副 舟 骨 源 性 平 足 症 发 病 特 点 分 析*
2015-06-01曹洪辉张传志卢卫忠匡志平王加俊
曹洪辉 张传志 卢卫忠*匡志平 王加俊
副 舟 骨 源 性 平 足 症 发 病 特 点 分 析*
曹洪辉 张传志 卢卫忠*匡志平 王加俊
目的 分析副舟骨源性平足症发病特点。方法 回顾性分析2006~2014年副舟骨源性平足症患者的临床资料,分析副舟骨源性平足症的发病特点。结果66例82足副舟骨源性平足患者,男24例,女42例,年龄15~90岁,平均(37.15±16.76)岁;单侧50例,双侧16例,其中64例为II型副舟骨,2例为I型副舟骨,由于副舟骨存在,胫后肌腱解剖异常而功能受损。根据平足症分期,I期17例,II期26例,III期15例,IV期8例,柔韧性平足47例,僵硬性平足19例。结论副舟骨源性平足症临床较为常见,为胫后肌腱功能障碍性平足症,各个年龄段均可能出现,其中女性、II型副舟骨发病率高。副舟骨异常存在导致胫后功能失调为副舟骨源性平足原因。
副舟骨;平足症;发病特点;回顾性分析
副舟骨是足部常见的先天畸形,其发生率在国外报道为10%~30%不等[1-3]。副舟骨源性平足症是指合并副舟骨的平足畸形,由于副舟骨异常存在,引起胫后肌腱解剖及功能异常,导致平足症发生,为胫后肌腱功能障碍 (posteriortibial tendondysfunction,PTTD)所致平足畸形[4]。副舟骨源性平足症在临床相对少见,既往相关报道不多,因此对该疾病的发病特点需进一步深入了解。本研究回顾性分析副舟骨源性平足发病特点,希望能为该病的诊治提供一定帮助。
1 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料
复习我院2006~2014年临床收治和门诊就诊66例82足副舟骨源性平足症患者,均有存在副舟骨并伴有平足症畸形,其中II型副舟骨64例,I型副舟骨2例。患者均经过临床及影像学证实。排除标准:先天性平足畸形、创伤后平足畸形和肿瘤侵犯骨骼所致平足畸形。
1.2 相关定义及测量方法
副舟骨分型采用Geist分型[1],分为三型:Ⅰ型为籽骨型,Ⅱ型为关节型,Ⅲ型为鸟嘴型。平足症分期采用Johnson和Strom分期法根据临床、病历生理和影像学检查分为四期[5]。副舟骨源性平足症定义:副舟骨引起胫后肌腱功能不全而导致的平足症,其主要临床表现为中足内侧隆起,疼痛和足部不同程度平足畸形[4]。足弓测量方法:负重位标准侧位片内侧楔骨高度。足部MRI检查方法:采用斜冠位扫描胫后肌腱走形,观察其与副舟骨关系。
1.3 研究方法
采用回顾性研究方法,分析副舟骨源性平足症患者年龄、性别、副舟骨分型、平足症分期及副舟骨与胫后肌腱关系。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS18.0(SPSS公司,美国)统计软件进行处理。数据描述采用均值±标准差表示,计算构成比。
2 结果
本研究回顾性分析66例82足副舟骨源性平足患者,其中男性24例,女性42例 (表1);总体年龄为15~90岁 (表2),平均年龄均值 (37.15±16.76)岁,单侧50例,双侧16例,其中64例为II型副舟骨,2例为I型副舟骨(表3),根据平足症分期,I期17例,II期26例,III期15例,IV期8例 (表4),柔韧性平足47例,僵硬性平足19例。足部MRI提示副舟骨存在导致胫后肌腱异常止于副舟骨 (II型)或副舟骨被胫后肌腱包绕 (I型),胫后肌腱不同程度受损。
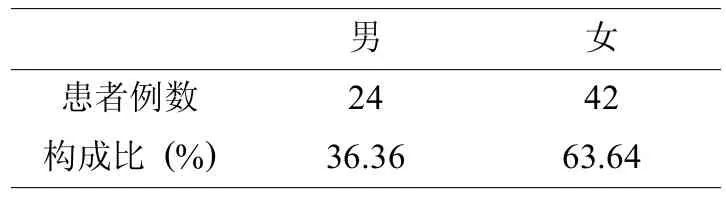
表1 66例82足副舟骨源性平足症患者性别分布

表2 66例82足副舟骨源性平足症患者年龄分布

表3 66例82足副舟骨源性平足症患者性别分布
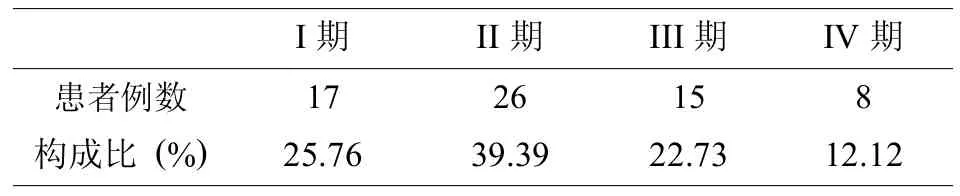
表4 66例82足副舟骨源性平足症患者平足分期
3 讨论
副舟骨为足部最大副骨,也是足部常见畸形,其发生率较高,Grogan报道副舟骨发生率为10%~14%,但不到1%患者有症状,其症状主要因骨性异常突起、平足畸形、骨折和骨缺血性坏死所致[6,7]。
副舟骨异常存在能否导致平足畸形,目前存在争议。有些学者认为,副舟骨存在可导致足舟骨处解剖异常,骨性异常突起而出现足部内侧疼痛症状,但是不能导致平足畸形,因为没有证据表明副舟骨患者足弓高度低于正常足,平足畸形和副舟骨只是偶然关联[8-10]。但大部分学者认为,副舟骨可以导致平足畸形,由于副舟骨存在导致足部胫后肌腱解剖异常,影响胫后肌腱功能,而导致平足症发生。其导致平足畸形的原因有:撞击原因[11]、胫后肌腱附着点异常[4,7]、机械力学原因[12]等。Kidner[11]认为副舟骨异常存在使胫后肌腱改变力线而受到撞击,胫后肌腱累积性损伤导致平足。Kiter等[7]通过尸体解剖研究发现,副舟骨异常全部附着副舟骨,胫后肌腱内旋功能减弱,距舟韧带稳定性差,距骨头下陷,造成平足畸形。Bernaerts[13]等认为由于副舟骨存在,胫后肌腱止点缩短,力臂减少而导致胫后肌腱应力增加,从而导致平足畸形。本组患者中,64例II型副舟骨伴平足畸形患者中,胫后肌腱全部附着于副舟骨上,由于胫后肌腱解剖附着点异常,在撞击和机械力学原因等条件下,造成胫后肌腱积累性损伤,胫后肌腱功能失调性,而出现平足畸形,为胫后肌腱功能失调类型平足畸形,为后天性平足。若胫后肌腱无解剖变异,其功能尚未出现受损时,足弓无塌陷,这也解释了副舟骨患者足弓高度未低于正常足。本组2例I型副舟骨伴平足畸形者,由于副舟骨在胫后肌腱内,在肌腱内撞击磨损胫后肌腱,导致胫后肌腱损伤,而导致平足畸形,为内部撞击机制。
副舟骨能否影响胫后肌腱解剖及功能异常,决定手术方案实施。目前手术方法主要有:单纯副舟骨切除术[9]、副舟骨切除后胫后肌腱重建术[4]、副舟骨切除胫后肌腱重建结合各式平足畸形截骨矫正术[14,15]、三关节融合术。术前评估胫后肌腱解剖尤其重要,既往对胫后肌腱和副舟骨关系,主要为局限于尸体解剖研究,或手术中所见。本组患者中,采用核磁共振检查,根据胫后肌腱解剖走形方向,用斜冠位扫描,能清楚显示胫后肌腱和副舟骨解剖关系,能为术前评估及手术方案制动提供有效帮助。
综合上述副舟骨源性平足症患者特点,副舟骨源性平足症为后天性平足畸形,为胫后肌腱功能失调性平足症,在长期慢性胫后肌腱功能受损情况下导致平足畸形,女性为高危人群,II型副舟骨为高危因素,胫后肌腱全部附着于副舟骨可能为副舟骨源性平足症的解剖基础,其处理原则可根据胫后肌腱功能失调性平足症进行处理。
本研究局限性为回顾性研究,只在临床或门诊统计副舟骨伴平足畸形患者,部分患者只是通过临床症状及影像学检查确诊,未手术进一步确诊副舟骨与胫后肌腱关系,病例量相对少,无相关解剖标本辅证,也未作生物力学测试。总之,副舟骨源性平足症在临床较为常见,临床医生需要提高对副舟骨源性平足症的认识和了解,为该病的预防、诊断、治疗提供合理的方案。
[1] Geist ES.The accessory scaphoid bone.J Bone Joint Surg,1925,7:570-574.
[2] Coskun N,Yuksel M,Cevener M,et al.Incidence of accessory ossicles and sesamoid bones in the feet:a radiographical study of the Turkish subjects.Surg Radiol Anat,2009,31(1):19-24.
[3] 曹洪辉,张传志,卢卫忠等.重庆地区副舟骨和副舟骨源性疼痛与平足症患病率及多因素相关分析.生物骨科材料与临床研究,2014,10(5)29-33.
[4] 曹洪辉,唐康来,邓银栓等.副舟骨切除结合胫后肌腱止点前置重建治疗副舟骨源性平足症.中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26 (06):686-690.
[5] Johnson KA,StromDE.Tibialis posteriordysfunction.ClinOrthop Relat Res,1989;239:196-206.
[6] Grogan DP,Gasser SI,Ogden JA.The painful accessory navicular: a clinical and histopathological study.Foot Ankle,1989,10:164-9.
[7] Kiter E,Erdag N,Karatosun V,et al.Tibialis posterior tendon abnormalities in feet with accessory navicular bone and at foot.Acta Orthop Scand,1999,70:618-21.
[8] Sullivan J A,Miller W A.The relationship of the accessory navicular to the development of theat foot.Clin Orth,1979,744:233-237.
[9] Jasiewicz B,Potaczek T,Kacki W,et al.Results of simpleexcision techniquein the surgical treatmentofsymptomaticaccessory navicular bones.Foot Ankle Surg,2008,14(2):57-61.
[10]Kanatli U,Yetkin H,Yalcin N.Therelationshipbetween accessory navicular and medial longitudinal arch:evaluation with a plantar pressure distribution measurement system.Foot Ankle Int,2003, 24(6):486-489.
[11]Kidner FC.The prehallux(accessory scaphoid)in its relation to flat-foot.Bone Joint Surg Am,1929,11:831-837.
[12]Kiter E,Erdag N,Karatosun V,Günal I.Tibialis posterior tendon abnormalities in feet with accessory navicular bone and flatfoot. Acta Orthop Scand,1999,70(6):618-21.
[13]Bernaerts A,Vanhoenacker FM,Van de Perre S,et al.Accessory navicular bone:not such a normal variant.JBR-BTR,2004,87(5): 250-252.
[14]Hong-hui Cao,Kang-lai Tang,Wei-zhong Lu,et al.Medial displacement calcaneal osteotomy with posterior tibial tendo reconstruction for the flexible flatfoot with symptomatic accessory navicular.TheJournalof Foot&AnkleSurgery,2014,53:539-543.
[15]KimJ,ParkC,MoonY,etal.Concomitant calcaneo-cuboid-cuneiform osteotomies and the modified Kidner procedure for severe flatfoot associated with symptomatic accessory navicular in children and adolescents.J Orthop Surg Res,2014,5 9(1):131.
A study on the characteristic of the flatfoot related with accessory navicular
Cao Honghui,Zhang Chuanzhi,Lu Weizhong,et al.Department of Orthopaedics,the Traditional Chinese Medical Hospital of Chongqing,Chongqing,400021,China
Objective To study on the characteristic of the flatfoot related with accessory navicular(AN).Methods The study designwas retrospective analysis.Toanalyzethecharacteristicof the flatfoot related with accessorynavicular.Results From 2006 to 2014,a total 66people 82feet,whichwerethe flatfoot related with accessory navicular,were studied. The series consisted of 24 male and 42 female patients,with a mean age of(37.15±16.76)years(range 15 to 90 years). Ofthe66patients,50hadunilateral at feet and16 bilateralatfeet.The typeI,Ⅱrespectivelyhave 2patients,64 patients. The function of posterior tibial tendon(PTT)were been destroyed because of the abnormal exist of accessory navicular. According of the stage of flatfeet,the stage I,II,III,IV respectively have 17 patients,26 patients,15 patients,8 patients.The flexible flatfeet were 47 patients and the rigidity flatfeet were 19 patients.Conclusions The flatfoot related with AN are the common disease in clinic and one of the posterior tibial tendon dysfunction(PTTD)flatfoot.All ages are possible and incidence rate is higher in women and type II AN.The reason which lead to the flatfoot related with AN is PTTD cause by the abnormally exist of AN.
Accessory navicular;Flatfoot;Characteristic of the disease;Retrospective analysis
R683
B
10.3969/j.issn.1672-5972.2015.03.014
swgk2014-10-0197
曹洪辉(1976-)男,硕士研究生,副主任医师。工作方向:关节外科与足踝外科疾病诊治。
*[通讯作者]卢卫忠(1967-)男,硕士研究生,主任医师。工作方向:关节外科与运动医学。
2014-10-29)
*课题项目:重庆市卫生局面上项目。课题名称:副舟骨与平足症相关性分析(2012-2-184)
重庆市中医院骨科,重庆400021
