Effect of Soil Organic Matter Content on Soil Physical and Chemical Indexes and Plant Diversity Indexes of Natural Secondary Karst Forest in Southern Guizhou Province,China
2015-02-24XiZHANGLiliWANG
Xi ZHANG,Lili WANG
1.Guizhou Academy of Forestry,Guiyang 550011,China;2.Guizhou University of Finance and Economics,Guiyang 550025,China
In vegetation-soil system,soil organic matter(SOM)is mainly from plantlitters,residues ofdead plants and debris of root system,as well as residues and excreta from animals and microorganism,it is a ubiquitous and very active component in the soil.SOM has long been considered as an iconic matter of soil fertility,and it interacts with main physical and chemical indicators of soil,thus it is one of the important factors affecting vegetative biomass and plant diversity.The researches on pure Chinese fir plantation and mingled forest[1],artificial sea-buckthorn forest of different restoration stages[2],and artificial experimental forest of tree and grass seed intercropping[3-4]showed that SOM and its components increased with the increase of species richness.During spontaneous recovery process,the diversity indexes of some plants in abandoned slope land[5],evergreen broad-leaf forest[6]and Karst forest[7]had significant correlation with SOM.The present research reports have mainly been about the correlation between SOM and the diversity indexes of a single layer and a single plant in the vegetation,thus the comparability and the systematicness have been poor,could not reflect the complex relationship between SOM and plant diversity indexes,and also have been lack of correlation analysis between SOM and soil physical and chemical indicators.There was still much confusion on the relationship between SOM and soil physical and chemical indicators and plant diversity indexes.In this study,the correlation between SOM and soil physical and chemical indicators and plant diversity indexes and its evolution law in spontaneous recovery process of Karst forest have been studied,to provide a scientific basis for?planting species selections and SOM managements in Karst rocky desertification control engineering.
Overview of the Study Area
The experiment was carried out at Maolan Experimental Site in Karst Forest Ecosystem Research Station of Guizhou,belonging to Chinese Forest Ecosystem Research Network(CFERN).Maolan National Nature Reserve is located at the border of Southern Guizhou province and Northern Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region(25°09′-25°20′N,107°52′-108°05′E),the elevation is among 430-1078.6 m,and generally at about 800 m.Soil forming rock here is mainly dolomite of middle-lower Carboniferous and limestone,which is the typical peak-cluster landform of Karst,the soil is mainly rendizina,the soil stratum is shallow and the rock coverage is high.It belongs to midsubtropical monsoon humid climate,the annual average temperature is 15.3℃,the average temperatures of July and January are respectively 26.4 and 8.3℃,≥10℃annual accumulated temperature reaches 5 727.9℃,the average annual rainfall is 1320.5 mm,and the average annual relative humidity is 83%[8].
Materials and Methods
Survey methods
The surveying route was established along core area,buffer area,experimental site and outer fringe area of the protected area.According to the changed forest landscape types,41 surveying plots in the reserve were set.
The sample-plotsurvey was completed within one month in summer,and the conventional coenology method was adopted.The area of each sample plot was 20 m×20 m,and the tree seedlings with DBH(diameter at breath height)≥5 cm were trees and with DBH<5 cm were shrubs.Plants in the shrub layer,tree layer and herb layer of each sample plot were investigated;the quadrat area of tree layer was 10 m×10 m,and each species name,DBH and height were recorded;the quadrat area of shrub layer was 5 m×5 m,and each species name,plant number,average diameter at base and height were recorded;the quadrat area of herb layer was 1 m×1 m,and each species name,plant number and average height were recorded.There were 3 quadrats respectively in shrub layer and herb layer of each sample plot,which respectively represented better,common and worse plant types in shrub layer and herb layer.
The soil profiles were digged in 3 quadrats respectively in the shrub layer and herb layer of sample plots,and then divided into A and B stratum according to soil spontaneous generation stratums,after that,about 1 kg soil sample was extracted from each stratum,finally,the main chemical indexes of the soil were analyzed in the lab;the soil from soil profiles of A and B stratum was extracted using cutting ring,then it was brought back to the lab to analyze its main physical indexes.At the same time,the conventional indexes,including soilthickness,pebble quantity and root quantity,were surveyed.The analysis of soil physical and chemical indicators could refer to the methods inForest Soil Analysis Method[9].
Data analysis and processing
The division of forest typesThe importance value of species in the tree layer of the sample plot was viewed as the classification index of forest types.
The importance value of species in the treelayer:IV=(RD+RP+RF)/3.
Hereinto,the calculation of relative density(RD),relative significance(RP)and relative frequency(RF)can refer to the method ofQuantitative Ecology[10].
Analysis of plant diversityMargalef index of abundance,Simpson index of ecological dominance,Shannon-Wiener index of information diversity and Pielou index of evenness of species were analyzed[10].
Margalef index:
Simpson index:
Shannon-Wiener index:
Pielou index:
Hereinto,Swas the quantity of species in the quadrat,Nwas total plants of all species in the quadrat,Niwasindividualnumberoftheithspecies,Pi(Ni/N)was the proportion of theithspecies in total plants.
The statistical analysis of the data was carried out using SPSS 17.0[11]and Excel 2003 software.
Results and Analyses
The forest type classification and stand structure
The surveying results showed that the research area was mainly dominated by mixed evergreen and deciduous broadleaved forests[12]in Karst.In the sample plots,there were 251 species of arbors which belong to 131 genera and 56 families,373 species of shrubs which belong to 188 genera and 93 families,and 163 species of herbs which belong to 91 genera and 56 families.The importance value of species in the tree layer and hierarchical clustering[11]were used to divide the sample plots into 6 forest types,and the number of each type of sample plots was among 3-12 (Table 1).Thereinto,type A wasAcersp.-Celtis tetrandrasubsp.sinensisforest,includingHandeliodendronbodinieri,Zelkora schneideriana,Eurycorymbus cavaleriei,Phoebe zhennanandArdisia depressa,etc.;type B wasKoelreuteria minor-Platycarya strobilaceaforest,includingPhotiniasp.,Sycopsis dunnii,Carpinussp.,Camelliasp.andClematoclethra scandens,etc.;type C wasDendrobenthamia japonicavar.chinensis-Cyclobalanopsis glaucaforest,includingCinnamomumsp.,Platycarya longipes,Machilussp.,EuonymusalatusandMetadinatrichotoma,etc.;type D wasCornus controversa-C.parvifloraforest,includingToxicodendronvericifluum,Prunus sp.,Viburnumdilatatum,Aeschynomene indicaandDiospyros kaki,etc.;type E wasLindera communis-Liquidambar formosanaforest,includingToona sinensis,Cryptocarya concinna,Celtisbungeana,Coptis chinensisandAlangiumchinense,etc.;type F wasLoropetalum chinense-Pinus massonianaforest,includingCyclobalanopsis glauca,Photinia davidsoniae,L.pulcherimavar.hemsleyana,Daphniphyllum salicifoliumandClausena dunniana,etc.
The composition of species of different forest types was different,and the indicators of stand structure were also different greatly.The average density of the plants in the tree layer was among 1 233-1 469 ind./hm2,and the differences among different types were not significant,the corresponding values of shrub layer and herb layer were respectively among 7 200-1 4038 and among 84 444-368 519 ind./hm2,the differences among parts of types were significant.Average DBH of plants in the tree layer and average diameter at base of plants in the shrub layer were respectively 10.04-11.58 and 0.79-1.28 cm,the differences among parts of these types were significant. Average heights of plants in the tree layer,shrub layer and herb layer were respectively 7.13-8.57,1.18-1.72 and 0.06-0.34 m,and the numbers of species were respectively 11-23,18-37 and 7-14,the differences among parts of these types were significant.In differentforesttypes,the average density of plants in different layers showed the trend of herb layer>shrub layer>tree layer,the average height showed the trend of tree layer>shrub layer>herb layer,the numberof species showed the trend of shrub layer>tree layer>herb layer,and the average diameter showed the trend of tree layer>shrub layer.
The diversity index of plants
As shown in Table 2,the significance of difference of the diversity index of plants in the same layer of different forest types was different.Margalef index,Simpson index,Pielou index and Shannon-Wiener index of the tree layer were respectively 2.52-5.44,0.65-0.94,0.75-0.93 and 1.72-2.87,these in the shrub layer were respectively 4.06-7.73,0.82-0.91,0.90-0.93 and 2.57-3.14,and these in the herb layer were respectively 1.21-2.78,0.55-0.79,0.83-0.94 and 1.52-2.24.Therefore,the variation trends of Margalef index and Simpson index followed the sequence of shrub layer>tree layer>herb layer,that of Pielou index was shrub layer>herb layer>tree layer,and that of Shannon-Wiener index was shrub layer>tree layer>herb layer.
SOM changeofdifferentforest types
In different forest types (in Table 3),SOM of soil A stratum was among 38.36-104.62 g/kg,and that of soil B stratum was 19.74-59.40 g/kg,thus A stratum>B stratum.The significance of difference of SOM in soil A stratum or B stratum of different forest types was different.
The correlation between SOM and soil physical indicators
SOM and soil physical indicators interact with each other in soil ecosystem.As shown in Table 4,the correlation coefficients between SOM and soil bulkdensity,masswatercontent,maximum water-holding capacity,capillary water-holding capacity,field water-holding capacity and total porosity reached significantlevel.SOM showed negative correlation with soil bulk density and positive correlation with soil porosity and water-holding capacity.Except soil bulk density,the correlation coefficients between SOMand soil physical indicators of A stratum were greater than that of B stratum,showing that SOM had greater effect on soil physical indicators of A stratum.

Table 1 Stand structure indexes of different forest types
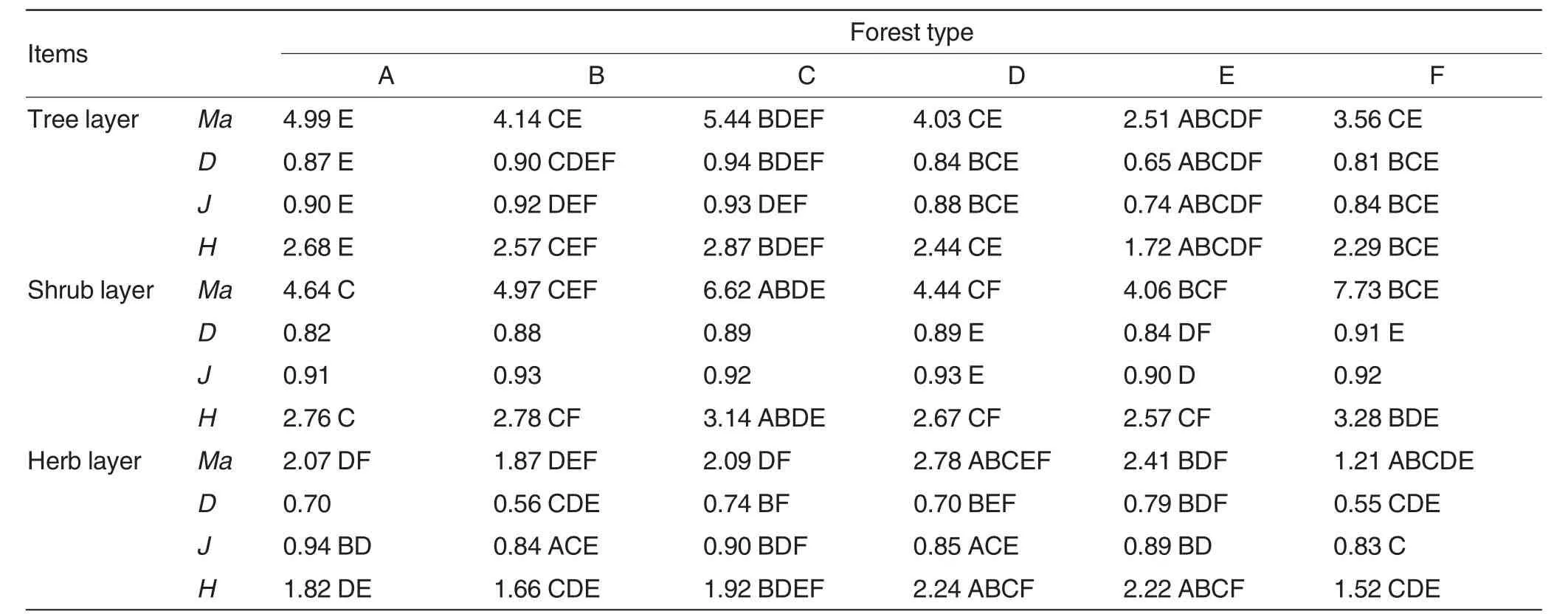
Table 2 Plant diversity of different forest types
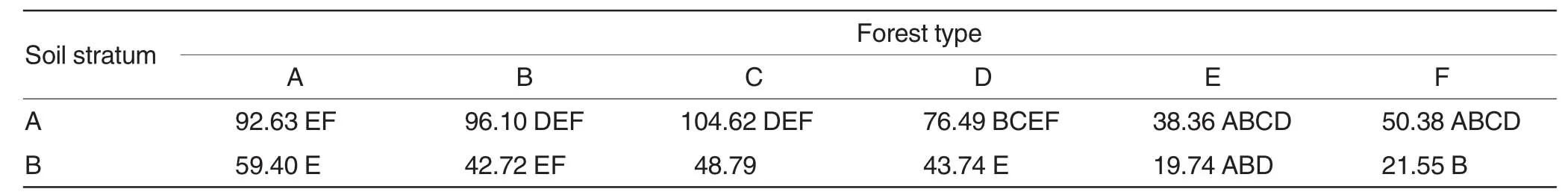
Table 3 SOM of different forest types g/kg
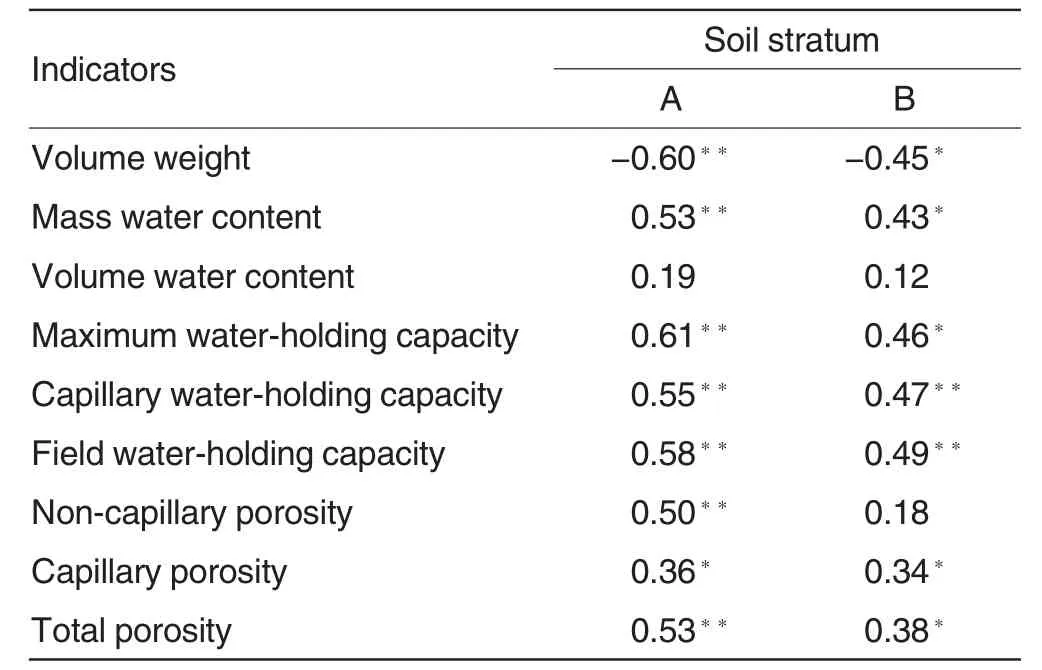
Table 4 The correlation coefficients between SOM and soil physical indicators
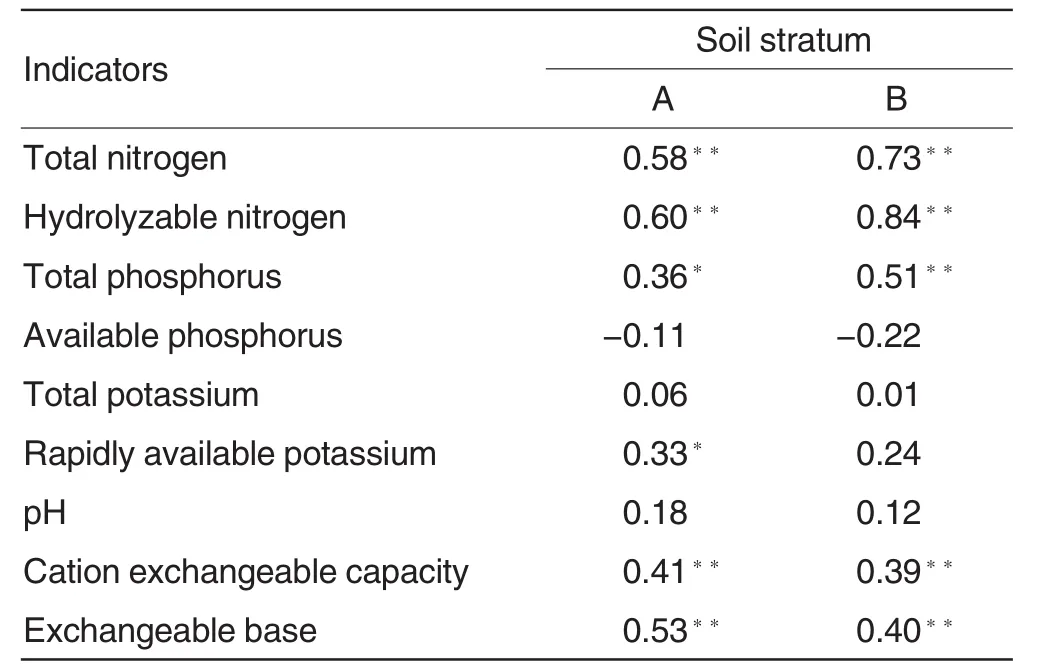
Table 5 The correlation coefficients between SOM and soil chemical indicators
As seen in Table 5,SOM had a negative correlation with available phosphorus content in the soil,but had a positive correlation with other chemical indicators of the soil.SOM had significant positive correlation with total nitrogen content,hydrolyzable nitrogen content,total phosphorus content,rapidly available potassium content,cation exchange capacity and exchangeable base content in the soil,showing that SOM is the comprehensive designator of main fertility indexes in the soil.phosphorus and potassium contents in the soil of Karst forest are lower[13],which is one of reasons causing the inapparent correlation between SOM and soil phosphorus and potassium contents.SOM in the soil saves the nutrient in the humification process,and releases the nutrient of the mineralizing process again,this complicated adsorption and desorption process is one of the reasons causing the negative correlation between SOM of Karst forest and soil available phosphorus content[14].From the absolute values ofcorrelation coefficientof view,except total nitrogen content,hydrolyzable nitrogen content and total phosphorus content in the soil,other indicators all followed the sequence of A stratum>B stratum.
The correlation between SOM and plant diversity index
The study(Table 6)showed that SOM of different soil stratums showed different degrees of correlation with plant diversity indexes of tree layer,shrub layer and herb layer,SOM in Astratum of soil showed significant positive correlation with Margalef index,Simpson index,Shannon-Wiener index and Pielou index of the tree layer,SOM in B stratum of soil showed significant positive correlation with Simpson index and Pielou index of the tree layer,although it had positive correlation with Margalef index and Pielou index,it was far from significance level.The correlation between SOM of soil A and B stratum and plant diversity indexes of shrub layer and herb layer was not significant and regular.These indicated that SOM of Maolan experimental site forest was significantly affected by plant diversity indexes of tree layer,while the plant diversity indexes of shrub layer and herb layer had not prominent effect on SOM.The multiple regression analysis showed that the multiple correlation between SOM in A stratum of soil and plant diversity indexes of different layers reached significant level(R=0.65**),the factor contribution rates[15]of plant diversity indexes in the tree layer,shrub layer and herb layer were 33.72%,45.79%and 20.49%,respectively;the multiple correlation between SOM in B stratum of soil and plant diversity indexes of different layers reached significant level(R=0.66**),the factor contribution rates of plant diversity indexes were 21.95%,15.06%and 63.00%,respectively.These indicated that in natureapproximatingmanagement,except paying attention to the cultivation of plant diversity of the tree layer,the improvement role of plant diversity of shrub layer and herb layer to SOM can not be ignored.In the contribution rates of plant diversity indexes of tree layer,shrub layer and herb layer,the corresponding values of Margalef index,Simpson index,Shannon-Wiener index and Pielou index to SOM of soil Astratumwere-1.55%,-1.15%,2.73%,16.16%,8.34%,1.73%,4.11%,3.80%,-6.17%,-11.90%,-32.50%and 9.85%,respectively;and the corresponding values of these to SOM of soil B stratumwere0.12%,0.80%,9.54%,18.39%,-6.67%,5.55%,-1.11%,-1.85%,-18.66%,-2.32%,5.74%and29.25%,respectively.The contribution rate showed the trend of Pielou index>Simpson index>Shannon-Wiener index>Margalef index,this provided a reference basis for selecting plant diversity index types in production and regulating and controlling soil SOM.

Table 6 The correlation coefficients between SOM and plant diversity indexes
From the further analysis,it can be found that the correlation coefficient between SOM of different soil stratumss and plant diversity indexes of the tree layer showed the trend of quadratic polynomial>straightline form,indicating that quadratic polynomial can better reflect the interrelation between them(Fig.1-Fig.2).The correlation coefficients of quadratic polynomial and straight line form between SOM of soil A stratum and different diversity indexes of the tree layer both reached significant or extremely significant level,and the correlation coefficients of quadratic polynomial and straight line form between SOM of soil B stratum and Simpson index and Pielou index reached significant level.The curve analysis showed that the response of Margalef index,Simpson index,Shannon-Wiener index and Pielou index of the tree layer to SOM of soil A stratum showed the trend of rising firstly and falling then,and the inflection point values were 4.97,0.97,2.76 and 0.95,respectively.The response of Simpson index and Pielou index to SOM of soil B stratum showed the trend of rising firstly and falling then,while the response of Margalef index and Shannon-Wiener index to SOM of soil B stratum showed the trend of falling firstly and rising then,the inflection point values had not ecological significance.These indicated that the response of different diversity indexes of plants in the tree layer to SOM of different soil stratums showed the phenomenon of non-linearization.
Conclusions and Discussions
According to importance values of species in tree layer and hierarchical clustering,41 surveying plots in the reserve were divided into 6 types,such asLindera communis-Liquidambar formosanaforest,Loropetalum chinense-Pinus massonianaforest,Acersp.-Celtis tetrandrasubsp.sinensisforest,Koelreuteria minor-Platycarya strobilaceaforest,Cornus controversa-C.parvifloraforest andDendrobenthamia japonicavar.chinensis-Cyclobalanopsis glaucaforest.SOM had significant differences in A or B stratum of soil among parts of forest types,and the species number,diameter,height and density,as well as Margalef index,Simpson index,Shannon-Wiener index and Pielou index of different forest types also had significantdifferences.These were similar to the previous research conclusions[16].
SOM is mainly from the vegetation part of vegetation-soil system,and belongs to soil,its composition and quantity are not only affected by major physical and chemical indicators of soil,but also affect major physical and chemical indicators of soil,and SOM effect on A stratum is greater than that of B stratum.The results showed that the soil porosity,water storage capacity,main fertility and nutrient indicators increased with SOM increment,thus improving SOM was beneficial to water conservation and fertility preservation of soil in Karst region.
Margalef index of abundance,Simpson index of ecological dominance,Shannon-Wiener index of information diversity and Pielou index of evenness of species were selected to comprehensively judge the relationship between plant diversity and SOM,the results showed that plant diversity indexes of tree layer had positive relationship with SOM,especially had significant correlation with SOM in A stratum of soil.This was similar to the previous research conclusion[1-2,5,7],while those in shrub layer and herb layer had not significant correlation with SOM. The multivariate analysis showed that total contribution rate of plant diversity indexes to SOM in A stratum of soil was in the order of shrub layer>tree layer>herb layer,and that to SOM in B stratum of soil was herb layer>tree layer> shrub layer,it was suggested that plant diversity measures of SOM management of vegetation restoration in Karst region were suitable for giving priority to tree species,and combining with shrub layer and herb species.
Besides plant litters,residues of dead plants and debris of root system,SOM also includes the biomass and diversity of soil fungi and soil enzyme,the correlation between these factors and plant diversity index has already been reported in another forest[1,3-4].In this paper,only the correlation between SOM and plant diversity of vegetation layer and physical and chemical indicators of soil during spontaneous recovery process in Karst forest was studied,and it was necessary to further study the correlation between SOM component and quantity and plant diversity index and soil physical and chemical indicators.In addition,the quantity and constituent of plant litters,residues of dead plants,debris of root system and animal excreta in dif-ferent forest and its age stages are different,plant diversity index affects the established forest soil microflora and vitality[1,3-4],and then affects SOM component and quantity,the influencing factors of SOM include multiple factors including plant diversity index.
During spontaneous recovery process,the correlation coefficient between SOM of different soil stratums and plant diversity indexes of the tree layer showed the trend of quadratic polynomial>straight line form,and the linear correlation was in accordance with previous studies[2,5,7].Based on analyzing the forming reason of quadratic polynomial,it was thought that SOM was influenced not only by plant diversity indexes of tree layer,but also by succession stage and structure indexes of forest stand.In the 7 sample plots with SOM>100 g/kg,the proportion ofthe sample plotsofKoelreuteria minor-Platycarya strobilaceaforest was 41.67%,and the corresponding values ofDendrobenthamia japonicavar.chinensis-CyclobalanopsisglaucaforestandCornus controversa-C.parvifloraforest were 14.29%and 11.11%,respectively,the diversity index ofDendrobenthamia japonicavar.chinensis-Cyclobalanopsis glaucaforest in the tree layer was the highest,these indicated that the forest type with high SOM proportion of sample plot,its plant diversity index of the tree layer may not be high;on the other hand,the correlation coefficient of SOM and DBH of 41 surveying plots was 0.34*,indicating that SOM showed the increasing trend with the increase of stand DBH.In the spontaneous recovery process,density of the large diameter-class stand of near-top and climax forest[16]was lower,the biomass and litterfall production were larger,and SOM increased continuously. The turning point of quadratic polynomial can be one of the important bases interpreting the complex relationship among plant diversity index and SOM,and after the further verification of afforestation[3-4]or vegetation recovery,it can be one of the reference bases of species quantitative management in Karst rocky desertification control engineering.
[1]WANG SL(汪思龙),HUANG ZQ(黄志群),WANG QK(王清奎),et al.Effects of species diversity of litter on the ecological functions ofCunninghamia lanceolata(Lamb.)Hook.plantation soil(凋落物的树种多样性与杉木人工林土壤生态功能)[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报),2005,25(3):474-480.
[2]LI DW(李登武),ZHANG WH(张文辉),REN ZZ(任争争),et al.Relationship between species diversity in different restoration stages ofHippophae rhamnoidesssp.sinensisplantations and soil fertility in the hilly and gully regions of Loess Plateau(黄土丘陵沟壑区沙棘人工林不同恢复阶段物种多样性与土壤肥力的关系研究)[J].Agricultural Research In The Arid Areas(干旱地区农业研究),2007,25(5):25-30.
[3]EISENHAUER N,BELER H,ENGELS C,et al.Plant diversity effects on soil microorganisms support the singular hypothesis[J].Ecology,2010,91(2):485-496.
[4]DONALD RZ,WILLIAM EH,DAVID CW,et al.Plant diversity,soil microbial communities,and ecosystem function:Are there any links[J].Ecology,2003,84(8):2042-2050.
[5]YANG XB(杨小波),ZHANG TL(张桃林),WU QS(吴庆书).The relationship between biodiversity and soil fertility characteristics on abandoned fields in the tropical region of southern China (海南琼北地区不同植被类型物种多样性与土壤肥力的关系)[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报),2002,22(2):190-196.
[6]CHEN GS(陈光升),ZHONG ZC(钟章成).Relationship between species diversity and soil factors of evergreen broad-leaved forest in Jinyun mountain,Chongqing(重庆缙云山常绿阔叶林群落物种多样性与土壤因子的关系)[J].Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology(应用与环境生物学报),2004,10(1):12-17.
[7]LANG HL(郎华林),LONG CL(龙翠玲).Relationship between species diversity and soil factors in Karst forest of different topography sites in Maolan natural reserve(茂兰自然保护区喀斯特森林物种多样性与土壤因子的关系)[J].Hubei Agricultural Sciences (湖北农业科学),2012,51(18):3988-3992.
[8]ZHOU ZX(周政贤).Scientific survey of Maolan Karst forest(茂兰喀斯特森林科学考察集)[M].Guiyang:Guizhou People’s Press(贵阳:贵州人民出版社),1987:1-23.
[9]State Forestry Administration of China(国家林业局).Analysis methods of forest soil(LY/T 1210-1275-1999)(森林土壤分析方法(LY/T 1210-1275-1999))[S].Beijing:Standards Press of China(北京:中国标准出版社),1999.
[10]ZHANG JT(张金屯).Quality ecology(数量生态学)[M].Beijing:Science Press(北京:科学出版社),2004:20,86-91.
[11]YU JY(余建英),HE XH(何旭宏).Mathematics statistics and SPSS application(数据统计分析与SPSS应用)[M].Beijing:People’s Post Press(北京:人民邮电出版社),2003:127-135,163-282.
[12]ZHANG X(张喜),LI KZ(李克之),LIAN B(连宾),et al.Studies on the floristics of Karst nature forests between southern and central areas in Guizhou Province,China(黔南和黔中喀斯特天然林植物区系研究)[J].Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany(热带亚热带植物学报),2009,17(2):114-121.
[13]LIU F(刘方),WANG SJ(王世杰),LUO HB(罗海波),et al.Microhabitats in Karst forest ecosystem and variability of soils(喀斯特森林生态系统的小生境及其土壤异质性)[J].Acta Pedologica Sinica(土壤学报),2008,45(6):1055-1062.
[14]QIN SJ(秦胜金),LIU JS(刘景双),WANG GP(王国平).Mechanism of phosphorus availability changing in soil(影响土壤磷有效性变化作用机理)[J].Chinese Journal of Soil Science(土壤通报),2006,37(5):1012-1016.
[15]ZHANG X(张喜),XUE JH(薛建辉),XU XT (许效天),et al.Forest surface runoff and its influence factors in Karst mountainous area in center of Guizhou Province,China(黔中喀斯特山地不同森林类型的地表径流及影响因素)[J].Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany(热带亚热带植物学报),2007,15(6):527-537.
[16]YU LF(喻理飞),ZHU SQ(朱守谦),YE JZ(叶镜中),et al.Dynamics of a degraded Karst forest in the process of natural restoration(退化喀斯特森林自然恢复过程中群落动态研究)[J].Forest Research(林业科学),2002,38(1):1-7.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Chemical Property Variation Trend Analysis and Quality Evaluation of Water in Wei River
- Effects of Plastic Film Mulching on Physical Characters of Soil and Yield and Yield Components of Sweet Potato
- Effects of Different Harvesting Dates on Yield and Quality of Silage Maize
- The Dynamic Changes in Cold Tolerance of Ground-cover Chrysanthemum Growing in the Open Field during the Overwintering
- Effects of Ppc Gene Construction of Monocotyledon on Seedling Growth of Transgenic Nicotiana tabacum
- Preliminary Test on a New Type of Antibacterial Substance
