用于求解Poisson方程的格子Boltzmann模型
2015-08-16王博宇闫广武
王博宇,闫广武
(吉林大学 数学学院,长春 130012)
用于求解Poisson方程的格子Boltzmann模型
王博宇,闫广武
(吉林大学 数学学院,长春 130012)
提出一个求解Poisson方程的格子Boltzmann模型.通过使用Chapman-Enskog展开和多尺度展开得到了在不同时间尺度下的系列偏微分方程及平衡态分布函数和具有三阶截断的误差修正Poisson方程.用该模型计算Kolmogorov流和Green-Taylor涡流,并与解析解进行比较,计算结果表明,数值结果与经典解析结果基本相符.
格子Boltzmann模型;Poisson方程;Kolmogorov流
0 引 言
格子Boltzmann方法(LBM)目前已经发展成为用于计算流体动力学(CFD)的可选择性方法[1-2].LBM可用于模拟单组分水动力学问题,包括悬浮微粒的多组分流体问题、磁流体力学、反应扩散系统、多孔介质流动问题及其他复杂系统.此外,格子Boltzmann模型广泛应用于模拟线性和非线性偏微分方程,如波动方程[3]、Burgers方程[4]、KDV方程[5]、非线性Schödinger方程[6]、Poisson方程[7]和复Ginzburg-Landau方程[8]等.
本文提出一种基于格子Boltzmann模型处理Poisson方程的新数值方法.其中Poisson方程为
(1)
在应用LBM求解方程(1)时,有两种选择:1)使用一种与时间无关的空间多尺度技术恢复该方程;2)使用时间多尺度技术恢复该Poisson方程.本文选用第二种方法.引入方程:
(2)
其中u(x,t)满足
(3)
则当t→∞时,方程(2)的解恰好是方程(1)的解.
目前,模拟Poisson方程的方法主要有有限差分法、有限单元法以及最小二乘法等[9-11].新的求解技术有分辨算法和预调节技术[12-13]、Trefftz方法[14]、平面波方法[15]、非协调Galerkin方法[16]、最小二乘法[17]和无网格薄板样条方法[18]等.本文提出一种一维和二维格子Boltzmann模型,并给出了数值算例.
1 格子Boltzmann模型
1.1不同时间尺度下的系列偏微分方程
定义fα(x,t)为在t时刻位于x处的单粒子分布函数.考虑一维或二维格子Boltzmann模型,在该模型中,一维或二维格子上具有b+1个离散速度,除静止粒子外,其他粒子沿路径移动到其他相邻格点上.如果考虑粒子到达某一个格点时发生了粒子间的碰撞,则格子Boltzmann方程为

其中:Ωα(fα(x,t))称为碰撞算子;ωα(x,t)表示附加项.在标准格子Boltzmann模型中,ωα=0.本文选取

其中:ε为Knudsen数;φα为独立于α的函数.一种简单碰撞算子是选取一个线性形式的具有弛豫时间τ的算符:
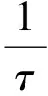

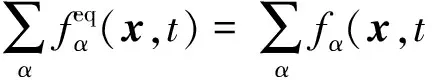
(7)
Knudsen数ε定义为ε=l/L,其中:l是粒子自由程;L是特征长度,可以被选为时间步长Δt.因此,格子Boltzmann方程(4)可写为
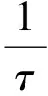
方程(8)中,Knudsen数ε被假设为小量,故可在小Knudsen数假设下进行Chapman-Enskog展开:
(9)
t0,t1,t2表示不同的时间尺度,定义为
(10)
及
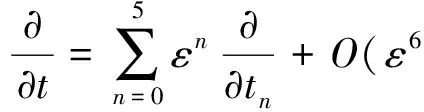
(11)
因此,可得一系列偏微分方程:
(12)
(13)
(14)
(15)

方程(12)~(15)又称为不同时间尺度下的系列偏微分方程,它适用于一维、二维及三维情形,其中3个多项式系数与弛豫时间τ有关:
(16)
(17)
(18)
式(16)~(18)为第二~第四个Chapman多项式,与文献[19]结果完全一致.
1.2Poisson方程的恢复
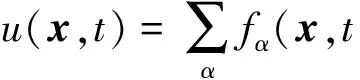
(19)
(20)
(21)
(22)
(23)
特别地,对于一维情形,这些矩函数可记为
(24)
(25)
(26)
(27)
(28)

图1 计算格子示意图Fig.1 Diagrammatic sketches of lattice
对于一维模型,考虑5-bit格子.离散化的速度向量为e=(0,c,-c,2c,-2c),其中:α=0,1,2,3,4;c表示速度.格子的示意图如图1所示.5-bit格子模型的平衡态分布函数由式(24)~(28)解出,分别为
(29)
(30)
(31)
(32)
(33)
1.3一维Poisson方程的格子Boltzmann模型
一维Poisson方程具有如下形式:
(34)
选取
(35)
(36)
(37)
(38)
(39)
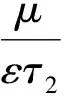
将式(12)+ε×式(13)+ε2×式(14)+ε3×式(15),并对α求和,可得:

如果选取(b+1)εφ=μ(ku-g),则修正后的一维Poisson方程为

方程(41)中,E2和E3由下式确定:
(42)
(43)
1.4二维Poisson方程
二维Poisson方程具有如下形式:
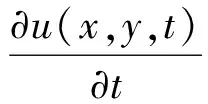
使用如图1(B)所示的二维格子,则粒子速度向量为
eα={(0,0),(c,0),(0,c),(-c,0),(0,-c),(2c,0),(0,2c),(-2c,0),(0,-2c)},α=0,1,…,8.
假设各阶矩为式(35)及
(45)
(46)
(47)
(48)
则平衡态分布函数记为
(49)

(51)
将式(12)+ε×式(13)+ε2×式(14)+ε3×式(15)并对α求和,得

如果选取(b+1)εφα=μ(ku-g)作为式(51)的源项,则修正后的二维Poisson方程为

其中:E2为式(42);
(54)
因此,可得具有三阶截断误差精度的Poisson方程:

(55)
2 数值算例
下面应用格子Boltzmann方法模拟一维和二维Poisson方程.
例1考虑Kolmogorov流:
(56)
边界条件为

如果u独立于y,则方程具有解析解:
(58)
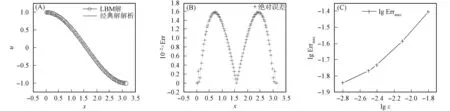
其数值计算结果如图2和图3所示.其中:图2(A)是LBM计算结果;图2(B)是解析解;图3(A)为LBM结果与解析解在y=0.2π处的比较;图3(B)为y=0.2π处的绝对误差曲线;图3(C)为lg Errmax对lgε在y=0.2π处的无穷模曲线.
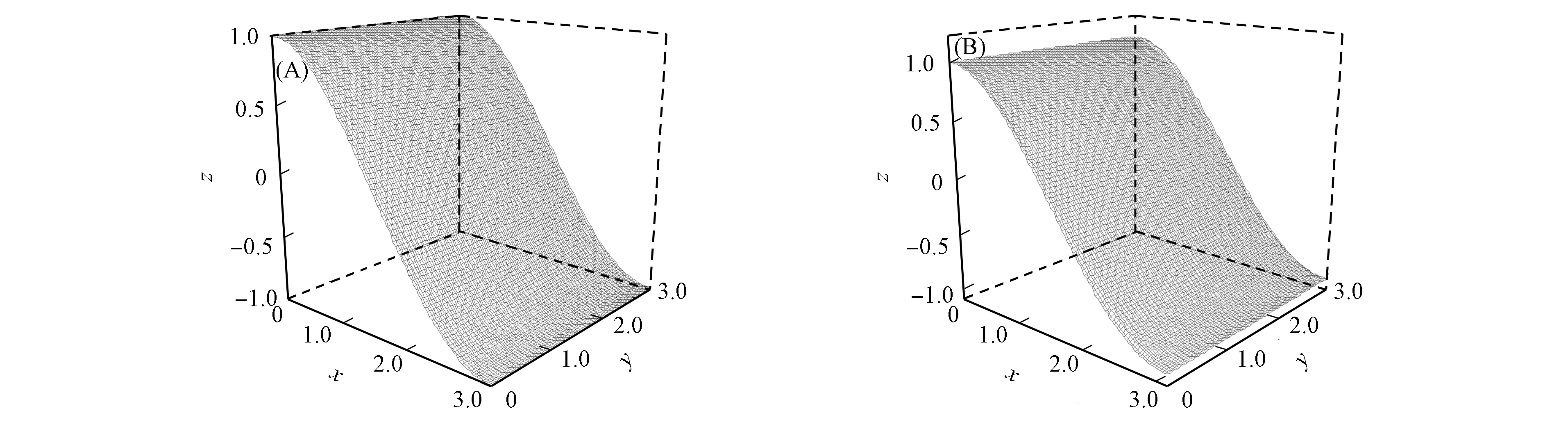
参数A0=1.0,c=168.0,μ=1.0,λ=c2;网格数M=101,Δ x=π/M=π/101,Δ t=ε=Δ x/c;迭代步数10 000.
参数c=168.0,μ=1.0,λ=0.43c2;网格数M=101×101,Δ x=Δ y=π/M=π/101,Δ t=ε=Δ x/c=Δ y/c.
例2考虑Green-Taylor涡流,其中流函数满足Poisson方程:
2u(x,y)+8π2u(x,y)=0, 0≤x≤1, 0≤y≤1;
(59)
边界条件为

(60)
方程(59)具有解析解:

(61)
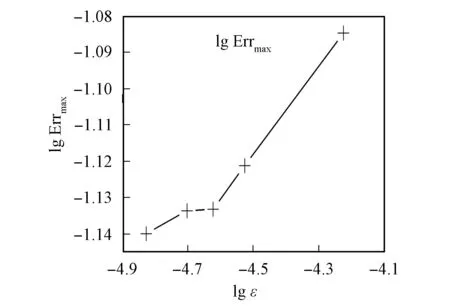
其解析解和数值解如图4所示.其中图4(A)和图4(B)分别为LBM数值解和解析解的表面图.由图4可见,LBM数值解与经典解析结果基本吻合.图5为绝对误差最大值Err=|uN-uA|和Knudsen数ε的关系曲线.由图5可见,LBM数值解的精度与网格密度成正比,这与模型的选取有关.

参数A0=1.0,c=168.0,μ=1.0,λ=c2;格子规模M=101×101,Δ x=Δ y=π/M=π/101,Δ t=ε=Δ x/c=Δ y/c;迭代步数为10 000.
参数c=168.0,A0=1.0,μ=1.0,λ=0.43c2.
综上,本文提出了求解Poisson方程具有高阶精度的格子Boltzmann模型.通过使用Chapman-Enskog展开和多尺度展开技术得到了系列偏微分方程及平衡态分布函数的高阶矩和修正后的具有三阶截断误差的Poisson方程;给出了LBM数值解与Kolmogorov流和Green-Taylor涡流精确解的比较,结果表明,数值结果与经典解析解基本吻合.
[1] CHEN Shiyi,Doolen G D.Lattice Boltzmann Method for Fluid Flows [J].Annu Fluid Mech,1998,30:329-364.
[2] Succi S.The Lattice Boltzmann Equation for Fluid Dynamics and Beyond [M].New York:Oxford University Press,2001.
[3] ZHANG Jianying,YAN Guangwu,SHI Xiubo.Lattice Boltzmann Model for Wave Propagation [J].Phys Rev E,2009,80:026706.
[4] Velivelli A C,Bryden K M.Parallel Performance and Accuracy of Lattice Boltzmann and Traditional Finite Difference Methods for Solving the Unsteady Two-Dimensional Burger’s Equation [J].Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications,2006,362(1):139-145.
[5] YAN Guangwu,ZHANG Jianying.A Higher-Order Moment Method of the Lattice Boltzmann Model for the Korteweg-De Vries Equation [J].Math Comput Simulat,2009,79(5):1554-1565.
[6] ZHANG Jianying,YAN Guangwu.A Lattice Boltzmann Model for the Nonlinear Schrödinger Equation [J].J Phys A:Math and Theore,2007,40(33):10393-10405.
[7] WANG Huimin,YAN Guangwu,YAN Bo.Lattice Boltzmann Model Based on the Rebuilding-Divergency Method for the Laplace Equation and the Poisson Equation [J].J Sci Comput,2011,46(3):470-484.
[8] ZHANG Jianying,YAN Guangwu.Lattice Boltzmann Model for the Complex Ginzburg-Landau Equation [J].Phys Rev E,2010,81:066705.
[9] Nabavi M,Kamran Siddiqui M H,Dargahi J.A New 9-Point Sixth-Order Accurate Compact Finite-Difference Method for the Helmholtz Equation [J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,2007,307(3):972-982.
[10] Babuska I,Osborn J.Handbook of Numerical Analysis [M].Vol.Ⅱ.Eigenvalue Problems.Amsterdam:North-Holland,1991:641-787.
[11] Chang C L.A Least Squares Finite Element Method for the Helmholtz Equation [J].Comput Methods Appl Mech Engrg,1990,83:1-7.
[12] Farhat C,Hetmaniuk U.A Fictious Domain Decomposition Method for the Solution of Partially Axisymmetric Acoustic Scattering Problems.Part Ⅰ:Dirichlet Boundary Conditions [J].Int J Numer Methods Engrg,2002,54(9):1309-1332.
[13] Farhat C,Macedo A,Lesoinne M.A Two-Level Domain Decomposition Method for the Iterative Solution of High Frequency Exterior Helmholtz Problems [J].Numer Math,2000,85(2):283-308.
[14] Li Z C.The Trefftz Method for the Helmholtz Equation with Degeneracy [J].Applied Numerical Mathematics,2008,58(2):131-159.
[15] JIN Bangti,Marin L.The Plane Wave Method for Inverse Problems Associated with Helmholtz Type Equations [J].Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements,2008,32(3):223-240.
[16] Douglas J,Jr,Santos J E,Shenn D.Nonconforming Galerkin Methods for the Helmholtz Equation [J].Numer Methods Partial Differential Equations,2001,17(5):475-494.
[17] Monk P,WANG Daqing.A Least-Squares Method for the Helmholtz Equation [J].Comput Methods Appl Mech Engrg,1999,175(1/2):121-136.
[18] Bouhamidi A,Jbilou K.Meshless Thin Plate Spline Methods for the Modified Helmholtz Equation [J].Comput Methods Appl Mech Engrg,2008,197(45/46/47/48):3733-3741.
[19] Holdych D J,Noble D R,Georgiadis J G,et al.Truncation Error Analysis of Lattice Boltzmann Methods [J].J Comput Phys,2004,193(2):595-619.
(责任编辑:赵立芹)
LatticeBoltzmannModelforPoissonEquation
WANG Boyu,YAN Guangwu
(CollegeofMathematics,JilinUniversity,Changchun130012,China)
A lattice Boltzmann model for the Poisson equation was proposed.By means of the Chapman-Enskog expansion and the multi-scale time expansion,a series of partial differential equations in different time scales was obtained.Moreover,the equilibrium distribution functions and the modified partial differential equation of the Poisson equation with the third-order truncation error were obtained.In numerical examples,the Kolmogorov flow and Green-Taylor vortex flow were simulated,and the comparison between numerical results of the lattice Boltzmann models and exact solutions were given.The numerical results are acceptable.
lattice Boltzmann model;Poisson equation;Kolmogorov flow
10.13413/j.cnki.jdxblxb.2015.03.11
2014-09-29.
王博宇(1992—),男,汉族,硕士研究生,从事流体力学与复杂系统数值模拟的研究,E-mail:bywang14@mails.jlu.edu.cn.通信作者:闫广武(1964—),男,汉族,博士,教授,博士生导师,从事复杂系统数值模拟的研究,E-mail:yangw_jlu@126.com.
国家自然科学基金(批准号:11272133).
O351.2
:A
:1671-5489(2015)03-0407-07
