿; 造瘘术; 会阴部
前庭大腺,又名巴氏腺,位于阴道口两侧。前庭大腺分腺体和导管两部分,导管是1条长约2.0 cm的细长管道,专门输送前庭大腺分泌的黏液,开口于小阴唇和处女膜之间的沟内,前庭大腺所分泌的黏液性物质经该管道输送到阴道口起润滑作用。巴氏腺平时不可触及。如果前庭大腺管阻塞,分泌物积聚而成前庭大腺囊肿。一旦感染即形成脓肿。目前常规方法是切开引流或造口术[1-3],但引流管易脱落,脓肿易复发[4], 造口术则易造成愈合缓慢、血肿和感染[5]。自2011年1月至2012年6月,我们对会阴部巴氏腺脓肿的患者采用造瘘术进行治疗,取得了满意的效果。现报道如下。
1 临床资料
本组患者共12例。均为女性;年龄28~38岁,平均31岁。病程4~10 d,脓肿长轴为3.0~5.0 cm,均有会阴部疼痛、红肿,伴行走不适。患者均无会阴部手术史,无性传播疾病及妇科疾病。
2 手术方法
患者取截石位,常规消毒铺巾,2%利多卡因局部麻醉,于巴氏腺开口处作长约0.5 cm切口,于该切口上方2.0~3.0 cm处另设计一长约0.5 cm切口,切开皮肤后,以血管钳钝性分离至巴氏腺脓腔内,排除脓液,以双氧水和洗必泰反复冲洗。将常规直径约6.0 mm医用橡胶管沿纵轴剪开,得到约6.0 cm 长半管,一端自一个切口置入,经过残腔由另一切口穿出,端端缝合成环状。术后每天予双氧水和洗必泰腔内冲洗,直至无脓性分泌物,之后每周至门诊复诊换药1次,要求患者在家中每次如厕之后以洗必泰清洗。
3 结果
12例患者置管期间均无不适主诉,无留置管脱落。4周后无困难取出环状导管,巴氏腺脓肿愈合,产生2个上皮化的窦道(图1)。随访2年以上,均无复发。
4 讨论
约有2%的女性会发生巴氏腺囊肿,35~50岁的女性相对高发,脓肿的发生率则是囊肿的3倍[6-7], 有症状的巴氏腺导管囊肿和巴氏腺脓肿均需要治疗[8]。目前巴氏腺脓肿的治疗方法主要有切开引流术和造口术[4,9-10],国外常采用Word导管留置造口[11-12],以上方法存在一些缺点,如局部炎性肿胀致引流不畅,引流管易滑脱,切口易粘连闭合,术后易复发[13-14]。其他治疗方法包括腔内注射高渗乙醇、碘酊、硝酸银棒、激光和微波破坏囊壁,这些方法则易造成前庭大腺功能破坏。
我们在前人的基础上加以改进[15],具有以下优势:⑴使用材料为医用橡胶管,有弹性,质较软,长期留置患者无明显不适,不影响患者的日常生活;⑵环状缝合,留置半管不易滑脱; ⑶较长的留置时间足够形成的管道上皮化,不易再次闭塞,降低复发率;⑷形成的2个管道将管道闭塞造成巴氏腺囊肿或脓肿的复发概率下降了50%;⑸保留腺体功能。为达到充分的效果,术中需要注意以下方面:⑴留置半管的大小约为医用橡胶导管(管径约6.0 mm)1/3周径;本组中有1例曾留置头皮针管,22个月后复发,我们分析是管道太细不利于窦道上皮化,窦道闭塞,脓肿复发;⑵2个切口必须明确与巴氏腺脓腔相通,避免2个切口在皮下形成无效通道。本术式取材方便,操作简单易行,值得推广。
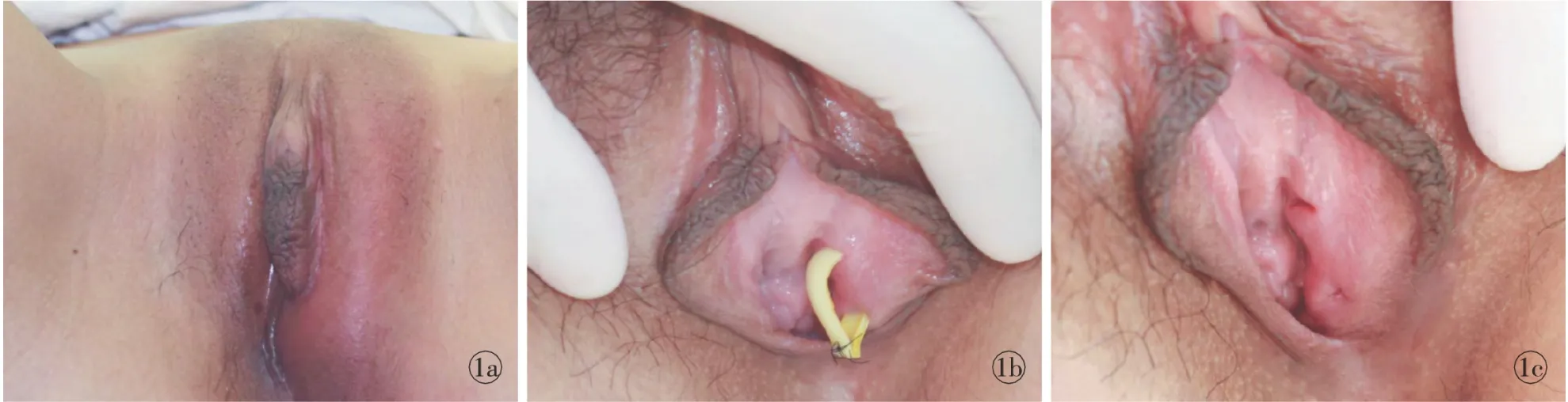
图1 左侧巴氏腺脓肿行造瘘术治疗前后对比 a.术前 b.术后即刻,脓腔内放置环状引流 c.术后4周拔除引流管后即刻,可见2个窦道口
Fig 1 Comparison between preview and postview of left bartholin gland abscess treated with fistulation. a. preview b. postview at once with a loop of tubing placed in the cavity. c. postview with two sinus tracts after drainage removal at 4 weeks.
[1] 郑丽君. 改良式巴氏腺囊肿造口术的疗效观察[J]. 浙江临床医学, 2003,5(1):55.
[2] 余 玉. 前庭大腺囊肿造口术式的临床研究[J]. 中国医药导报, 2007,4(9):39.
[3] Mayeaux EJ Jr, Cooper D. Vulvar procedures: biopsy, bartholin abscess treatment, and condyloma treatment[J]. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am, 2013,40(4):759-772.
[4] Omole F, Simmons BJ, Hacker Y. Management of Bartholin′s duct cyst and gland abscess[J]. Am Fam Physician, 2003,68(1):135-140.
[5] Horowitz I, Buscema J, Woodruff J. Surgical conditions of the vulva[M]∥Rock J, Thompson J, eds. Te Linde′s Operative Gynaecology. 8th edn. PA: Lippincott-Raven, 1997:890-893.
[6] Yuk JS, Kim YJ, Hur JY, et al. Incidence of Bartholin duct cysts and abscesses in the Republic of Korea[J]. Int J Gynaecol Obstet, 2013,122(1):62-64.
[7] Heller DS, Bean S. Lesions of the Bartholin gland: a review[J]. J Low Genit Tract Dis, 2014,18(4):351-357.
[8] Hill DA, Lense JJ. Office management of Bartholin gland cysts and abscesses[J]. Am Fam Physician, 1998,57(7):1611-1616,1619-1620.
[9] Li SF, Gennis P. Treatment of bartholin abscesses[J]. J Emerg Med, 2011,41(2):187.
[10] Ozdegirmenci O, Kayikcioglu F, Haberal A. Prospective randomized study of marsupialization versus silver nitrate application in the management of bartholin gland cysts and abscesses[J]. J Minim Invasive Gynecol, 2009,16(2):149-152.
[11] Haider Z, Condous G, Kirk E, et al. The simple outpatient management of Bartholin's abscess using the Word catheter: a preliminary study[J]. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol, 2007,47(2):137-140.
[12] Reif P, Elsayed H, Ulrich D, et al. Quality of life and sexual activity during treatment of Bartholin's cyst or abscess with a Word catheter[J]. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol, 2015 Mar 10.
[13] Stenchever MA. Comprehensive gynecology[M]. 4th ed. St. Louis: Mosby, 2001:482-486,645-646.
[14] Wechter ME, Wu JM, Marzano D, et al. Management of Bartholin duct cysts and abscesses: a systematic review[J]. Obstet Gynecol Surv, 2009,64(6):395-404.
[15] Kushnir VA, Mosquera C. Novel technique for management of Bartholin gland cysts and abscesses[J]. J Emerg Med, 2009,36(4):388-390.
Clinical observation of fistulation for Bartholin gland abscess
ZHUJi,LYUChuan,ZHAOHui,etal.
(DepartmentofPlasticSurgery,ChanghaiHospital,SecondMilitaryMedicalUniversity,Shanghai200433,China)
Objective To explore a simple and effective method of treatment of a Bartholin gland abscess. Methods Between January 2011 and June 2012, 12 patients with Bartholin gland abscess were treated with fistulation in our department. Their clinical materials and follow-up results were retrospectively analyzed. Under local anesthetic, two incisions were made respectively in the area of the duct orifice and a loop of tubing was placed, allowing for drainage of the abscess. The abscess cavity was sterilized every day until there was no purulent secretion produced. Results The 12 patients with were with no complaints during the tube replacement. The Bartholin gland abscess healed with two epithelialized sinus tracts after the device was removed smoothly at 4 weeks postoperatively. There were no recurrences of Bartholin gland abscess after over 2 years following up. Conclusion Fistulation is a simple and effective method to treat Bartholin gland abscess.
Bartholin gland abscess; Fistulation; Perineum
朱 吉(1979-),女,江苏人,主治医师,博士.
薛春雨,200433,上海长海医院 整形外科,电子信箱:xcyfun@sina.com
10.3969/j.issn.1673-7040.2015.07.010
R711.3
A
1673-7040(2015)07-0412-03
2015-04-10)
