番茄钵苗自动移栽钵体物理机械特性试验
2015-07-05梁喜凤蔡阳阳王永维
梁喜凤, 蔡阳阳, 王永维
(1.中国计量学院机电工程学院,杭州310018;2.浙江大学生物系统工程与食品科学学院,杭州310058;3.台州市汇科农业机械技术开发有限公司,浙江 台州318050)
番茄钵苗自动移栽钵体物理机械特性试验
梁喜凤1,2*, 蔡阳阳1, 王永维2,3
(1.中国计量学院机电工程学院,杭州310018;2.浙江大学生物系统工程与食品科学学院,杭州310058;3.台州市汇科农业机械技术开发有限公司,浙江 台州318050)
蔬菜钵苗钵体的物理机械特性,是设计全自动蔬菜移栽机取苗机构、栽植器等关键部件的重要依据。以苗龄为23 d的番茄钵苗为试验对象,利用Instron 5543万能试验机对其进行平板压缩、穿刺和蠕变试验,并随机选取30株钵苗进行500 mm高度的散落试验。研究表明:钵体受压时其抗压力与变形关系为非线性变化,钵体屈服点的抗压力为3.15 N,取苗机构设计时取苗夹取力要超过钵体屈服点的抗压力;钵体穿刺初期穿刺力与位移呈近似线性关系,随着变形的增加穿刺力在一定范围内保持不变,钵体穿刺后期穿刺力显著增加;钵体蠕变特性符合Burgers模型的蠕变规律,在加载力为5 N、保持时间为120 s条件下钵体的平均蠕变量为0.398 9 mm;钵体散落试验显示钵体平均散落率为22.73%,掉落后钵体保持完整,满足机械栽植要求。
蔬菜移栽机; 番茄钵体苗; 物理机械特性
Journal of Zhejiang University (Agric. & Life Sci.), 2015,41(5):616-622
蔬菜可提供人体所必需的多种维生素和矿物质,是人们日常饮食中必不可少的食物之一。我国是世界上最大的蔬菜生产国,2011年全国蔬菜种植面积达到1.97×1011m2[1]。约有60%以上的蔬菜品种采用育苗移栽方式种植,移栽作业仍以人工为主[2]。然而,传统的人工移栽方式不仅劳动强度大、生产效率低,而且栽植质量差、种植成本高,难以实现短时间大面积移栽[3]。因此,加大蔬菜移栽机械的研发力度,实现蔬菜移栽机械化已成为农业生产的迫切需要[4]。
目前,国内蔬菜移栽机主要有链夹式[5]、导苗管式[6]、吊篮式[7-9]及挠性圆盘式[10]等,移栽作业停留在半机械水平,移栽过程中需要人工辅助喂苗,致使移栽效率受到限制。国内学者通过运动分析、样机试验等方法对移栽机的结构参数和运动参数进行优化,试制自动移栽机械,初步实现了蔬菜自动移栽的功能要求[11-14]。然而,蔬菜自动移栽机的设计主要集中在取苗机构和栽植机构的研发上,设计目标也仅仅是满足插穴取苗、栽植种苗的功能要求,没有将结构设计与蔬菜钵苗钵体本身的物理机械特性联系起来分析设计[15]。
蔬菜钵苗自动移栽是一项综合性技术,需要将移栽机的设计与作业对象相结合。对钵苗钵体的物理机械特性进行研究,进而优化设计取苗机构和栽植机构等移栽机核心部件,将更加符合实际需要。本文以番茄穴盘苗为研究对象,测试分析与移栽机械设计直接相关的番茄钵苗钵体物理机械特性。通过钵体压缩试验,分析钵体的抗压力-变形变化规律,确定钵体在取苗过程中受夹持力特性。经过钵体穿刺试验,分析钵体在取苗夹持时穿刺力作用规律。通过钵体蠕变试验并结合Burgers模型描述,分析钵体的蠕变特性。同时对钵体进行500 mm高度的散落试验,得到钵体散落率,分析钵体移栽过程中的散落特性。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
试验于2014年1月19日在浙江大学生工食品学院进行。试验材料选用Alisa番茄穴盘苗,育苗穴盘为隆基育苗穴盘,72孔穴,穴深为45 mm,上口径尺寸为40 mm×40 mm,下口径尺寸为20 mm×20 mm。育苗基质采用浙江大学蔬菜所育苗用有机土,草炭和蛭石比例为2∶1。在PRX-350型智能人工气候箱中培养番茄穴盘苗,育苗时间为2013年12月28日至2014年1月19日,苗龄为23 d。钵苗形成后,钵苗根系在基质里穿插、缠绕、网络,形成根土复合体即钵体[16]。随机选取20株番茄苗,利用游标卡尺(精度为0.02 mm)测量番茄钵苗的物理参数。钵体的含水率采用干湿质量法测量,分别测量钵体的湿质量和干质量,计算钵体的含水率[15]。测得番茄钵苗主要生长指标和钵体几何参数见表1。
表1 番茄钵苗主要生长指标和钵体几何参数
Table 1 Main growth indexes of tomato seedlings and geometric parameters of the seedling pots

几何参数Geometricparameters数值Values钵苗苗高Seedlingheights/mm120.26~143.64钵苗茎粗Seedlingdiameters/mm2.00~4.06钵体上边长Lengthsofpotupperedge/mm36.62~39.16钵体下边长Lengthsofpotloweredge/mm17.46~19.86钵体高度Potheights/mm43.02~44.88钵体含水率Potwatercontent/%80.36~81.75
试验主要仪器为Instron 5543万能试验机(美国Illinois Tool Works公司),直径为100 mm的P100平板探头,直径为5 mm的P5圆柱形探头;TD型电子天平(精度为0.01 g)。试验材料和主要仪器见图1。

A:番茄钵苗钵体;B:Instron 5543万能试验机.A: Tomato seedling pot; B: Universal testing machine Instron 5543.图1 试验材料和主要仪器Fig.1 Experimental materials and major instruments
1.2 试验方法
钵体压缩试验采用平板压缩方式,利用Instron 5543万能试验机和P100平板探头,自上而下加载,加载速度为1 mm/s。由于钵体为四棱台形状,需要预先构建倾斜载物台,保持钵体和压缩平板接触面水平。试验时,随机选取10株番茄钵苗,重复测试20 mm压缩量下钵体的抗压特性。
钵体穿刺试验采用Instron 5543万能试验机和P5圆柱形探头,测试模式为压缩测试力,加载速度为1 mm/s。钵体在穿刺开始前进行预处理,在每个钵体顶端均匀选取4个穿刺位点进行穿刺试验[17]。试验时,随机选取10株番茄钵苗,重复测试30 mm穿刺位移下钵体的穿刺特性曲线。
钵体蠕变试验采用平板压缩方式,利用Instron 5543万能试验机和P100平板探头,加载力设置为5 N,蠕变保持时间为120 s。试验时,随机选取10株番茄钵苗,重复测试钵体在特定加载力下的蠕变特性,并得出钵体的平均蠕变量。
在自动移栽过程中,钵体由取苗机构带至栽植机构上方释放,钵体下落至栽植机构内基质会造成损失,钵体以一定高度下落后钵体保持完整是机械化植苗的关键。为了区分钵体散落后是否为裸苗,定量分析钵体散落特性,定义散落过程中钵体散落率P,表达式为

式中:m1为散落前钵体的质量,g;m2为散落后钵体的质量,g.
钵体散落试验测试500 mm跌落高度钵体的基质损失率情况,搭建500 mm高度的散落平台,随机选取30株番茄钵苗,剪去钵体外部的钵苗茎叶。试验时,钵体以自由落体的方式从500 mm高度的散落平台跌落,记录散落前后钵体的质量并计算钵体散落率。
2 结果与分析
2.1 钵体压缩试验
蔬菜自动移栽时,需要考虑到取苗机构对钵体的挤压力。为得到钵体受取苗机构作用力时的抗压力与变形间的关系,选取1组试验数据进行多项式回归(图2),回归决定系数R2为0.995,回归方程为
y=0.010 3x3-0.174 9x2+1.447 4x-1.306 5。

图2 番茄钵苗钵体抗压力-变形回归曲线Fig.2 Pressure-deformation regression curve of compression experiment for tomato seedling pots
由图2可知,钵体抗压力-变形曲线前期阶段为非线性,且抗压力随着变形的增加变化较小,其原因是该阶段钵体比较松软,基质间空隙较多,受压时钵体基质颗粒间出现滑动、坍塌和重新排列,从而使得钵体在受压变形时其抗压力变化较小,钵体表现出生物屈服软化特性。随着钵体不断受压,其内部基质趋于紧密,曲线显示钵体抗压力急剧增加,钵体表现出生物压实硬化特性。在压缩过程中,钵体抗压力与变形关系为非线性曲线,没有明显的线弹性。
同时对回归方程进行求导,将变形为5.64 mm的点定义为钵体屈服点M,此时钵体抗压力为3.15 N。屈服点M的斜率是回归方程斜率的最小点,其斜率为K=0.46,将此斜率K定义为钵体的压缩刚度。钵体受压时在屈服点内会出现生物屈服软化现象,取苗夹取力在此范围内容易出现松弛,不利于钵体的夹取,所以钵苗自动移栽时选择的夹取力要超过屈服点压力。
2.2 钵体穿刺试验
由于钵体和育苗穴盘间的间隙极小,移栽时取苗机构无法直接挤压夹取钵苗,取苗机构一般先通过取苗针对钵体进行穿刺,再夹紧取出钵苗。图3A是钵体穿刺试验的穿刺力-位移曲线,表征钵体在穿刺时穿刺力和位移之间的关系曲线。选取图3A曲线的1组数据进行回归,如图3B所示,得到钵体穿刺时的穿刺力与穿刺位移的回归曲线。由图3A可以看出,在钵体穿刺试验过程中,其穿刺力随着穿刺位移的增加而增大,但在不同的位移处表现出来的变化趋势完全不同。为了更好地分析钵体穿刺规律,如图3B所示,分阶段对测试数据进行回归分析,回归方程式为

A:钵体穿刺力-位移曲线;B:钵体穿刺载荷-穿刺位移回归分析. A: Puncturing force-displacement curve of the pots; B: Puncturing loads-puncturing displacement regression curve of the pots.图3 番茄钵苗钵体穿刺特性曲线Fig.3 Puncture property curve of puncture experiment for tomato seedling pots
回归方程的决定系数R2分别为0.997、0.804、0.997,均大于0.800,说明该方程与试验拟合良好,试验误差较小[18]。通过回归方程可以知道,当穿刺位移小于13.5 mm时,穿刺载荷随着穿刺位移的增加而增大,并呈线性关系;当穿刺位移大于13.5 mm且小于19.5 mm时,随着穿刺位移的增加,穿刺载荷基本保持不变;当穿刺位移大于19.5 mm时,穿刺载荷随着穿刺位移的增加而显著增大,穿刺载荷与穿刺位移的关系为非线性曲线。
对于钵苗钵体这种特定的农业物料,内部是钵苗根系和钵体基质的复合体,表现出较复杂的穿刺特性。初始阶段的线性变化原因在于随着穿刺位移的增加圆柱形探头与钵体的接触面积增大,且接触面积的增大与位移呈正比关系,导致摩擦力线性增加;中间阶段由于圆柱形探头进入钵苗根部区域,受到的阻力相对较小,导致穿刺载荷在钵体中部能够基本保持不变,此时的穿刺载荷约为5 N;最后阶段由于圆柱形探头与钵体的接触面积持续增加,且钵体中部根系的作用,穿刺载荷显著增大,表现出非线性曲线关系。
2.3 钵体蠕变试验
在取苗过程中,钵体处于一个定压力下的蠕变状态中,必须明确有关力学特性和确定其基本参数,这样才能使得取苗机构的设计、计算具有理论性和实用性,达到数量化的描述。图4是恒定载荷条件下钵体的蠕变特性曲线,表征钵体的蠕变位移随时间的变化规律。

图4 番茄钵苗钵体蠕变特性曲线Fig.4 Creep property curve of creep experiment for tomato seedling pots
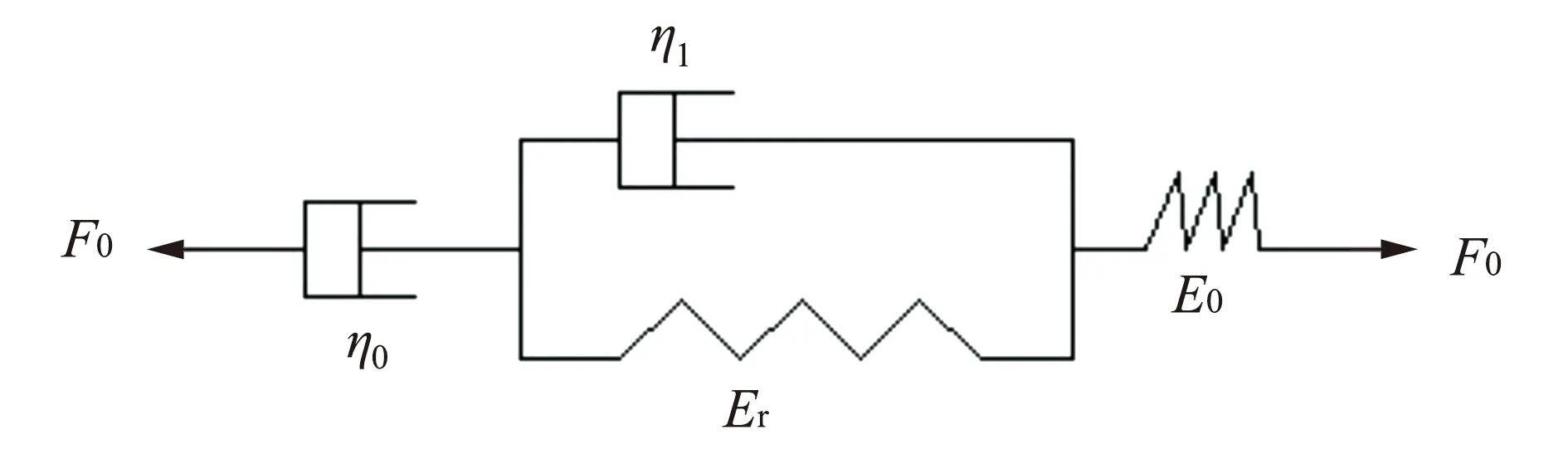
图5 Burgers模型示意图Fig.5 Schematic diagram of Burgers model
蠕变模型采用四元件的Burgers模型,如图5所示,该模型在外力作用下同时呈现出弹性变形和黏性流动变形,可以较好地描述黏弹性物料的性质[15,19-21]。因此,选择Burgers模型来分析钵体的蠕变特性,其蠕变变形随时间变化的关系式为
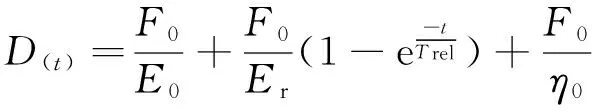
式中:D(t)为任意时间t时的变形量,mm;t为蠕变时间,s;F0为恒定载荷,N;E0和Er为弹性系数,N/mm;e是自然对数的底数,e=2.718 28;Trel为延迟时间(Trel=η1/Er),s;η0和η1:黏性系数,N·s/mm.
依据最小二乘法原理,利用Matlab软件对钵体蠕变试验数据进行拟合,并作回归分析,求出其蠕变特性参数及相关系数,钵体拟合方程的决定系数R2为0.981,由蠕变特性参数可得钵体蠕变过程Burgers拟合方程为
D(t)=-9.599 4 et+0.000 8t+9.439 2。
图6为钵苗钵体蠕变试验和模拟结果,通过比较可以看出蠕变模拟结果与本试验结果吻合较好,表明Burgers模型能够很好地描述钵体在压缩过程中的蠕变特性。此外,在加载力为5 N,保持时间为120 s的条件下钵体的平均蠕变量为0.398 9 mm,可见其蠕变量较小,机械夹取时夹紧松弛受钵体蠕变量变化的影响不大。

图6 钵苗钵体蠕变试验结果和模拟结果Fig.6 Experimental and simulation results of seedling pot creep deformation
2.4 钵体散落试验
蔬菜自动移栽机从穴盘中取苗后,夹持钵体至释放点,取苗机构释放钵体使其落至栽植机构内。这是由于受到碰撞和冲击作用,钵体基质会造成损失,这一过程中钵体基质的损失情况对设计取苗机构和栽植机构具有重要影响。试验将随机选取的30株番茄苗钵体标记序号,并称钵体质量m1,然后依次进行500 mm高度散落后再次称钵体质量m2,通过计算钵体散落率P,判断钵体移栽散落过程对钵体基质的影响。试验结果如表2所示,番茄苗钵体散落后最小散落率为18.36%,最大散落率为28.23%,平均散落率为22.73%。由于钵体是一个根土复合体,在试验条件下钵体散落后只是表面部分基质损失,掉落后钵体主体形状完整,依然为钵苗,满足自动移栽要求。从分析试验的过程可知,部分番茄苗的根系不够发达,钵体基质比较松散,都会造成散落后基质损失率偏大。

表2 番茄苗钵体散落率试验结果
3 结论
3.1 番茄钵苗钵体受压时,其抗压力与变形关系为非线性曲线。当变形为5.64 mm时,钵体屈服点出现,对应的钵体抗压力为3.15 N。取苗时取苗机构的夹取力应超过钵体的屈服点压力,才有利于夹紧且不容易出现松弛。
3.2 钵体是钵苗根系和基质的复合体,钵体穿刺位移在0~13.5 mm范围内穿刺力随穿刺位移呈线性增加,穿刺位移在13.5~19.5 mm范围穿刺力基本保持不变,当钵体穿刺位移大于19.5 mm时穿刺力急剧增加。
3.3 在加载力为5 N、保持时间为120 s条件下番茄钵苗钵体的平均蠕变量为0.398 9 mm,钵体蠕变特性符合Burgers模型的蠕变规律,拟合方程的决定系数R2为0.981。
3.4 苗龄为23 d的番茄钵苗钵体在500 mm散落高度自由跌落,钵体散落率为18.36%~28.23%,平均钵体散落率为22.73%,钵体散落后只是钵体表面基质损失,主体形状完整,依然为钵苗,有利于移栽作业的完成。
[1] 王素玲,陈明均.我国蔬菜流通现状及发展对策.中国蔬菜,2013(7):1-5. Wang S L, Chen M J. The present circulation situation and development countermeasures of vegetable in China.ChinaVegetables, 2013(7):1-5. (in Chinese)
[2] 王君玲,高玉芝,李成华.蔬菜移栽生产机械化现状与发展方向.农机化研究,2004(2):42-43. Wang J L, Gao Y Z, Li C H. The present situation and development direction of the vegetable transplanting production mechanization.JournalofAgriculturalMechanizationResearch, 2004(2):42-43. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 薛党勤,侯书林,张佳喜.我国旱地移栽机械的研究进展与发展趋势.中国农机化学报,2013,34(5):8-11. Xue D Q, Hou S L, Zhang J X. Development trend and research progress of nonirrigated farmland transplanting in China.JournalofChineseAgriculturalMechanization, 2013,34(5):8-11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 叶秉良,刘安,俞高红,等.蔬菜钵苗移栽机取苗机构人机交互参数优化与试验.农业机械学报,2013,44(2):57-62. Ye B L, Liu A, Yu G H,etal. Parameters optimization with human-computer interaction method and experiment of vegetable seedling pick-up mechanism.TransactionsoftheChineseSocietyforAgriculturalMachinery, 2013,44(2):57-62. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 金诚谦,吴崇友,袁文胜.链夹式移栽机栽植作业质量影响因素分析.农业机械学报,2008,39(9):196-198. Jin C Q, Wu C Y, Yuan W S. Analysis on affecting factors of the operating quality of the clip-chain transplanter.TransactionsoftheChineseSocietyforAgriculturalMachinery, 2008,39(9):196-198. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 倪向东,梅卫江.导管式番茄移栽机的设计.农机化研究,2011(2):84-87. Ni X D, Mei W J. Design on the tomato transplanting machine.JournalofAgriculturalMechanizationResearch, 2011(2):84-87. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 崔巍,赵亮,宋建农,等.吊杯式移栽机栽植器运动学分析与试验.农业机械学报,2012,43(10):35-38. Cui W, Zhao L, Song J N,etal. Kinematic analysis and experiment of dibble-type planting devices.TransactionsoftheChineseSocietyforAgriculturalMachinery, 2012,43(10):35-38. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 刘洋,李亚雄,赵华伟,等.吊篮式移栽机双工位喂苗机构的设计.石河子大学学报:自然科学版,2010,28(5):628-630. Liu Y, Li Y X, Zhao H W,etal. A design of duplex working positioned picking seedling machinery of bastkate-type transplanter.JournalofShiheziUniversity:NaturalScience, 2010,28(5):628-630. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 封俊,秦贵,宋卫堂,等.移栽机的吊杯运动分析与设计准则.农业机械学报,2002,33(5):48-50. Feng J, Qin G, Song W T,etal. The kinematic analysis and design criteria of the dibble-type transplanters.TransactionsoftheChineseSocietyforAgriculturalMachinery, 2002,32(5):48-50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 王石,王笑岩,李成华.挠性圆盘式蔬菜移栽机运动仿真分析.农机化研究,2013(10):42-45. Wang S, Wang X Y, Li C H. Analysis of kinematic simulation of soft disc-type vegetable seedling transplanter.JournalofAgriculturalMechanizationResearch, 2013(10):42-45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 叶秉良,俞高红,陈志威,等.偏心齿轮-非圆齿轮行星系取苗机构的运动学建模与参数优化.农业工程学报,2011,27(12):7-12. Ye B L, Yu G H, Chen Z W,etal. Kinematics modeling and parameters optimization of seedling pick-up mechanism of planetary gear train with eccentric gear and non-circular gear.TransactionsoftheChineseSocietyofAgriculturalEngineering, 2011,27(12):7-12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 金鑫,李树君,杨学军,等.蔬菜穴盘苗取苗机构分析与参数优化.农业机械学报,2013,44(增刊1):1-6. Jin X, Li S J, Yang X J,etal. Analysis and parameter optimization for vegetable plug seedling pick-up mechanism.TransactionsoftheChineseSocietyforAgriculturalMachinery, 2013,44(Suppl.1):1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 陈建能,王伯鸿,任根勇,等. 蔬菜移栽机放苗机构运动学模型建立与参数分析.农业机械学报,2010,41(12):48-53. Chen J N, Wang B H, Ren G Y,etal. A kinematics modeling and parameters analysis of seven-linkage vegetable seedling transplanting mechanism.TransactionsoftheChineseSocietyforAgriculturalMachinery, 2010,44(12):48-53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 俞高红,陈志威,赵匀,等.椭圆—不完全非圆齿轮行星系蔬菜钵苗取苗机构的研究.机械工程学报,2012,48(13):32-39. Yu G H, Chen Z W, Zhao Y,etal. Study on vegetable plug seedling pick-up mechanism of planetary gear train with ellipse gears and incomplete non-circular gear.JournalofMechanicalEngineering, 2012,48(13):32-39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 韩绿化,毛罕平,胡建平,等.穴盘苗自动移栽钵体力学特性试验.农业工程学报,2013,29(2):24-29. Han L H, Mao H P, Hu J P,etal. Experiment on mechanical property of seedling pot for automatic transplanter.TransactionsoftheChineseSocietyofAgriculturalEngineering, 2013,29(2):24-29. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 韩绿化,毛罕平,缪小花,等.基于穴盘苗力学特性的自动取苗末端执行器设计.农业机械学报,2013,44(11):260-265. Han L H, Mao H P, Miao X H,etal. Design of automatic picking up seedling end-effector based on mechanical properties of plug seedlings.TransactionsoftheChineseSocietyforAgriculturalMachinery, 2013,44(11):260-265. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 马庆华,王贵禧,梁丽松. 质构仪穿刺试验检测冬枣质地品质方法的建立.中国农业科学,2011,44(6):1210-1217. Ma Q H, Wang G X, Liang L S. Establishment of the detecting method on the fruit texture of Dongzao by puncture test.ScientiaAgriculturaSinica, 2011,44(6):1210-1217. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 刘宇欣,肖志刚,杨庆余,等.挤压复合酶法制备玉米多孔淀粉工艺参数优化.农业机械学报,2013,44(4):171-178. Liu Y X, Xiao Z G, Yang Q Y,etal. Optimization of technology parameters of corn porous starch by extrusion-enzyme synergistic method.TransactionsoftheChineseSocietyforAgriculturalMachinery, 2013,44(4):171-178. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] Cenkowski S, Bielewicz J, Britton M G. A single kernel creep and recovery test.TransactionsoftheAmericanSocietyofAgriculturalandBiologicalEngineers, 1991,34(6):2484-2490.
[20] 陆秋君,王俊,黄会明,等.番茄整果在常温贮藏中的蠕变特性试验.浙江大学学报:农业与生命科学版,2006,32(2):168-172. Lu Q J, Wang J, Huang H M,etal. Study on the creep property of intact tomatoes stored at normal temperature.JournalofZhejiangUniversity:Agriculture&LifeSciences, 2006,32(2):168-172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 杨晓清,王春光.河套蜜瓜静载蠕变特性的试验研究.农业工程学报,2007,23(3):202-207. Yang X Q, Wang C G. Creep properties of Hetao muskmelon under static loading.TransactionsoftheChineseSocietyofAgriculturalEngineering, 2007,23(3):202-207. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Experiment on physical and mechanical properties of tomato seedling pot for automatic vegetable transplanter.
Liang Xifeng1,2*, Cai Yangyang1, Wang Yongwei2,3
(1.CollegeofMechanicalandElectricalEngineering,ChinaJiliangUniversity,Hangzhou310018,China; 2.CollegeofBiosystemsEngineeringandFoodScience,ZhejiangUniversity,Hangzhou310058,China; 3.TaizhouHuikeAgriculturalMachineryTechnologyDevelopmentCompanyLimited,Taizhou318050,Zhejiang,China)
China is the largest country of vegetable production in the world, and more than 60% vegetable varieties are planted by seedling transplanting, which mainly depends on manual work. However, there are some shortcomings in the traditional manual transplanting, such as high labor intensity, low productivity, poor quality and high cost. It is necessary to do some researches on the vegetable transplanters to adapt to the requirements of the mechanization of agricultural production. Currently, the domestic vegetable transplanters are mainly clip-chain transplanter, seedling guide tube transplanter, nacelle-type transplanter and flexible disc transplanter. The transplanters can meet the basic seedling transplanting requirements, but still stays in the semi-mechanization level. The research work of the vegetable transplanter is mainly focused on the design and optimization of the seedling picking and transplanting mechanism. However, automatic vegetable transplanter needs integrated knowledge and technology, the research on which should also combine the structural design with the physical and mechanical properties of vegetable seedling pot. Thus, it will be helpful for further optimal design of the key components of automatic vegetable transplanter, such as the picking seedling mechanism and the transplanting mechanism.
Tomato seedlings with the age of 23 d were used as experiment objects. The physical and mechanical properties of the tomato seedling pot have been tested and analyzed, which were directly related to the transplanting machine design. Tablet compression of seedling pot has been done with a universal testing machine Instron 5543 and P100 flat probe. In the experiment, the regular pressure-deformation was analyzed and the clamping force characteristics of pot during seedling picking were determined. Pot puncture test using a universal testing machine Instron 5543 and P5 cylinder probe has been done to analyze the puncture characteristics of seedling pot during seedling picking. At the same time, to analyze the creep characteristics of seedling pot, creep test has been done using a universal testing machine Instron 5543 and P100 flat probe and combined with the describe of Burgers model. Then a scatter platform with 500 mm height was built and pots were scattered from the platform. The scattering rate of seedling was obtained and the scattering characteristics during transplanting were analyzed. Testing results show that the relationship between the capacity of resistance for compression and deformation was non-linear. The capacity of resistance for compression on yield point was 3.15 N when the deformation of the pot was 5.64 mm, so the picking seedling force should exceed the calculated yield point in the design of picking seedling machinery. In the puncturing process, the relationship between puncturing force and displacement was approximately linear at the displacement of 0 to 13.5 mm, and then it remained constant in the displacement range of 13.5 mm to 19.5 mm , while it increased significantly when the puncturing displacement was greater than 19.5 mm. Seedling pot creep property conformed to the creep law of Burgers model, and the average creep value was 0.398 9 mm in the condition of loading force of 5 N with 120 s retention time. In the scattering process, the tests showed the average scattering rate of seedling was 22.73%, and the seedling pots kept intact after falling, which met the requirements of mechanical planting.
The research results on the physical and mechanical properties of vegetable seedling pot will provide important data for the design on the key components of automatic vegetable transplanters.
vegetable transplanters; tomato seedling pot; physical and mechanical properties
国家高技术研究发展计划(863)资助课题(2012AA10A504); 浙江省自然科学基金项目(LQ13E050003)。
2015-03-26;接受日期(Accepted):2015-07-10;网络出版日期(Published online):2015-09-18
S 223.9
A
*通信作者(Corresponding author):梁喜凤(http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8373-2482),E-mail:lxfcjlu@163.com
URL:http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/33.1247.s.20150918.1812.024.html
