棉花磷脂酶C基因的克隆及参与油脂代谢的功能分析
2015-06-28袁哈利谢全亮李鸿彬
梁 卓,谭 兰,袁哈利,谢全亮,王 斐,李鸿彬
(石河子大学生命科学学院,农业生物技术重点实验室,新疆石河子832003)
棉花磷脂酶C基因的克隆及参与油脂代谢的功能分析
梁 卓,谭 兰,袁哈利,谢全亮,王 斐,李鸿彬*
(石河子大学生命科学学院,农业生物技术重点实验室,新疆石河子832003)
以陆地棉胚珠和纤维为实验材料,利用RT-PCR技术克隆得到磷脂酶C(Phospholipase C,PLC)基因(Gh-PLC,GenBank登录号:KR154219),将棉花磷脂酶C基因转化拟南芥,分析其在油脂代谢过程中的重要作用。测序鉴定显示,GhPLC基因的全长开放读码框为1 524bp,编码包含508个氨基酸的蛋白质,理论分子量约为55kD。序列比对分析显示,GhPLC属于典型的碱性磷酸酶超家族的磷脂酶。利用pET32a-GhPLC原核表达获得分子量约为55kD左右的重组蛋白GhPLC;酶活力分析显示,重组GhPLC蛋白具有较高的将卵磷脂(PC)催化为二酰甘油(DAG)的酶活力。半定量RT-PCR结果表明,GhPLC基因参与棉花种子和纤维发育过程。构建植物过量表达载体35S∷GhPLC并转化哥伦比亚野生型拟南芥,转基因拟南芥中GhPLC基因的表达和PLC酶活力显著提高,且转基因拟南芥种子的油脂含量提高了5.3%。
棉花;胚珠和纤维;磷脂酶C;油脂含量;拟南芥
Key words:Gossypium hirsutum;ovule and fiber;phospholipase C;oil content;Arabidopsis
植物磷脂酶C(phospholipase C,PLC)是一种脂质水解酶,在种子发育过程广泛存在,在植物的生长发育过程发挥重要作用[1]。植物中PLC包括磷脂酰肌醇特异性磷脂酶C(phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C,PI-PLC)、非特异性磷脂酶(non-specific phospholipase C,NPC)和糖基磷脂酰肌醇特异性磷脂酶(glycosylphosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C,GPI-PLC)。PLC在脂类代谢、膜再建及脂类信号分子(inositol triphosphate,IP3、DAG、phosphatidic acid,PA)和游离脂肪酸(free fatty acid,FFA)的产生等方面都有很重要的催化活性,同时可能参与细胞信息传递、膜运输及降解、分化和生殖、种子萌发与衰老等生理过程[2-6]。
植物中首先发现的非特异性PLC活性蛋白NPC4,定位于质膜,催化分解磷脂产生磷元素的极性头部和DAG,产生的DAG可直接或间接的脱酰生成软脂酸,软脂酸随后由半乳糖酯合酶催化生成半乳糖酯用于脂质的再生[7-9]。目前关于PLC功能研究主要集中在植物对盐、干旱、高温及病害防御反应中的调节作用[10-12],如拟南芥磷脂酶C参与植物的花生长发育、响应激素信号以及应对环境因子的反应等[13-14],也有一些研究表明其对棉花种子和纤维发育过程中的脂质合成与代谢具有重要作用[15-17]。
棉花(Gossypium hirsutum)是经济价值较高的农作物,除了棉花纤维在纺织工业的利用外,棉籽油的利用也越来越成为热点。目前关于PLC参与棉花胚珠和纤维发育的相关研究鲜有报道。本研究从棉花开花后15d的胚珠和纤维组织中克隆GhPLC基因,并分析GhPLC基因在种子油脂形成过程中的重要作用,为进一步了解GhPLC基因在脂质合成代谢等方面的重要功能及进一步培育高含油量作物品种提供基础。
1 材料和方法
1.1 植物材料
植物材料为陆地棉栽培品种‘徐-142’,棉花在大田种植,收集棉花开花后0~40d发育的胚珠和纤维材料。
1.2 方 法
1.2.1 棉花胚珠和纤维总RNA的提取 根据改良的CTAB法提取棉花开花后0~50d发育的胚珠和纤维材料的RNA[18-19]。所使用的研钵经121℃高温烘烤2h,其他器皿用DEPC水处理[20]。
1.2.2 GhPLC基因克隆 根据GenBank棉花EST数据库中获得PLC基因的序列信息,分析和比对后,该基因具有完整的开放读码框,利用Primer Premier 5.0设计引物克隆PLC基因的完整开放读码框,并在上下游引物的两端分别添加EcoRⅠ和XhoⅠ的酶切位点(下划线),设计使用的引物见表1。以总RNA为模板,用反转录试剂盒合成cDNA[21],通过PCR扩增获得GhPLC基因的完整开放读码框。
1.2.3 蛋白质序列比对和结构域分析 蛋白质序列比对和进化树构建分别利用DNAMAN和MEGA(Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis)软件完成。
1.2.4 pET32a-GhPLC原核表达载体的构建、诱导表达和酶活力分析 将克隆得到的GhPLC基因片段连接到pET32a载体,构建pET32a-GhPLC,利用双酶切方法进行鉴定[5-6]。将构建成功的pET32a-GhPLC表达载体转化大肠杆菌表达菌株BL21(DE3)感受态细胞,用IPTG诱导表达,蛋白表达情况用SDS-PAGE分析[19]。
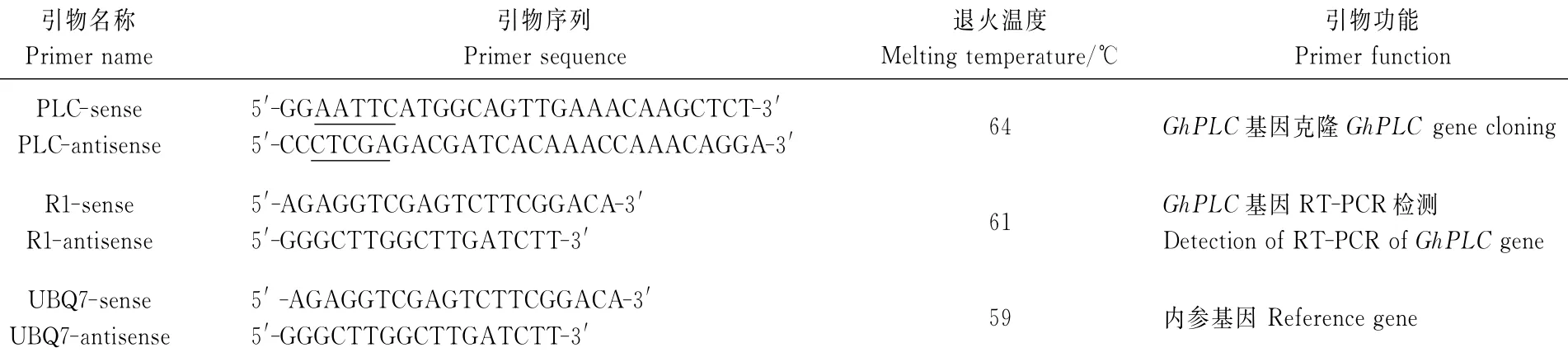
表1 使用的引物序列列表Table 1 List of used primer sequences
PLC活力分析参考王常高等[22]的方法,酶反应体系为0.25mol/L Tris-HCl(pH 7.2),0.001mol/L ZnCl2,60%山梨醇(W/V)和10nmol/L NPPC。取2mL向其中添加100μL磷脂酶C样品,37℃保温反应30min。利用分光光度法测定酶反应液在410nm处的吸光度A,得到PLC酶解NPPC产生对硝基苯酚的量,从而定量PLC的酶活大小。酶活计算公式:酶活力(U/mL)=1.363 6×103×A/t,式中:A为吸光度;t为反应时间。
1.2.5 棉花GhPLC基因表达分析和酶活力分析
根据改良的CTAB法提取棉花开花后0~50d不同发育时期的纤维和胚珠材料总RNA[19]。将RNA反转录成cDNA并作为模板,以UBQ7为内参基因,进行GhPLC基因的表达分析,引物序列见表1。棉花PLC活力分析参考王常高等[22]的方法。
1.2.6 拟南芥的遗传转化及油脂含量的测定 采用农杆菌介导的滴花法对开花期的拟南芥进行浸染转化[23]。用酸水解法测定拟南芥种子的油脂含量。将种子在研钵中研碎,置于离心管中并加入灭菌蒸馏水和盐酸,混匀,75℃中水浴后离心,加入95%乙醇和乙醚,混匀后离心,分离上清液置于三角瓶中并蒸干,置于烘箱中烘干并称重,参考郝晓云等[24]的方法进行油脂含量计算;数据显著性检验用ANOVA软件分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 棉花GhPLC基因克隆
利用CTAB法提取棉花胚珠和纤维材料总RNA,以反转录得到的cDNA为模板,根据Gen-Bank的序列信息,利用PCR扩增获得特异性目标条带(图1),经测序和序列比对鉴定后得到的基因命名为GhPLC(登录号为KR154219)。GhPLC基因的全长开放读码框包含1 524个碱基对,编码由508个氨基酸组成的蛋白质。
2.2 GhPLC序列比对与进化树构建
将GhPLC编码的氨基酸序列与其它植物的PLC氨基酸序列进行比对,不同物种的NPC在氨基酸序列上保守性较高,GhPLC属于碱性磷酸酶超家族的非特异性磷酸单酯酶,具有磷酸酯酶的典型酯催化结构域和一个特异性的cAMP和cGMP依赖的蛋白激酶磷酸化位点(图3,A)。选取植物中已知的PLC氨基酸序列,利用MEGA软件构建分子进化树,GhPLC属于NPC类的成员,与可可树Tc-PLC在进化上亲缘关系较近(图3,B)。
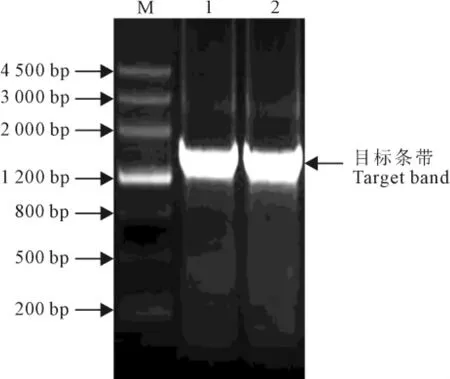
图1 GhPLC基因克隆电泳结果M.DNA分子量标准;1、2.PCR产物电泳条带Fig.1 Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products of GhPLCgene cloning M.DNA molecular weight standard;1,2.Electrophoresis bands of PCR products
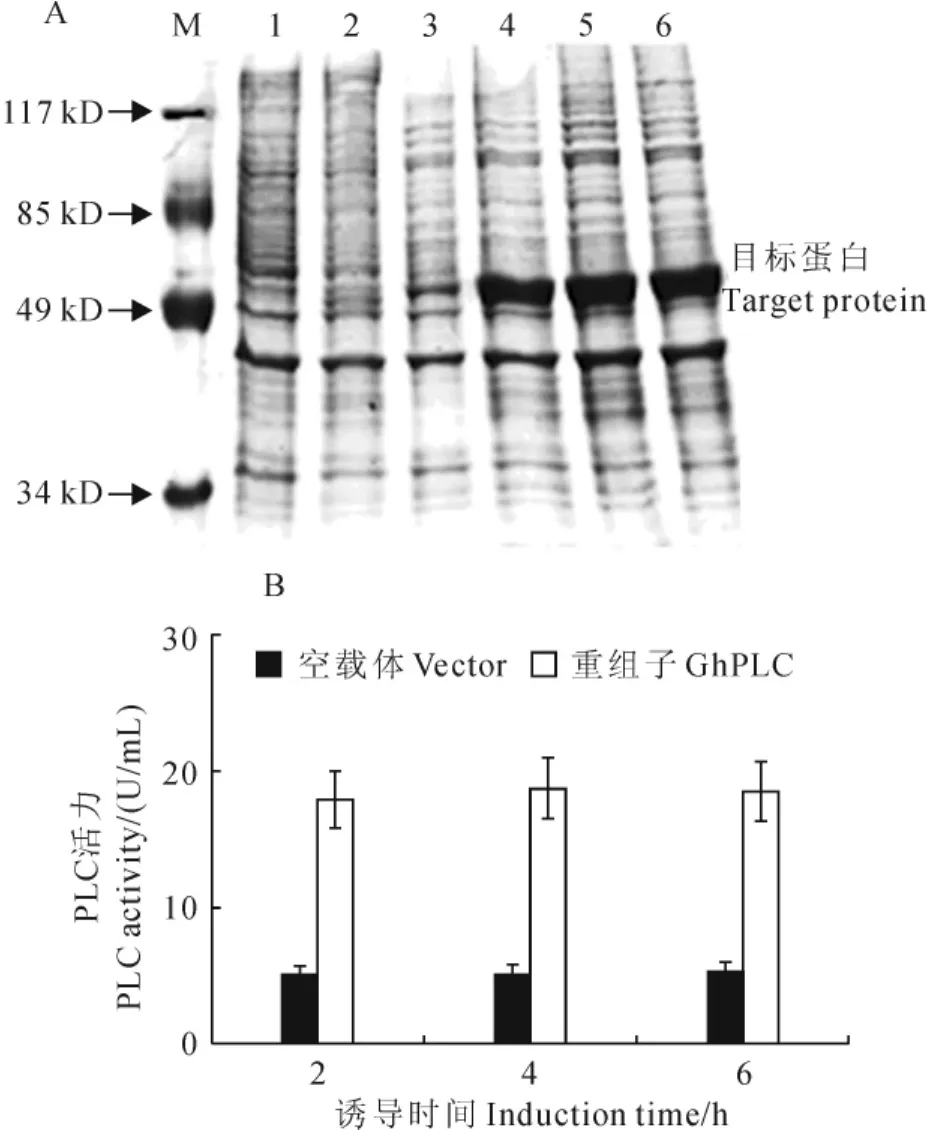
图2 GhPLC重组蛋白SDS-PAGE分析(A)与酶活性测定(B)A.GhPLC重组蛋白SDS-PAGE分析;M.蛋白质分子量标准;1.pET32a空载体(不诱导);2.pET32a空载体(IPTG诱导2h);3.重组体诱导前的蛋白表达;4~6.诱导2h、4h、6h的蛋白表达;B.GhPLC重组蛋白的酶活性分析Fig.2 SDS-PAGE analysis(A)and enzyme activity assay(B)of recombinant GhPLC protein SDS-PAGE analysis of recombinant GhPLC protein;M.Protein marker;1.Protein lysate of pET32avector without induction;2.Protein lysate of pET32avector induced by IPTG for 2h;3.Protein lysate of recombinant GhPLC without induction;4-6.Protein lysate of recombinant GhPLC induced by IPTG for 2h,4hand 6h;B.Enzyme activity of recombinant GhPLC assay
2.3 重组GhPLC蛋白的诱导表达与酶活力测定
将经过筛选、鉴定后构建成功的pET32a-Gh-PLC重组子转入大肠杆菌表达菌株BL21(DE3)中,用IPTG进行诱导表达,SDS-PAGE蛋白质电泳分析诱导后蛋白的表达情况。成功诱导出Gh-PLC重组蛋白,该重组蛋白分子量约为55kD左右(图2,A);对诱导产生的重组GhPLC蛋白酶活力分析发现重组蛋白在诱导2h后就具有较高的酶活力(图2,B)。
2.4 GhPLC组织表达特征分析
通过半定量RT-PCR分析GhPLC基因在棉花不同组织中的表达情况,GhPLC基因在干种子中几乎没有表达,在根、茎、叶中有一定表达,在发育的胚珠与纤维组织中有一定表达(图4,A)。进一步检测胚珠和纤维不同发育时期的PLC活力,开花后15~25d的胚珠和纤维组织中具有较高的PLC活力(图4,B)。
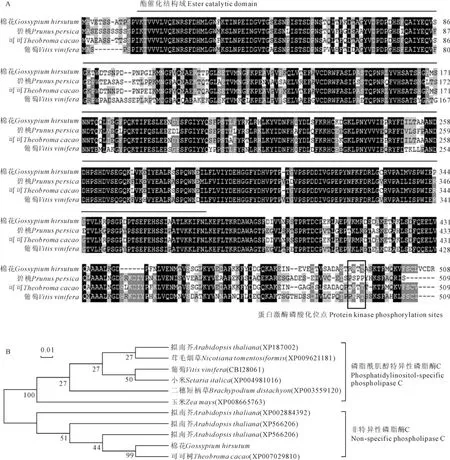
图3 棉花GhPLC氨基酸序列与其他物种PLC序列的多重序列比对(A)与进化树构建(B)分支上的数字表示Bootstrap验证中基于1 000次重复该节点可信度的百分比;标尺代表遗传距离Fig.3 Amino acid sequence alignment(A)and phylogenetic tree construction(B)of GhPLC and other plant PLCs The numbers at the branch nodes represent the reliability percent of Bootstrap values based on 1 000replications;The scale bar represents genetic distance
2.5 转基因拟南芥种子油脂含量分析
在经过筛选、鉴定获得多个过量表达转基因拟南芥株系中,2个转基因株系OE3和OE5中,Gh-PLC基因在拟南芥中具有稳定的表达,在转录水平和蛋白质酶活性水平表达较高(图5)。
在2个转基因株系OE3和OE5中,OE5株系中GhPLC的表达较高,选择OE5转基因株系进行油脂含量测定,用酸水解法测定成熟种子的油脂含量,野生型和转基因拟南芥种子的油脂含量分别为24.3%和29.6%,转基因拟南芥种子的油脂含量提高了5.3%(图6)。
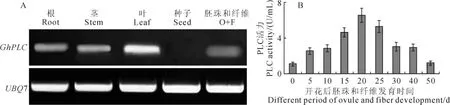
图4 GhPLC基因的表达特征分析Fig.4 GhPLCexpression characteristic analysis

图5 转GhPLC基因拟南芥的鉴定WT.野生型拟南芥;OE3和OE5分别表示过量表达的转基因拟南芥株系3和株系5Fig.5 Identification of transgenic GhPLC Arabidposis plants WT represents wide type Arabidopsis plants;OE3and OE5indicate overexpression transgenic Arabidopsis line 3and line 5respectively
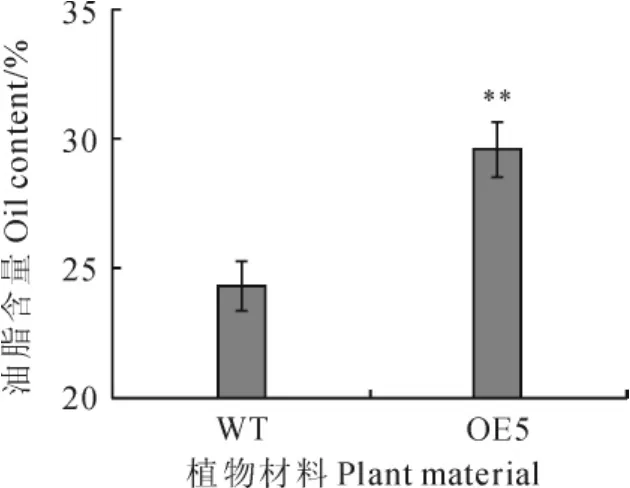
图6 转基因拟南芥种子油脂含量分析WT.野生型拟南芥;OE5.过量表达的转基因拟南芥株系5;**.P<0.01Fig.6 Oil content analysis of transgenic Arabidposis seeds WT represents widetype Arabidopsis plant;OE5shows overexpression transgenic Arabidopsis line 5;**indicates P<0.01
3 讨 论
NPC能水解诸多磷脂衍生物产生DAG和磷酸胆碱,由此生成的DAG可以和脂酰-CoA生成油脂。近期的研究发现NPC相关的脂质代谢在器官发育中可能起重要作用[8-9,25]。目前已从拟南芥、可可树等物种中克隆了PLC基因[26-28]。本研究从发育的棉花胚珠和纤维组织中克隆得到GhPLC基因,这也是在棉花中首次报到该基因。GhPLC基因在棉花胚珠和纤维组织中有一定表达,尤其在开花后15~25d的胚珠和纤维材料中表达较高,暗示了GhPLC基因可能与胚珠和纤维的发育相关,这与PLC在植物器官发挥重要作用的报道相似。磷脂酶C可以催化产生多种脂肪酸的衍生物,可以作为信号分子参与细胞发育过程[29],多个脂肪酸合成相关基因以及脂肪酸的组成和含量对于胚珠和纤维发育具有重要意义[29-30]。本实验结果显示GhPLC基因在发育的胚珠与纤维组织中有一定表达,重组GhPLC蛋白具有较高的催化产生脂肪酸的酶活力,这暗示了GhPLC基因可能通过调控细胞脂质代谢进一步参与胚珠和纤维的发育过程。
磷脂酶C催化产生的脂肪酸的衍生物可以进一步参与到油脂的再生合成,脂质代谢与种子含油量密切相关,PLC属于脂肪酶家族,多个脂肪酶家族成员均能够促进细胞内油脂的合成[24,31],与脂质代谢相关的多类不同基因都能够参与种子油脂含量,如ACC合成酶、三酰基甘油酯合成相关酶等[3234]。本研究将棉花GhPLC转化拟南芥,转GhPLC基因拟南芥种子含油量提高了5.3%,表明棉花GhPLC与种子油脂含量之间的密切联系,推测棉花GhPLC与这些已报道的酶具有类似的功能,可能具有催化油脂合成的功能。棉花GhPLC作为NPC家族的成员之一,能够通过磷脂产生细胞内信号分子如DAG、磷脂酸和三磷酸肌醇[35],这些信号分子可能能够与细胞内的Ca2+信号共同作用参与激素信号或调控脂质代谢。
[1] WANG F W(王法微),WANG Q(王 骐),DENG Y(邓 宇),et al.Advance in the research of phospholipase C gene family[J].Biotechnology Bulletin(生物技术通报),2014,12(6):33-39(in Chinese).
[2] ZHANG W H,QIN C B,ZHAO J,et al.Phospholipase Dα1-derived phosphatidic acid interacts with ABI1phosphatase 2Cand regulates abscisic acid signaling[J].PNAS,2004,101(25):9 508-9 513.
[3] QIN C B,WANG X M.The Arabidopsis phospholipase D family characterization of a calcium-independent and phosphatidylcholine-selective PLDζ1with distinct regulatory domains[J].Plant Physiology,2002,128(3):1 057-1 068.
[4] WANG X M.Regulatory functions of phospholipase D and phosphatidic acid in plant growth,development,and stress responses[J].Plant Physiology,2005,139(2):566-573.
[5] ZHENG P Z,ALLEN W B,ROESLER K A.Phenylalanine in DGAT is a key determinant of oil content and composition in maize[J].Nature Genetics,2008,40(3):367-373.
[6] LI M Y,HANG Y Y,WANG X M.Phospholipase D and phosphatidic acid mediated signaling in plants[J].Biochim.Biophysic.Acta,2009,1 791(9):927-935.
[7] WANG S W,DENG X P,ZHANG S Q,et al.Maintenance of chloroplast structure and function by overexpression of the rice monogalactosyldiacylglycerol synthase gene leads to enhanced salt tolerance in tobacco[J].Plant Physiology,2014,165(3):1 144-1 155.
[8] NAKAMURA Y.Phosphate starvation and membrane lipid remodeling in seed plants[J].Progress in Lipid Research,2013,52(1):43-50.
[9] JOUHET J,MARECHAL E,BLOCK M A,et al.Phosphate deprivation induces transfer of DGDG galactolipid from chloroplast to mitochondria[J].Journal of Cell Biology,2004,167(5):863-874.
[10] ZHENG S Z,LIU Y L,LI B,et al.Phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C9is involved in the thermotolerance of Arabidopsis[J].Plant Journal,2012,69(4):689-700.
[11] VOSSEN J H,HALIEM A A,FRADIN E F,et al.Identification of tomato phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C(PI-PLC)family members and the role of PLC4and PLC6in HR and disease resistance[J].Plant Journal,2010,62(2):224-239.
[12] PETERS C,LI M,NARASIMHAN R,et al.Nonspecific phospholipase C NPC4promotes responses to abscisic acid and tolerance to hyperosmotic stress in Arabidopsis[J].Plant Cell,2010,22(8):2 642-2 659.
[13] KOCOURKOVA D,KRCHOVA Z,PEJCHAR P,et al.The phosphatidylcholine-hydrolysing phospholipase C NPC4plays a role in response of Arabidopsis roots to salt stress[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2011,62(11):3 753-3 763.
[14] CANONNE J,FROIDURE N S,RIVAS S.Phospholipases in action during plant defense signaling[J].Plant Signaling and Behavior,2011,6(1):13-18.
[15] WANG X C,LI Q,JIN X,et al.Quantitative proteomics and transcriptomics reveal key metabolic processes associated with?cotton fiberinitiation[J].Journal of Proteomics,2014,114(2):16-27.
[16] YUAN D,TU L,ZHANG X.Generation,annotation and analysis of first large-scale expressed sequence tags from developing fiber of Gossypium barbadense L.[J].PLoS One,2011,6(7):e22758.
[17] SONG W Q,QIN Y M,SAITO M,et al.Characterization of two cotton cDNAs encoding trans-2-enoyl-CoA reductase reveals a putative novel NADPH-binding motif[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2009,60(6):1 839-1 848.
[18] JIANG J X(蒋建雄),ZHANG T ZH(张天真).Extraction of total RNA in cotton tissues with CTAB-acidic phenolic method[J].Cotton Science(棉花学报),2003,15(3):166-167(in Chinese).
[19] LI X N(李学宁),DU J W(杜军伟),LI H B(李鸿彬).Cloning,prokaryotic expression and purification of a cotton dehydroascorbate reductase gene[J].Journal of Shihezi University(Nat.Sci.Edi.)(石河子大学学报·自然科学版),2010,24(5):542-545(in Chinese).
[20] XIA L Q(夏兰芹),GUO S D(郭三堆).A method of RNA fast extracting in cotton tissues[J].Cotton Science(棉花学报),2000,12(4):205-207(in Chinese).
[21] TIAN D P(田大鹏),GE J(葛 娟),LI H B(李鸿彬),et al.Cloning,functional sequence analysis and prokaryotic expression of cotton GhDHAR2cDNA[J].Biotechnology Bulletin(生物技术通报),2012,7(2):65-69(in Chinese).
[22] WANG CH G(王常高),LI W(李 伟),GAN X(干 信),et al.Bacillus mycoides phospholipase C purification and preparation research[J].Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin(安徽农学通报),2007,13(8):55-56(in Chinese).
[23] ZHANG P(张 萍),WANG F(王 斐),XU D X(徐登献),et al.Cotton GhACO3gene promotes adventitious root development of Arabidopsis thaliana and tobacco[J].Acta Bot.Boreal.-Occident.Sin.(西北植物学报),2011,31(12):2 394-2 398(in Chinese).
[24] HAO X Y(郝晓云),CAI Y ZH(蔡永智),YUAN H L(袁哈利),et al.Overexpression of a cotton GDSL lipase increases the oil content of BrassicanapusL.[J].Journal of Chinese Cereals and Oils Association(中国粮油学报),2014,29(6):63-68(in Chinese).
[25] LIU L(刘 露),TIAN H(田 华),DUAN Y(段 愿),et al.Preparation of phospholipase C and removal of rapeseed colloidal by phospholipase C[J].Farm Machinery(农业机械),2013,42(5):32-36(in Chinese).
[26] YUKI N,KOICHIRO A,TATSURU M.A novel phosphatidylcholine-hydrolyzing phospholipase C induced by phosphate starvation in Arabidopsis[J].The Journal of Biological Chemisitry,2005,280(9):7 469-7 476.
[27] SUE G R.Regulation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C[J].Annual Review of Biochemistry,2001,70(20):281-312.
[28] PAN Y Y(潘延云),ZHU ZH G(朱正歌),SUN D Y(孙大业).Plant phosphplipase C and its involved in signal transduction[J].Plant Physiology Communication(植物生理学通讯),2005,41(2):229-234(in Chinese).
[29] QIN Y M,HU C Y,PANG Y,et al.Saturated very long chain fatty acids promote cotton fiber and Arabidopsis cell elongation by activating ethylene biosythesis[J].Plant Cell,2007,19(11):3 692-3 704.
[30] SHI Y H,ZHU S W,MAO X Z,et al.Transcriptome profiling,molecular biological,and physiological studies reveal a major role for ethylene in cotton fiber cell elongation[J].Plant Cell,2006,18(3):651-664.
[31] WEI M W(魏明玉),ZHOU J(周 佳),YAN S ZH(闫素珍),et al.Cloning and expression analysis of an oil-content related lipase(BnSDP1)gene in Brassica napus[J].Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Science(中国油料作物学报),2011,33(4):338-343(in Chinese).
[32] THELEN J J,OHLROGGE J B.Both antisense and sense expression of biotin carboxyl carrier protein isoform 2inactivates the plastid acetylcoenzyme A carboxylase in Arabidopsis thaliana[J].Plant Journal,2002,32(4):419-431.
[33] ZOU J,KATAVIC V,GINLIN E M.Modification of seed oil content and aeyl composition in the Brassicaceae by expression of a yeast sn-2aeyltransferase gene[J].Plant Cell,1997,9(6):909-923.
[34] JAKO C,KUMAR A,WEI Y.Seed-specific over-expression of an Arabidopsis cDNA encoding a diacylglycerol aeyltransferase enhances seed oil content and seed weight[J].Plant Physiology,2001,126(9):861-874.
[35] ZHANG W H,YU L J,ZHANG Y Y,et al.Phospholipase D in the signaling networks of plant response to abscisic acid and reactive oxygen species[J].Biochimica Biophysica Acta,2005,1 736(1):1-9.
(编辑:宋亚珍)
Cloning of a Phospholipase C Gene fromGossypium hirsutum and Its Functional Analysis of Participating in Lipid Metabolism
LIANG Zhuo,TAN Lan,YUAN Hali,XIE Quanliang,WANG Fei,LI Hongbin*
(College of Life Sciences,Key Laboratory of Agrobiotechnology,Shihezi Universtiy,Shihezi,Xinjiang 832003,China)
AGossypium hirsutumphospholipase C(GhPLC,GenBank Accession Number:KR154219)gene was cloned using RT-PCR method from developing ovule and fiber tissues,and the function of lipid metabolism was analyzed through transforming GhPLCinto Arabidopsis.Sequencing identification showed that the full open reading frame of GhPLCwas 1 524bp containing aprotein of 508amino acids with a theoretical molecular weight of 55kD.Sequence alignment analysis displayed that GhPLCgene belongs to the classical alkaline phosphatase superfamily.The recombinant proteins of GhPLC was obtained with molecular weight of 55kD by prokaryotic expression of pET32a-GhPLC.Enzyme activity determination showed that recombinant GhPLC proteins has high activity of catalyzing phosphatidylcholine(PC)to diacylglycerol(DAG).Semi-quantitative PCR analysis indicated that GhPLCgene participates in cotton seed and fiber development.Plant overexpression vector 35S∷GhPLC was constructed and transformed into Columbia wildtype Arabidopsis.Transgenic GhPLC Arabidopsis showed significant promotion both in transcription and enzyme levels,and the oil content of transgenic Arabidopsis seeds increased with 5.3%higher than widetype.
Q785;Q789
A
10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2015.06.1085
1000-4025(2015)06-1085-07
2015-02-03;修改稿收到日期:2015-04-22
兵团项目(2012BB050,2014CD003);国家自然科学基金(31260039);石河子大学杰青项目(2012ZRKXJQ03)
梁 卓(1987-),男,在读硕士研究生,从事植物发育生物学研究。E-mail:540496573@qq.com
*通信作者:李鸿彬,博士,教授,主要从事植物分子生物学与基因工程研究。E-mail:lihb@shzu.edu.cn
