变速箱开发中的全自动验证测试
2015-03-15RolfBraun,MaximilianGaβmann,ZhangJilin等
变速箱开发中的全自动验证测试
0 引言
0 Motivation
在变速箱开发过程中,上百种的样件变速箱被组装用于内部试验和客户的测试。整车制造商也需要样件变速箱对其整车进行优化。在安装在整车上和发货前,样件变速箱需要进行包含重要功能的验证测试。在这里,验证测试由特殊的电机作为驱动的台架组成。如图1,变速箱被电机驱动,输出端可通过变速箱内部零件锁止或者安装由涡流制动的制动器。
传统的做法是人工控制测试台(转速和扭矩)和变速箱的功能(换挡)。这意味着,在测试的时候操作者通过用户界面或者按钮手动调整或者激活每个测试步骤。基于时间序列的测量数据被分析和显示在在线的显示器上。对于数据的评价非常主观并且很难与极限值进行比较。最后导致的结果是,只有非常粗糙的数据被记录了下来。这对数据统计分析非常不利。
During the course of transmission development,hundreds of prototype transmissions are assembled,both for internal trials and for customer tests.The development partners(vehicle manufacturers)also require the prototypes for overall vehicle optimization in development.Prior to installation in the vehicle or to delivery to customers,the prototype transmissions undergo a release test run that tests the most important basic functions.In the case described here,the release test is performed on a special electric test bench as shown in Fig.1,whereby the transmission is driven by an electric motor and the output side can be optionally braked or put under a load torque by an eddy current brake.
The conventional method is to manuallycontrol or actuate both the test bench(speed and torque)and the transmission functions(gear changes).This means that during the test run,the test bench driver manually actuates or adjusts the individual test steps and events on a user interface or by pushing buttons.The time sequences of the measurement data are displayed and analyzed online on the screen.This evaluation is very subjectively colored and comparison with strict limit values can be difficult.At the end of the test run in the conventional procedure,only the raw data from the measuring is archived.This makes statistical analysis more difficult and evaluations made may not be immediately understandable later.

图1 测试台Fig.1 Test bench
为此设计了一套自动化的验证测试的分析方法,该方法可确保测试的重复性,并且可以对测量数据进行自动测量、评价,包括与极限值的比对结果(OK/NOK)。另外还能对特征值进行自动报告、自动统计记录以及自动评估。同时该方法还可以用于对新型变速箱(新概念和新功能)自动测试程序的开发和将该测试方法应用与量产的EOL测试台上。
The objective on introduction of the automated release test run described here was to design the test procedure including pre-conditioning to be reproducible so that it would also be possible to achieve automated evaluation of the measurement data,including OK/NOK evaluation with respect to defined limit values.Additionally,automated reporting as well as statistical recording and evaluation of characteristic values were implemented.Another objective is to develop automatic test procedures for new transmission concepts or new functions and to transfer them to the EOL(End Of Line)release test bench in volume production assembly.
1 测试流程
为了优化测试搭建时间,台架布置被设计成无输出端连接的且变速箱的所有功能均能被验证的形式。整个自动验证测试由9个阶段组成。具体如图2。
测试台的运行由程序自动控制,这里使用的是ZF的PASU系统(基于UNIX的测试台自动化控制系统)。程序采用分步的运行模式,并且由于在其中包含和变速箱通讯的CAN接口,所以要求软件柔性化设计来匹配相应的变速箱的CAN需求和不同的换挡曲线。在开始进行试验前,变速箱的液位由人工进行调整。并且对各个档位进行换挡保证变速箱油进入各个离合器。变速箱的液位调整是在P挡下参照并且通过液位螺栓孔来进行的。这时也对变速箱无负载下的驻车档功能也进行了验证。
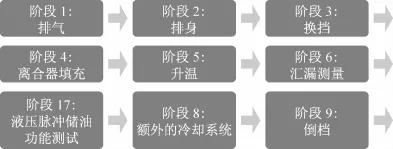
图2 在自动验证测试中的测试阶段Fig.2 Test phases in the automated release test run
1.1 阶段1:排气
首先进行的是排气程序,主要是通过对单独的离合器施加连续的压力脉冲来实现。每次,为了防止锁死,两个离合器交替的被脉冲驱动。这个测试程序和在量产线上的终验收测试台(EOL)的测试程序一致。进行排气的目的是识别和降低由空气导致的压力形成的延迟。为了评价和分析排气阶段和压力形成过程,单个离合器的填充脉冲压力以叠加曲线的方式进行显示。
1.2 阶段2和阶段3:暖机和换挡
这个阶段包含对所有的档位进行结合(含液力变矩器锁止离合器),并且在固定档位且中度负荷下对变速箱进行暖机使其到达运行温度。同时对各个档位的传动比进行检查。
1.3 阶段4,离合器填充
通常自动变速箱里的离合器直接连接两个传递扭矩的轴系或者齿轮零部件,它的多片摩擦片组由带内齿的摩擦片,带外齿的摩擦片和摩擦片保持架组成。如下图3所示。
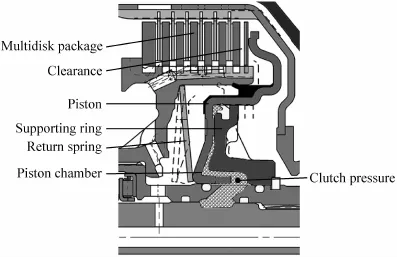
图3 8HP50的离合器CFig.3 Clutch C in the 8HP50
在这里由活塞来驱动多片摩擦片组,为了实现这个目的,润滑油被注入活塞腔形成压力驱动活塞。当压力消失后由碟形弹簧对活塞进行回位。
当测试运行时每个离合器被方形脉冲驱动5次,每次通过强制锁死变速箱内部原件建立扭矩。这意味着在某个档位下不仅在档的三个离合器被结合,而且第四个离合器也被结合。这时,由于液力变矩器锁止离合器的作用,变速箱的输入转速被降低到一个很低的区间。
这个阶段的主要目的是对离合器填充特征进行评价。如果是带压力传感器的样品变速箱,可以通过离合器压力传感器进行评价。如果是量产的变速箱(不带压力传感器)可以通过转速和扭矩曲线来进行评价。
如下的特征值用于对填充阶段进行评价:
关闭的反应时间,填充压力,填充时间和打开的反应时间和排空时间。如图4。

图4 离合器填充测试Fig.4 Testing clutch filling
反应时间是从换挡命令开始(电信号)到第一个压力反馈结束。影响反应时间的因素有电流的泄漏、CAN的通讯时间、阀体内部阀的惯性和摩擦力、润滑油的特性。填充压力的影响因素有碟形簧的簧力和活塞的摩擦力。它是由压力建立阶段的活塞的移动距离来决定的。填充时间是从第一个填充压力的时间开始计算,然后压力增加到完全有效值使其快速填充,使活塞到达多片摩擦片组的时间结束。从另外一方面这个填充时间反应了离合器的间隙,或者活塞到摩擦片组的行程。当离合器打开时,其反应时间是从压力明显下降开始到排空时间直至压力完全卸除终止。碟形簧的簧力和密封件直接对排空时间产生影响。
当无法测量变速箱离合器的压力时,填充时间的评价通过换挡信号和和涡轮的转速来进行。测量值通过内置于程序的额定值进行比较,来判断OK或者NOK。另外这些值被转换为Excel格式用于统计分析。
1 Procedure
In order to save setup time when necessary,the test procedure is designed so that all important transmission functions can also be tested without the output side being connected.The test procedure of the automated release test run consists essentially of 9 phases,as shown in Fig.2.
The test bench is controlled by a step control program that runs automatically.The equipment used here is a ZF test bench automation software(PASU)on a UNIX basis.The step control program also includes the transmission control via a corresponding CAN interface.This requires the implementation of software modules tailored to the variants and containing the corresponding CANspecifications as well as the appropriate shift sequences.
Before the start of the test run itself,the transmission is pre-conditioned manually as this is necessary to adjust the oil level.This entails shifting all gears for the first time to fill all the clutches.The oil level is adjusted in the running transmission via the oil overflow bore in position P.Also included here is a manual parking lock check in load-free state.
1.1 Phase 1:Venting cycle
The automated test run starts with a newly introduced venting cycle which involves applying an individual number of consecutive pressure impulses to each clutch.Each time,two different clutches receive impulses together in an interlaced sequence in order to avoid force locking.This procedure is already matched to the procedure on the End of Line(EOL)test bench in volume production assembly.The purpose of the venting cycle during pre-conditioning is in particular to identify and reduce delays in pressure buildup caused by original air.To evaluate the venting cycle,the filling impulses of one clutch are shown in an overlapping way so that the pressure buildup can be analyzed.
1.2 Phases 2 and 3:Warming up and changing gears
This is followed by changes into all gears including engaging the lock-up clutch and a constant-speed drive under medium load to warm the transmission up to operating temperature.At the same time,the procedure tests whether the individual gears are engaged,force locking is created,and the corresponding gear ratios are achieved.
1.3 Phase 4:Clutch filling
Typically,the clutches in automatic transmissions connect two torque-carrying shafts or gearset components to each other and consist of a multidisk package with outer and inner multidisks each held in a multidisk carrier,as shown in Figure 3.
The task of the piston is to compress the multidisk package,and for this purpose pressurized oil is applied to the corresponding surface inside the piston chamber.The disk springs open the clutch in the non-pressurized state.
During the test run,each clutch is closed five times under load with a square pulse.Each time,force locking is created even without a connected output side by locking the transmission internally.This means that the clutch to be tested is activated as the fourth clutch while one gear is already activated by three engaged clutches.During this process,the speed of the transmission input shaft is braked at low speed against the torque of the open lock-up gear/torque converter.
In this phase,the filling behavior of the clutch in question is evaluated.In the case of prototype transmissions in which pressure connections of clutch pressures are installed,the pressure characteristics are evaluated.In the case of transmissions without pressure connections(e.g.with volume production housings),the speed and torque curves can be used for evaluation.
Comparative values are evaluated for the following characteristics relating to clutch filling:response time for closing,filling pressure,filling time and response time for opening as well as emptying time,as shown in Fig.4.
The response time when closing results from the time difference between the shift command(electric signal)and the first pressure reaction.The response time is influenced by low-dispersion current times and the task time of the CAN as well as by inertia and frictional forces of the valves and the oil columns to be moved.The filling pressure of the clutch is mainly influenced by the spring force of the return element(disk spring)and the piston frictional forces.It is determined by the pressure level that builds up while the piston moves.The filling time is the time difference between the first pressure reaction and the pressure increase during the effective rapid filling when the piston reaches the multidisk package.It is an indicator of the clutch clearance,or the piston stroke up to contact with the multidisk package.In the case of opening,the response time results from the shift command to the first significant pressure drop and the emptying time up to complete pressure loss in the clutch.The multidisk spring force and the sealing elements again play a role in the emptying time.
In the case of transmissions without pressure connections,the rapid filling time is evaluated as the difference between the shift command up to the reaction of the turbine speed(speed of intake).The measured values are automatically compared with the defined limit values and correspondingly evaluated as OK or NOK.Additionally,the values are entered in an XLS file and statistically evaluated there.
1.4 阶段5和阶段6:升温和泄漏测试
为了测量变速箱内部的泄漏,变速箱的油温需要上升到100°C左右。变速箱的泄漏通过转速饱和度来确定。这意味着,在额定的系统压力下,油泵泵出的油量可以转换为泄漏油量的测量。在系统压力15 bar且所有离合器打开状态下对第一个泄漏比较值进行测量。转速的饱和度在这里基于油泵的特征曲线、泵出的油量、液压模块的泄露和泵的内部泄漏。单个离合器的泄漏通过离合器结合时比较基础泄漏和总泄漏来决定。
测试的过程是由转速降低和升高组成。从期望的饱和度降低到明显的非饱和区间,然后从非饱和区间升高到饱和区间。从而通过转速可以测得在什么点对应了15 bar的系统压力。这样就可以和额定值进行比较,并且记录统计。
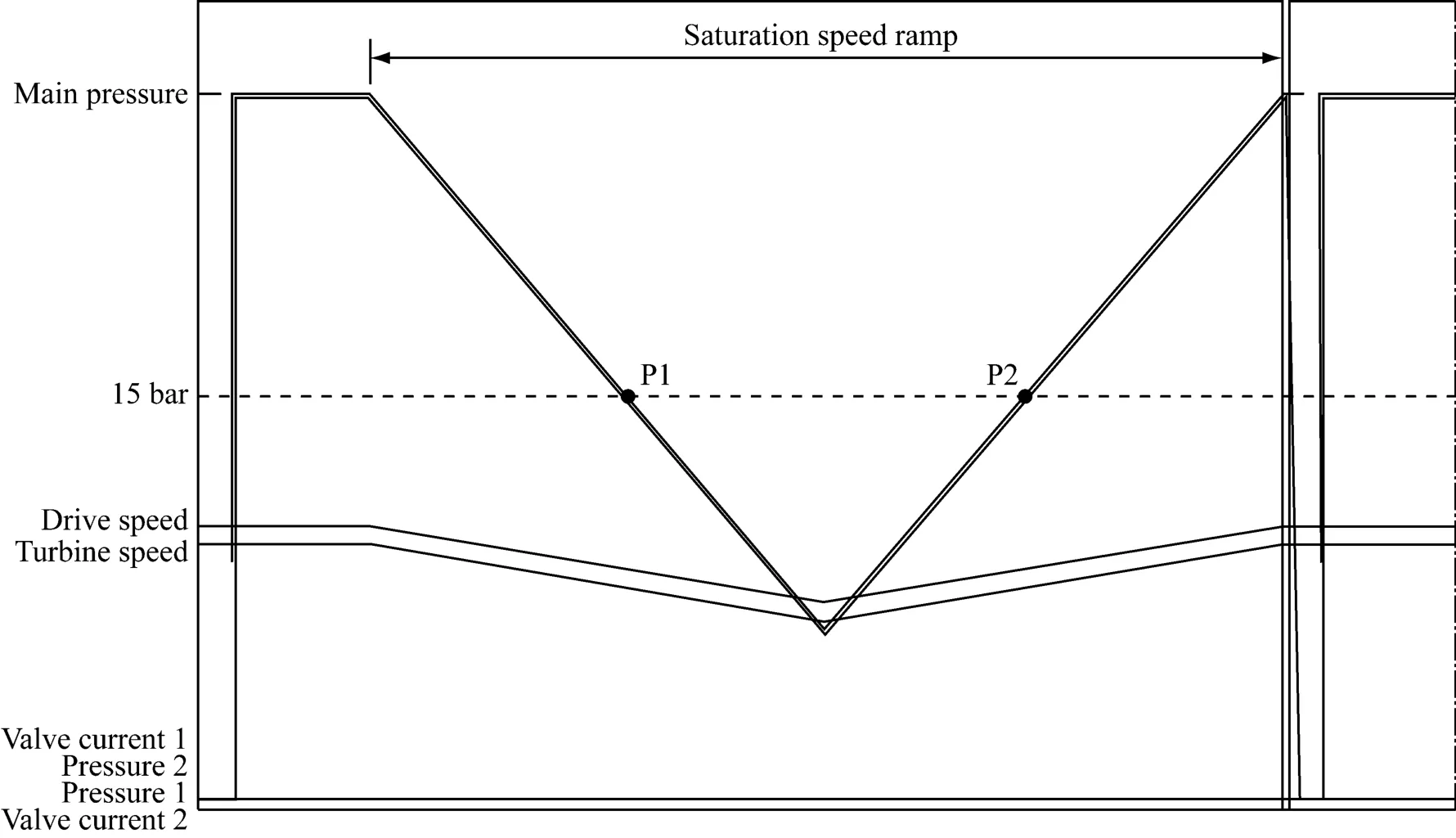
图5 泄漏测试Fig.5 Leakage measurement
1.5 阶段7:液压脉冲储油功能测试
液压脉冲储油功能(HIS)是基于发动机启停技术设计,它用于支持油泵的快速启动.在变速箱运行过程中多余的油储存于HIS元件中,当快速启动时元件中的油被释放入液压控制单元的主回路和离合器中。基于此,三个离合器在300 ms内被足够压力的油液填充并结合。
HIS测试在变速箱静止时(油泵静止时)进行。HIS功能在系统压力降低为0时被激活。液压脉冲的高度和持续时间被用于对其功能的验证。这些数据也被保存用于分析。
1.6 阶段8:额外的冷却系统
重载变速箱的应用可以加载额外的冷却系统。当离合器在高负载下压力超过极限值结合时,系统自动提供额外的冷却液(油量)。此功能通过测量在稳定工况下(离合器压力增加或者降低到限值)次要压力的不饱和度。如果额外冷却系统功能正确,次要压力会明显下降。如图6所示。
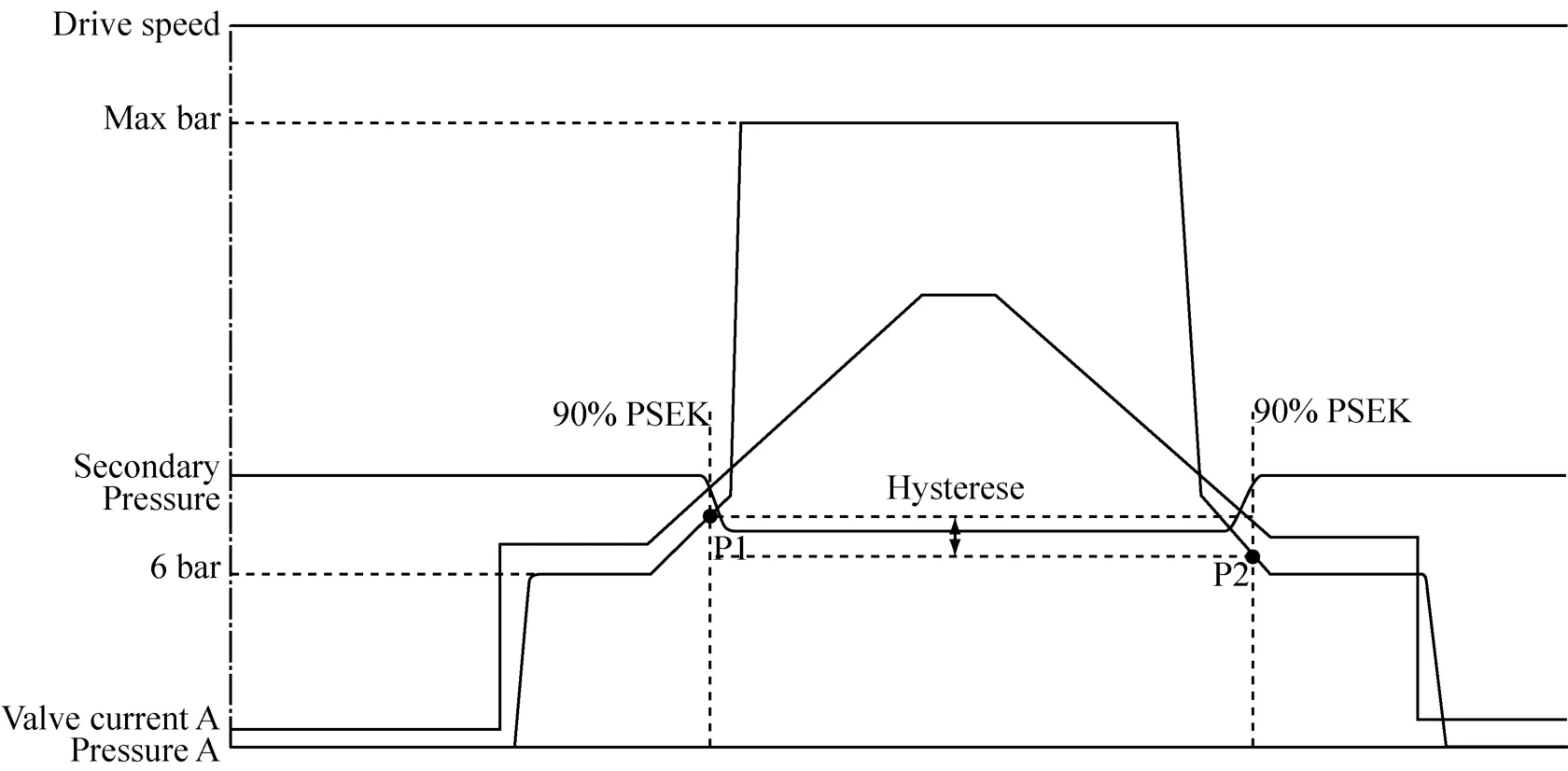
图6 额外冷却系统的测试Fig.6 Testing the additional cooling system
1.7 阶段9,倒档
因为有缺陷的零部件可以导致拖曳转矩的增加和离合器温度的上升,所以倒档的速度耐久强度在一个单独的阶段进行。测试时,对转速做一个小的改变进而变速箱的拖曳转矩进行监控。
2 数据分析和报告
数据的分析基于IMC的FAMOS软件。通过使用扩展命令包安装的功能,测试的数据通过序列被编辑并评价。
在分析时的对话框对应不同的测试阶段,其用于分析的结构由50个序列,子序列,和子对话框组成。(见图7)。特殊的特征序列可以被动态编辑。例如:当用于离合器分析时,离合器的名字,离合器的压力,还有测试的触发信号都被传递到这个序列。
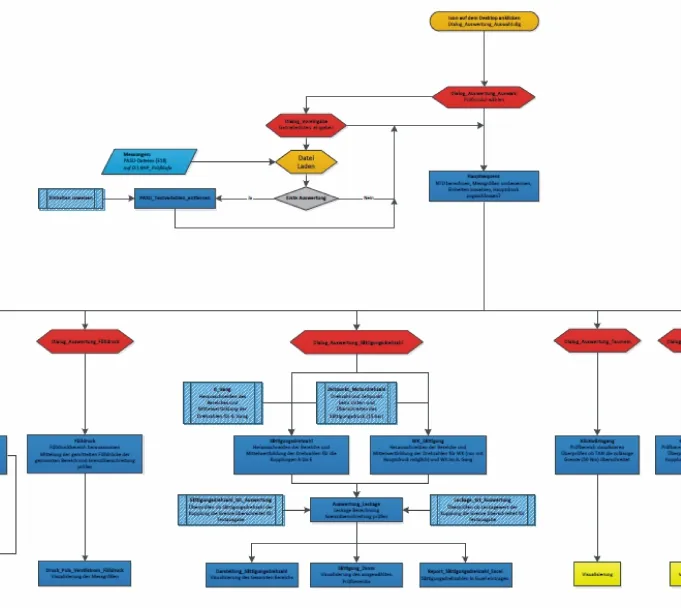
图7 FAMOS分析序列(摘要)Fig.7 FAMOS analysis sequences(excerpt)
通过FAMOS的可编辑对话框,用户界面可以被自定义如图8,在定义好用户界面的测试台,用户可以直接预先选择。例如:单个独立的阶段,变量和自动目标值的比对,可视化的结果等。并且用于统计分析的重要的特征值被自动导入数据库。
另外,为了文档管理,包含重要特征数据的PDF格式的测试报告可以通过按钮一键自动生成。如图9所示。
3 结论
测试台覆盖了对所有的类型的8HP(通用型,全驱型)进行安装和进行自动测试。每个测试的运行时间(含搭建)据尺寸的不同大约在20-25分钟。
变速箱功能参数的极限值由特殊的变速箱通过实验来确定。在这里变速箱的尺寸和特征参数被故意设置到偏差的极限值。同理,离合器的间隙和碟形簧的簧力也被设定到极限值。
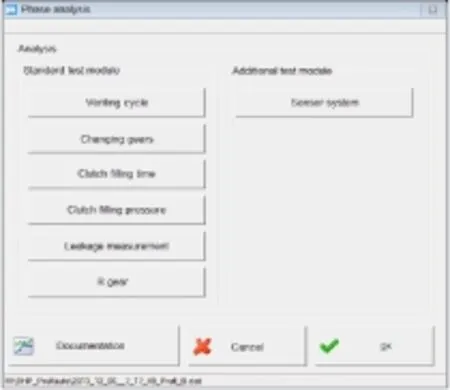
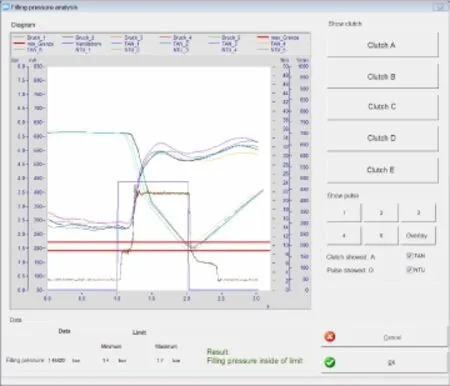
图8 在台架上FAMOS的分析Fig.8 FAMOS analysis on the test bench
此外,错误模拟也通过特殊准备的样件变速箱来进行。参数被故意设置到偏差外或者零部件通过错误的安装。通常下,测试结果会超过限值。
由于需要在试验台上对变速箱的控制系统和CAN通讯进行评价,可能会有非常多的错误导致测试程序的顺利运行和评估的中断。为了避免此类情况的发生,一个不断优化的程序段被用于对测试台程序控制和评估进行故障分析。
由于自动化,整个测试质量被明显的改进,测试程序现在可以以可重复性的方式自动比对实测值和额定值。并且可以自动分析获得统一精确的结果。再者,通过对自动变速箱的控制和柔性化的离合器控制系统,可以集成额外的测试功能模块。在这之前的人工控制模式下是无法实现的。
通过记录统计分析离合器的泄漏值和特征参数,可以让我们在产品开发的早期获得大量的参数。这些信息可以引用到新产品开发和程序的标定当中。
1.4 Phases 5 and 6:Warming up and leakage measurement
For measurement of the internal transmission leakages("consumers"),the transmission is first warmed up to an increased operating temperature of 100°C.The internal transmission leakages are indirectly determined by measuring the saturation speed.This means the speed at which a defined system pressure threshold is reached and the oil pump transports exactly the quantity that is"consumed"as leakage in the transmission at the corresponding operating point.The first comparison value for the base leakages is measured without engaged clutches at a pressure threshold of 15 bar.The saturation speed measured here can be converted based on the geometric pump capacity into the delivery quantity that corresponds to the internal leakage of the hydraulic control unit plus the internal pump leakage.The individual clutch leakagesare calculated from the difference between the base leakage and the total leakage when the corresponding clutch is engaged.
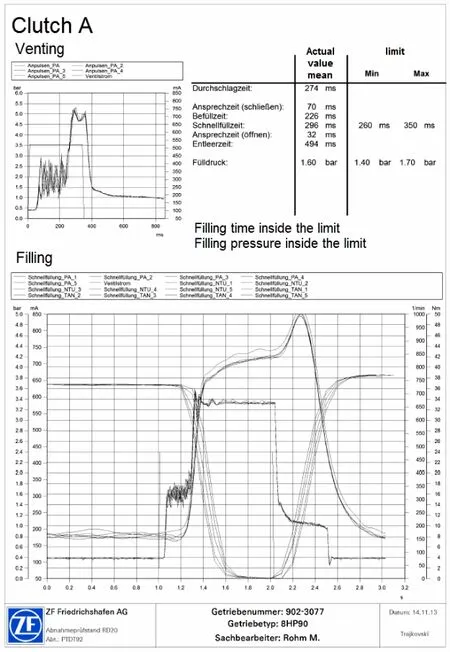
图9 测试报告Fig.9 Report
The procedure during this measurement is that the input speed is reduced in a double ramp from above the expected saturation speed to significantly below it,then increased again,as shown in Figure 5.Then the speeds determined at which the system pressure falls below or rises above the 15 bar threshold are evaluated.The comparison values de-termined in this way are also compared with the defined limits and made accessible for statistical analysis in a database.
1.5 Phase 7:Hydraulic impulse oil storage testing
The hydraulic impulse oil storage(HIS)in the transmission hydraulically supports the oil pump during rapid starting(start-stop function).The HIS is filled during operation with excess oil which on rapid starting is released into the primary hydraulic circuit of the transmission supplying the clutches.This way,three clutches can be filled and engaged within 300 ms to generate force locking for setting off.
HIS testing is performed with the transmission stationary and correspondingly stationary oil pump.The HISis triggered when the system pressure drops to zero.The height and length of the pressure impulse in the system during triggering the store are analyzed.
1.6 Phase 8:Additional cooling system
The additional cooling system is an optional functionality for heavy applications.When the clutch is engaged,an increased volume flow of coolant is automatically applied when the clutch pressure exceeds a threshold value during gear changes under high load.The function is tested by measuring an unsaturated secondary pressure at a stationary operating point while the corresponding clutch pressure is increased and decreased again beyond the threshold value in a double ramp.If the additional cooling system is functioning correctly,the secondary pressure drops significantly,as shown in Fig.6.
1.7 Phase 9:Reverse gear
The speed endurance strength of the reverse gear is tested in a separate phase because faulty components can cause an increased drag torque with corresponding increased heat in a clutch.During the test,the transmission drag torque is monitored over a slow speed ramp and for evaluation automatically compared with the fixed limits.
2 Data analysis and reporting
The analysis is performed with the measured data analysis tool FAMOS from IMC.This enables programming of evaluation sequences with pre-installed functions from an extensive command pool.
The entire software architecture for the analysis consists of some 50 sequences,sub-sequences,and sub-dialogs for the individual test phases which are accessed by the analysis dialog during analysis(see Fig.7).A special characteristic of the sequences is that they can by parameterized dynamically,i.e.when a clutch is analyzed,the name of the clutch,the clutch pressure,and the measurand of the triggering signal are transferred to the sequence.
With the help of the FAMOS Dialog Editor,a user interface was designed as shown in Figure 8.Working with this directly on the test bench,the user can pre-select e.g.the variables and subsequently start the automatic analysis including target value comparison of the individual test steps,then visualize the results.Important characteristic values are automatically input into the database,where they are available for statistical analysis.
Additionally,for the purposes of documentation,a report can be generated at the push of a button with the most important characteristic values and output in pdf format,as shown in Figure 9.
3 Results
The installation and implementation of the automated test run for 8HP transmissions with standard and four-wheel drive is complete for all three sizes.We were able to roughly halve the testing time to approx.20-25 min(depending on size),plus setup time.
The limit values(target values)for the main transmission functions were verified by experiments with limit sample transmissions.Here,the dimensions or characteristic values of the corresponding characteristics were deliberately set to the tolerance limit.In the case of clutches,this applies for instance to the clutch clearance and the multidisk spring force.
Additionally,error simulations were carriedout with specially prepared prototype transmissions where characteristics were deliberately set outside the permitted tolerances or parts were installed in a faulty way.As expected,the test results for these transmissions were outside the permitted limits.
Due to the complexity of both the transmission control system and the CAN communication on the test bench as well as the evaluation,there is a broad scope for error which can disrupt the smooth running of the test program,including the evaluation.For this reason,an ongoing optimization phase is designed to enable troubleshooting both in the test bench control program and also in the evaluation routines.
A significant improvement in the test run quality is shown by the fact that,due to the automation,the test program now runs in a reproducible way so that the analysis by means of target/actual comparisons is more objective.Additionally,the automation capability of the analysis enables a complete evaluation and seamless documentation of the results.Furthermore,the automatic transmission control makes it possible to integrate additional test modules with flexible clutch control systems.This would not be feasible in practice with conventional manual control.
The recording and statistical analysis of leakage values and characteristic values of clutch filling behavior allow us to reach conclusions about the spread of parameters as early as the development stage.This information can therefore be applied at an early stage in new designs or in the calibration of necessary program maps in the software.
Automated Release Test Run in Transmission Development
Dipl.-Ing.(FH)Rolf Braun,Maximilian Gaβmann,Zhang Jilin,Dr.Rolf Gall,ZF Friedrichshafen AG,Friedrichshafen
全自动验证测试建立的目的是为了增加样件变速箱的验证测试效率并对其进行比较分析。因此分步程序被用于对测试台的控制来确保可重复的测试流程。这意味着新的测试阶段程序可以直接插入到旧的测试阶段程序中,这在以往的人工操作中是很难实现的。数据测量由FAMOS测量工具实现。良好的人机界面可以让操作员对不同的模块结果直接进行可视化预读。为了对测试结果进行管理,包含变速箱的主要功能的数据的测试报告由系统自动生成。
To increase the efficiency of release testing of prototype transmission,and to make comparative analysis and evaluation possible,an automated release test run was established.
变速箱 全自动验证测试 离合器测试
Transmission Automated release test Clutch test
U467.3
B
1006-8244(2015)04-003-11
In it,a step control program for the test bench control unit ensured a reproducible test procedure.This meant that additional,new test phases could be integrated that were not possible in manual operation.The measurement data is analyzed with the FAMOS measurement data analysis tool.A user-friendly user interface allows the test bench driver to visualize the results of the individual test modules as soon as they are completed.The permitted limit values are shown simultaneously.To document the results,a release test report is automatically issued,detailing the key functional data of the transmission.
