不同类型的膝关节假体对站立时静态稳定性的影响研究
2015-06-27米尔阿里木木尔提扎赵巍王利袁宏
米尔阿里木·木尔提扎,赵巍,王利,袁宏*
(1.新疆医科大学研究生学院,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830011;2.新疆自治区人民医院骨科中心关节外科,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830001)
不同类型的膝关节假体对站立时静态稳定性的影响研究
米尔阿里木·木尔提扎1,赵巍2,王利2,袁宏2*
(1.新疆医科大学研究生学院,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830011;2.新疆自治区人民医院骨科中心关节外科,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830001)
目的 探讨人工全膝关节置换术(total knee arthroplasty,TKA)中选用固定平台(fixed-bearing)型(PFC-sigma)和旋转平台(rotating-platform)型(PFC-RP)膝关节假体对膝关节骨关节炎(knee osteoarthritis,OA)患者术后躯体静态稳定性产生的影响。方法 对2011年1月至2013年12月在我院接受单侧TKA的OA患者45 例(选用旋转平台型假体PFC-RP的患者21 例,选用固定平台型假体PFC-Sigma的患者24 例)进行分析。术前、术后6个月和术后1年时采用HSS评分标准对术侧膝关节进行功能评估,并用重心测量仪对患者进行站立平衡试验,连续记录躯体重心位置(gravity center position,GCP)。对GCP在水平方向上转移程度(medio-lateral displacement,ML-X range)以及GCP漂移轨迹(locus of GCP,LG)进行量化并分析两组患者之间的静态稳定性、术侧膝关节恢复情况以及术后并发症发生率的差异性。结果 TKA后单位时间内GCP在水平方向上平均位置由初始位置逐渐向术侧转移,且两组患者之间ML-X range上变化程度差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05),而选用PFC-RP型假体的患者LG水平明显较选用PFC-Sigma的患者小,且差异性有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 两组患者术后术侧膝关节恢复情况、并发症发生率无明显差异性,而选PFC-RP型假体的患者较PFC-Sigma的患者具有更好的静态时稳定性。
人工全膝关节置换术;骨关节炎;旋转平台型;固定平台型;静态时稳定性
人工全膝关节置换术(total knee arthroplasty,TKA)已在治疗晚期膝关节骨关节炎(osteoarthritis,OA)疾病中取得了良好的疗效。OA的病理性改变能够影响到膝关节本体感觉,从而影响到患者维持躯体平衡的能力[1]。而人体维持躯体平衡能力对顺利进行日常活动、维持静态时姿势稳定性极为重要[2]。有关报道指出患者经TKA后膝关节本体感觉能够部分恢复[3],这样患者运动协调功能和膝关节稳定性较术前得到明显改善[4]。随着生物材料技术的进一步成熟,目前 TKA中已普遍使用固定平台型(fixed-bearing)假体PFC-Sigma与旋转平台型(rotating-platform)假体PFC-RP等第三代人工关节假体,并取得令人满意的疗效[5-9]。在实际临床中骨溶解、假体无菌性松动以及聚乙烯垫片的磨损等均是影响TKA长期疗效以及增大TKA翻修难度的重要因素,国内外学界一致认为以上因素与术中选用的假体类型密切相关[10-12]。目前国内外大部分研究中仅以术后膝关节活动功能和假体长期存活率作为判断手术是否成功的金标准。有关研究指出选用PFC-Sigma型或PFC-RP型假体对术后关节功能、假体长期存活率以及解除疼痛等均无明显差异性[13]。而尚无详细临床研究对选用PFC-Sigma型或PFC-RP型假体对患者静态时稳定性的影响进行比较。本研究目的在于比较采用PFC-Siga型假体与PFC-RP型假体的患者在TKA术后6个月、术后1年时的关节疼痛、活动功能恢复情况以及患者静态稳定性的差异性,并对其原因进行初步分析。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 本研究通过我院伦理委员会审批通过,所有患者被纳入之前均给予详细解释,术前每位患者均与手术医师进行详细谈话,自愿地选择术中选用的假体类型,并签署本研究知情同意书。分析2011年1月至2013年12月在我院接受单侧TKA的45 例患者,其中选用旋转平台型假体(PFC-RP,Depuy)的患者21 例,选用固定平台型假体(PFC-Sigma,Depuy)的患者24 例。本研究纳入标准为:所有患者均为右侧膝关节骨关节炎,对侧膝关节无明显异常。排除标准为:膝关节重度外翻或内翻畸形超过15°,患有神经系统或严重的内科基础性疾病,类风湿病,术侧下肢接受过手术治疗,双下肢不等长,随访期间服用影响躯体平衡性及视力的药物的患者。
1.2 手术方法 所有手术均在垂直层流性手术室全麻状态下完成。手术入路均取标准的膝关节正中髌旁切口,使用髓外导向进行胫骨截骨,用髓外导向进行股骨髁截骨。股骨与胫骨假体均使用骨水泥固定。所有手术均未进行髌骨表面置换。装完假体后均对膝关节周围的软组织进行适当地调整。所有患者围手术期预防性应用抗生素,预防术后静脉血栓。在术后1 d开始逐渐进行康复训练,包括下肢连续被动运动,主动或辅助下进行逐渐增大膝关节活动幅度以及行走步态训练等专业功能康复锻炼。
1.3 临床评价 根据美国特种外科医院(hospital special knee scores,HSS)评分标准对患者术前、术后6个月,术后1年时的膝关节功能恢复情况进行评定[14]。本研究中通过重心测量仪对患者躯体重心(gravity center position,GCP)进行测定。让每位患者在重心测量仪上无扶助条件下站立1 min,并让患者注视前方3 m远处固定目标物。在测量时间内确保无外物进入患者视线干扰(见图1)。每2秒进行一次GCP测定,连续记录1 min内的GCP位置。分别对GCP在单位时间内水平方向上转移程度(medio-lateral displacement,ML-X range) 和GCP漂移轨迹(locus of GCP,LG)进行量化分析。单位时间内LG能够表示由人本体感受性反射控制的维持躯体平衡性能力[15-16]。若在进行上述试验的过程中,患者在规定的时间内无法站立平稳或要求停顿时该次操作视为无效,进行重新测取。
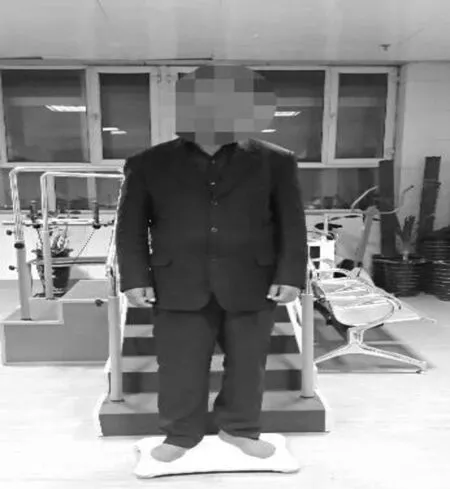

图1 患者在术后6个月时进行站立平衡试验
1.4 统计学方法 利用SPSS 17.0统计学软件进行处理研究有关的数据。根据术中选用的假体类型分PFC-RP组和PFC-Sigma组。两组患者术前、术后6个月、术后1年时的相关变量进行配对t检验。为较客观描述患者术后GCP转移情况,需算出患者在测量时间内的所有GCP的横轴平均位置,故在研究中描述平准值与表均差时利用95%的可信区间。用卡方检验来比较两组之间总的并发症发生率差异性。为使研究中混淆因素降低,我们尽可能地排除在骨质、对疼痛耐受程度、术后康复过程等方面存在差异性的患者,且均选用同一家公司的两种假体。本研究有关GCP数据均取上图中平移距离,以图中单元格为计量单位(见图2~3)。从图中获取有关数据时,以患者术侧(右侧)为水平轴(X轴)方向上的正方向(+),左侧为负方向(*),患者站在测量仪上面对方向为纵轴(Y轴)方向上的正方向(+),后侧为负方向(*)。以P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2 结 果
本研究中45 例患者,其中选用PFC-RP的患者21 例,选用PFC-Sigma的患者24 例。两组患者平均年龄、术前体重、身高、体重指数(body mass index,BMI),术前术侧膝关节HSS评分之间的差异性均无统计学意义(见表1)。
2.1 术侧膝关节HSS评分 本研究中PFC-Sigma组与PFC-RP组之间在术前、术后6个月及术后1年时,术侧膝关节HSS评分差异均无统计学意义。术后患侧膝关节HSS评分均较术前时有明显变化,且差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05,见表2)。
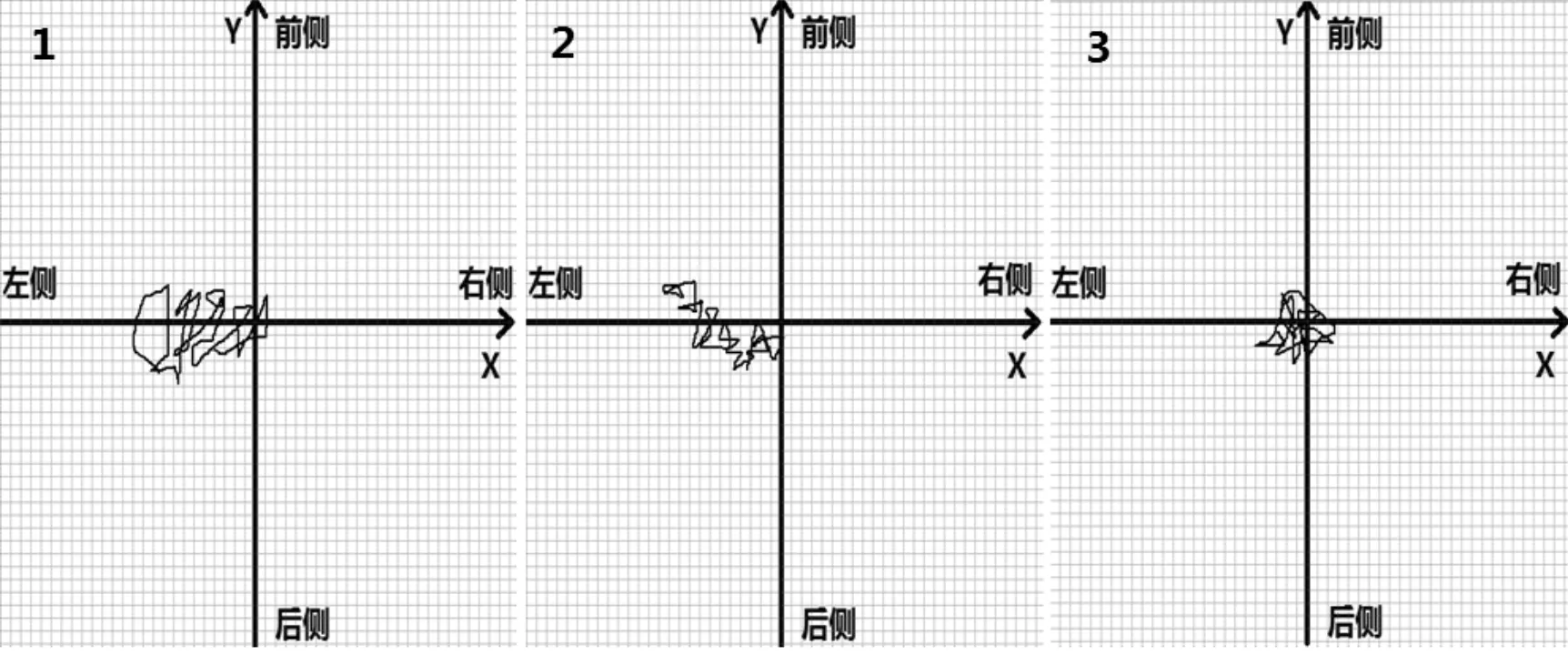
a 术 前 b 术后6个月 c 术后1年
图2 1 例选用PFC-Sigma型假体的患者在术前、术后6个月、术后1年时行GCP飘移轨迹LG
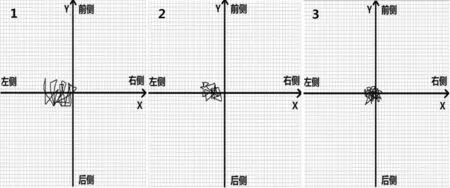
a 术 前 b 术后6个月 c 术后1年
图3 1 例选用PFC-RP型假体的患者在术前、术后6个月、术后1年时行GCP飘移轨迹LG

表1 两组患者术前一般情况比较
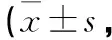
表2 两组患者HSS功能评分对比分)
2.2 并发症
2.2.1 切口感染 两组中均有2 例患者术后早期(术后3~7 d)出现膝关节术区发红,皮温持续高等感染症状。以上4 例患者均积极进行抗炎或切开清创对症处理后症状明显好转或消失。对切口周围渗出液进行一般细菌培养,培养结果均为无菌生长。2 例PFC-RP组患者术后出现膝关节肿胀,对其进行消肿或关节腔穿刺抽出对症处理后,症状明显好转。并对患者进行凝血相关检查。两组患者术后早期出现切口愈合有关的并发症率之间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
2.2.2 术后疼痛 14%的PFC-Sigma组患者和9.5%的PFC-RP组患者术后出现膝关节周围疼痛症状,给予止痛并康复对症治疗后疼痛症状有效缓解并逐渐消失。
2.2.3 其他并发症 研究中两组患者均未出现术后膝关节脱位,明显骨溶解等症状。1 例PFC-Sigma患者出现术侧下肢深静脉血栓,给予抬高患肢并进行抗凝对症处理3周后再次进行下肢血管彩超检查,未发现下肢静脉血栓(见表3)。

表3 两组患者术后出现的并发症(例)
2.3 稳定性 研究中发现两组患者在术后6个月和术后1年时,在水平方向上患者GCP均由初始位置逐渐向术侧方向转移,与术前时平均位置比较其转移差异均有统计学意义(P<0.01)。而术后6个月和术后1年时,水平方向上GCP较术前转移程度两组患者之间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,见表4)。
术后6个月、术后1年时,两组患者LG水平均较术前逐渐变小。跟术前时LG水平比较差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。而术后6个月、术后1年时,两组患者之间LG水平的差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05,见表4,见图2~3)。
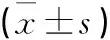
表4 两组患者之间稳定性指标对比
3 讨 论
TKA选用PFC-Sigma型假体已取得较好的临床疗效[17-21],在术后10~15年的随访中发现假体存活率甚至高达90%以上[22-23],并且在年轻和高龄患者中均有较好的效果[24-25]。然而,因传统PFC-Sigma型假体设计原因,可能出现的假体聚乙烯垫片磨损、骨溶解等现象均可能导致假体松动甚至可能需要二次手术[26]。从假体设计理论上分析,PFC-RP型假体与PFC-Sigma型假体相比,胫骨平台处有旋转轴,更能改善术后膝关节活动,允许胫骨平台在纵轴上旋转,有效减少聚乙烯垫片磨损,减轻假体骨水泥界面受到的压力,从而减少发生骨溶解和假体松动的可能[27-28]。目前许多文献从TKA后临床疗效、假体存活寿命、术后影像学以及关节活动功能等方面比较PFC-RP型假体与PFC-Sigma型假体的区别,结果显示两种假体之间均无明显差异性[29-35]。而目前国内外尚无研究分析出选用两种假体对患者术后静态稳定性的影响。本研究中两组患者术后膝关节恢复程度差异无统计学意义。
我们可以推测随着患者术后关节功能恢复,术侧膝关节负重量逐渐增大,而对侧膝关节负重量逐渐减少,术侧膝关节疼痛逐渐减轻,患者逐步恢复躯体的平衡。本研究中,TKA后患者GCP由初始位置逐渐向术侧方向转移,且患者维持躯体平衡性能力逐渐得到改善。
影响躯体稳定性的主要因素有膝关节疼痛、下肢肌力减弱及本体感觉减退等[16]。膝OA患者下肢肌力及膝关节本体感与同性别和年龄段的人群相比减弱较明显,故膝OA患者躯体不稳定性更显著[36]。随膝OA病程进展,关节腔及周围组织中的感受器数量减少,导致患者膝关节本体感觉减退,从而影响患者躯体平衡性[36-38]。TKA目的在于长期缓解或消除关节疼痛,改善膝关节功能,从而提高生活质量。目前关于TKA对关节本体感觉及躯体平衡性的影响存在较多的争议。有些学者认为患者本体感觉通过TKA能够得到改善,从而患者维持躯体平衡性较术前有所提高[39-40],相反有文献指出TKA后,患者减退的本体感觉和躯体稳定性未见明显改善[41-43]。本研究中所有患者术后LG均较术前时明显变小,表明术后患者躯体平衡性经TKA逐渐好转,其中PFC-RP组患者LG变化程度较PFC-Sigma组较为明显。笔者认为原因可能为与PFC-RP假体设计中胫骨平台处有旋转轴,允许胫骨在纵轴上旋转,这样帮助患者站立时更好地维持静态稳定性。而本研究中假体均选用同一家公司产品,除胫骨平台处是否有旋转轴外,两种假体其余部分均相同,故我们可以排除TKA中由于选用假体类型不同而导致的对关节本体感觉影响。
本研究存在的局限性有:a)我们前瞻性地对两种设计相似的假体类型进行队列比较分析。虽然两组之间年龄、性别、术前一般临床特征、术前关节功能等变量均无明显差异,但由于本研究中选择假体时不能够严格按盲法执行,故前瞻性研究可能未能够更有效地限制选择偏倚和其他潜在的混淆变量。b)由于研究样本量较小,且取95%的可信区间,故本研究方案可能不能够有效地识别两组患者之间的变量差异性,这样容易导致Ⅱ型错误。比较两组患者术后发生的并发症时,由于样本量和并发症发生的数量较小,且随访时间较短。故我们认为还需进一步扩大样本量和随访时间,以便研究结果更为精确。c)本研究由于条件有限,故研究方案较为简略。因患者前庭神经、视线以及认知能力等因素均能够影响到患者的本体感觉,从而影响到患者维持躯体平衡性能力。本研究未能够像类似研究中一样分别对患者在闭眼和睁眼时进行测量[16],或对患者双下肢分别进行单侧下肢站立平衡试验[44],这样对患者本体感觉、术后躯体稳定性变化的分析结果可能更为精确。d)未能对患者术前特点进行更详细地分类并分析,如术前不同内外翻程度、病程长短、对侧膝关节情况及其本体感觉等因素。研究中未对随访期不同阶段的患者体重是否有变化及体重变化对患者躯体中心是否产生相应地影响做出更深度地分析。
研究中两种假体组患者膝关节功能及躯体静态稳定性均较术前明显改善,其中PFC-RP组患者较PFC-Sigma组患者躯体稳定性变化更为明显。TKA围手术期极为重要,尤其是膝OA患者躯体稳定性退变较同年龄段人群更明显。TKA术后前几个月内患者躯体稳定性甚至较术前更弱,故笔者认为选用PFC-RP型假体也许能够有效减少老年患者术后跌倒摔伤的概率。然而,本研究随访时间较短,至于两种假体的长期疗效和对患者关节功能恢复以及躯体稳定性的影响需进行长期随访,有待进一步细致的研究。
[1]Gage WH,Frank JS,Prentice SD.Organization of postural responses following a rotational support surface perturbation,after TKA:sagittal plane rotations[J].Gait Posture,2007,25(1):112-120.
[2]Hinman RS,Bennell KL,Metcalf BR.Balance impairments in individuals with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis:a comparison with matched controls using clinical tests[J].Rheumatology(Oxford),2002,41(12):1388-1394.
[3]Leitch KK,Dalgorf D,Borkhoff CM.Bilateral total knee arthroplasty-staged or simultaneous?Ontario′s orthopedic surgeons reply[J].Can J Surg,2005,48(7):273-276.
[4]Swanik CB,Lephart SM,Rubash HE.Proprioception,kinesthesia,and balance after total knee arthroplasty with cruciate-retaining and posterior stabilized prostheses[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),2004,86(2):328-334.
[5]Kim YH,Kim JS,Choe JW.Long-term comparison of fixed-bearing and mobile-bearing total knee replacements in patients younger than fifty-one years of age with osteoarthritis[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),2012,94(10):866-870.
[6]Kim YH,Yoon SH,Kim JS.The long-term results of simultaneous fixed bearing and mobile-bearing total knee replacements performed in the same patient[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Br),2007,89(10):1317-1320.
[7]Callaghan JJ,Wells CW,Liu SS.Cemented rotating-platform total knee replacement:A concise follow-up,at a minimum of twenty years,of a previous report[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),2010,92(7):1635-1638.
[8]Ritter MA.The anatomic graduated component total knee replacement:a long-term evaluation with 20-year survival analysis[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Br),2009,91(6):745-749.
[9]Rodriguez JA,Bhende H,Ranawat CS.Total condylar knee replacement:A 20-year followup study[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,2001(5):388-391.
[10]Duffy GP,Crowder AR,Trousdale RR,etal.Cemented total knee arthroplasty using a modern prosthesis in young patients with osteoarthritis[J].J Arthroplasty,2007,22(2):67-71.
[11]Gioe TJ,Glynn J,Sembrano J.Mobile and fixed-bearing (all-polyethylene tibial component) total knee arthroplsaty designs.A prospective randomized trial[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),2009,91(2):2104-2107.
[12]Sharkey P,Hozack W,Rothman R.Why are total knee arthroplasties failing today?[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,2002,5(7):404-407.
[13]O.Bailey K,Ferguson E,Crawfurd P.No clinical difference between fixed-and mobile-bearing cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty:a prospective randomized study[J].Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc,2014,24(5):42-48.
[14]Slupik A,Bialoszewski D.A comparative analysis of the clinical utility of the Staffelstein-score and the hospital for special surgery knee score (HSS) in monitoring physiotherapy of total knee replacement patients-preliminary study[J].Ortop Traumatol Rehabil,2009,11(1):37-45.
[15]Swanik CB,Lephart SM,Rubash HE.Proprioception,kinesthesia,and balance after total knee arthroplasty with cruciateretaining and posterior stabilized prostheses[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),2004,5(86):328-334.
[16]Bakirhan S,Angin S,Karatosun V.A comparison of static and dynamic balance in patients with unilateral and bilateral total knee arthroplasty[J].Eklem Cerrahisi,2009,20(4):93-101.
[17]Insall JN,Hood RW,Flawn LB.The total condylar knee prosthesis ingonarthrosis.A five to nine-year follow-up of the first one hundred consecutive replacement[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),1983,65(5):619-628.
[18]Callahan CM,Drake BG,Heck DA.Patient outcomes following tri-compartmental total knee replacement.A meta-analysis[J].JAMA,271(17):1349-1357.
[19]Tarkin IS,Bridgeman JT.Successful biologic fixation with mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty[J].J Arthroplasty,2005,20(4):481-486.
[20]Buechel FF Sr.Long-term follow up after mobile-bearing total knee replacement[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,2002,14(3):40-50.
[21]Stern SH,Insall JN.Posterior stabilized prosthesis.Results after follow-up of nine to twelve years[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),1992,74(7):980-986.
[22]Dixon MC,Brown RR,Parsch D.Modular fixed-bearing total knee arthroplasty with retention of the posterior cruciate ligament.A study of patients followed for a minimum of fifteen years[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),2005,87(3):598-603.
[23]Dennis DA,Clayton ML.Posterior cruciate condylar total knee arthroplasty.Average 11-year follow-up evaluation[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,1992,13(281):168-176.
[24]Diduch DR,Insall JN,Scott WN.Total knee replacement in young,active patients.Long term follow-up and functional outcomes.[J]J Bone Joint Surg(Am),1997,79(4):575-582.
[25]Parsch D,Krüger M,Moser MT.Follow-up of 11-16 years after modular fixed-bearing TKA[J].Int Orthop,2009,33(2):431-435.
[26]Colizza WA,Insall JN,Scuderi GR.The posterior stabilized total knee prosthesis.Assessment of polyethylene damage and osteolysis after a ten-year-minimum follow-up[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),1995,77(11):1713-1720.
[27]Alessandro Bistolfi,Giuseppe Massazza,Gwo-Chin Lee.Comparison of fixed and mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty at a mean follow-up of 116 months[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),2013,95(16):11-18.
[28]Nakamura E,Banks SA,Tanaka A.Three-dimensional tibio-femoral kinematics during deep flexion kneeling in a mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty[J].J Arthroplasty,2009,24(7):1120-1124.
[29]Kim YH,Koo HK,Kim JS.Comparison of fixed-bearing and mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasties[J].Clin Orthop Relat,2007,92(12):101-115.
[30]Smith H,Jan M,Mahomed NN.Meta-analysis and systematic review of clinical outcomes comparing mobile bearing and fixed bearing total knee arthroplasty[J].J Arthroplasty,2011,26(8):1205-1213.
[31]Kelly NH,Fu RH,Wright TM,etal.Wear damage in mobile-bearing TKA is as severe as that in fixed-bearing TKA[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,2003,5(1):123-130.
[32]Geiger F,Mau H,Kru¨ger M.Comparison of a new mobile-bearing total knee prosthesis with a fixed-bearing prosthesis:a matched pair analysis[J].Arch Orthop Trauma Surg,128(3):285-291.
[33]Matsuda S,Mizu-uchi H,Fukagawa S.Mobile-bearing prosthesis did not improve mid-term clinical results of total knee arthroplasty[J].Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc,18(10):1311-1316.
[34]Kim YH,Choi Y,Kim JS.Osteolysis in well-functioning fixed-and mobile-bearing TKAs in younger patients[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,1999,468(11):3084-3093.
[35]Jacobs W,Anderson P,Limbeek J.Mobile bearing vs fixed bearing prostheses for total knee arthroplasty for post-operative functional status in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis[J].Cochrane Database Syst Rev,2012,10(3):31-34.
[36]Marks R,Quinney HA,Wessel J.Proprioceptive sensibility in women with normal and osteoarthritic knee joints[J].Clin Rheumatol,1993,12(2):170-175.
[37]Brandt KD,Dieppe P,Radin EL.Etiopathogenesis of osteoarthritis[J].Rheum Dis Clin North Am,2008,34(3):531-559.
[38]Barrett DS,Cobb AG,Bentley G.Joint proprioception in normal osteoarthritic and replaced knees[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Br),1991,73(1):53-56.
[39]Swanik CB,Lephart SM,Rubash HE.Proprioception,kinaesthesia,and balance after total knee arthroplasty with cruciate retaining and posterior stabilized prostheses[J].J Bone Joint Surg(Am),2004,86(2):328-334.
[40]Wada M,Kawahara H,Shimada S.Joint proprioception before and after total knee arthroplasty[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,2002,3(8):161-167.
[41]Farquhar S,Snyder-Mackler L.The chitranjan ranawat award:the non-operated knee predicts function 3 years after unilateral total knee arthroplasty[J].Clin Orthop Relat-Res,2010(468):37-44..
[42]Pap G,Meyer M,Weiler HAT.Proprioception after total knee arthroplasty:a comparison with clinical outcome[J].Acta Orthop Scand,2000,71(2):153-159.
[43]Fuchs MD,Thorwesten L,Niewerth S.Proprioceptive function in knees with and without total knee arthroplasty[J].Am J Phys Med Rehabil,1999,78(1):39-45.
[44]Sung Do Cho,Chang Ho Hwang.Improved single-limb balance after total knee arthroplasty[J].Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc,2013(21):2744-.2750.
[45]Stan G,Orban H,Orban C.The influence of total knee arthroplasty on postural control[J].Chirurgia,2013,6(10):874-878.
The Influence of Fixed-bearing and Rotating-platform Total Knee Arthroplasty on Static Body Balance in knee osteoarthritis
Mieralimu Muertizha1,Zhao Wei2,Wang Li2,etal
(1.The Postgraduate School of Xinjiang Medical University,Urumqi 830011,China;2.Department of Joine Surgery,Orthopaedic Center,People′s of Xinjiang,Urum 830011,China)
Objective To compare the static body balance between fixed -bearing total knee arthroplasty (PFC-Sigma) and rotating-platform total knee arthroplasty(PFC-RP) in patients′ who suffered from unilateral knee osteoarthritis.Methods Forty-five patients with single osteoarthritis of right knee who underwent TKA at our department from January 2011 to December 2013 were prospectively analyzed.21consecutive patients were replaced with rotating-platform total knee design (PFC-RP)and the others with fixed-bearing design (PFC-Sigma).The measurements were performed using the corresponding instrument and subjects completed consecutive double-limb standing balance trials for three times.The Medio-lateral displacements and Locus Length of GCP (LG) in unit-time were derived from the instrument.All the patients were evaluated with HSS and complete balance trails pre-operatively,sixth month and one year postoperatively.Clinical outcome complication rates and body static balance were compared.Results The mean GCP in the medio-lateral direction shifted to the operative side in both groups after surgery,there was no significant difference in ML-Xrange between the groups(P>0.05).The value of Locus of GCP(LG) was smaller in PFC-RP group than PFC-Sigma group(P<0.05).Conclusion Our study demonstrated no advantage of the rotating-platform arthroplasty over fixed-bearing arthroplasty with regard to clinical results and complication rates at one year follow-up.However,rotating-platform arthroplasty has a better body static balance than fixed-bearing arthroplasty.
total knee arthroplasty;osteoarthritis;rotating-platform;fixed-bearing;body static balance
新疆维吾尔自治区研究生科研创新项目基金(XJGRI 2014093);*本文通讯作者:袁宏
1008-5572(2015)01-0020-06
R687.4+2
B
2014-09-11
米尔阿里木·木尔提扎(1988- ),男,医师,新疆医科大学研究生学院,830011。
