美洛昔康抑制人结肠癌细胞增殖与Wnt/β-catenin 信号的关系研究
2015-06-09何百成秧茂盛
周 密,何百成,秧茂盛,2
(1.重庆市生物化学与分子药理学重点实验室,重庆 400016; 2.吉首大学医学院药理教研室,湖南 吉首 416000)
美洛昔康抑制人结肠癌细胞增殖与Wnt/β-catenin 信号的关系研究
周 密1,何百成1,秧茂盛1,2
(1.重庆市生物化学与分子药理学重点实验室,重庆 400016; 2.吉首大学医学院药理教研室,湖南 吉首 416000)
目的 研究美洛昔康(meloxicam,Mel)对人结肠癌细胞LoVo增殖抑制作用及其机制。方法 以人结肠癌细胞株LoVo为研究对象,体外药物敏感试验(结晶紫染色)和流式细胞术(FCM)分析Mel对细胞的增殖抑制作用;流式细胞术和HE染色检测Mel对细胞凋亡的影响;萤光素酶报告质粒检测Mel对Wnt/β-catenin通路信号转导的影响;Western blot检测Mel对细胞内β-catenin蛋白水平的影响。结果 与对照组相比,Mel能抑制LoVo细胞增殖,72 h、100 μmol·L-1Mel的细胞抑制率高达(57.635±3.86)%(t=10.044,P=0.001);Mel能诱导LoVo细胞凋亡,24 h、60 μmol·L-1Mel的细胞凋亡率达到(33.6±1.7)%(t=30.166,P=0.001);Mel能降低TCF/LEF及Myc/Max报告质粒的萤光素酶活性,24 h、60 μmol·L-1Mel 可使TCF/LEF和Myc/Mac报告的荧光素酶活性分别降至(40.05±2.79)%(t=14.864,P=0.001)和(35.9±2.38)%(t=16.904,P=0.001);Mel能下调细胞内β-catenin蛋白水平,40 μmol·L-1Mel在24、48 h时,可将β-catenin蛋白水平分别降至(71±3.78)%(t=7.353,P=0.003)、(52.66±3.57)%(t=11.724,P=0.001)。结论 Mel能抑制LoVo细胞增殖并促进其凋亡,其机制可能与抑制 Wnt /β-catenin通路信号转导,降低细胞内β-catenin蛋白水平有关。
美洛昔康;人结肠癌LoVo细胞;增殖抑制;凋亡诱导;Wnt /β-catenin信号;β-catenin蛋白
美洛昔康(meloxicam,Mel)是一种烯醇胺类的非甾体抗炎药(NSAIDs),是临床上控制风湿性疾病的主要药物之一,其胃肠道副作用较少、肾毒性较低。目前已有研究显示,Mel在不同类型肿瘤包括胃癌、乳腺癌、肺癌、结肠癌等具有增殖抑制和凋亡诱导作用,但相关机制还有待阐明[1-3]。结肠癌(colorectal carcinoma, CRC)是一种发病率和死亡率呈逐年上升的恶性肿瘤,在常见的胃肠道恶性肿瘤中,结肠癌的发病率位居全球第2位。结肠癌诊疗技术的发展为患者带来了一定的福音,但晚期患者的预后仍不理想,5年生存率仍维持在50%左右[4]。早期结肠癌的首选治疗方式是手术切除,而晚期或复发病例则以药物治疗为主。研究表明,Wnt信号通路在肠道发育和肿瘤发生过程中扮演重要角色;β-catenin 蛋白水平调节因子发生突变,可导致β-catenin蛋白的胞质和核累积,使Wnt信号通路被过度激活,可能参与结肠癌的发生[5-6]。因此,β-catenin 可能是结肠癌的药物治疗靶点。本工作研究Mel对结肠癌LoVo细胞增殖、凋亡的影响及其相关机制,期望能给Mel的抗肿瘤新用途提供初步的实验研究基础与相关的理论依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试剂及细胞培养人结肠癌LoVo细胞购自ATCC(American Type Culture Collection);Meloxicam购自西安昊轩生物科技有限公司;试验所用抗体购自Santa Cruz Biotechnology公司;Lipofectamine购自Invitrogen公司;培养细胞采用DMEM高糖培养基(含10%胎牛血清、100 kU ·L-1青霉素和0.1 g·L-1链霉素)、DMEM培养基和胎牛血清均购自Hyclone;培养条件为5% CO2和37 ℃。其它常用的生物化学和分子生物学试剂均为分析纯。
1.2 实验设计及分组分为对照组和实验组。实验组使用Mel处理,Mel用DMSO溶解,设立20、40、60、80和100 μmol·L-1五个实验组;对照组的处理是使用相同体积的DMSO。
1.3 结晶紫染色法评估增殖生长至对数期的细胞铺于24孔板,每孔的细胞数目为5×103,分别使用20、40、60、80和100 μmol·L-1的Mel或加入DMSO溶剂处理。药物作用细胞24、48和72 h后进行结晶紫染色以检测细胞增殖情况,每个时间点的试验重复3次。移除培养基,用预冷PBS(4 ℃)洗3次去除残余培养基。每孔加入用PBS缓冲、用体积分数为 0.1的甲醛配制的饱和结晶紫溶液0.2 mL, 室温下孵育25 min后,弃结晶紫染液,用PBS清洗3次以除去未与细胞结合结晶紫。将24孔板置于室温下晾干后进行扫描。每孔加入体积分数为 0.2 的乙酸 0.2 mL震荡 10 min以溶解结晶紫,采用全自动酶标仪测定OD值(λ =590 nm)定量。
1.4 流式细胞术检测细胞周期和凋亡将生长至对数期的细胞接种于6 孔板,每孔细胞数目为1×105,贴壁后按实验分组分别加入20、40、60 μmol·L-1的Mel或加入DMSO溶剂处理24 h,用无EDTA的胰蛋白酶消化收集细胞后,用预冷PBS(4 ℃)洗涤2次,随后重悬于1 mL PBS(4 ℃)。收集的细胞通过流式细胞术进行细胞周期和凋亡分析,每组试验重复3次。
1.5 萤光素酶报告质粒法将生长至对数期的细胞接种于T25培养瓶,每瓶细胞数为1×106。 细胞贴壁后,每个T25用Lipofectamine转染3.0 μg LEF/TCF4报告质粒(pTOP-Luc)和E-box报告质粒(pBG-Myc/Max-Luc),转染6 h后换DMEM培养基培养。换液12 h后消化细胞,并接种于24孔板中,每孔的细胞数目为5×103,细胞贴壁后按实验分组分别加入20、40、60 μmol·L-1的Mel进行干预或加入DMSO溶剂处理。24 h后,充分裂解细胞,样品上机检测。萤光素酶活性测定Wnt/β-catenin信号通路活性,方法参照试剂盒(美国NEB公司)说明书;BCA 法测定抽提总蛋白浓度用于结果校正;每组重复3次。
1.6 HE染色每组取对数期2×103个细胞进行细胞爬片,24 h后分别使用20、40、60 μmol·L-1的Mel或加入DMSO溶剂干预。加药24 h后弃培养基,用体积分数为0.95的酒精固定细胞,用苏木精和伊红分别对细胞核、细胞质进行染色,然后进行梯度乙醇脱水、二甲苯透明,最后滴加中性树脂封片。凋亡细胞鉴定经典的形态学特征使用正置显微镜(日本Nikon),每组试验重复3次。
1.7 Western blot 实验将对数期细胞接种于6 孔板中,每孔中的细胞数为1×105,分别使用20、40 μmol·L-1的Mel和DMSO溶剂处理,并设溶剂对照,相同条件下分别培养24 h、48 h后收集细胞,抽提各组总蛋白,细胞裂解和溶胞产物通过煮沸10 min变性,采用BCA法进行总蛋白定量;总蛋白用10%的变性聚丙烯酰胺不连续凝胶(SDS-PAGE)进行电泳,将目标蛋白从凝胶电转至PVDF 膜,随后按Western blot常规方法进行操作,化学发光法ECL显影,凝胶成像仪(美国BIO-RAD公司)成像并分析结果;每组试验重复3次。
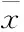
2 结果
2.1 Mel对细胞增殖的影响结晶紫染色及细胞周期分析结果显示(Fig 1),Mel干预组与对照组相比增殖明显受到抑制,量化结果显示(Tab 1),Mel的增殖抑制作用表现为时间和浓度依赖性。流式细胞周期结果显示,G1期细胞明显增多,细胞DNA合成受到阻滞。Mel能明显抑制人结肠癌LoVo细胞增殖。

Fig 1 Effects of meloxicam on the proliferation of LoVo cells
LoVo cells were treated with different concentrations of meloxicam for 24, 48 and 72 h, followed by crystal violet viability assay and flow cytometry analysis. A: Crystal violet staining results; B: Flow cytometry measurement of cell cycle.
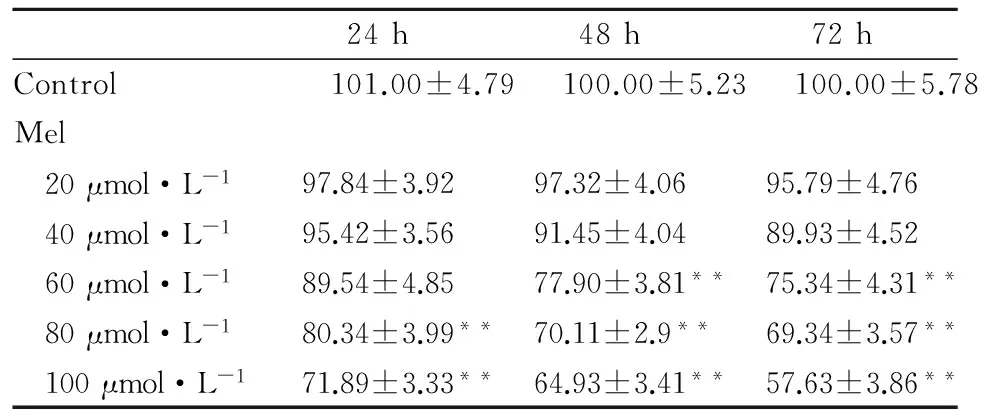
Tab 1 The analysis results of the crystal violet staining
**P<0. 01vscontrol group.
2.2 Mel对细胞凋亡的影响流式细胞分析及 HE染色结果显示(Fig 2),分别使用20、40 和 60 μmol·L-1Mel处理LoVo细胞24 h后,细胞凋亡率以浓度依赖的方式而增加,对照组的凋亡率为(4.47±0.19)%,而20、40 和 60 μmol·L-1的Mel组的细胞凋亡率分别为(10.04±0.56)%(t=16.324,P=0.001)、(16.14±0.71)%(t=25.145,P=0.001)、(33.6±1.7)%(t=30.766,P=0.001)。HE染色结果直观地显示,在(400×)正置显微镜下,细胞凋亡的经典形态学变化包括细胞收缩,核固缩,细胞伪足减少等。Mel能促进LoVo 细胞凋亡。
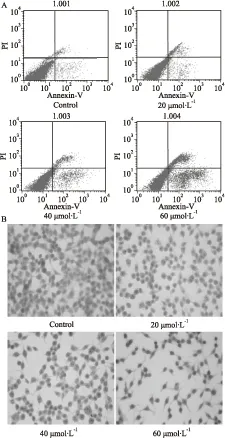
Fig 2 Effects of meloxicam on apoptosis in LoVo cells
LoVo cells were treated with different concentrations of meloxicam for 24 h, followed by flow cytometry measurement of cell apoptosis and H&E stain. A: Flow cytometry measurement of apoptosis; B: HE stain results.
2.3 Mel对Wnt/β-catenin信号转导的影响根据萤光素酶报告质粒结果(Fig 3),TCF/LEF转录活性数值:与对照组比较,20 μmol·L-1组降至(91.23±4.78)%(t=1.87,P=0.141);40 μmol·L-1组降至(62.79±3.05)%(t=9.074,P=0.003);60 μmol·L-1组降至(40.05±2.79)%(t=14.864,P=0.001)。Myc/Max转录活性数值:与对照组比较,20 μmol·L-1组降至(88.64±4.91)%(t=2.45,P=0.074);40 μmol·L-1组降至(55.28±3.35)%(t=11.044,P=0.001);60 μmol·L-1组降至(35.9±2.38)%(t=16.904,P=0.001)。Mel作用后,LoVo细胞中LEF/TCF4与c-Myc/Max的转录活性明显降低,且呈浓度依赖性。Mel能明显下调细胞Wnt /β-catenin通路的信号转导。
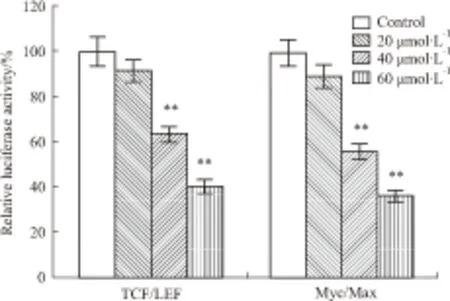
Fig 3 Effects of meloxicam on Wnt/β-catenin pathway signaling transduction of LoVo cells
pTOP-luc and p-SEB-Myc/Max-luc plasmids were employed to transfect LoVo cells. Then,cells were treated with different concentrations of meloxicam for 24 h, followed with luciferase activity quantitative.**P<0. 01vscontrol group.
2.4 Mel对细胞β-catenin蛋白水平的影响Western blot试验结果显示(Fig 4),在24 h时间点,与对照组相比,20 μmol·L-1组的β-catenin蛋白水平降至(92.1±4.56)%(t=1.900,P=0.134);40 μmol·L-1组降至(71.05±3.78)%(t=7.353,P=0.003)。在48 h 时间点,与对照组相比,20 μmol·L-1组的β-catenin蛋白水平降至(88.08±3.34)%(t=2.801,P=0.054);40 μmol·L-1组降至(52.66±3.57)%(t=11.724,P=0.001)。Mel能明显下调LoVo细胞中β-catenin蛋白表达水平,且呈时间和浓度依赖性。
3 讨论
结肠癌是一种发病率和致死率均较高的恶性肿瘤。因此,探讨结肠癌细胞增殖凋亡的相关因素及其分子机制,将有利于寻找新的治疗途径。目前认为,Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的激活可能是结肠癌的病理机制之一,多数结肠癌细胞均有β-catenin突变[7-10]。已有的证据表明,Mel可降低结肠癌、乳腺癌、食管癌和胃癌等的发病风险,提高抗癌治疗的效果[11]。然而,Mel的抗癌作用机制尚不十分清楚。
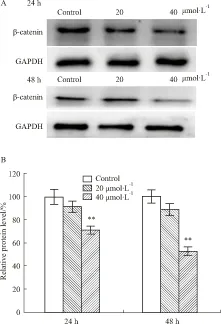
Fig 4 Effects of meloxicam on protein level of β-catenin in LoVo cells
本实验结果显示,Mel能抑制人结肠癌细胞LoVo的增殖,促进LoVo细胞凋亡,而且这种抑制增殖或促进凋亡作用均具有时间和浓度依赖性。此外,Mel可降低LoVo细胞中β-catenin蛋白水平;β-catenin的下调可抑制肿瘤细胞生长和促进细胞凋亡,进而下调或抑制结肠癌细胞中过度激活的Wnt/β-catenin信号通路。可见,Mel对人结肠癌细胞LoVo的抑制增殖或促进凋亡作用可能与干扰Wnt/β-catenin信号通路有关。然而,Mel是如何调节β-catenin蛋白表达的?如何抑制Wnt信号通路的?其详细机制还有待于进一步的深入研究。总之,本研究结果给Mel的抗肿瘤新用途提供初步的理论依据与实验基础,对结肠癌的临床防治具有一定的参考价值,对研究其它类似药物的临床新用途具有借鉴意义。
[1] Yokouchi H, Kanazawa K, Ishida T, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors for non-small-cell lung cancer: A phase Ⅱ trial and literature review[J].MolClinOncol, 2014, 2(5):744-50.
[2] Ayakawa S, Shibamoto Y, Sugie C, et al. Antitumor effects of a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor meloxicam alone and in combination with radiation and/or 5-fluorouracil in cultured tumor cells[J].MolMedRep, 2009, 2(4):621-5.
[3] Naruse T, Nishida Y, Hosono K, et al. Meloxicam inhibits osteosarcoma growth invasiveness and metastasis by COX-2-dependent and independent routes[J].Carcinogenesis, 2006, 27(3):584-92.
[4] 尹丽颖,李凤金,边晓燕,等. 辽东楤木叶总皂苷对结肠癌HT-29细胞的生长抑制作用及机制研究[J]. 中国药理学通报,2013,29(11):1545-8.
[4] Yin L Y, Li F J, Bian X Y, et al. Growth inhibitory effect of total saponins from leaves of Aralia elatl Seem on human colon cancer and its related mechanism[J].ChinPharmacolBull, 2013, 29(11): 1545-8.
[5] Wu K, Yang Q, Mu Y, et al. Berberine inhibits the proliferation of colon cancer cells by inactivating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling[J].IntJOncol, 2012, 41(1):292-8.
[6] Saini M K, Sanyal S N. Piroxicam and c-phycocyanin prevent colon carcinogenesis by inhibition of membrane fluidity and canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling while up-regulating ligand dependent transcription factor PPARgamma[J].BiomedPharmacother, 2014, 68(5):537-50.
[7] Sebio A, Kahn M, Lenz H J. The potential of targeting Wnt/beta-catenin in colon cancer[J].ExpertOpinTherTargets, 2014,18(6):611-5.
[8] Hamada S, Urakawa H, Kozawa E, et al. Nuclear expression of beta-catenin predicts the efficacy of meloxicam treatment for patients with sporadic desmoid tumors[J].TumourBiol, 2014,35(5):4561-6.
[9] 杨秋珺,周龙洋,刘映孜,等.小檗碱抑制HCT116细胞生长与Wnt/β-catenin信号的关系研究[J].中国药理学通报,2012,28(9):60-4.
[9] Yang Q J, Zhou L Y, Liu Y Z, et al. Study on the correlation between the anti-proliferation effect of berberine on HCT116 cells and Wnt/β-catenin signaling[J].ChinPharmacolBull, 2012,28(9):60-4.
[10] 史 玲,苏 坚,廖前进,等. 二烯丙基二硫下调LIMK1抑制人结肠癌SW480细胞迁移与侵袭[J].中国药理学通报,2011,27(2):200-5.
[10] Shi L, Su J, Liao Q J, et al. Diallyl disulfide inhibits migration and invasion in human colon cancerSW480 cells by downregulating expression of LIMK1[J].ChinPharmacolBull,2011,27(2),200-5.
[11] Xin B, Yokoyama Y, Shigeto T, et al. Inhibitory effect of meloxicam, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor and ciglitazone a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ligand on the growth of human ovarian cancers[J].Cancer, 2007, 110(4):791-800.
Anti-proliferative effect of meloxicam and Wnt/β-catenin signal in colon cancer cells
ZHOU Mi1, HE Bai-cheng1, YANG Mao-sheng1,2
(1.ChongqingKeyLaboratoryofBiochemistryandMolecularPharmacology,Chongqing400016,China;2.DeptofPharmacology,SchoolofMedicine,JishouUniversity,JishouHunan416000,China)
Aim To investigate the inhibitory effect of meloxicam (Mel) on human colon cancer LoVo cells and its mechanism. Methods Crystal violet staining assay and flow cytometry assay were performed to determine the anti-proliferative effect of Mel. Flow cytometry assay and H&E assay were used to evaluate the apoptotic effect of Mel. Luciferase reporter plasmid ISRE-Luc was employed to measure the effect of Mel on the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling transduction. Western blot assay was used to detect effect of Mel on the expression level of β-catenin protein. Results Compared with the control group, the inhibitory rate of cell proliferation at 72 h and 100 μmol·L-1Mel was (57.635±3.86)% (t=10.044,P=0.001); the cell apoptotic rate at 24 h and 60 μmol·L-1Mel was (33.6±1.7)% (t=30.166,P=0.001); the transcriptional activities of TCF/LEF and Myc/Max at 24 h and 60 μmol·L-1were (40.05±2.79)% (t=14.864,P=0.001) and (35.9±2.38)% (t=16.904,P=0.001) respectively; the levels of intracellular β-catenin protein at 24 h or 48 h and 40 μmol·L-1were (71±3.78)%(t=7.353,P=0.003)or (52.66±3.57)%(t=11.724,P=0.001)respectively. Conclusion Mel may inhibit proliferation and promote apoptosis of LoVo cells by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin pathway signaling transduction and decreasing intracellular β-catenin protein level.
meloxicam; human colon cancer LoVo cells; anti-proliferation; apoptosis; Wnt /β-catenin signal; β-catenin protein
时间:2015-3-3 11:08 网络出版地址:http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/34.1086.R.20150303.1108.020.html
2014-12-02,
2015-01-28
国家自然科学基金资助项目(No 81071462,81372120)
周 密(1987-),女,硕士生,研究方向:分子药理学,E-mail:137127220@qq.com; 秧茂盛(1965-),男,博士,教授,研究方向:药理学,通讯作者,Tel: 0743-8759168, E-mail:1724041576@qq.com
10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2015.03.020
A
1001-1978(2015)03-0396-05
R329.24;R329.25;R735.350.22;R979.1
