Ethical inspection about laboratory animals
2015-05-22NaiBinYANGXiaoJunPANJingJingCHENGJiaQiangLINJiaYinZHU
Nai-Bin YANG, Xiao-Jun PAN, Jing-Jing CHENG, Jia-Qiang LIN, Jia-Yin ZHU
1. The First Affiliated Hospital, 2. Affiliated Stomatology Hospital, 3. Laboratory Animal Center, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325000, China
Ethical inspection about laboratory animals
Nai-Bin YANG1+, Xiao-Jun PAN1+, Jing-Jing CHENG2, Jia-Qiang LIN2, Jia-Yin ZHU3
1. The First Affiliated Hospital, 2. Affiliated Stomatology Hospital, 3. Laboratory Animal Center, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325000, China
doi 10.13459/j.cnki.cjap.2015.06.004
Laboratory animals and animal experiments are foundaons and important support condions for life sciences, especially for medical research. The animal experiments have drawn extensive aenon from the society because of the ethical issue. This paper takes Wenzhou Medical University as an example to give a brief introducon to the ethical review about laboratory animals in the university so as to further draw aenon and concerns from the public about the ethical issue of laboratory animals. We successively introduce its scienf i c projects, nurturing environment and ethical review of laboratory animals.
ethical review; laboratory animals; 3Rs principle
Overview of scientif i c research in Wenzhou Medical University
With the constant and fast development of Chinese economy, Chinese government has put huge and bold investment in basic medical research in recent years. As one of the medical academies, Wenzhou Medical University is among the support list of key provincial-level universities of Zhejiang Province. It's formerly called Wenzhou Medical College, and was renamed as Wenzhou Medical University in 2013. In the past six years, it has made great strides in its research capacity. From 2009 to 2014, an annual average of 71.5 research projects of the university have been funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China, with an average annual growth of 17.9%(Tab.1, Fig.1); the average amount of annual subsidies granted by National Natural Science Foundation committee of China was 28,755,000 RMB, with an average annual growth of 30.58%(Tab.1, Fig.2); and an annual average of 545 SCI papers were published[1], with an average annual growth of 28.52% (Tab.1, Fig.3). All these progress in research capacity are partly contributed by laboratory animals.
As foundations and preconditions for medical research, laboratory animals play an important role in basic medical research. There is a integrated experimental building named “Qiuzhen”, which means “pursuit of truth” in Chinese, in the quiet corner of our campus. It is Laboratory Animal Center of Wenzhou Medical University, a department with strict management system and annually providing more than 100, 000 laboratory animals for researchers, teachers and students of Wenzhou Medical University. Since accurate, reliable and comparable features are required in medical scientif i c research, we usually purchase, introduce and feed laboratory animals complied with international standards from fixed origins including SPF animals of variety of species and strain, which are used for meeting almost all scientif i c experiments, biological products and verif i cation. We annually provide more than 100,000 laboratory animals for research and teaching of our university, including 70 thousand mice, 18 thousand rats and 13 thousand rabbits, however, researchful need of researchers, teachers and students are still not fulfilled, resulting in a long queue waiting for making appointments for laboratory animals.
Although it is only a triple-storey building, there are 19 laboratories, 6 preparation rooms, 2 storerooms and 1 mass detection(MD) room for laboratory animals. About 30,000 specif i c pathogen free (SPF) animals are fed here, including mice, Rats, rabbits,etc. To prevent interference from other elements in scientific research, we set up parclose environment laboratory on the second ff oor, a standard nurturing environment for laboratory animals. It is totally-enclosed, equipped with ventilating duct, with the constantly-controlled 23°C temperature, 40%-70% relative humidity, ventilation by 15 times per hour, air cleanliness of 10,000 class. Passwords input and fi ngerprint checkage are required before entering this laboratory. Wearing disinfectant coats, hats, shoes and respirators and then going through air shower are also required before entering into parclose environment laboratories. People without the feeding qualification are forbidden to enter. To relieve the tension of laboratory animals, we play soft music while they are feeding. Materials used in this laboratory must be coped under high pressure steam sterilizer in advance. Air, materials, personnel and laboratory animals are all shied along one-way ff ow route and also cages, fodder, instruments, drugs and other materials must go through strict disinfection and sterilization. Once you go out from feeding rooms, you must abide by strict procedure for reentrance. To maintain strict feeding environment, our center spend thousands of utility bills for one day. Moreover, feeding of laboratory animals calls for so strict that we must conf i rm laboratory animals are on monitor for every moment, even on Chinese New Year's Eve.

Tab. 1 Overview of 2009-2014 Scientific Research of Wenzhou Medical University.
Monument for laboratory animals
Laboratory animals make a great contribution to human health.ere is a little monument in behind of our laboratory animal center. It was built in 2012, mainly to mourn sacrificed animals for scientific research. Lots of researchers, teachers and students come here to mourn them aer fi nishing experiments and lay wreaths to them on Tomb-sweeping Day every year. We demand ourselves to respect and cherish lives of animals and avoid adding nonexperimental injury to them to the greatest extent. If there are any students who violate procedure of scientific research and maltreat laboratory animals, we would stop and correct them at once.
Ethical Inspection about laboratory animals in Wenzhou Medical University
To further strengthen biosafety of laboratory animals and regulatory management of animal experiments at the university, protect health of our staf f and students and safety of the campus environment, and safeguard the animal welfare, Wenzhou Medical University set up Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee on May 8, 2009, issued the Articles of Association of Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee under Wenzhou Medical College, and demanded that it's necessary to file an application and submit the Tab of Animal Experimental Ethical Inspection(Tab.2) to Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee under Wenzhou Medical College and obtain approval and the approval number before starting any experiment involving laboratory animals. The Tab mainly includes three parts:
(1) It's demanded by animal experimental ethical inspection that laboratory animals shall be supplied by institutions that having the Production License for Laboratory Animals. It's not allowed to buy laboratory animals from any company or individual without the Production License for Laboratory Animals. If a task group needs to buy laboratory animals by itself, it must file an application to Laboratory Animal Centre of the university and put on records before buying.
(2) Animal experiments should follow the 3Rs principle: reduction, ref i nement and replacement, to control the number of animals strictly, minimize the consumption of animals or use unconscious animal materials instead.
(3) In the experiment process, it's necessary to be kind to animals, standardize feeding and operation, adopt anesthesia and euthanasia death, and package, recover and incinerate carcasses in a unif i ed way. No company or individual shall throw away any animal carcass after experiments or natural death without authorization.
In recent years, Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee under Wenzhou Medical University had approved 340 copies of the Tab of Animal Experimental Ethical Inspection, with an annual average of 68 copies and an average annual growth of 161.94%.e trend of approved copies of animal experimental ethical inspection of Wenzhou Medical University is listed in Figure 4.
There are three other major medical universities in Zhejiang province. Among them, one university have approved about 200 copies of the Tab of Animal Experimental Ethical Inspection per year, but the other two universities didn't start the work of Animal Experimental Ethical Inspection until now. In many developing districts or developing countries, the work of laboratory animal ethics is also still at its preliminary stage[2]. Ethics problems in both animal experiment and clinical research drew extensive attentions recently [3, 4].
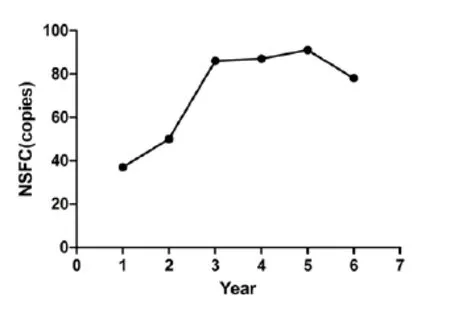
Fig. 1 Research projects of Wenzhou Medical University annually funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China in the past six years.

Fig. 2 Subsidies of Wenzhou Medical University annually granted by National Natural Science Foundation committee of China in the past six years.
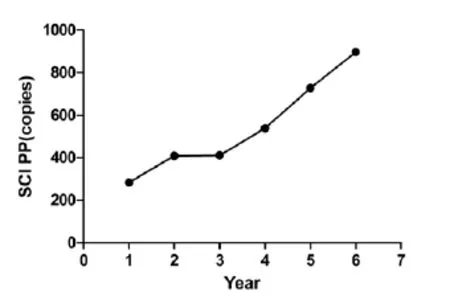
Fig. 3 SCI papers annually published by researchers of Wenzhou Medical University in the past six years.
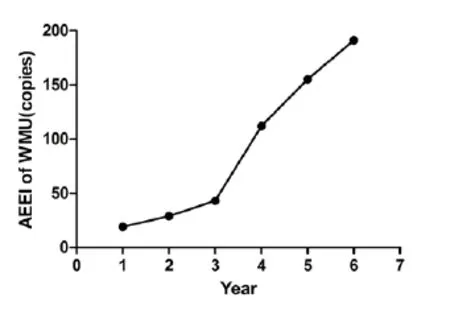
Fig. 4 Trend of approved copies of animal experimental ethical inspection of Wenzhou Medical University.
Conclusion
Through animal experimental ethical inspection, researchers of Wenzhou Medical University have been fully aware of the importance of ethics and welfare of laboratory animals, which has a positive signif i cance on further standardizing management of laboratory animals.
Conf l ict of interest
Authors declare no conf f ict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by fund of science and technology project of Wenzhou (Y20140601).
1. Zhang YS, Wu AM, Yu JF. A bibliometric analysis of papers in Wenzhou Medical College based onSCIE from 2001 to 2010[J]. J Wenzhou Med Coll, 2013, 43(6): 411-417.
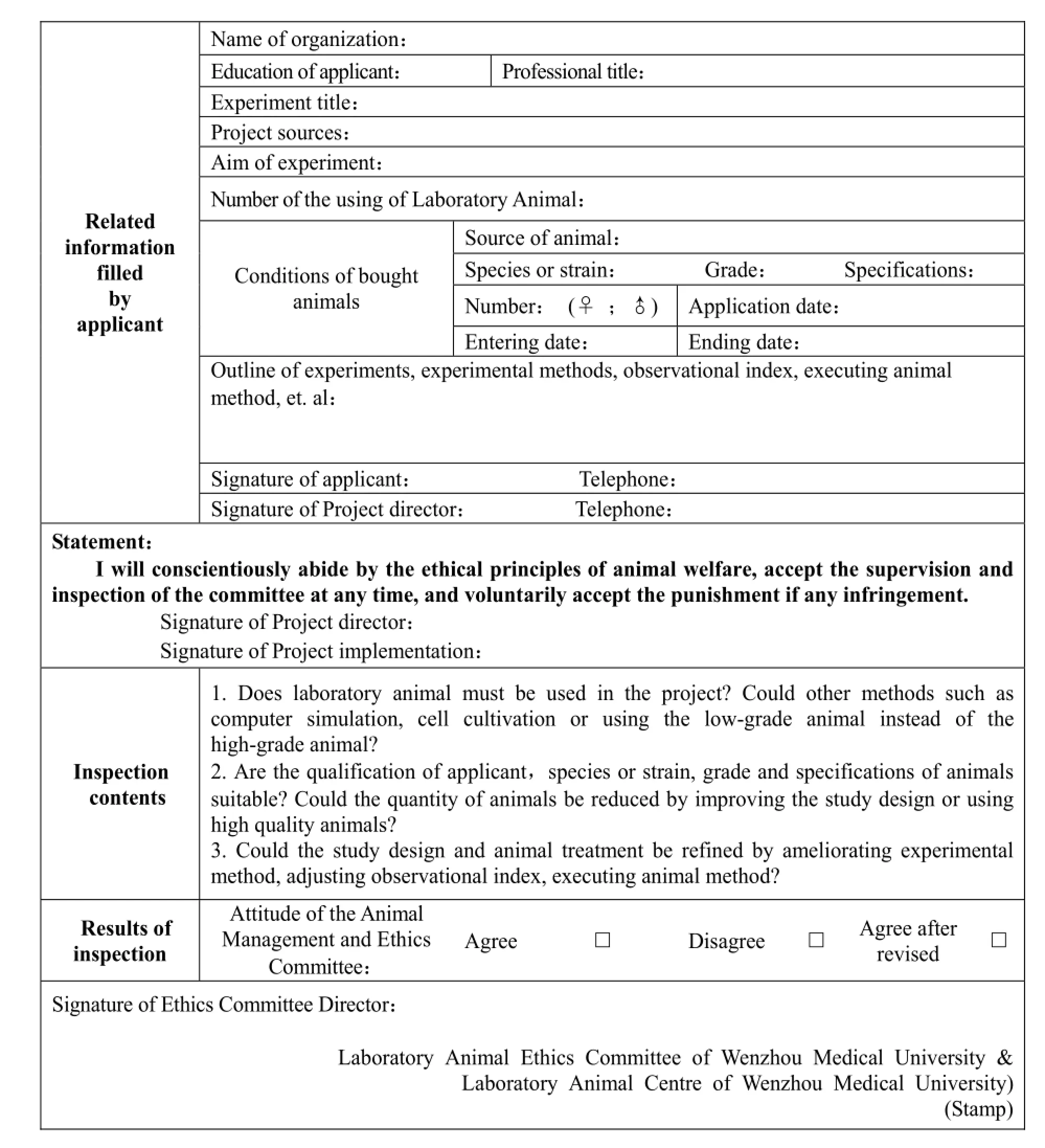
Tab. 2 The table of animal experimental ethical inspection of laboratory animal centre, Wenzhou medical university. (ID number):
2. Paprocka-Lipinska A. About the genesis of the first Polish local research ethics committee[J]. Pol Merkur Lekarski, 2014, 37(222): 365-368.
3. Keirns CC. Everyday ethics and ebola: planning for the unlikely[J]. Am J Bioeth, 2015, 15(4): 68-70.
4. Taylor HA, Kuwana E, Wilfond BS. Challenging cases in research ethics[J]. Am J Bioeth, 2015, 15(4): 75.
Jia-Yin Zhu, Laboratory Animal Center, Wenzhou Medical University, University town, Wenzhou 325035, China. Tel: 86-577-86689908, Fax: 86-577-86689908;
E-mail: zjiayin@163.com
+ese two authors contributed equally to this work
Received 2015-10-10; accepted 2015-11-18
杂志排行
中国应用生理学杂志的其它文章
- A mini review: Tau transgenic mouse models and olfactory dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease
- Better parameters of ventilation-CO2output relationship predict death in CHF patients
- Association between endothelial nitric oxide synthase (ENOS) G894T polymorphism and high altitude (HA) adaptation: a meta-analysis
- Flow cytometric analysis of circulating microvesicles derived from myocardial ischemic preconditioning and cardioprotection of ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats
- Synergisms of cardiovascular effects between iptakalim and amlodipine, hydrochlorothiazide or propranolol in anesthetized rats
- Effects of curcumin on sodium currents of dorsal root ganglion neurons in type 2 diabetic neuropathic pain rats
